Biology exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/252
Last updated 1:41 AM on 11/25/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
253 Terms
1
New cards
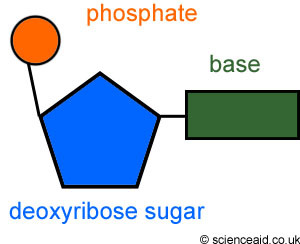
Nucleotide
A building block of DNA, consisting of a sugar covalently bonded to a base and a phosphate group.
2
New cards
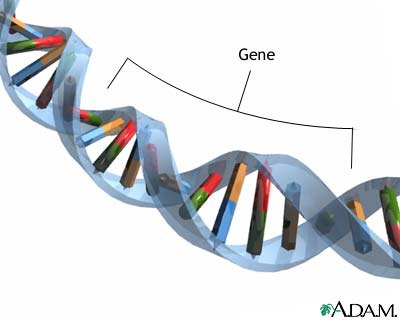
Gene
A section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific characteristic e.g. hair colour
3
New cards
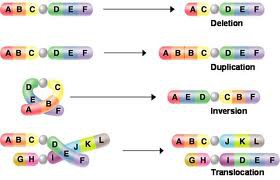
Mutation
A change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information by changing the sequence of amino acids
4
New cards
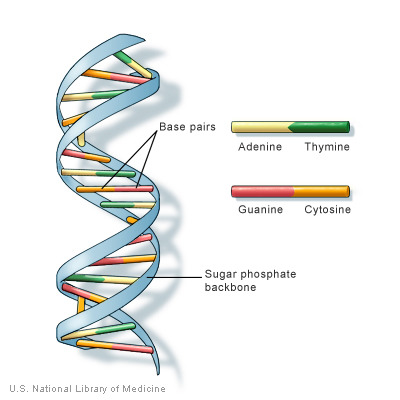
DNA
A complex polymer containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes. Codes for amino acids which make proteins.
5
New cards
Double helix
The shape of a DNA molecule
6
New cards
Base
A-T and C-G are the examples.
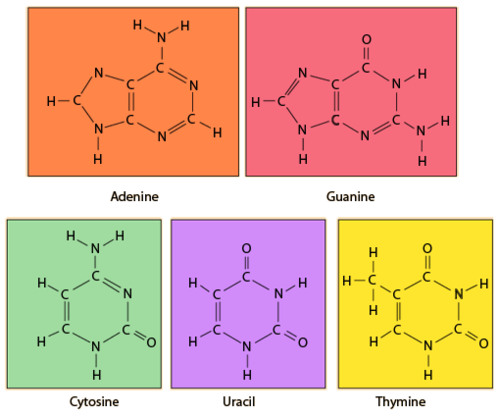
7
New cards
T
The Base Pair A matches with
8
New cards
C
The Base Pair G matches with
9
New cards
Complementary Bases
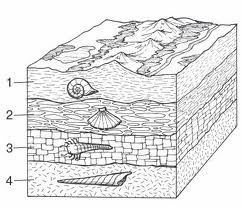
The fact that A bonds with T and G with C shows that A and T and G and C are
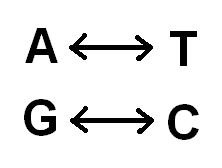
10
New cards
Rosalind Franklin
British scientist who generated x-ray diffraction pictures of DNA, that provided evidence of of double helix data about DNA

11
New cards
global warming
An increase in the average temperature of the earth's atmosphere (especially a sustained increase that causes climatic changes)

12
New cards
atmosphere
A mixture of gases that surrounds a planet or moon.
13
New cards
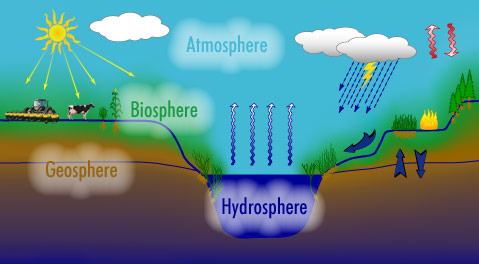
Biosphere
Consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere.
14
New cards
Geosphere
the solid part of the earth consisting of the crust and outer mantle
15
New cards
Hydrosphere
all the waters on the earth's surface, such as lakes and seas, and sometimes including water over the earth's surface, such as clouds.

16
New cards
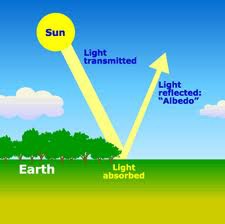
Albedo
the percentage of incoming sunlight reflected from a surface
17
New cards
terrestrial
Relating to the Earth or to land; worldly

18
New cards
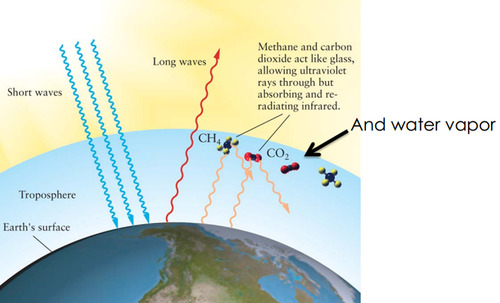
terrestrial radiation
the radiation emitted by Earth to outer space
19
New cards
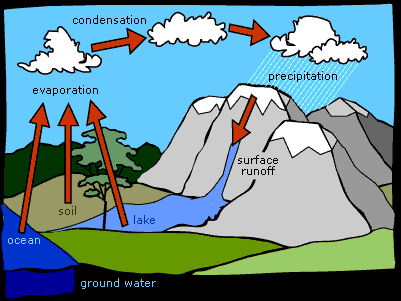
water cycle
The continual movement of water among Earth's atmosphere, oceans, and land surface through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation
20
New cards
Condensation
The change of state from a gas to a liquid

21
New cards
Evaporation
The change of a substance from a liquid to a gas

22
New cards
Infiltration
the process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil
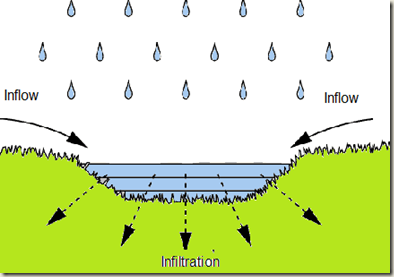
23
New cards
Precipitation
Any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth's surface.
24
New cards
Runoff
water that flows over the ground surface rather than soaking into the ground

25
New cards
Transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
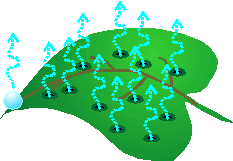
26
New cards
carbon cycle
The organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again
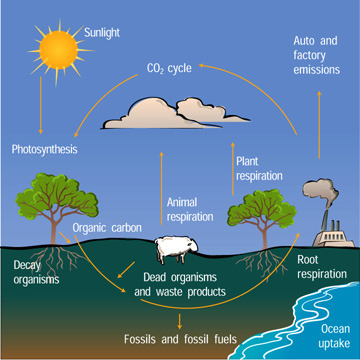
27
New cards
Respiration
The process by which cells break down simple food molecules to release the energy they contain.
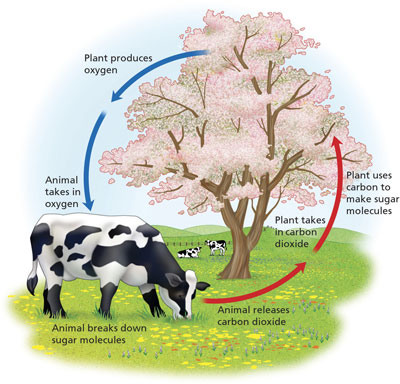
28
New cards
fossil fuels
resources that come from the remains of long ago plants and animals to form coal, oil and natural gas.
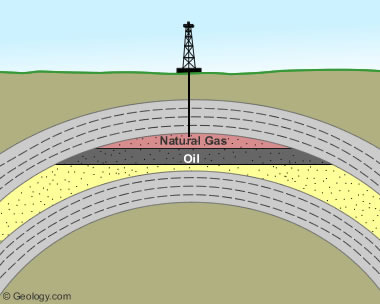
29
New cards
Photosynthesis
Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars
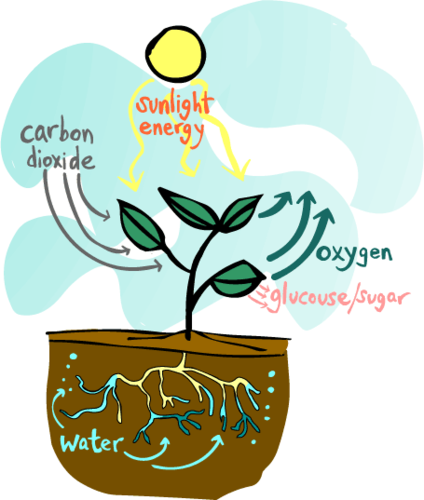
30
New cards
greenhouse effect
Natural situation in which heat is retained in Earth's atmosphere by carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and other gases
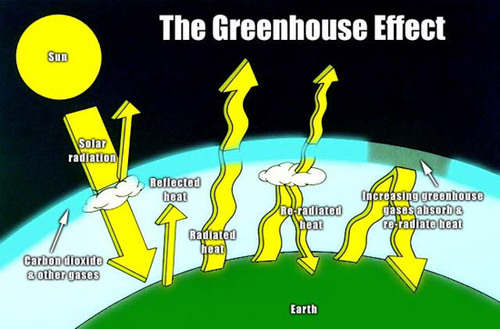
31
New cards
climate change
a change in global or regional climate patterns, in particular a change apparent from the mid to late 20th century onwards and attributed largely to the increased levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide produced by the use of fossil fuels.
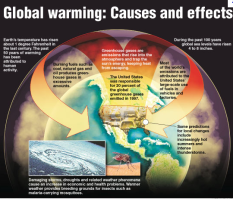
32
New cards
emissions
gases released into the air, especially by cars and factories

33
New cards
carbon dioxide
a colorless, odorless gas produced by burning carbon and organic compounds and by respiration. It is naturally present in air (about 0.03 percent) and is absorbed by plants in photosynthesis.

34
New cards
carbon footprint
the total carbon dioxide emissions produced by an individual, group, or location

35
New cards
coral bleaching
Occurs when a coral becomes stressed and expels most of its colorful algae, leaving an underlying ghostly white skeleton of calcium carbonat

36
New cards
ocean acidification
when CO2 dissolves in seawater, it reacts with water to form carbonic acid, which lowers ocean pH
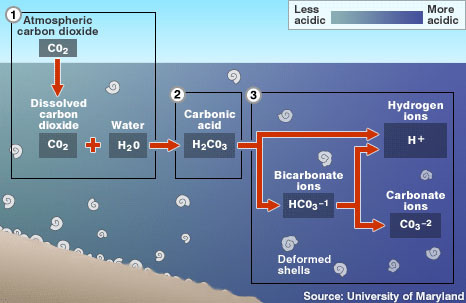
37
New cards
Conduction
The direct transfer of heat from one substance to another substance that it is touching.
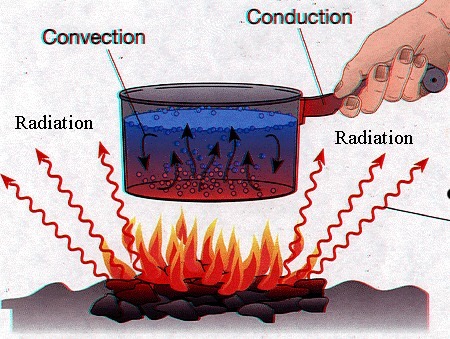
38
New cards
Convection
The transfer of thermal energy by the circulation or movement of a liquid or gas
39
New cards
La Nina
A climate event across the Pacific Ocean, it is caused by Strong Trade winds. It causes Australia to have extra rainfall.
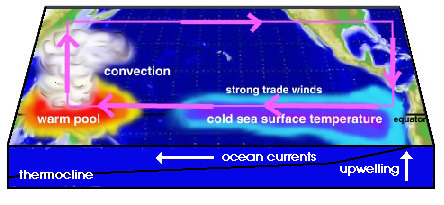
40
New cards
El Nino
A climate event in the mid Pacific Ocean, it is caused by weak Trade winds. It causes Australia to have extra dry weather and droughts.
41
New cards
Carbon sinks/reservoirs
Anything that absorbs more carbon than it releases; examples: forests, soils, oceans and the atmosphere
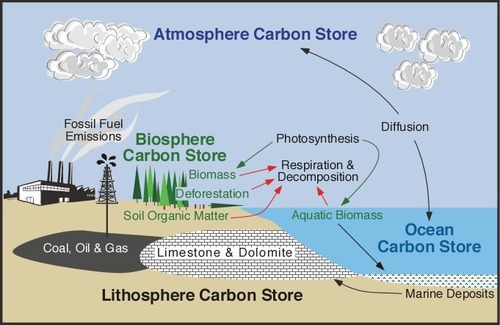
42
New cards
renwable energy sources
examples -Solar, Wind, Hydro they never run out.

43
New cards
Evolution
Change in a species over time
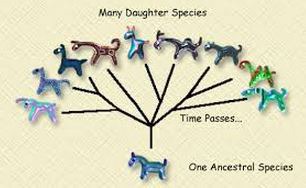
44
New cards
Fossil
Any trace or remains of an organism that lived long ago

45
New cards
Law of Superposition
The farther down in the rock layer an organism is the older it is

46
New cards
Examples of fossils
Bones, Imprints, Teeth

47
New cards
Comparative Embryology
Comparison of fetal development to show common ancestry
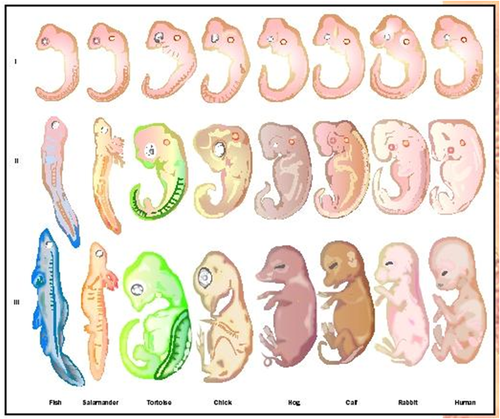
48
New cards
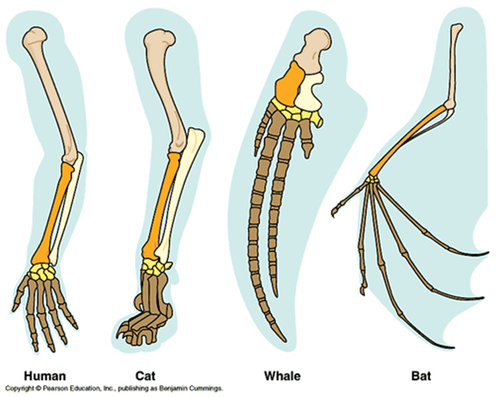
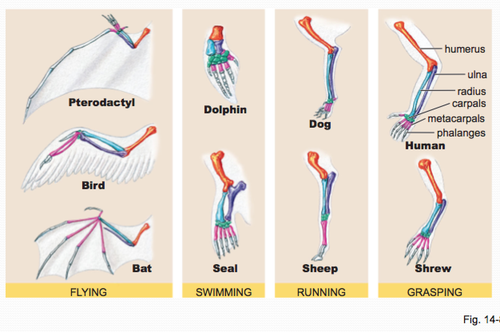
Homologous Structures
Having the similar body structures but not always the same function
49
New cards
Homologous structure - example
Leg of cat and human arm
50
New cards
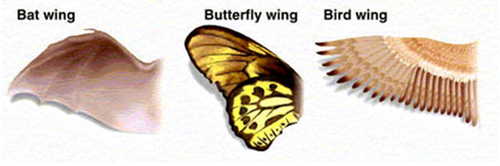
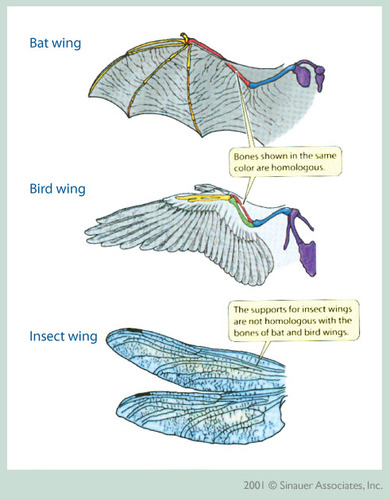
Analogous Structure
Having different body structures although used for the same purpose
51
New cards
Analogous structure - example
Bird wing and insect wing
52
New cards
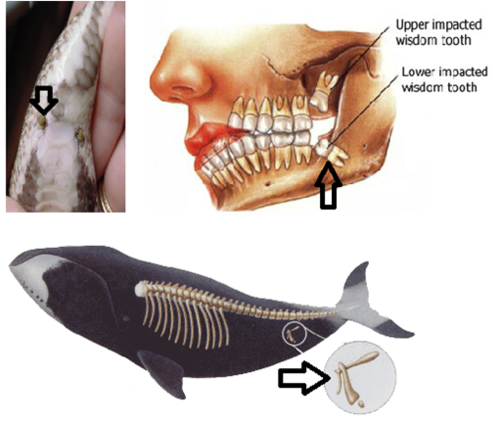
Vestigial organ
Remnants of ancient ancestors that have little to no function
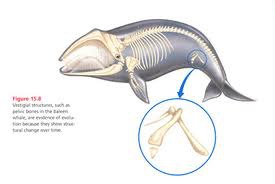
53
New cards
Vestigial organ - example
Wisdom teeth
54
New cards
Comparative Biochemistry
Comparison of DNA sequence can show common ancestry
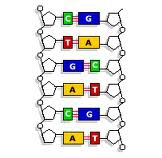
55
New cards
survive and reproduce
Organisms with well suited traits
56
New cards
What causes a population to become separated?
Natural disaster, isolation
57
New cards
What is most likely the reason there are gaps in the fossil record?
they haven't found all the fossils yet
58
New cards
older
Fossils deep in the Earth's crust are most likely
59
New cards
age of fossils,past events ,life on earth
What information does the fossil record supply evidence for?
60
New cards
homologous structures
How do we know all organisms come from a common ancestor?
61
New cards
fossils, embryology, homologous structures, vestigial structures & DNA
How do scientists determine evolutionary relationships among species?
62
New cards
Fossil records
the millions of fossil that scientists have collected are
63
New cards
Embryology
similar in early development
64
New cards
Homologous structures
body parts that are structural similar in related species and that provide evidence for a common ancestor
65
New cards
Fossils
the preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past
66
New cards
Comparative Anatomy, DNA, Biogeography, embryology, & fossils
The 5 main points of evidence for evolution
67
New cards
evolution
the gradual change in a species over time
68
New cards
False
The presence of gill slits and a tail in the early stages of development of an embryo indicates its future as a fish.
69
New cards
ordovicians
444 mya; global cooling/ glaciation (severe in ice age); 86% of life
70
New cards
late devonian
375 mya; land olants caused erosion ➡️nutrient runoff into ocean➡️ a large bloom➡️ o2 depletion; 75% of life
71
New cards
permian
215 mya; volcanism and methane released from bacteria (global temp surge/ ocean acidification); 96% of life
72
New cards
triassic
200 mya; no clear cause (maybe ocean acidification or sea level drop?); 96% of life
73
New cards
Cretaceous
66 mya; giant meteor (6-9 mi wide at impact ➡️93 mi diameter crater!); 76% of life
74
New cards
holocene
NOW; anthropogenic (human caused) climate change and habitat life; ?% of life
75
New cards
Great Oxygenation Event
2.5 bya; evolution of photosynthetic bacteria (cyano bacteria) caused o2 accumulation in atmosphere➡️ killed other bacteria that found o2 toxic; o2 revolution
76
New cards
Mammoths and mastodons
Cenozoic

77
New cards
Pangaea breaks apart, 1st early mammals, dinosaurs, birds, 1st flowering plants. K-T Extinction (Asteroid Chicxulub)
Mesozoic
78
New cards
Oldest rocks
Precambrian
79
New cards
Ice ages and mountain ranges: Forming-Alps and Himalayas
Mammoths & Humans
Mammoths & Humans
Cenozoic

80
New cards
"The P-T" or "The Great Dying mass extinction
Occurs at the end of the Paleozoic Era

81
New cards
1st single-cell Algea and Bacteria, 1st multicellular animals
Precambrian
82
New cards
Earth forms & Cools
Beginning of Precambrian

83
New cards
1st land plants, fish, insects, snails, clams & pangea has formed,
Paleozoic

84
New cards
Oxygen is in atmosphere
2000mya

85
New cards
absolute age
the numeric age of an object or event, often stated in years before the present, as established by an absolute-dating process, such as radiometric dating
86
New cards
radiometric dating
method used to determine the age of rocks using the rate of decay of radioactive isotopes
87
New cards
relative dating
Method of determining the age of a fossil by comparing its placement with that of fossils in other layers of rock
88
New cards
half-life
length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay
89
New cards
phylogenic tree/cladogram
a diagram that depicts the lines of evolutionary descent of different species, organisms, or genes from a common ancestor.
90
New cards
Gradualism
A proposed explanation in evolutionary biology stating that new species arise from the result of slight modifications (mutations and resulting phenotypic changes) over many generations.
91
New cards
punctuated equilibrium
the hypothesis that evolutionary development is marked by isolated episodes of rapid speciation between long periods of little or no change.
92
New cards
divergent speciation
When two or more similar species become more and more different.
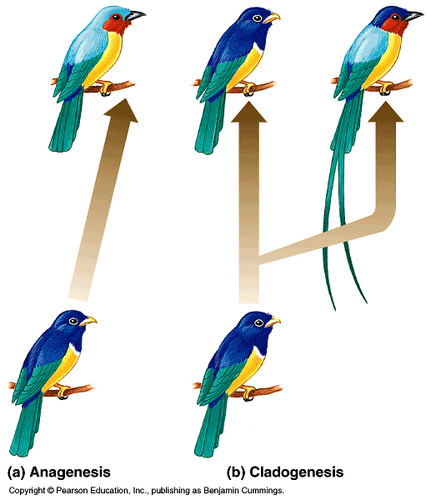
93
New cards
phyletic speciation
abrupt mutations in a few genes occur in a species over time, related to punctuated equilibrium

94
New cards
Morphology
structure and appearance of an organism
95
New cards
Fossil
A preserved remnant or impression of an organism that lived in the past.

96
New cards
abiotic synthesis
the building of biological molecules from inorganic precursors
97
New cards
Reduced Atmosphere Hypothesis
Early earth conditions where there was no free oxygen in the atmosphere
98
New cards
Miller-Urey Experiment
Two scientists attempted to reproduce the condition of the (assumed) earth's primitive ocean's under a reducing atmosphere. They produced some of the key molecules to life (amino acids and nucleotides).
99
New cards
prokaryotic cell
A type of cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles; found only in the domains Bacteria and Archaea.
100
New cards
Eukaryotic cells
Contain a nucleus and other organelles that are bound by membranes.