Honors Chemistry B - Unit 3: Gas Laws
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
"you have mass so you matter" - steward
Last updated 5:00 AM on 4/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
1
New cards
welcome back.
2
New cards
let’s play a game of “some, none, or all” (flip me!)
i give you a statement, you tell me if that statement is true for all, some, or no gases
3
New cards
gases are matter
all
4
New cards
gases are flammable
some
5
New cards
gases are visible
some
6
New cards
gases react
some (REMEMBER: noble gases!)
7
New cards
yay you did it! next section
hi
8
New cards
true or false: gases weigh differently depending on their molar mass
true!
9
New cards
how do gases move?
process called **diffusion**
* gas moves from high to low concentration
* ie: when you burn a candle you can smell it
* gas moves from high to low concentration
* ie: when you burn a candle you can smell it
10
New cards
why do gases move at different speeds?
* the more weight, the slower the gas is
* or vice versa, the less it weighs the speedier it is
* or vice versa, the less it weighs the speedier it is
11
New cards
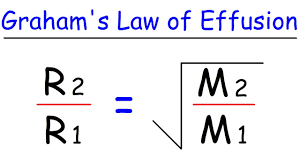
what is the law that relates the speed of gases to their molar mass?
graham’s law
12
New cards
what are the four parts of kinetic molecular theory
gases…
1. are made of tiny particles, travelling in straight lines
2. do not occupy volume
3. collisions between molecules are perfectly elastic
4. no attractive or repulsive forces between the particles
1. are made of tiny particles, travelling in straight lines
2. do not occupy volume
3. collisions between molecules are perfectly elastic
4. no attractive or repulsive forces between the particles
13
New cards
temperature
measure of **kinetic energy**
14
New cards
volume
amount of space an object occupies
15
New cards
what determines volume for gases?
size of container
16
New cards
pressure
force of gas particles hitting the container
17
New cards
if particles are rapidly and frequently hitting the sides of the container, would the pressure be higher or lower?
higher
18
New cards
how does area affect pressure?
higher area → lower pressure
lower area → higher pressure
magic.
lower area → higher pressure
magic.
19
New cards
what is STP?
Standard Temperature & Pressure
* pressure → 1 atm
* temperature → 273 K
* pressure → 1 atm
* temperature → 273 K
20
New cards
now we get into the actual gas laws :D
yay
21
New cards
==Dalton’s Law==, what’s the tea?
==Dalton’s Law - Partial Pressure==
* the total pressure of a gas mixture = the sum of the different gas components
* **not** dependent on the __weight__ of the gas, only the __amount__ (it’s why we use moles!)
* the total pressure of a gas mixture = the sum of the different gas components
* **not** dependent on the __weight__ of the gas, only the __amount__ (it’s why we use moles!)
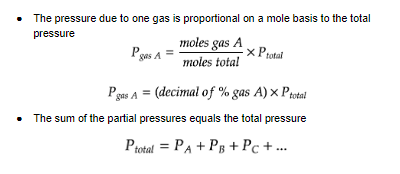
22
New cards
Example Problem: A mixture of 4.5% H2, 76% O2, and 19.5% N2 has a total pressure of 2.3 atm. What is the partial pressure of each of the gases?
PH2= 0.10 atm; PO2 1.75 atm; PN2= 0.45 atm
23
New cards
Next: @@Boyle’s Law@@
@@Boyle’s Law@@
* changes pressure and volume
* when moles and temperature are constant, presuure and volume have an **inverse** relationship
* when one goes up, other goes down, and vice versa
* changes pressure and volume
* when moles and temperature are constant, presuure and volume have an **inverse** relationship
* when one goes up, other goes down, and vice versa

24
New cards
what kind of container would gas have to be in to undergo @@Boyle’s Law@@?
flexible container (like a balloon) because the volume is changing
25
New cards
Example Problem: a gas occupies 1.65L at 1.00 atm what will be the new volume if the pressure becomes 3.00 atm?
0\.520L
26
New cards
Charles’ Law
Charles’ Law
* V1/T1=V2/T2
* V and T change, directly related
* n and P are constant
* V1/T1=V2/T2
* V and T change, directly related
* n and P are constant
27
New cards
Example Problem: When 10.5 L of gas at 20C is heated, the volume increases to 21 L. What is the new temperature in Celsius? Assume no other changes in the gas.
313 C
28
New cards
%%Gay-Lussac’s Law%%
%%Gay-Lussac’s Law%%
* P1/T1=P2/T2
* P and T change, directly related
* n and V constant
* P1/T1=P2/T2
* P and T change, directly related
* n and V constant
29
New cards
When a gas has a pressure of 500 mmHg at 25C and is expanded to standard pressure, what happens to the temperature?
The temperature would rise to 452.96 K because the pressure and temperature are directly related
30
New cards
^^Combined Gas Law^^
^^Combined Gas Law^^
* P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
* amount of gas (moles) is the only constant
* P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
* amount of gas (moles) is the only constant
31
New cards
Ideal Gas Law
PV=nRT
* predicts behavior of gas
* used to find one missing variable when you have the other three
* predicts behavior of gas
* used to find one missing variable when you have the other three
32
New cards
what does the “R” stand for?
“R” → universal gas constant
* 0.0821 (atm x L)/(K x mol)
* 0.0821 (atm x L)/(K x mol)
33
New cards
what is the formula(s) to find molar mass?
M=m/n
* M → Molar Mass
* m → mass
* n → mols
\
M=dRT/P
* M → Molar Mass
* m → mass
* n → mols
\
M=dRT/P
34
New cards
how do you find density?
d=m/v
35
New cards