Teas
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:37 PM on 12/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
1
New cards
Matter
Anything that has mass and volume
2
New cards
Mass
The quantity or measurement of matter
3
New cards
Volume
The amount of space something takes up
4
New cards
forms of energy light, heat, sound
What are some things that do not classify as matter
5
New cards
Color, size, volume, density, boiling/melting point, solubility, reactivity, combustibility, and flammability
What are some properties of matter
6
New cards
solid, liquid, gas
What are the 3 forms of matter
7
New cards
Solid
Molecules are tightly packed and don't have much room to move. They vibrate in a fixed place, making the object hard and rigid. Has a definite shape and volume
8
New cards
Liquid
Molecules are spaced out a bit more. They are able to move free and quick. Have a definite volume but take the shape of their containers
9
New cards
Gas
Molecules are even more far apart, they are able to move more free and quicker than liquid. Creates high Kinetic Energy/ has neither a definite shape nor volume
10
New cards
Deposition
When a gas turns into a solid
11
New cards
Sublimation
When a solid turns into a gas
12
New cards
Melting
When a solid becomes a liquid.
13
New cards
Freezing
liquid to solid
14
New cards
vaporizing (evaporating)
changing from a liquid to a gas
15
New cards
Condensation
The change of state from a gas to a liquid
16
New cards
As temperature increases
atmospheric pressure at sea level decreases
17
New cards
As the temperature decreases
atmospheric pressure increase
18
New cards
melting, vaporization, sublimation
Heating Curve includes
19
New cards
Molecules are absorbing energy (heat) and a decrease in cohesion between molecules
What happens in a heating curve?
20
New cards
the action or fact of forming a united whole
What is cohesion
21
New cards
molecules release energy resulting in a decrease in temperature causing cohesion to increase between the molecules as a result they have no room to room
What happens in a cooling curve
22
New cards
condensation, freezing, deposition
A cooling curve includes
23
New cards
Pure Substance
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties
24
New cards
Mixture
A material made up of two or more different chemical substances which are not chemically bonded.
25
New cards
Element
cannot be broken down into simpler substances by any chemical reaction.
26
New cards
Compound
is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds.
27
New cards
Homogeneous mixture
The composition is uniform throughout the sample and there are no distinct boundaries (can't be seen easily ex: Salt and Water)
28
New cards
Heterogeneous mixture
The composition varies and there are distinct boundaries (can be seen easily ex: Water and Oil)
29
New cards
Proton
Has a positive charge
30
New cards
Electron
Has a negative charge
31
New cards
Neutron
Contains no charge at all
32
New cards
Nucleus
In the center of every atom contains a
33
New cards
protons and neutrons
What subatomic particles can be found in the Nucleus
34
New cards
Electrons
What subatomic particle can be found outside of the nucleus in the orbitals
35
New cards
Atoms
What do subatomic particles make up?
36
New cards
Elements
What do atoms make up?
37
New cards
Diatomic
Any element that is made up of two atoms in it's natural form
38
New cards
H2, F2, Br2, I2, N2, O2, CI2
What are the 7 Diatomic elements?
39
New cards
Molecule
Consists of 2 or more atoms. It can consist of the same type of atoms or different types of atoms
40
New cards
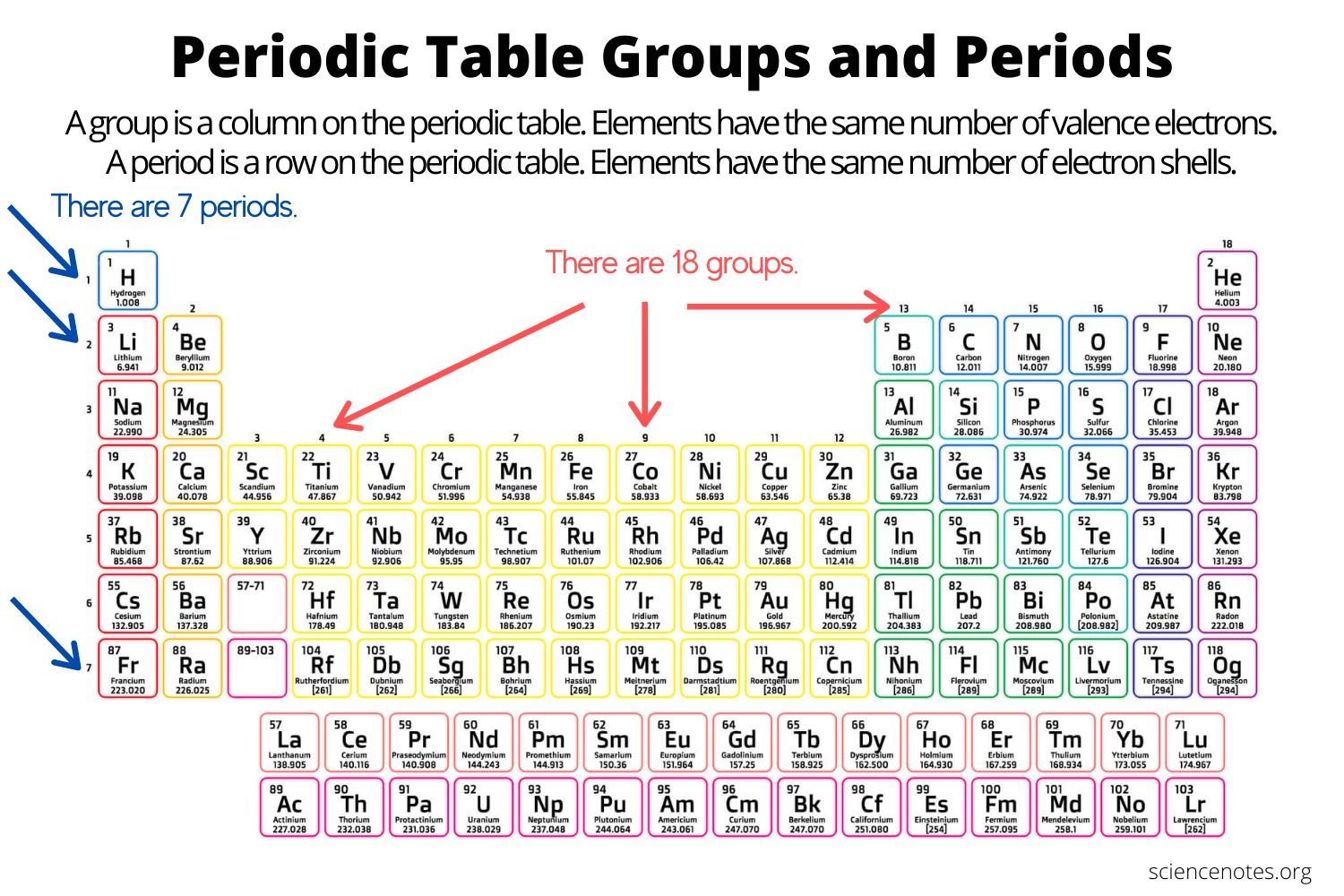
groups/families
Columns on the periodic table are referred to as
41
New cards
Periods
The rows going on a periodic table are referred to as
42
New cards
Properties of Metals
Shiny Metallic Luster
\
* Great Heat and Electrical Conductors
* Ductile (able to be compressed into a thin wire)
* Malleable (Flexible, able to hammer into shape without breaking)
* High Density + Boiling Point
* Forms Positive Ions (Cations)
\
* Great Heat and Electrical Conductors
* Ductile (able to be compressed into a thin wire)
* Malleable (Flexible, able to hammer into shape without breaking)
* High Density + Boiling Point
* Forms Positive Ions (Cations)
43
New cards
Properties of Non-Metals
\- Dull Appearance
\- Poor Heat and Electrical Conductor
\- Brittle- easily breaks
\- Low density
\- Low melting + Boiling Point
\- Forms both cations and anions
\- Poor Heat and Electrical Conductor
\- Brittle- easily breaks
\- Low density
\- Low melting + Boiling Point
\- Forms both cations and anions
44
New cards
properties of metalloids
- Have properties of both metals and non-metals
45
New cards
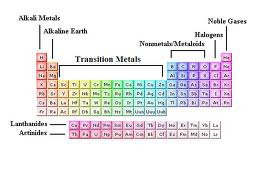
Akali Metals
\- Highly Reactive
\
\- Forms Cations with a +1 charge
\
\- Forms Cations with a +1 charge
46
New cards
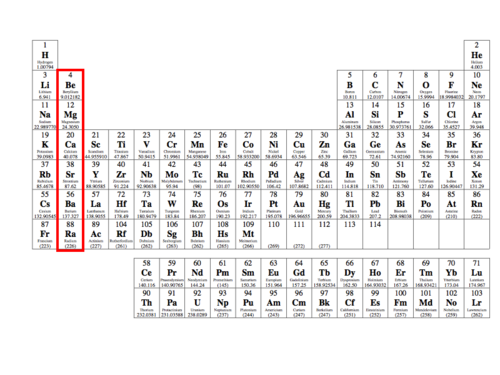
Alkaline Earth Metals
\- Highly Reactive but not as reactive as Alkali Metals
\
\- Forms Cations with a +2 Charge
\
\- Forms Cations with a +2 Charge
47
New cards
Halogens
\- Diatomic Elements
\
\- Form Anions with a -1 Charge
\
\- Form Anions with a -1 Charge
48
New cards
noble gases
\- Non-Reactive + most stable
\- Inert Gases"
\- Outermost orbit of these noble gas elements are completely filled with electrons
\- Inert Gases"
\- Outermost orbit of these noble gas elements are completely filled with electrons
49
New cards
number of protons
What does the atomic number represent?
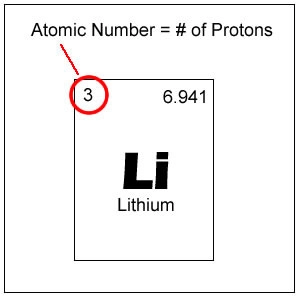
50
New cards
The average number of protons and neutrons for all natural isotopes of an element.
What does the atomic mass represent?
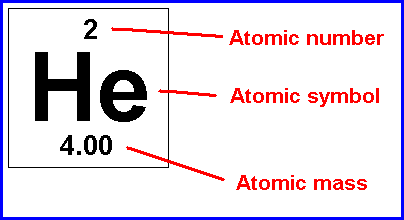
51
New cards
Mass Number
The number of protons and neutrons in an atom. It is a whole number

52
New cards
Neutral Atoms
- Has the same amount of protons and electrons
53
New cards
atomic mass - atomic number
How to find the amount of Neutrons of an atom?
54
New cards
Atomic Mass
The average number of protons and neutrons for all natural isotopes of an element. It is a decimal number
55
New cards
Ion
An atom with a charge is classified as an
56
New cards
gains or loses electrons
An atom gets a charge when it
57
New cards
Cation
Has more protons than electrons
58
New cards
Anion
Has more electrons than protons
59
New cards
The octet rule states
Elements combine in such a way that each atom has 8 electrons filling their valence shell. In order for this to happen each atom must give up, gain or share electrons.
60
New cards
Noble Gases
The most stable elements, naturally having a full valence shell
61
New cards
they have fewer electrons in their outer shell
metals lose electrons because
62
New cards
they have more electrons in their outer shell
nonmetals gain electrons because
63
New cards
ionic bond
Atoms that form lose or gain electrons (transfer of electrons) occur between a metal and a non-metal
\
often between metals (generally loses electrons) and nonmetals (generally tends to gain electrons)
\
(Ex: NACI, KCI, CACL2)
\
often between metals (generally loses electrons) and nonmetals (generally tends to gain electrons)
\
(Ex: NACI, KCI, CACL2)
64
New cards
covalent bond
atoms that form share electrons (nonmetal + nonmetal)
\
Ex: H2O, O2, CO2, C6H12O6
\
Ex: H2O, O2, CO2, C6H12O6
65
New cards
polar covalent bond
When the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms is \>0.5 this is called a
66
New cards
nonpolar covalent bond
If the electronegativity is less than 0.5, the covalent bond is called a
67
New cards
Valence Shell
The outermost energy level or "shell" of an atom
68
New cards
Valence electrons
determines the atoms capabilities associated with chemical reactions
69
New cards
How many electrons can fit in energy levels 1-5
2 e-fit on the first energy level
8 e-fit on the second energy level
18 e-fit on the third energy level
32 e-fit on the fourth energy level
8 e-fit on the second energy level
18 e-fit on the third energy level
32 e-fit on the fourth energy level
70
New cards
Helium which has
In group 8 all elements have 8 valance electrons except
71
New cards
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons
72
New cards
What are the 2 factors that affect the size of an atom or the "atomic radii"
1\. The distance of the electron to the proton
\
2\. The amount of protons in the nucleus
\
2\. The amount of protons in the nucleus
73
New cards
Attract to each other
Opposite charges
74
New cards
Repel each other
Same charges
75
New cards
Atomic Radii
The size of an atom. It is the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost electron
76
New cards
Ionization Energy (IE)
The energy required to remove one or more valence electrons from gaseous atom
77
New cards
Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom to attract electrons, to form a chemical bond
78
New cards
Chemical Reaction
the conversion of one or more substances into a completely new substance
79
New cards
The Reactant
The substance that you begin with in an equation is called
80
New cards
The Product
the substance that you end with in an equation is called
81
New cards
combination synthesis reaction
Starting off with 2 or more reactants that combine to make 1 product
82
New cards
decomposition reaction
1 reactant that is broken down into 2 or more products
83
New cards
single-displacement reaction
1 reactant is replaced by another
84
New cards
combustion reaction
A substance reacts with oxygen gas, releasing energy in the form of light and heat. These reactions must involve O2 as one reactant
85
New cards
The Arrhenius Theory states
\- Acids release hydrogen (H+) ions in a solution
\
\- Bases release hydroxide (OH-) ions in solution
\
\- Bases release hydroxide (OH-) ions in solution
86
New cards
Bronsted-Lowry theory states
* States that acids are proton donors
\
* States bases are proton acceptors
\
\
* States bases are proton acceptors
\
87
New cards
Acids
Likely to begin with an H and the H is attached to a non-metal
88
New cards
Bases
Likely to have OH in them or a metal attached to H
89
New cards
hydrochloric acid
a STRONG acid that is found in our stomach and aids in the digestion of proteins
90
New cards
Plasma
A state of matter that is often found in the stars. It is a gas that is ionized, meaning that electrons have been stripped from the atoms
91
New cards
Mole
The unit used to measure the amount of a substance (ex: number of atoms, molecules, or mass of a substance)
92
New cards
Endothermic Reactions
Reactions that absorb heat are called (ex: temperature increases when cooking an egg (heat is absorbed from the pan to cook the egg)
93
New cards
Exothermic Reactions
Reactions that release heat are called (Ex: The concentration of reactants of water vapor into rain releasing energy in the form of heat)
94
New cards
Equilibrium
Rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse action
95
New cards
dynamic equilibrium
When the forward and reverse reactions are occurring at the same time
96
New cards
static equilibrium
when concentrations of the reactants and products are not changing
97
New cards
activation energy
The minimum amount of energy that is needed for a chemical reaction
98
New cards
Cohesion
The process of a similar molecule surrounding and binding to another molecule
99
New cards
Adhesion
The process of dissimilar molecules binding to another molecule
100
New cards
Solvent
A substance that dissolves in another substances