Water Cycle
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What is a model?
a representation of an object or system
What is a system?
A set of interrelated components working together
What does a system consist of?
Inputs, stores and outputs with a series of flows or connections between them
What can systems be classified as?
- Isolated systems
- Closed systems
- Open systems
Describe an isolated system
There aren't any interactions with anything outside the system boundary - no input or output of energy or matter
Describe a closed system
When energy, but NOT matter is exchanged
Describe an open system
a system that exchanges both energy and mass with its environment
What is an input?
The addition of matter and/or energy into a system
What is an output?
The movement of matter and or energy out of a system.
What is a flow/transfer?
A form of linkage between one store/component and another that involves movement of energy or mass
What is a store?
A place where water is stationary within the water cycle
Why is the Global Hydrological cycle an example of a closed system?
•Energy from the sun enters and leaves the system.
•No water enters or exits the cycle.
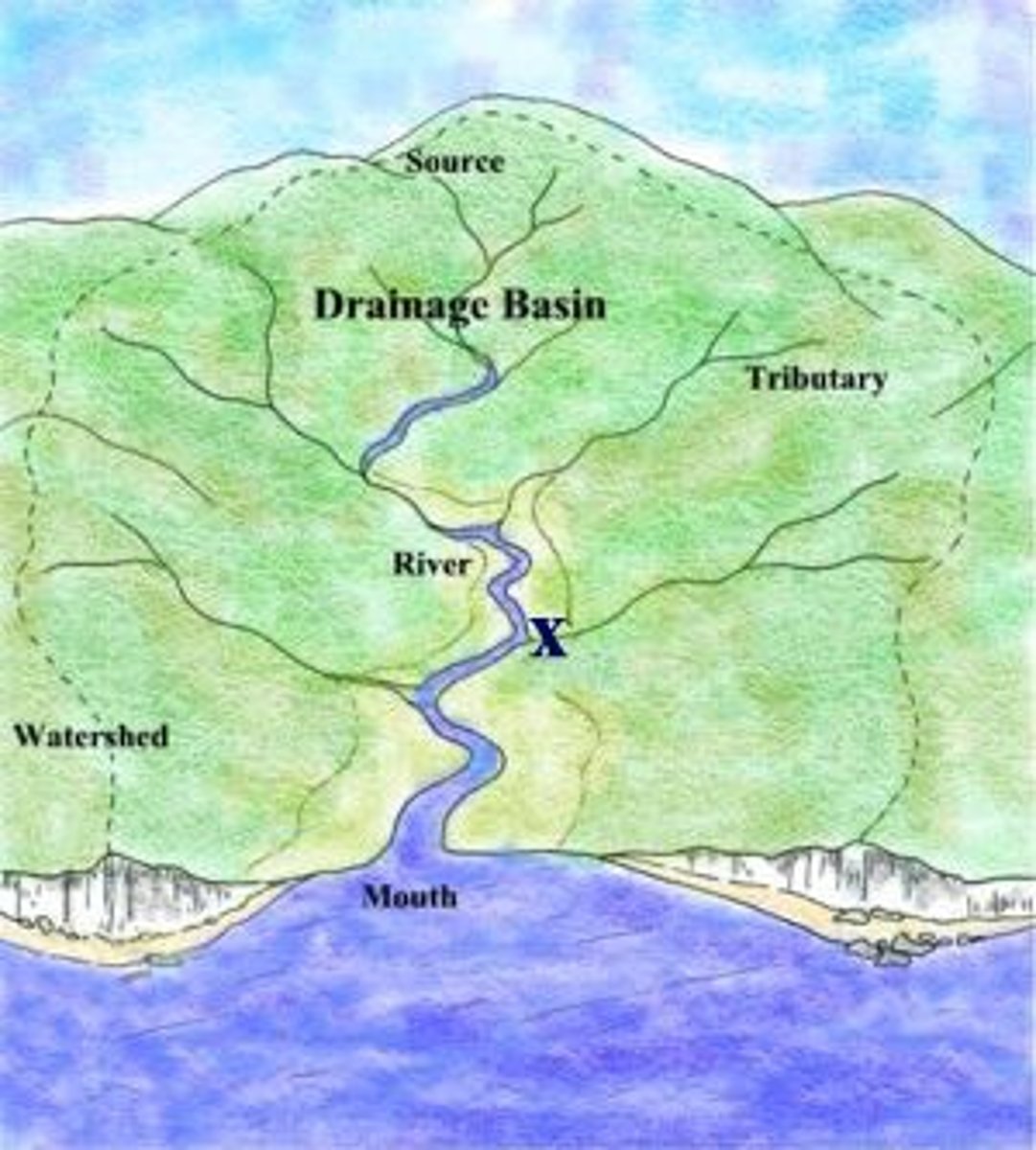
Why is the drainage basin cycle an example of a open system?
•Energy enters and leaves the drainage basin.
•But mass (water, sediment etc) also enters and leaves.
What is a subsystem?
A component of a larger system
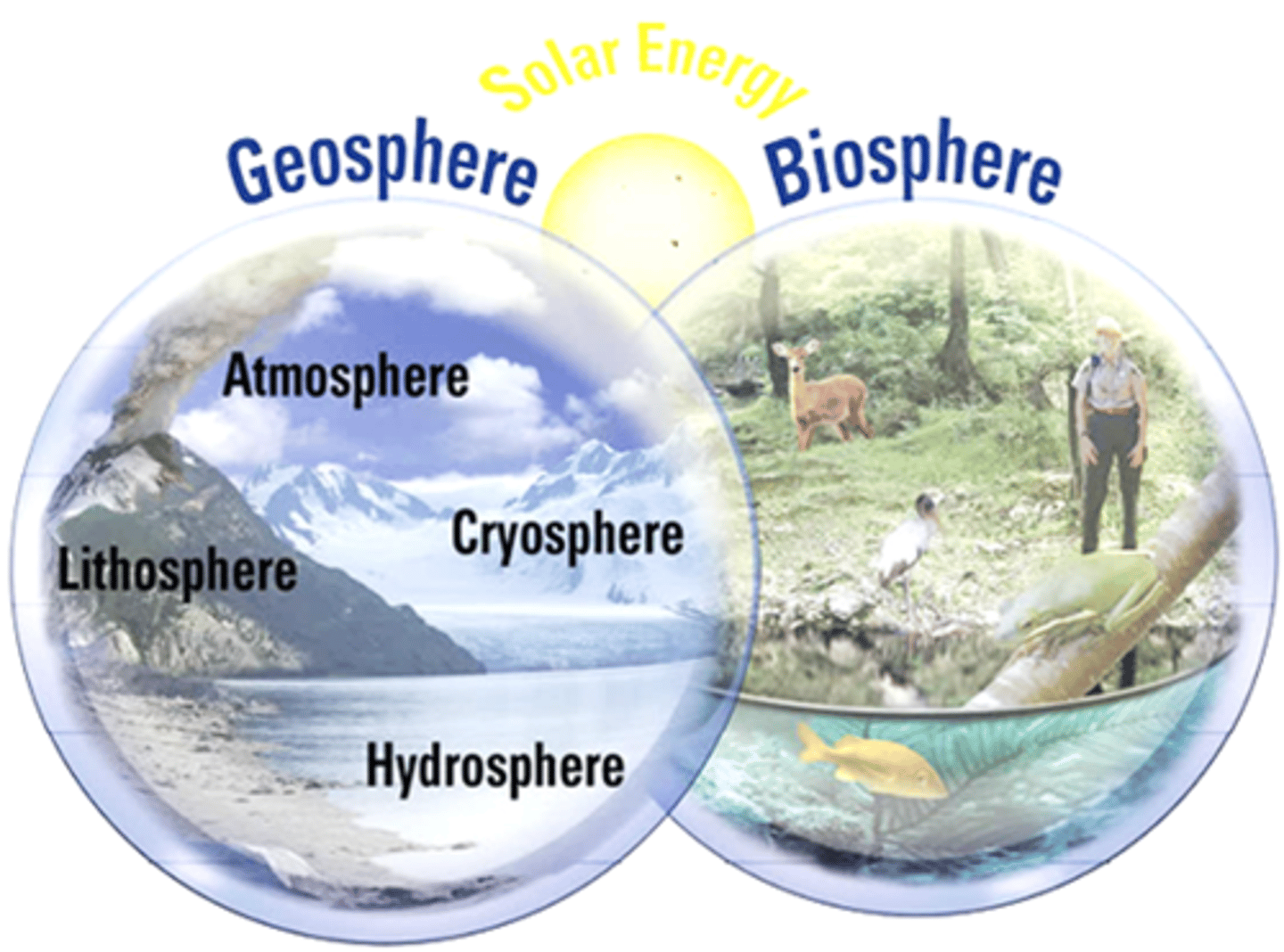
how many subsystems does earth have?
5 - all open systems
List the 5 subsystems of earth
- atmosphere
- cryosphere
- hydrosphere
- biosphere
- lithosphere
What is dynamic equilibrium?
Where there is a balance between inputs and outputs
When does feedback occur?
when a change in one part of a system leads to a change in another part
What are the two types of feedback?
positive and negative
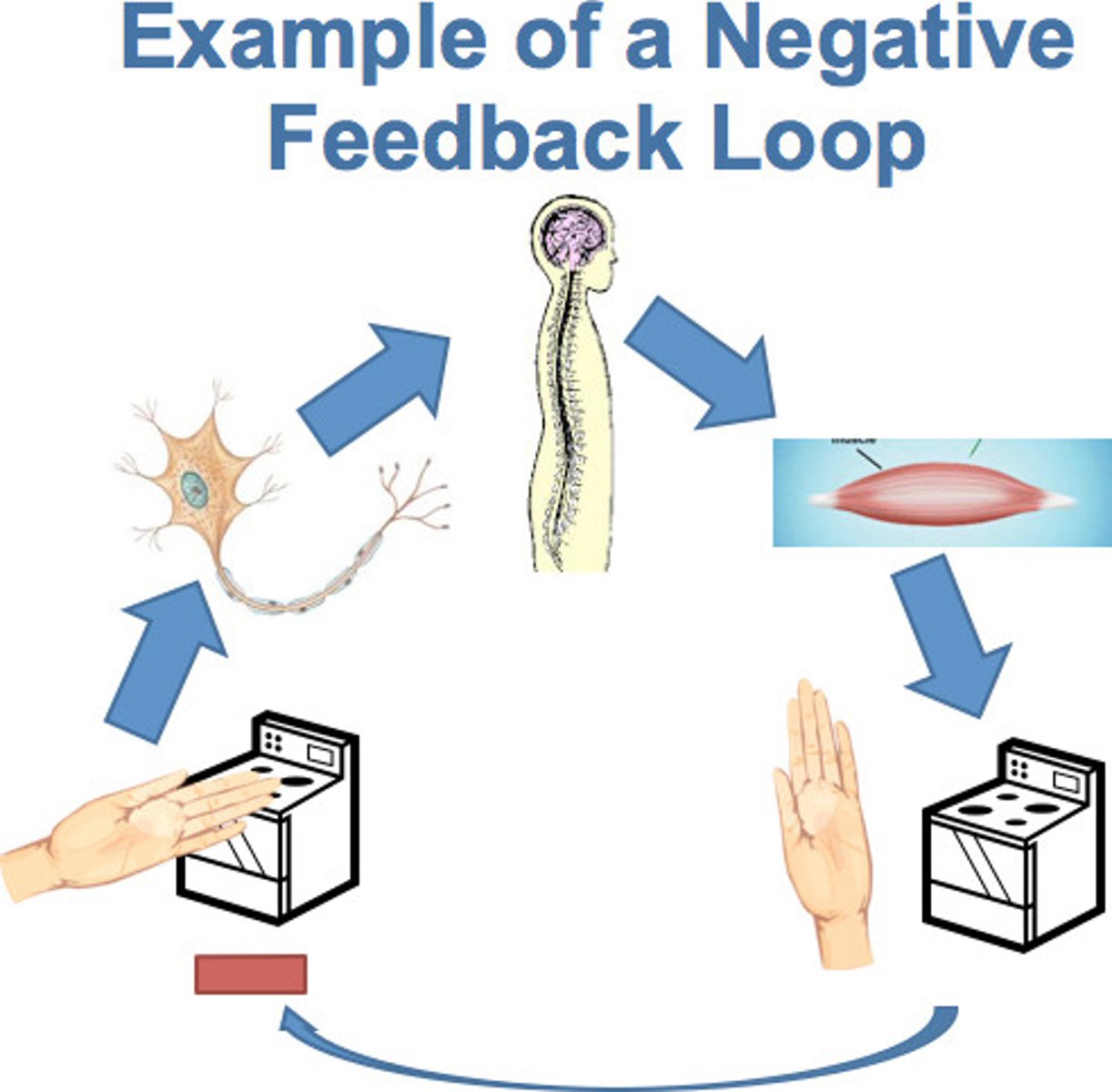
Describe negative feedback
dampens down change, keeping the system in equilibrium: is self-regulating to restore balance.
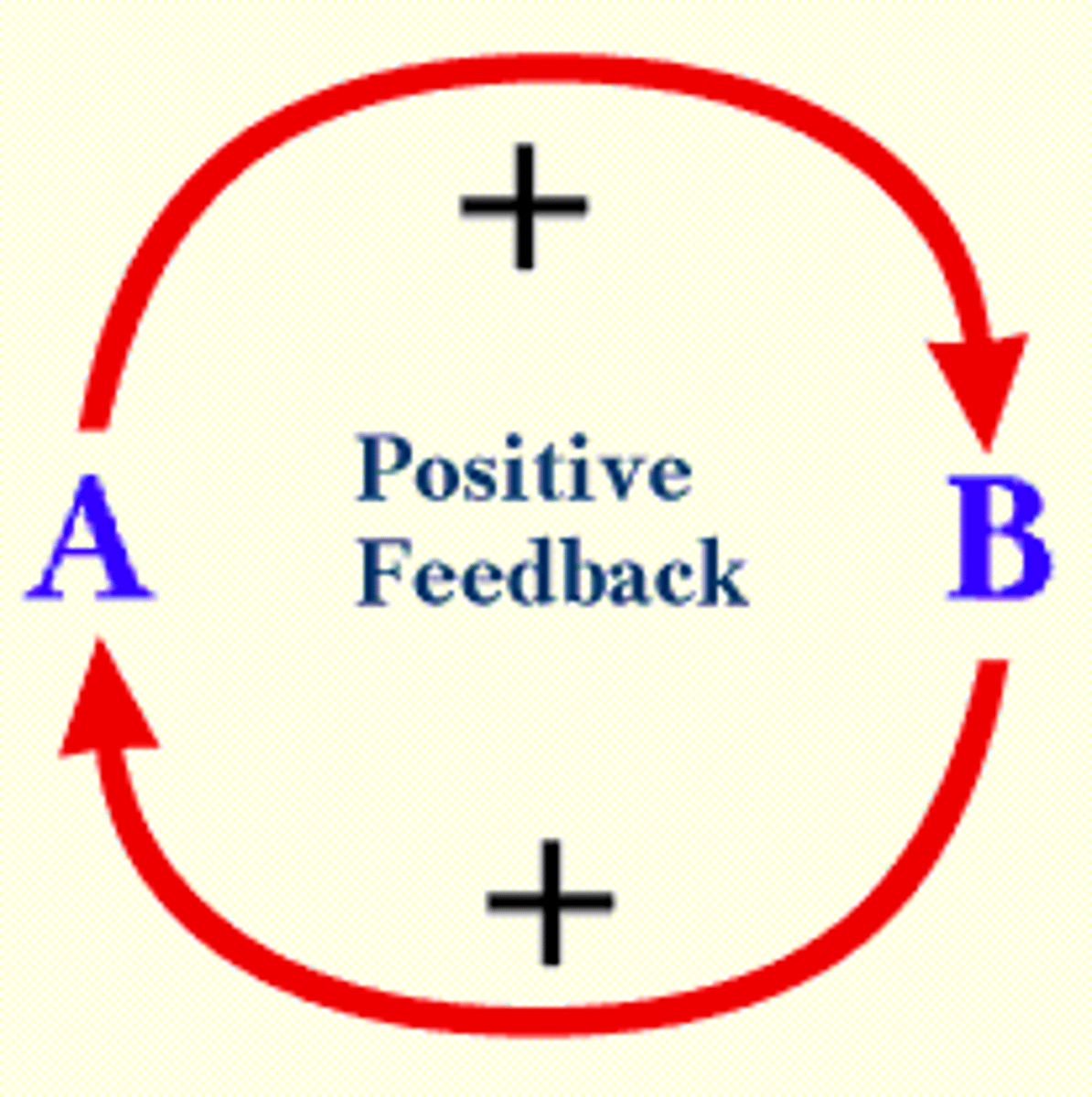
Describe positive feedback
amplifies change: one change leads to another, pushing the system away from a steady state in a natural system.
Give an example of positive feedback in the water cycle
Higher temperatures increase the melting of snow and ice, leading to reduction of surface albedo so more sunlight absorbed by land and sea. Temperatures increase further, which leads to further melting.
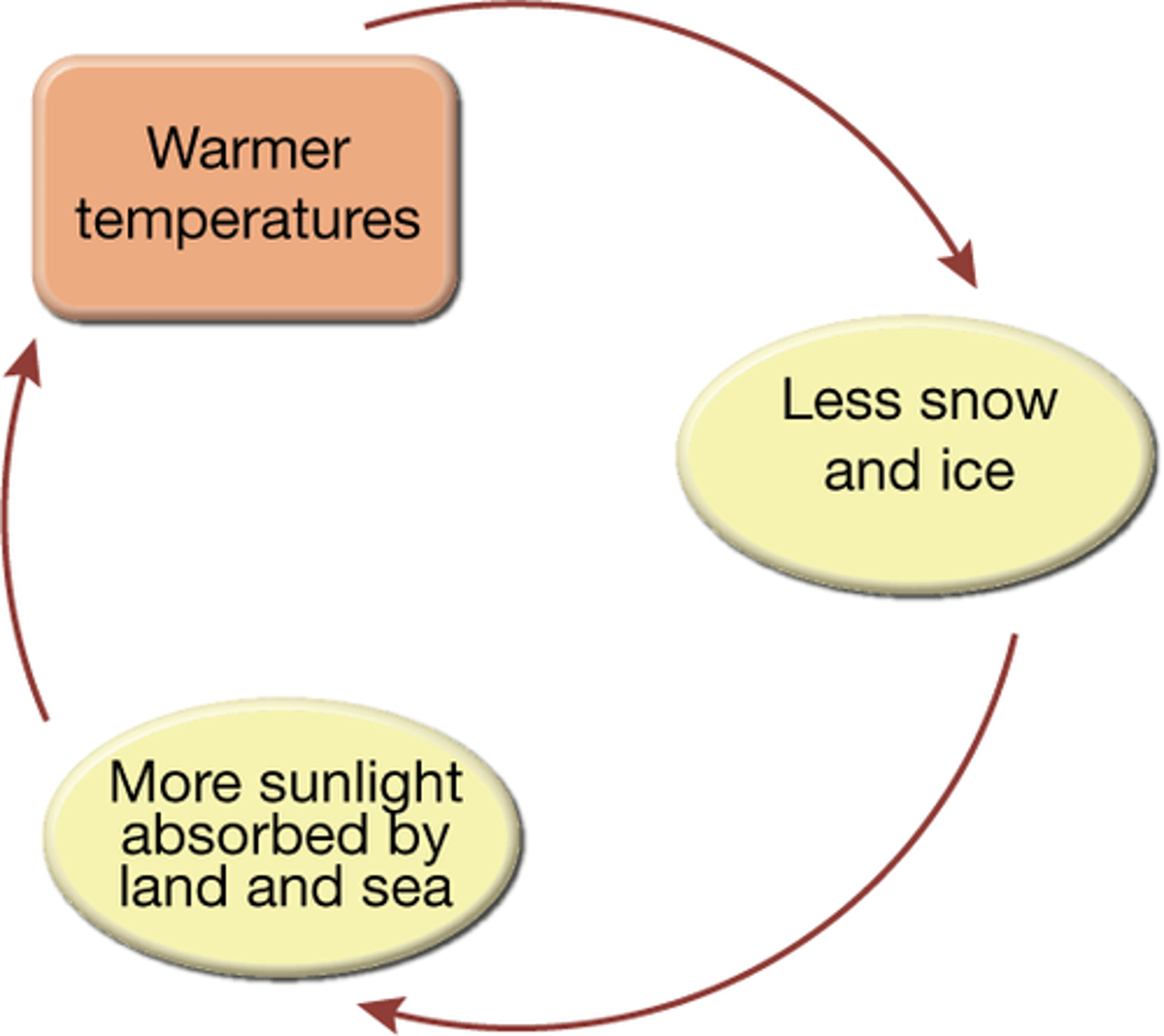
How much faster is the amplified warming in the Artic from the ice-albedo feedback?
about 3-4 times the global average
Define albedo
the proportion of the incident light or radiation that is reflected by a surface
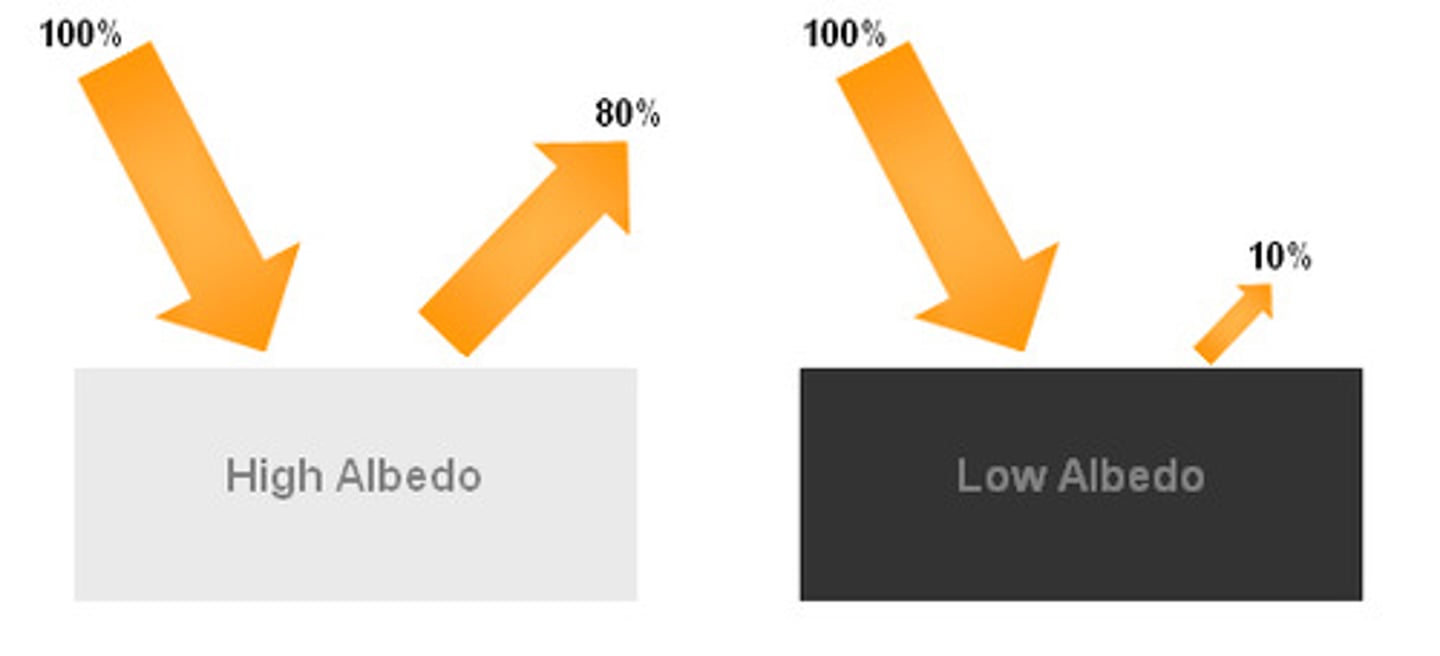
What is a tipping point?
the point at which a fundamental shift in the behaviour of a system occurs
How can a tipping point be reached?
after a build-up of internal change, or caused by external forces.
How much of the Earth's surface is covered by water?
71%
What percentage of all water on earth is fresh?
3%

How much of the fresh water is frozen?
79%

How much freshwater is groundwater?
20%
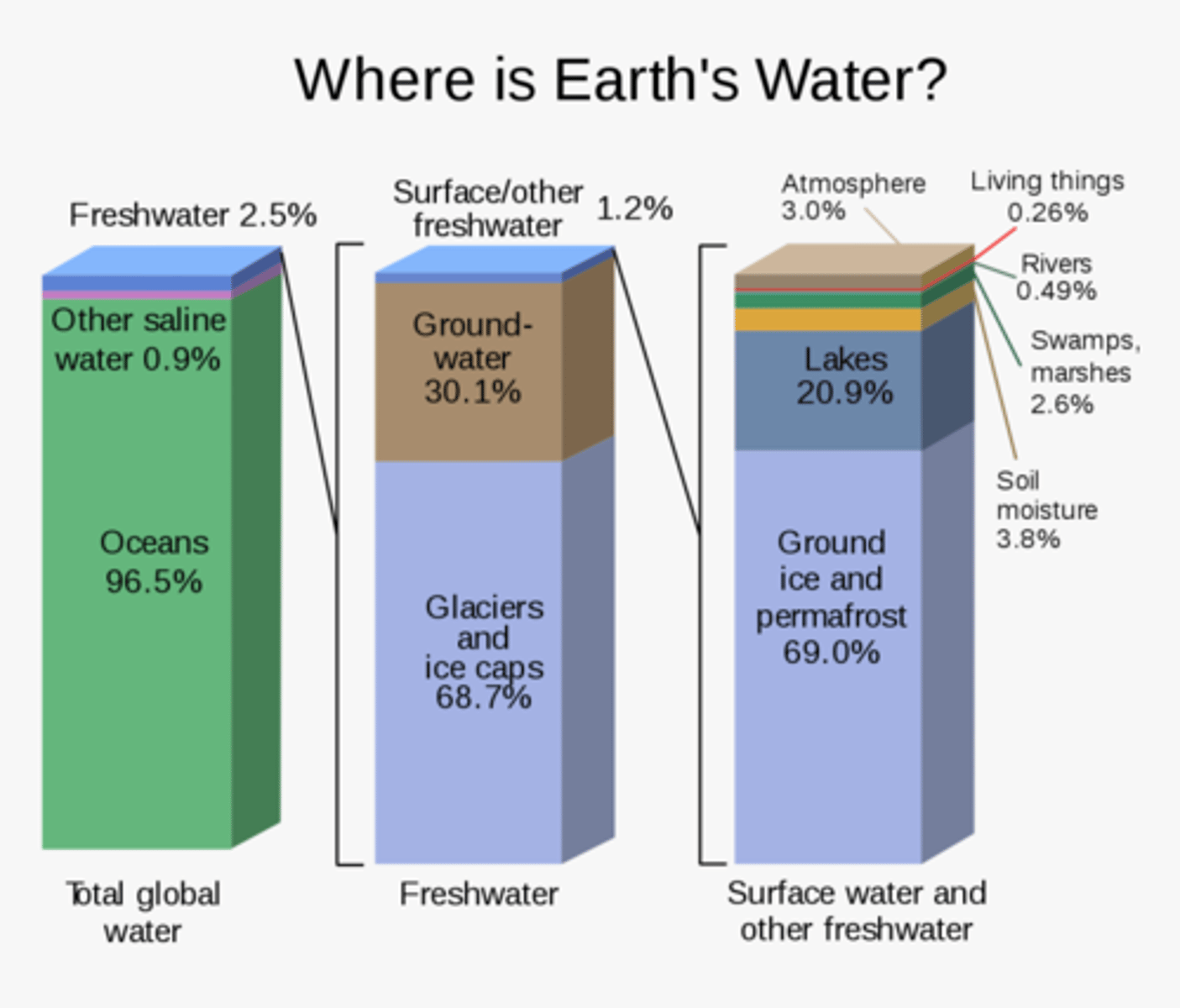
How much freshwater is easily accessible surface water?
1%
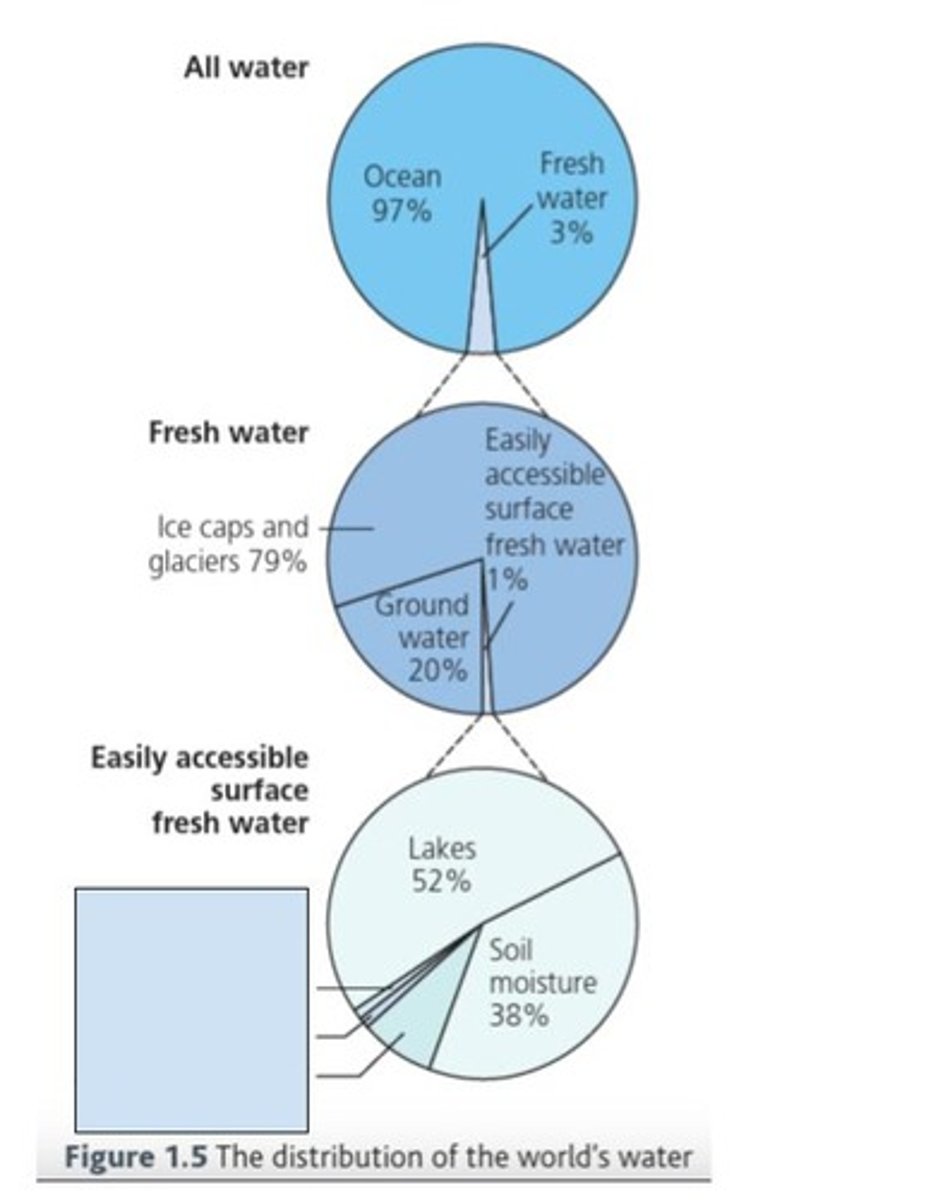
How much of easily accessible surface fresh water is stored in lakes?
52%

How much of easily accessible surface water is stored in rivers?
1%
How much of easily accessible surface water is stored in atmospheric water vapour?
8%
How much of easily accessible surface water is stored in soil moisture?
38%
How much water is stored in the ocean?
1.4 billion km3
How much water is stored in ice and snow?
27.3 million km3
How much water is stored in ground water?
22.9 million km3
How much water is stored in lakes?
176,000km3
How much water is stored in soil moisture?
16,000km3
How much water is stored in the atmosphere?
13,000 km3 (~ 0.001%)
How much water is stored in rivers?
2,000km3
How much water is stored in plants and animals?
2,000km3
Describe the global distribution of oceanic water
There are 5 oceanic bodies of water and several smaller seas covering approx 72% of the Earth's surface.
What are the 4 major stores of water?
lithosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, atmosphere
Describe the lithospheric store of water
Includes all liquid water in the rocks and soil as groundwater and soil moisture - accounts for about 1/3 of fresh water on earth.
Describe the hydrosphere
All the liquid water on earth's surface, including rivers, lakes, seas and oceans - oceans account for almost 97% of all water on earth
How much fresh water on earth is accounted for by ice?
about 2/3
What are cryospheric water stores composed of?
Sea ice, ice caps, ice sheets, Alpine glaciers and permafrost

Describe the global distribution of cryospheric water stores
Mainly in high altitude and high latitude areas
What is included in terrestrial water stores?
Rivers, lakes, wetlands, groundwater, soil water and biological water

What is the smallest of the major stores of water?
The atmosphere
What is the most common form of atmospheric water store?
Water vapour
Why is water vapour important?
it absorbs, reflects and scatters incoming solar radiation, keeping the atmosphere at a temperature that can maintain life
Define residence time
The average time a molecule of water will spend in one of the stores
What is the residence time of oceans?
3600 years
What is the residence time of icecaps?
15,000 years depending on size
What is the residence time of deep groundwater?
10,000 years
What is the residence time of shallow groundwater?
100-200 years
What is the residence time of rivers and lakes?
2 weeks to 10 years
What is the residence time of soil moisture?
2-50 weeks
What is the residence time of atmospheric moisture?
10 days
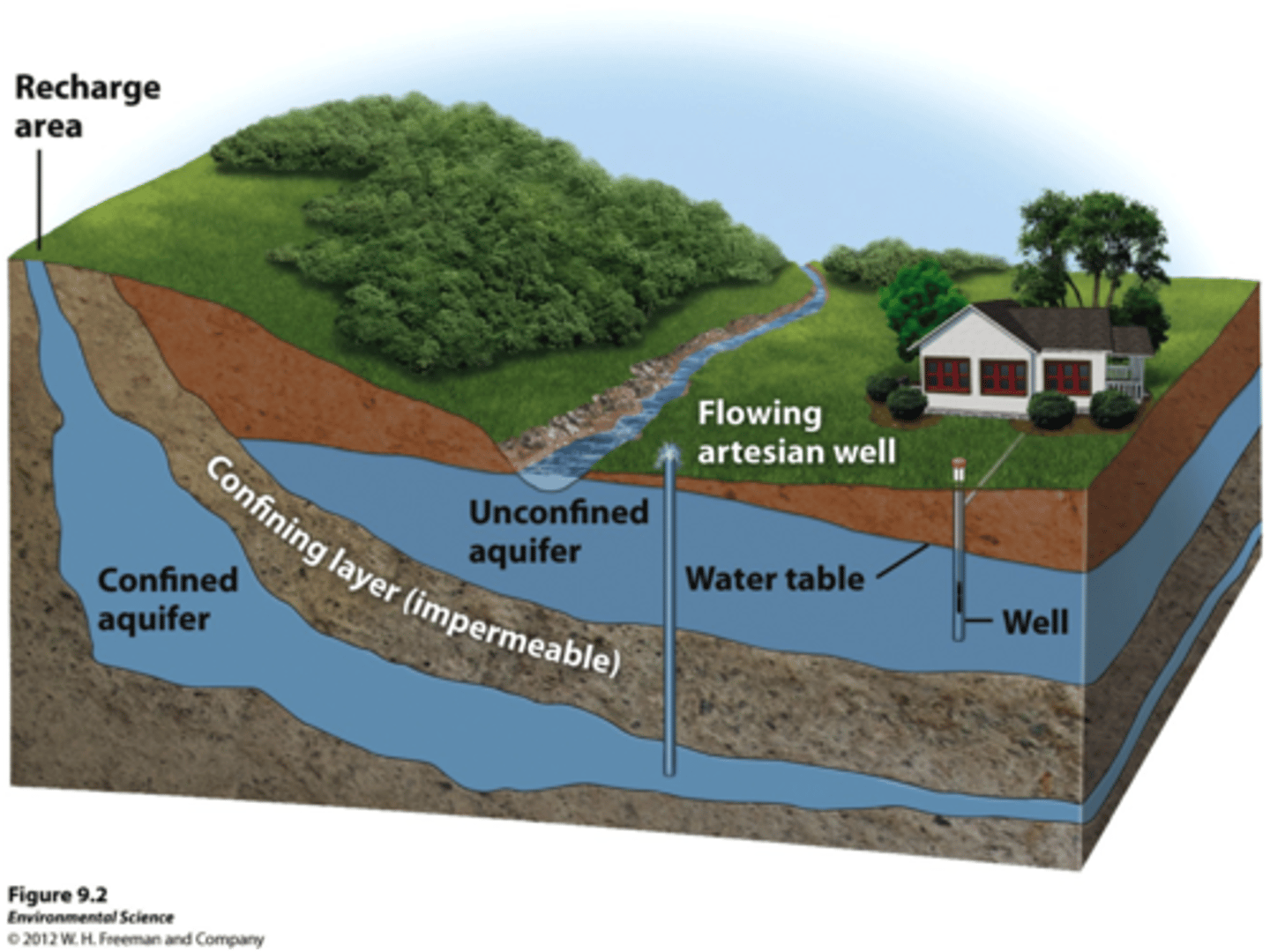
What is an aquifer?
permeable rock that can contain or transmit groundwater
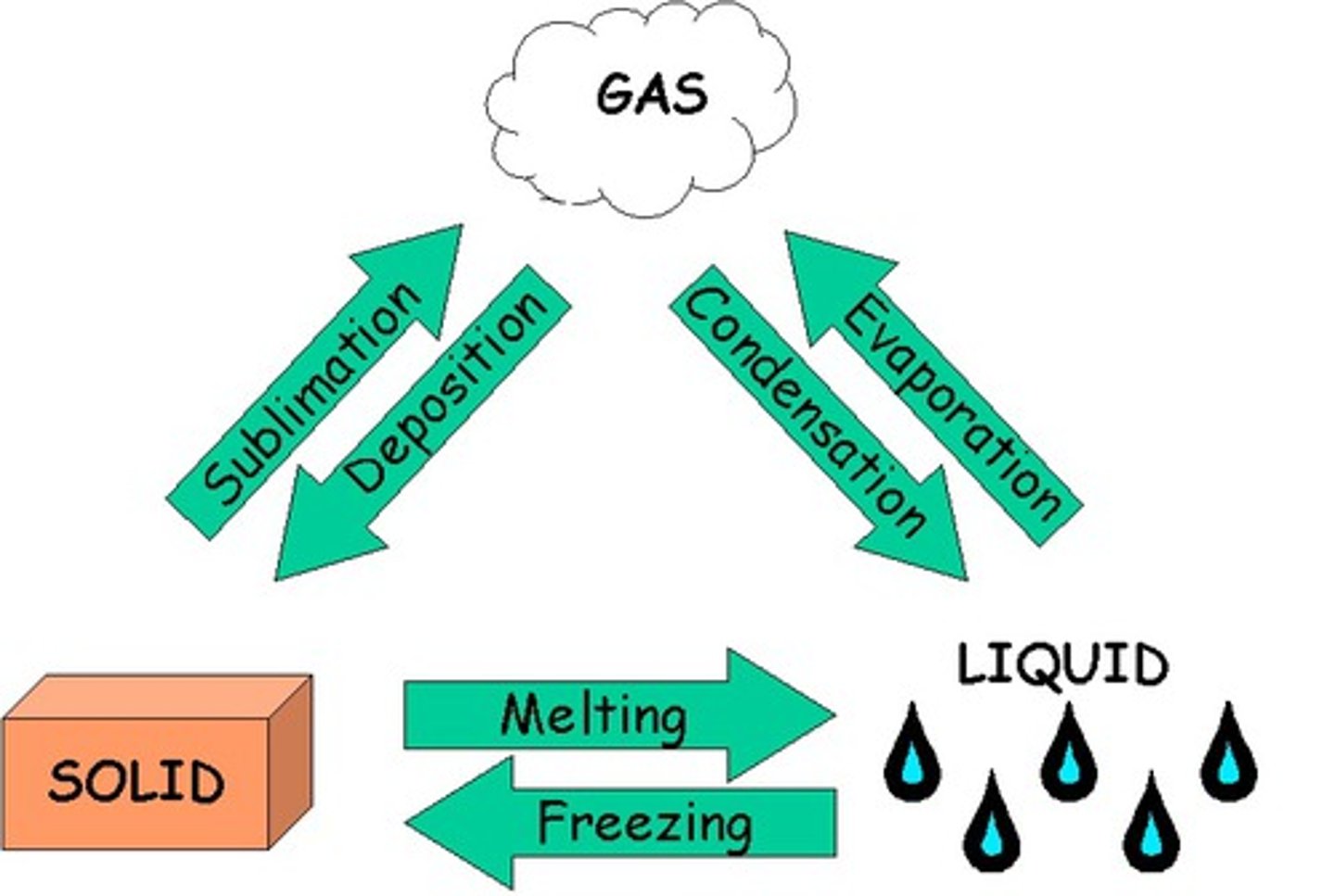
List some processes of water
- evaporation
- condensation
- cloud formation
- precipitation
- cryospheric processes
What is latent heat?
The heat absorbed or released during a change in the physical state of water.
What is evaporation?
When a liquid turns into a gas
What is needed for evaporation?
heat energy
What is evapotranspiration?
combination of evaporation and transpiration
What is evapotranspiration affected by?
temperature, wind, humidity, amount of solar energy, availability of water and surface area
What is condensation?
The change of state from a gas to a liquid
How does condensation occur?
Occurs when air cools and is less able to hold water vapour (dew point). Water molecules condense onto nuclei (dust, smoke) or onto surfaces (e.g. grass) which form water droplets or frost.

What is the dew point?
the atmospheric temperature below which water droplets begin to condense and dew can form.
What are the three methods of condensation?
- Conduction cooling
- Radiation cooling (normal)
- Expansion cooling
What is meant by conduction cooling?
contact cooling leads to condensation when moist air comes into contact with a cold object.

What is meant by radiation cooling?
air loses heat to space by long wave radiation from clouds and gas
What happens in expansion cooling?
air forced to rise - it expands as it rises into thinner air. When gas expands its temperature falls, so the air cools.
When does precipitation occur?
when air can no longer hold condensed water
What is the troposphere?
the lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere, where weather occurs
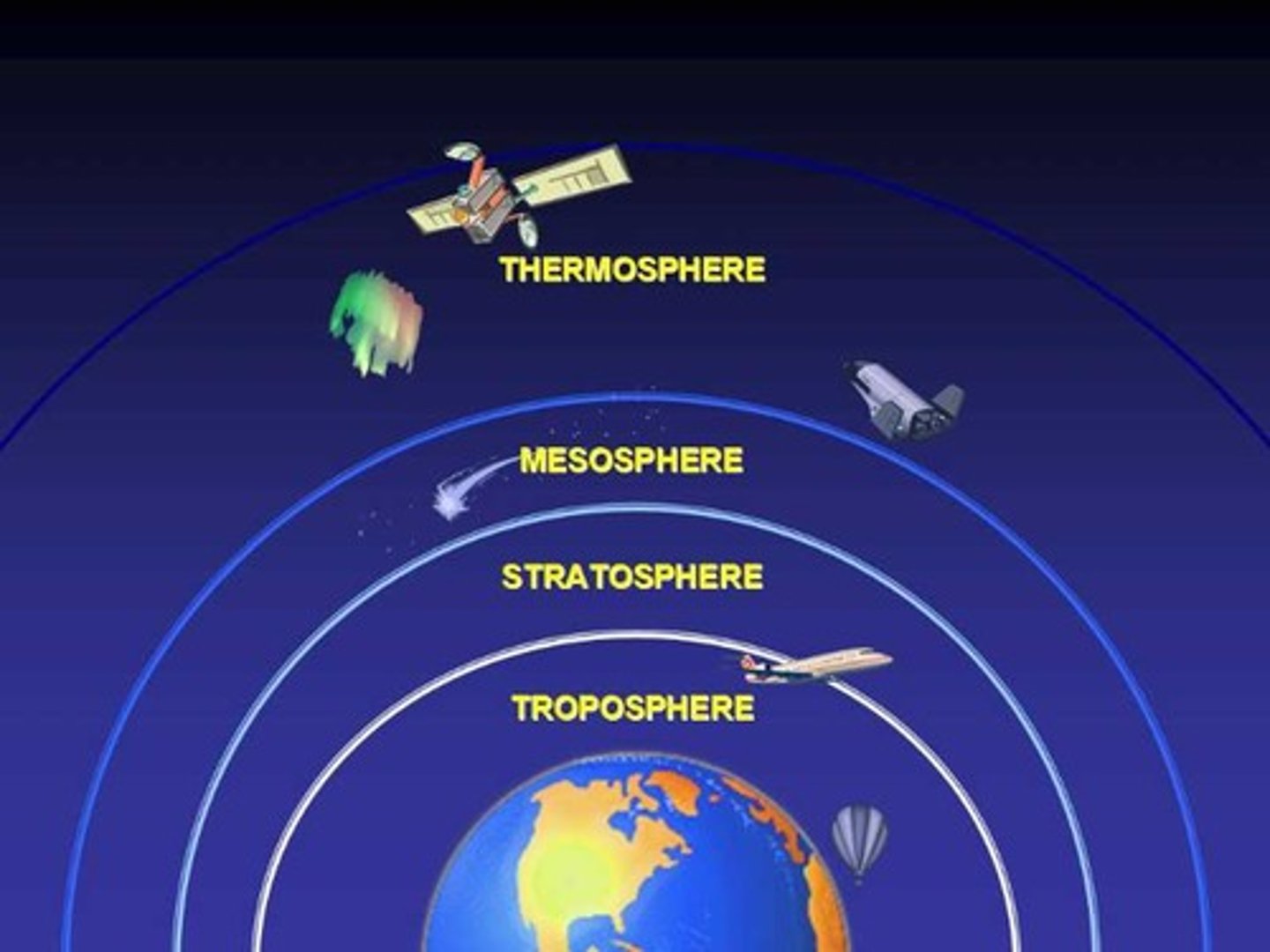
How much of the atmosphere's water vapour does the troposphere contain?
approximately 99%
Why does the troposphere get cooler as you go up?
•The troposphere is mainly heated from the ground as the earth's surface absorbs more solar radiation than the air.
•The surface is warmed by the sun, transferring heat to the air above through conduction.
•This warm air rises via convection.
•As the air cools, it condenses.
What is referred to by air pressure?
The weight of the earth's atmosphere pressing down on everything
Why does air pressure decrease as altitude increases?
If air rises less pressure is exerted on it and it expands. - referred to as adiabatic expansion
What is adiabatic expansion?
The expansion of a parcel of air due to a decrease in pressure. Expansion causes cooling.
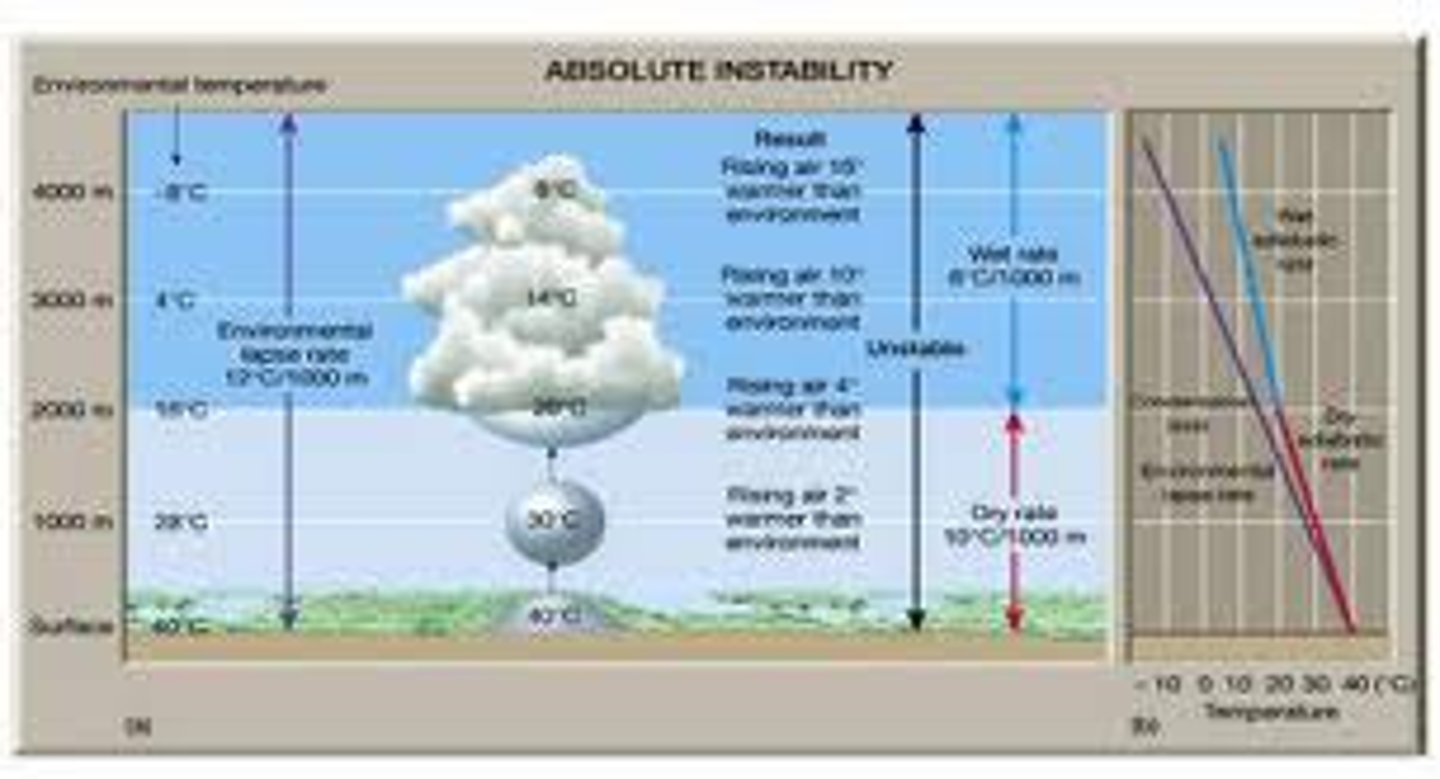
What is meant by lapse rates?
how quickly the air changes temperature
What is the lapse rate of dry air?
cools 9.8 degrees every 1000m
What temperature is known as the dew point?
8 degrees
What is the lapse rate of saturated/wet air?
cools 6 degrees every 1000m.
What are clouds?
water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere
When do clouds form?
- When air is saturated as it has cooled below the dew point or evaporation means air has reached maximum water holding capacity
- Condensation nuclei are present
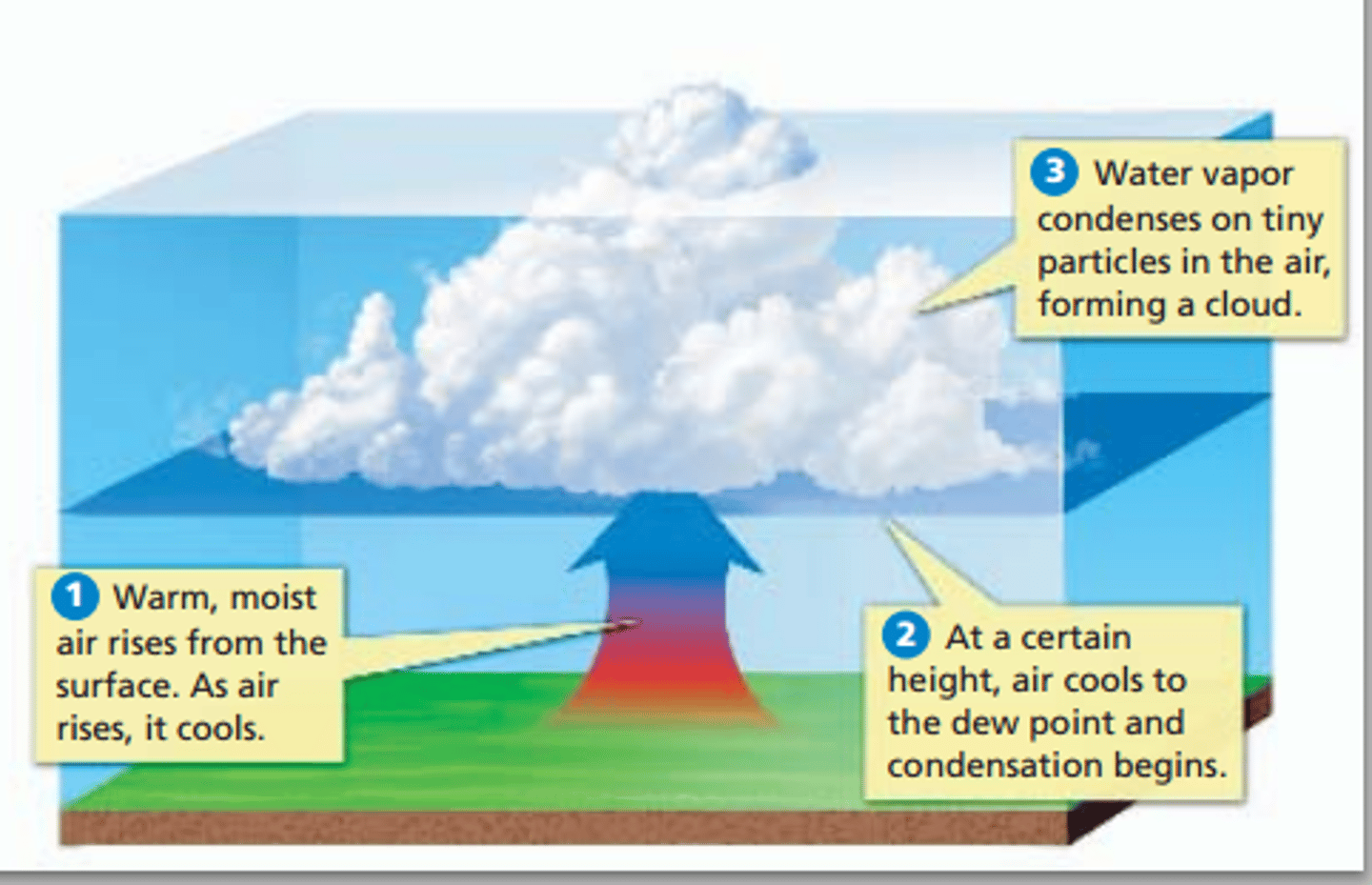
How do clouds form?
Water vapor in the air condenses around condensation nuclei to form cloud droplets. Droplets combine - become heavy enough to fall as precipitation
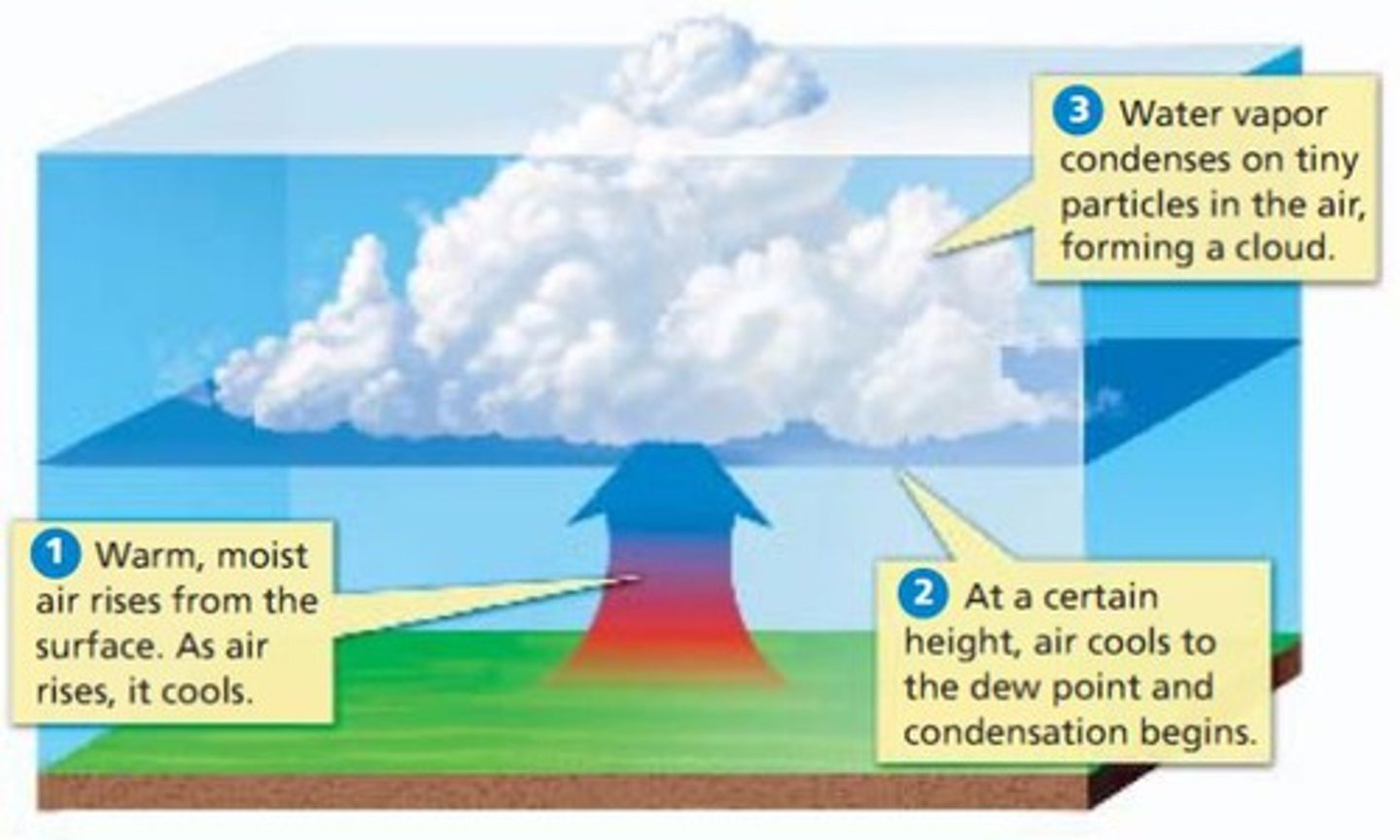
The greater the amount of --------- in the cooling air, the greater the condensation and cloud formation.
moisture
When can condensation (directly leading to precipitation) occur?
- air temperature is reduced to a dew point
- volume of air increases as it rises and expands but there is no addition in heat (adiabatic cooling)
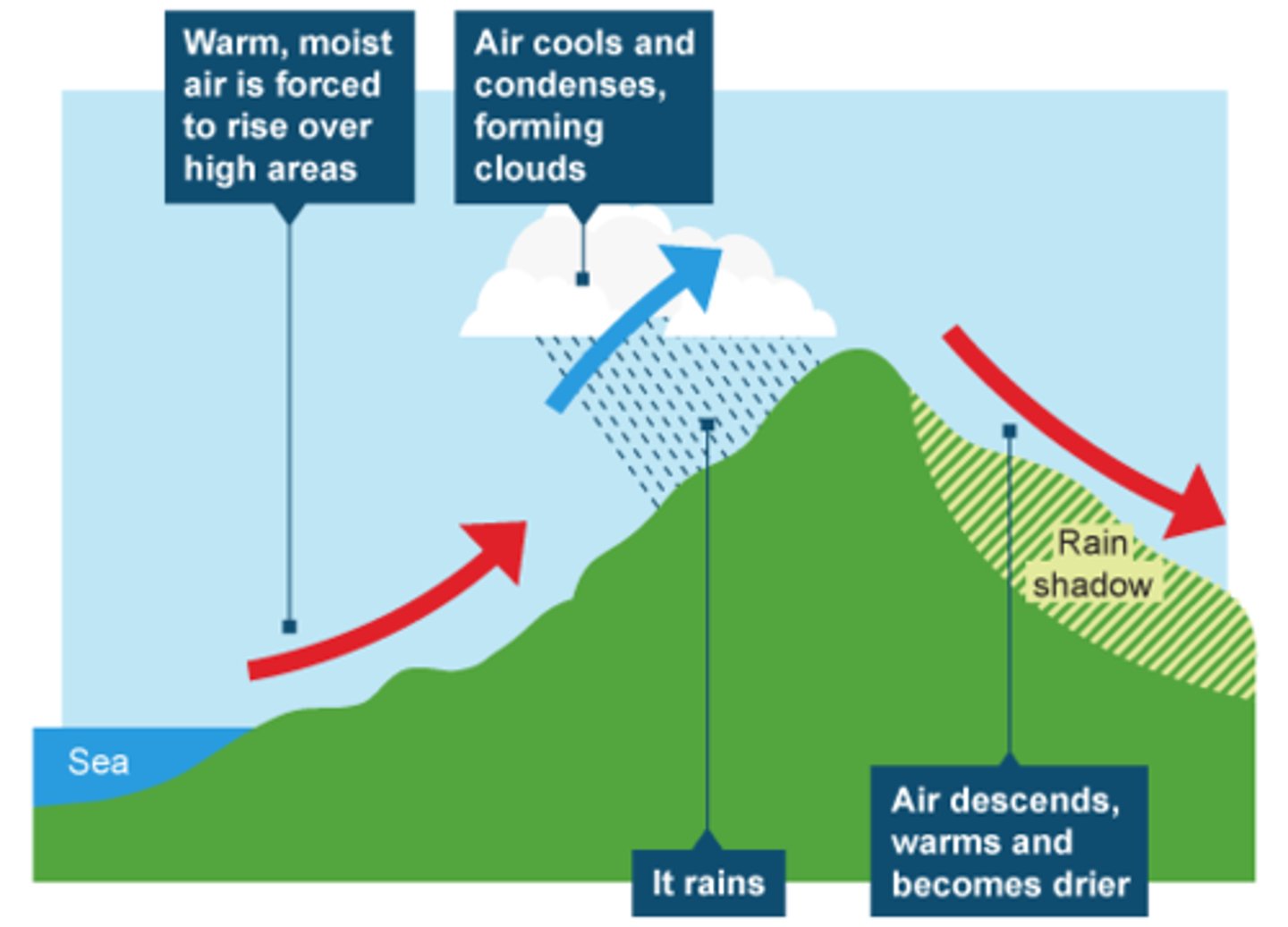
What is orographic rainfall?
caused by uplifting and cooling of moist air over mountains
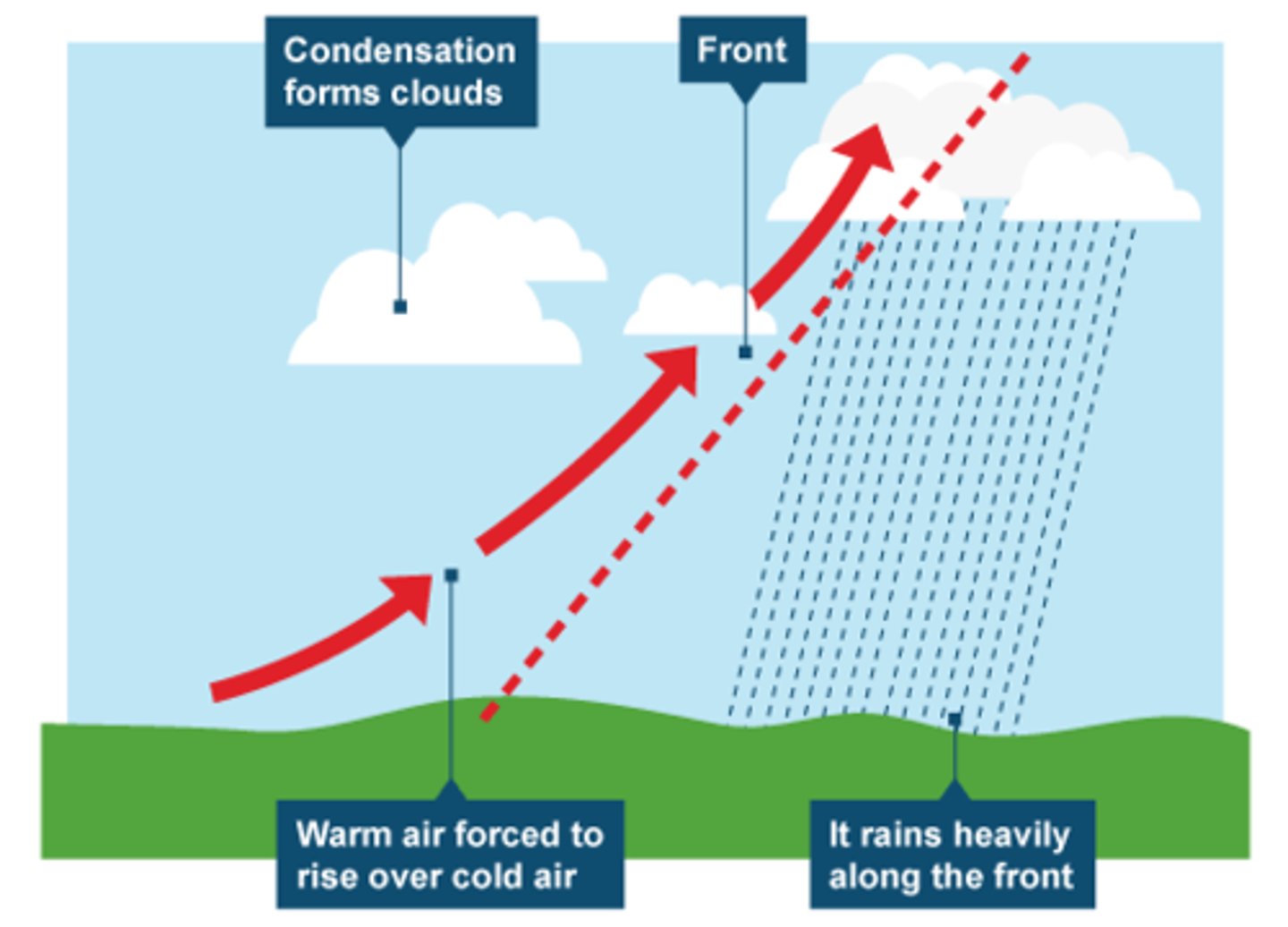
What causes frontal rainfall?
Air masses of different temperatures and densities meeting, with the warm air rising over the cool sinking air
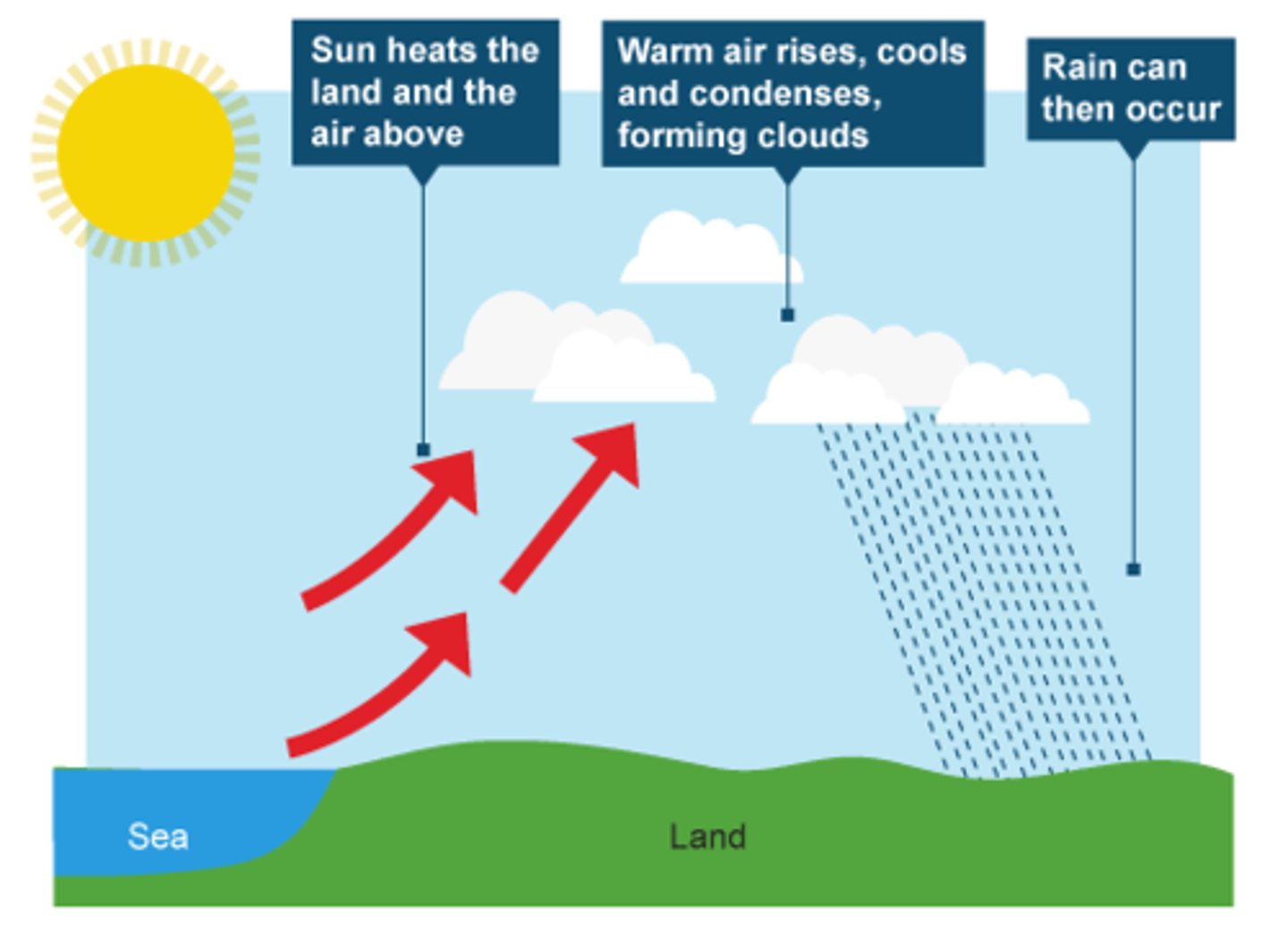
What causes convectional rainfall?
Warm air rising from hot surfaces on a sunny day
List 3 cryospheric processes
- accumulation
- ablation
- sublimation
What is accumulation?
The addition of mass to the glacier (from precipitation)
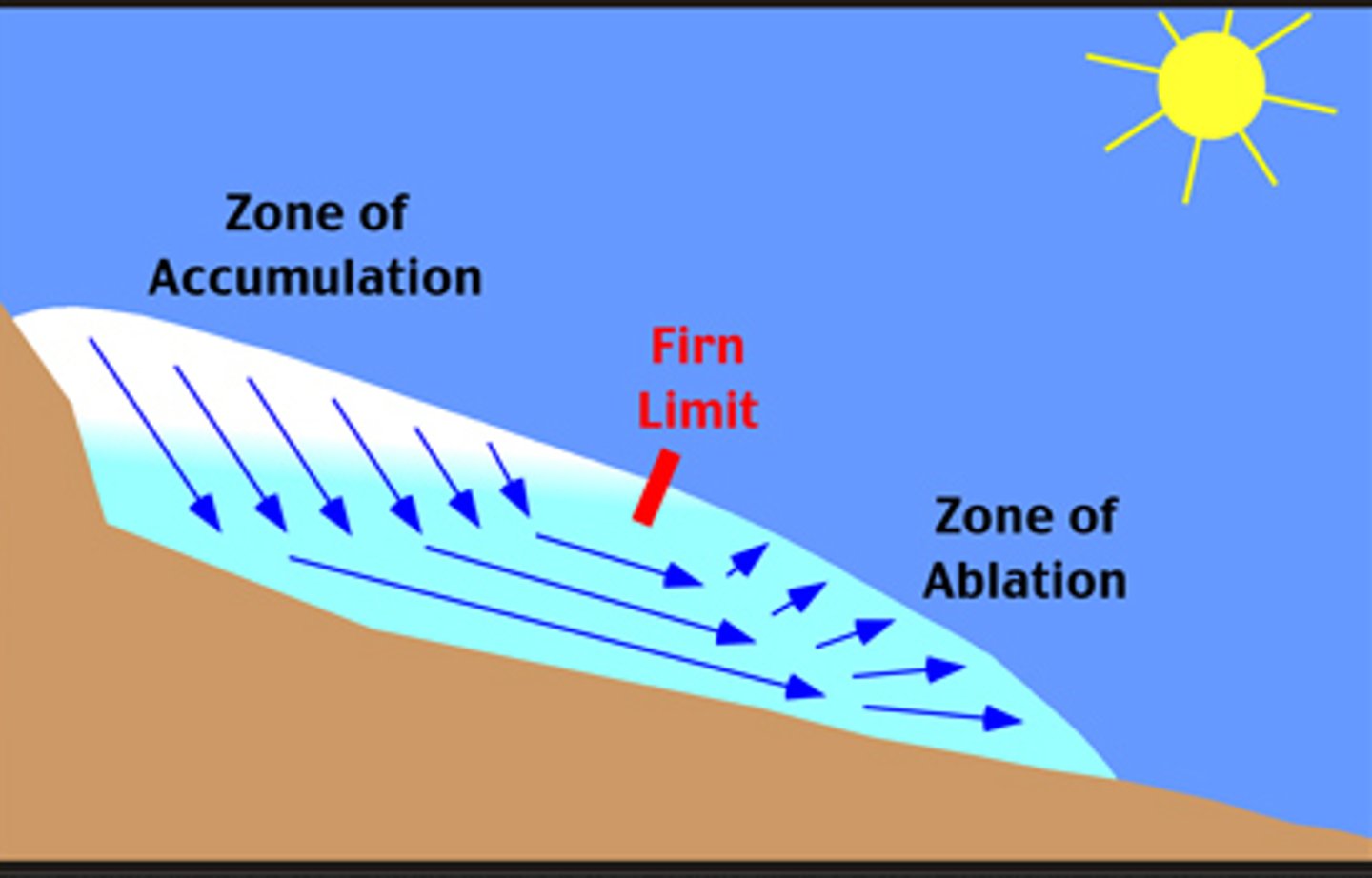
What is ablation?
The loss of mass from the glacier (meltwater)
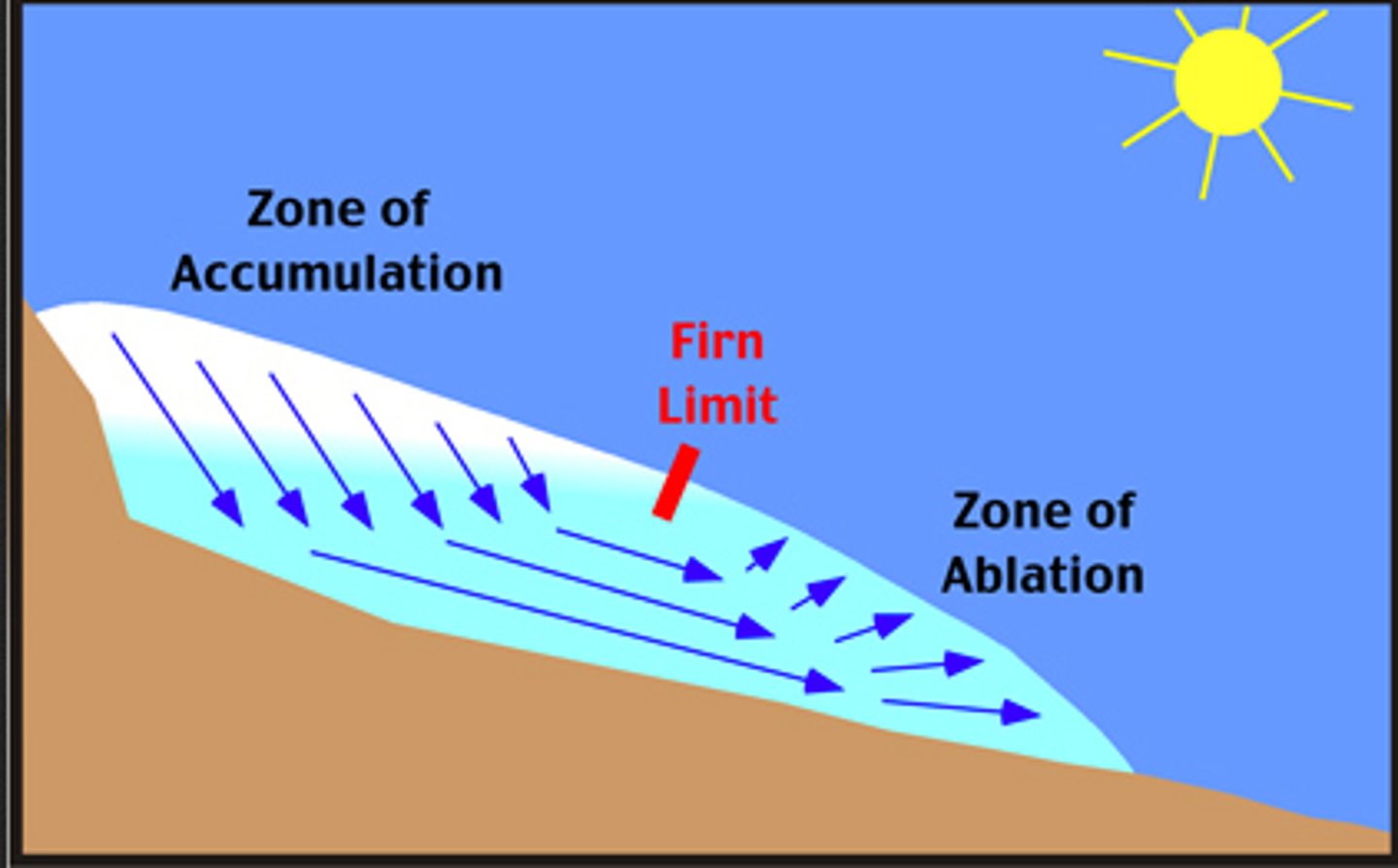
What is sublimation?
Ice changing directly into water vapor
What is a drainage basin?
An area of land drained by a river and it's tributaries