OPTICAL SECTIONING MICROSCOPY
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Why are microscopy tools needed?
Most biological tissue is not see through (opaque)
RI
Refractive index, the way light bends through other light sources
Light microscope uses
resolution
targeted contrast
magnification
What are the problems with biological tissue?
• Opaque
• Does not transmit visible light well (lipid bilayers in the cell membrane)
RI differences
Not great for light microscopy
3 ways to solve opaque problem of biological tissue
use small samples (cell cultures)
Section/Cut Tissue to manageable size
Tissue Clearing
cultured cells can transmit almost all light through them
good for studying intracellular activity
Why would smaller cell cultures not be the best? How could this problem be solved?
Not the best for understanding how the cells are combining together or learning about the intact tissue
Trim tissue into ultra thin sections to get around the issue
Optical Sectioning
Increases both contrast and resolution by eliminating out of focus light using rejection techniques
What does rejecting out of focus information improve?
Contrast and Resolution
Contrast
The ratio between the brightest and darkest regions of the image
Resolution
The ability to differentiate between 2 distinct points or objects
2 ways to create Optical Section
• Reject out-of-focus emission light (pinhole, structured illumination)
Limit excitation volume
3 Methods to get an optical section
Confocal Microscopy
2-Photon Microscopy
Lightsheet Microscopy
Large pinhole diameter =
Larger optical section
Smaller pinhole diameter =
Smaller optical section
How does confocal microscopy generate an optical section?
By physically rejecting out of focus light using an aperture placed in a conjugated focal plane
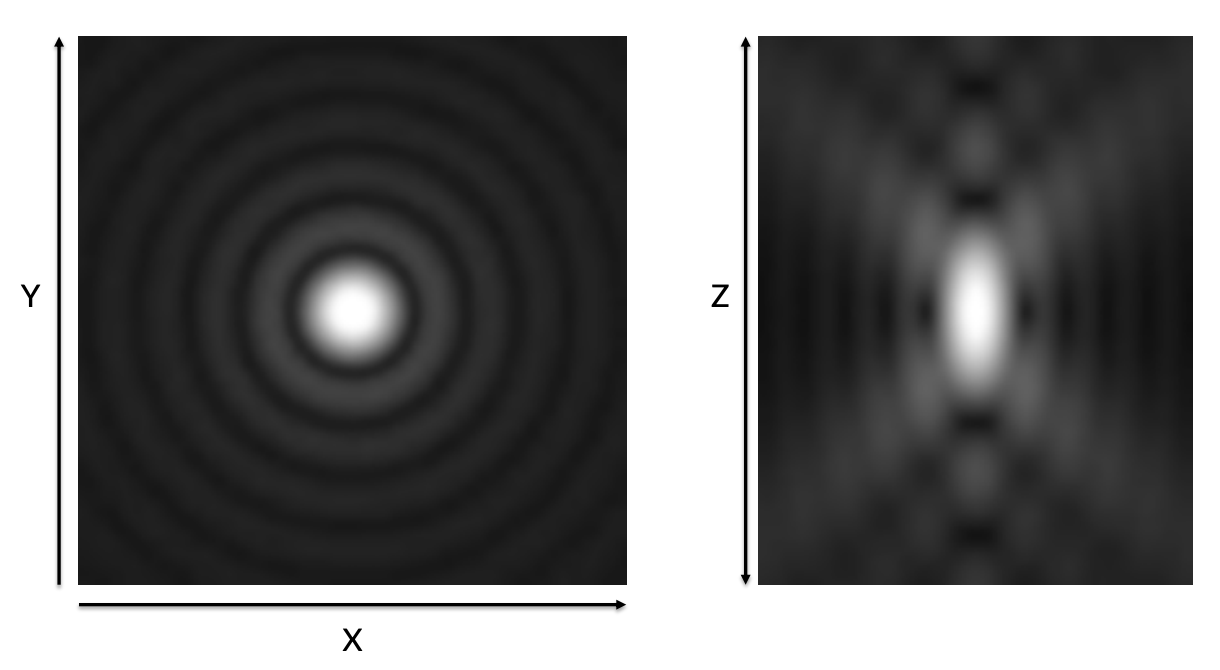
What does this image show?
Airy Pattern/Airy Disc
How the microscope sees a small point of light. Each individual fluorophore is seen as a spot in the center the rings surrounding are diffraction rings
What is a raster scanning device?
Confocal microscopes are a type of raster scanning device. Each pixel must be scanned in order to build an image. This is a slow process
Fluorescence signal is reduced as _____
Diameter is reduced
2 Photon microscopy
Uses a different laser system to go through thicker tissue samples using NIR wavelengths
Good method for LIVE intact tissue
No aperture means significant improvement in photon collection
Tissue Clearing STEPS
1. Hydrogel embedding – passive diffusion
2. Polymerization – crosslink hydrogel under pressure and heat
3. Clearing – active electrophoretic field with detergent (SDS)
4. Labeling – IHC steps more effective with no lipid to permeabilize
5. Mounting/Imaging – using RI matching solution to hydrogel
LightSheet microscopy
Generates an optical illumination section via cylindrical light shaping optics
Fluorescence is detected perpendicular to illumination
Sample can be moved in 4 dimensions
What is the main advantage of light sheet microscopy?
camera based
faster
less photo damage, longer observation periods
Does not collect out of focus fluorescence
Disadvantages of LightSheet
• Only illuminates a thing plane at a time
• Requires tissue clearing