AP Unit 6 Lesson 1 - Circulatory Structures/Functions + BP
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Circulatory System
Blood brings nutrients (oxygen, glucose) to cells and brings wastes (C02) away from cells via circulation
Circulatory System pt. 2
Aorta / Artery / Arteriole
Colour: Red (some exceptions)
Carries blood away from the heart
Contains O2 blood + nutrients
Circulatory System pt. 3
Vena Cava / Vein / Venule
Colour: Blue (some exceptions)
Carries blood towards the heart
Contains dO2 blood and waste
Circulatory System pt. 4
● Pulmonary Circulation: blood circulation in heart and lungs
dO2 blood travels from heart → lungs via arteries
O2 blood travels from lungs → heart via veins
● Systemic Circulation: blood circulation in the body
O2 blood travels from heart → body via arteries
dO2 blood travels from body → heart via veins
Pulmonary Circulation - Heart Anatomy Diagram
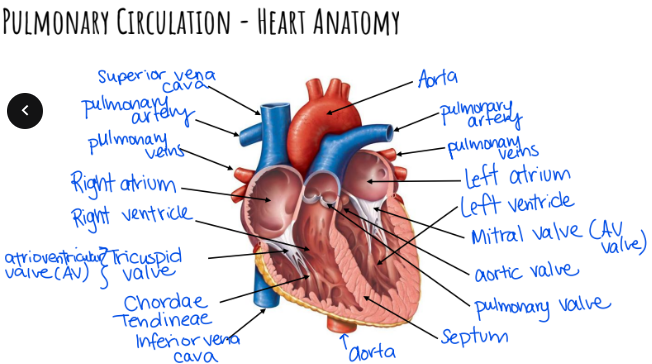
Pulmonary Circulation of Blood Flow Diagram
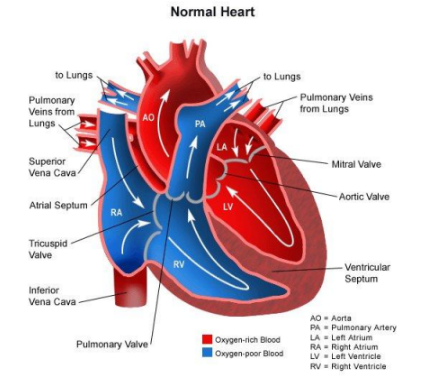
Pulmonary Circulation of Blood Flow Text
1. Deoxygenated blood enters Right Atrium via Superior / Inferior Vena Cava
2. Right Atrium contracts, forces blood through Tricuspid Valve into Right Ventricle
Pulmonary Circulation of Blood Flow Text pt. 2
Right Ventricle contracts, blood travels through Pulmonary Valve into Pulmonary Artery
Pulmonary Arteries take deoxygenated blood to capillaries of lungs where they are oxygenated (CO2 out, O2 in; via diffusion)
Pulmonary Circulation of Blood Flow Text pt. 3
Oxygenated blood then moves to Left Atrium through Pulmonary Veins
Left Atrium contracts, forcing blood through Mitral Valve into Left Ventricle
Left Ventricle contracts, forces blood through Aortic Valve into Aorta then to the rest of the body
Pulmonary Circulation - The Beat
Septum: separates oxygenated & deoxygenated blood
Chordae Tendineae: fibrous strings that support atrioventricular valves
Pulmonary Circulation - The Beat pt. 2
Heartbeat Sounds
Lub: AV valves close after atria push blood into ventricles (start of heartbeat)
Dub: Semilunar valves close after ventricles pump blood out (end of heartbeat)
Heart Murmurs: occur when there are problems with valves closing
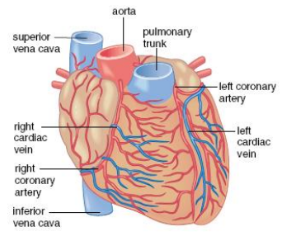
Heart Needs Blood Too
Coronary Arteries: branches off the aorta and wraps around heart to supply blood to the heart muscles
Cardiac Veins: dump blood with heart muscle wastes into right atrium
Controlling the Heartbeat + Diagram
Nodal Tissues: exhibit characteristics of both nerves & muscles, allowing the heart to beat without conscious control
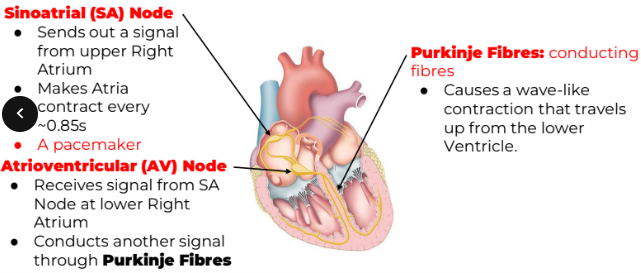
Controlling the Heartbeat pt. 2
Medulla Oblongata: contains a cardiac control center that can alter Heart Rate (HR) via an autonomic nervous system
Adrenal Medulla: releases protein hormone epinephrine (adrenaline) to increase HR in response to stress
Controlling the Heartbeat pt. 3
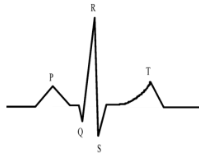
Reading an Electrocardiogram (ECG)
P wave: Atria contract
QRS wave: Ventricles contract & Atria relax
T wave: Ventricles relax
Blood Pressure
Systole: Contraction of Heart Muscle
Diastole: Relaxation of Heart Muscle
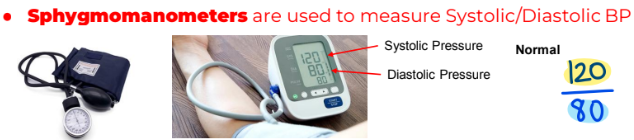
Sphygmomanometers are used to measure Systolic / Diastolic BP
Normal: 120 / 80
Blood Pressure - Conditions
Hypertension: Blood pressure is higher than normal
Hypotension: Blood pressure is lower than normal
Blood Pressure - Conditions pt. 2
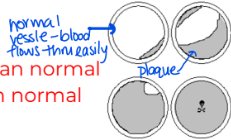
Atherosclerosis: hardening of arteries due to plaque buildup from saturated fats / cholesterol
Aneurysm: a bulge or ballooning in the wall of a blood vessel due to a weakened area
Blood Pressure - Conditions pt. 3
Angina Pectoris: Radiating pain in left arm due to insufficient blood flow
Thrombus: Stationary clot attached to blood vessel wall that slows blood flow
Blood Pressure - Conditions pt. 4
Embolus: Thrombus - dislodged, moves along with blood
Embolism: Embolus - gets stuck, entirely blocking blood flow
Stroke: portion of brain dies due to lack of oxygen