Working Memory Model (WMM)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is the working memory model?
created by Baddeley and Hitch (1974) was a development of the multi-store model of memory.
This model suggests that STM consists of a number of different stores rather than a single store. This shows us how theories develop over time as science evolves.
What is dual-task technique?
the procedure where participants carry out 2 tasks at once
What was Baddeley and Hitch (1974) experiment?
participants preformed dual-task techniques
one where participants perform 2 tasks simultaneously that both involve listening (same sense), they perform them less well than if they did them separately
another where participants perform 2 tasks simultaneously listening and vision (different senses), with no issues
What does the experiment suggest?
there are different stores for visual and auditory processing
Describe or draw the WMM?
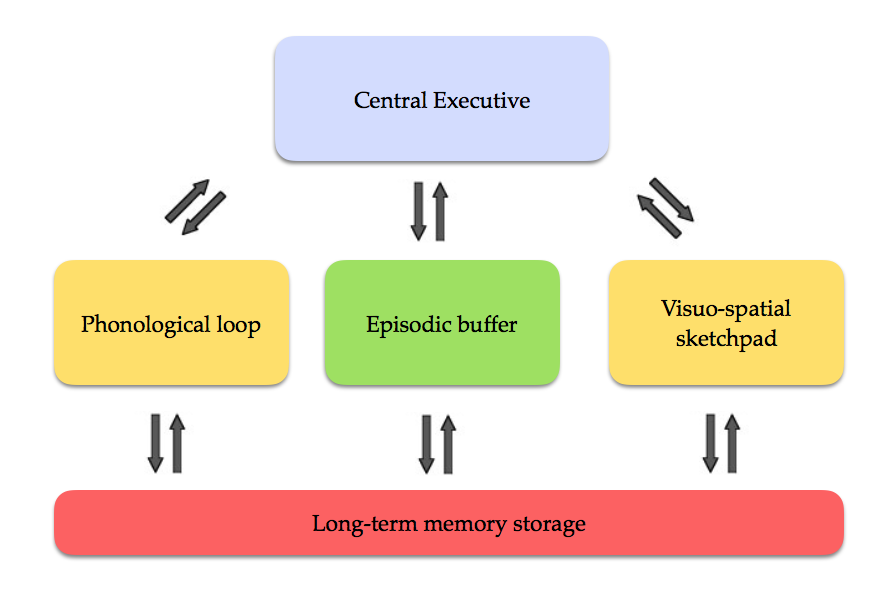
WMM
What are the 4 hypothesised components of the STM?
central executive, phonological loop, episodic buffer, and visuo-spatial sketchpad
What is the central executive component?
attention control system of the STM (aka CEO)
most important
directs attention towards a task
can focus attention and divide attention between 2+ sources and switch attention between tasks
allocates sensory information to the sub-systems based on the modality (e.g. auditory, visual)
receives information from the sub-systems once it has been processed by them
capacity: limited (cannot attend to a lot of things at the same time)
modality-free (can process any sensory information)
What are the 2 ways attention control can occur in the central executive?
automatic level and supervisory attention
What is automatic level?
based on habits that rely on schemas in LTM
controlled automatically by stimuli
e.g. routine actions and places that demand little attention
What is supervisory attention?
responsible for planning and decision-making
capable of considering alternative strategies and choosing the best option
e.g. emergency situations, situations that require self-regulation
What is the phonological loop?
auditory component of the STM
What are the 2 components of the phonological loop?
phonological store and articulatory control system
What is the phonological store?
aka inner ear
passive system
capacity: limited
Function: Temporarily holds verbal and auditory information
receives information directly from sensory memory in the form of auditory material, and LTM and the articulatory control system in the form of verbal information
Example: Hearing a phone number and briefly remembering it.
What is the articulatory control system?
aka inner voice
active system
Function: Actively rehearses and refreshes information in the phonological store to prevent decay
converts written text into a phonological code through subvocalization (silently pronouncing words in your head)
Also responsible for producing speech
Example: Repeating a phone number in your head to remember it
What is articulatory surpression?
participants are asked to repeat words such as “the” or “one” while they memorize a list of words. These studies show that simultaneous tasks decrease the accuracy of recall of information because the phonological rehearsal system is overloaded.
this supports the WMM
What is the visuospatial sketchpad?
visual component of the STM (aka inner eye)
temporary store for visual and spatial information from either sensory memory or LTM
capacity: limited
What are the 2 types of processing in the visuospatial sketchpad?
visual and spatial processing
Visual Processing
interpreting what things look like
Spatial Processing
the ability to tell where objects are in space and the relationship between things
e.g. how far the baseball is in relation to your body, finding your way around the house
What is the episodic buffer?
temporarily holds several sources of active information (auditory, visual, information from the LTM) simultaneously while you consider what is relevant in the present situation
integrates information to create a memory trace
modality free
capacity: limited
1 study that support the WMM
landry and bartling (2011), Dual-task techniques, Word length effect, Case of K.F
What are 2 strengths of the WMM?
Significant supporting research
specific studies
Brain scans have shown brain activity in different areas of the brain when carrying out verbal and visual tasks
supports the idea that there are different parts of memory for visual and verbal tasks
Case studies on patients with brain damage
supports the theory that there is more than one STM store
This model helps us understand why we are able to multitask when using different senses for tasks and are unable when using the same
What are 2 limitations of the WMM?
Over-simplified
fails to explain…
the processes involved in LTM, the interaction among the 4 components, memory distortion, or the role of emotion in memory formation
does not address how other sensory information is processed, and spatial memory is underdeveloped
The role of the central executive is unclear despite being the most important part of the model. It is impossible to measure its limited capacity separate from the phonological loop and the visuospatial sketchpad
unclear how the episodic buffer integrates information from the other components with the LTM is unclear and its role is under developed