Psychology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:24 AM on 1/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
1
New cards
psychodynamic psychology
focus on life experience, connects concious and unconcious mind, how childhood shapes person
2
New cards
unconscious mind
what we are unaware of, defines neurotic behaviour (what we dotn have to think about)
3
New cards
dopamine
hormone responsible for pleasure, reward, motivation, too much or too little leads to disorders
4
New cards
abnormal behaviours
atypical reactions compared to context and culture
5
New cards
Psychoanalytic theory
freuds id, superego, and ego
6
New cards
id
innate desires, pleasure seeking, aggression, sexual impulse
7
New cards
superego
morals, ethics, values, parental senses
8
New cards
ego
common behavioiur
9
New cards
sublimation
defence mechanism; relieving stress in socially acceptable way
10
New cards
Denial
defense mechanism; blocking from awareness
11
New cards
regression
defense mechanism; moving back in psychological time
12
New cards
displacement
defense mechanism; subsition unacceptable (anger issues, ie)
13
New cards
projection
defense mechanism; place worries on someone else
14
New cards
compensation
defense mechanism; over achieve in different field
15
New cards
personality
traits, behaviours, motive
16
New cards
extrovert
energize from social situations
17
New cards
introvert
energize from alone time
18
New cards
cognitive psychology
studies thought, mental process
19
New cards
sensory memory
memories that recieve no attention, last 1/2 of a second. capacity is large and encoding system is sense specific
20
New cards
short-term memory
memory that recieves some attention and lasts 15-30s. capacity can store 5-9 items and encoding is auditory based.
21
New cards
long-term memory
memory is linked in meaningful way and remains for unlimited period. capacity is unlimited.
22
New cards
behavioural psychology
studies what people do and act on, needs empirical evidence to prove
23
New cards
learning
change in knowledge as result of experiment
24
New cards
mental distress
is common and revesible, occurs when put in some stress, is a mild concern, angry upset
25
New cards
mental health problem
significant functional impairment of moderate concern, hopeless grief
26
New cards
mental health disorder
persistent functional impairment of severe concern, depression anxiety diagnosable
27
New cards
ivan pavlov
discovered classical conditioning and conditioned reflex
28
New cards
carl jung
theorized about collective unconcious, and made trait theory of sensation intuition, feeling and thinking
29
New cards
albert bardura
learning by observation, formed cognitive process theory, attention retention reproduction motivation
30
New cards
sigmund freud
developed psychoanalysis (treating mentally ill and theory to explain human behaviour) and developed psychosexual development
31
New cards
psychosexual development
personality development in childhood 5 stages
32
New cards
oral stage PSD
children use mouth for pleasure, around age 0-1
33
New cards
anal stage PSD
children potty train, use bladder and anus for pleasure, age 1-3
34
New cards
phallic stage PSD
children discover genitalia for pleasure, age 3-6
35
New cards
latency stage PSD
sex drive inactive but socializing occurs, age 6-puberty
36
New cards
genital
libido is active and sexual attraction begins, intercourse is goal, begins at puberty
37
New cards
jean piaget
developed theory of cognitive development
38
New cards
cognitive development
childrens intelligence undergoes changes
39
New cards
sensorimotor stage CD
uses senses to discover things, association with feeling, age 0-2
40
New cards
preoperational stage CD
symbolic thinking, grammar begins, imagination is key, age 2-7
41
New cards
concrete operational stage CD
children begin to appreciate concepts, knowledge of permanent, unchangeable things is begun, age 7-11
42
New cards
formal operational stage CD
free thinking occurs, hypothetical thinking can happen, age 11+
43
New cards
Erik erikson
developed psychosocial stages of development
44
New cards
psychosocial development
social awareness and morality in people develops
45
New cards
**Trust vs. mistrust**
**trusting in parents occurs, Birth to 1**
46
New cards
**Autonomy vs. shame and doubt**
prefrences and independance, children feel secure in themselves, 1-3
47
New cards
**Initiative vs. guilt**
socializing with others typically happens, 3-5
48
New cards
**Industry vs. inferiority**
children begin comparing themselves to others, 5-12
49
New cards
**Identity vs. confusion**
children figure out who they are and where they fit in to society, 12-13
50
New cards
**Intimacy vs. isolation**
people build long term relationships, 18-40
51
New cards
**Generativity vs. stagnation**
people begin to give to others, 40-65
52
New cards
**Integrity vs. despair**
people reflect on their life, 65+
53
New cards
classical conditioning
associating something that naturally causes a reaction to something that doesn’t, making that reaction occur on command when the other is displayed
54
New cards
operant conditioning
using reinforcement to control behaviour
55
New cards
observational learning
association based on watching others
56
New cards
phineas gage
rod lodged through frontal cortex, no harmful brain damage but a loss of personality and a growth in anger
57
New cards
charles whitman
brain tumour pressing on amygdala, shot several people
58
New cards
henry molaisen
suffered from seizures, removed hypocampus and amygdala, lost memory of past 11 years and could not make new memories
59
New cards
little albert
classically conditioned baby to be afraid of mouse by associating it with loud noise, failure to decondition the child and passed away at age 6
60
New cards
pavlovs dog
classically conditioned to salivate at sound of bell
61
New cards
b f skinner
discovered operant conditioning
62
New cards
positive reinforcement
adding a factor to increase behaviour
63
New cards
negative reinforcement
removing a factor to increase behaviour
64
New cards
universal emotions
joy, anger, sadness, fear, disgust, surprise
65
New cards
teenage brain
very adaptable
66
New cards
frontal lobe
planning, decision making and speech
67
New cards
parietal lobe
sensory control, behind frontal and above occipital
68
New cards
temporal lobe
auditory, under frontal beside occipital
69
New cards
occipital lobe
vision, back and bottom
70
New cards
thalamus
sensory and motor functions, deep in middle of brain
71
New cards
hypothalamus
regulates temp., thirst, hunger, sleep, 24h clock, mood, and sex drive, below thalamus
72
New cards
amygdala
fight or flight, emotion and fear
73
New cards
hippocampus
learning and memory, under cerebral cortex
74
New cards
pons
transfers data in cerebrum and cerebellum
75
New cards
medula
breathing, heart rate, digestion, sneezing, swallowing
76
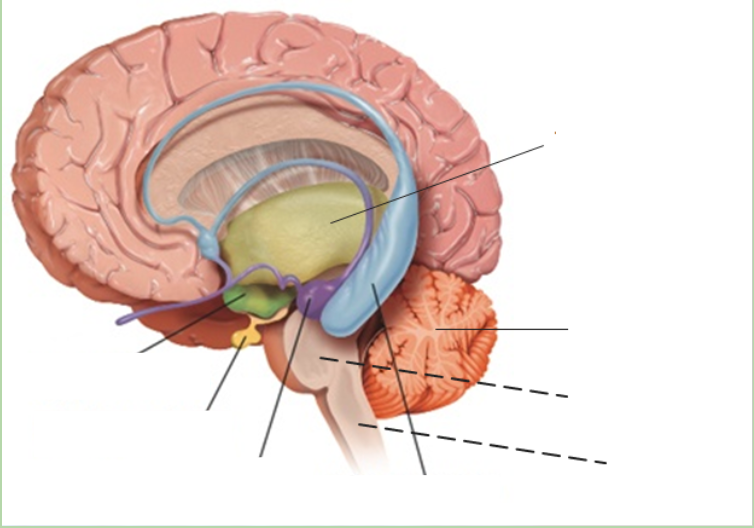
New cards
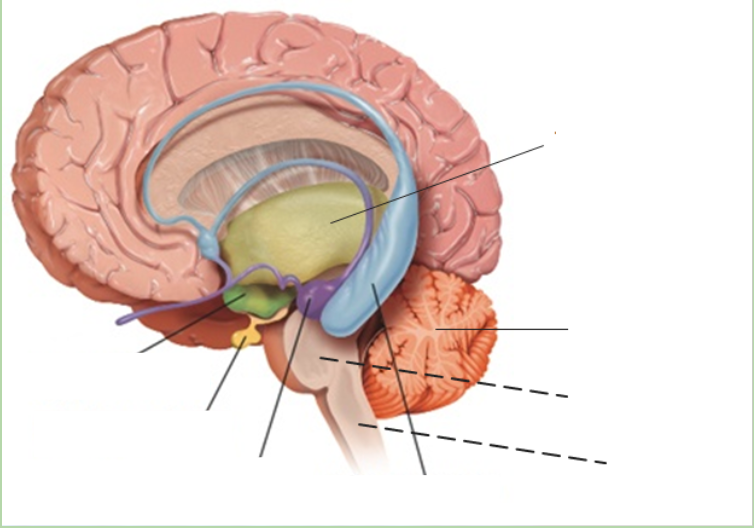
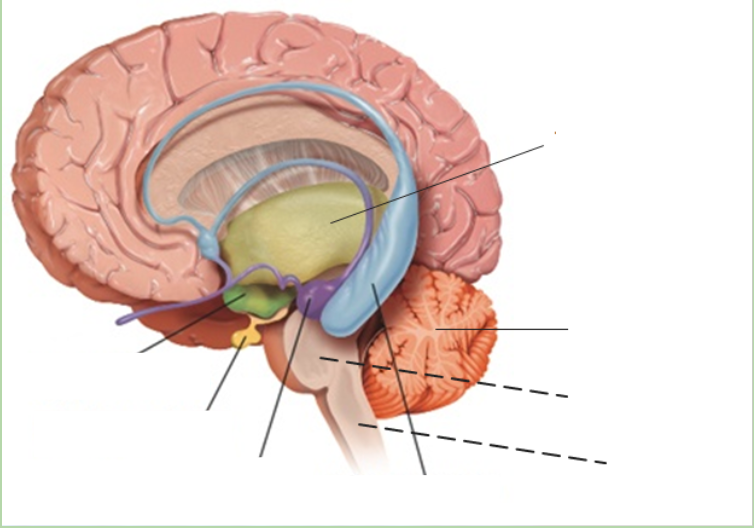
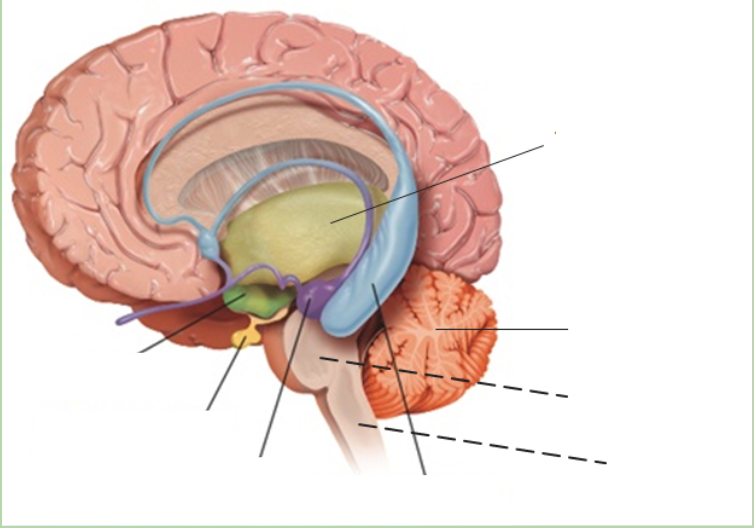
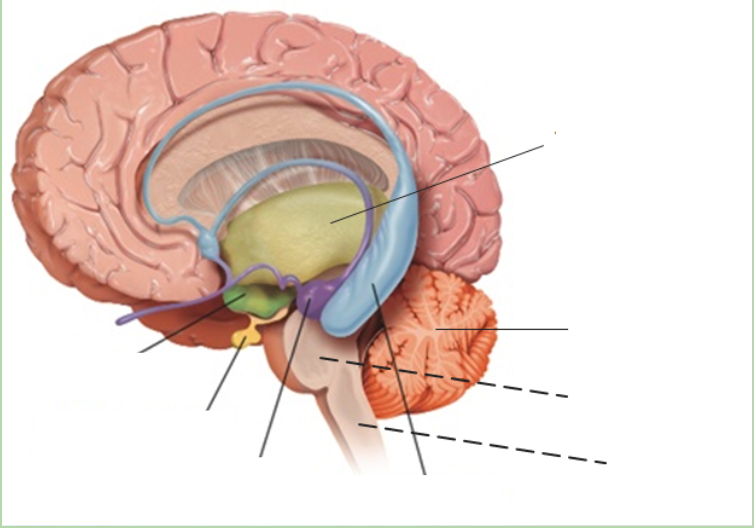
thalamus
what is the grey area?
77
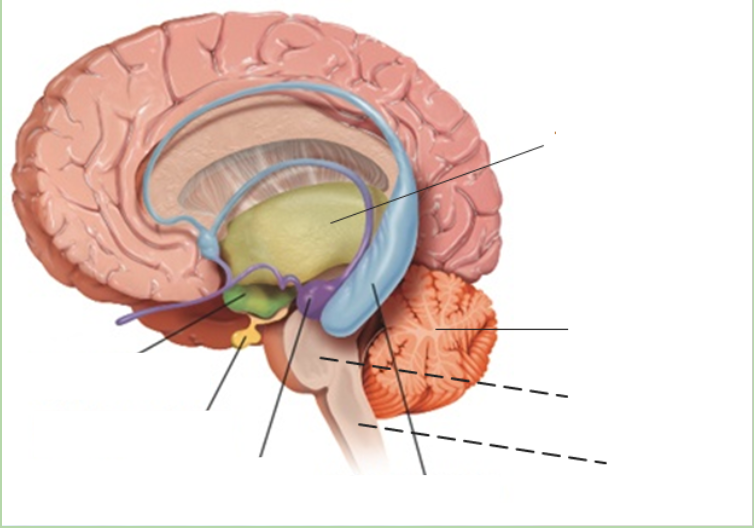
New cards
hypothalamus
what is the green area?
78
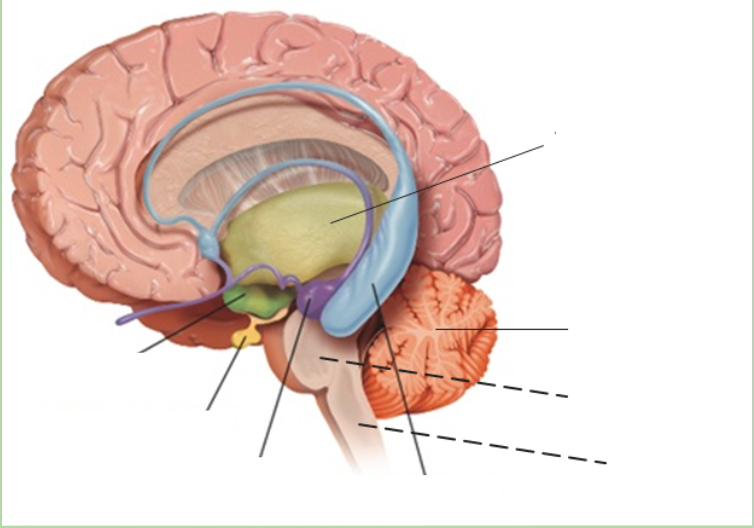
New cards
amygdala
what is the purple area?
79
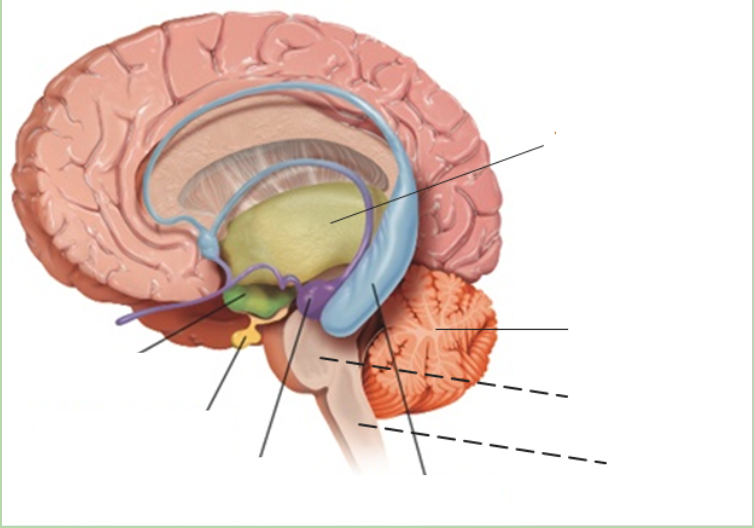
New cards
hippocampus
what is the blue area?
80
New cards
cerebrum
what is the pink area?
81
New cards
cerebellum
what is the orange area?
82
New cards
pons
what is under the purple area?
83
New cards
medula
what is at the bottom of the brainstem?