SCH3U- Bonding, Naming and Reactions Test Review October 2023
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
T/F - true or false, correct the false (underlined word) FiB- Fill in the blank
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
T/F : Valance Electrons are those electrons found in the outmost shells of an atom
True
T/F A Lewis Symbol is a diagram that shos the number of valance electrons for an atom
True
T/F A single displacement rxn is one in which two or more simple substances combine to form a ore complex substance
False, double displacement rxn
The nitrate ion (NO3-) is soluable with most positive ions
False,all
If an atom gains two extra electrons, it has a charge of…
-2
The octet rule states
atoms are stable when they ahve 8 valence electrons
IF Cl gains one electron, how many valence electrons does it now have
8
When using Lewis symbols, the number of dots represents
only the valence electrons
The lewis symbols of elements down a group of the period table have
the same amt of dots
Draw the lewis symbol for Phosphorus
Refer to the paper for the answer unless i wasnt lazy and put a picture in here

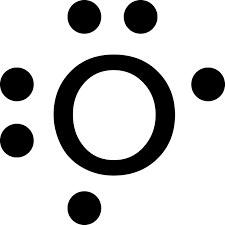
Draw the lewis symbol for Oxygen
Refer to the paper for the answer unless i wasnt lazy and put a picture in here
AN ion with a -2 charge has
two extra electrons
A sacrificial anode for the protection of iron is
a metal that oxidizes more easily (is more reactive) than iron
the poly atomic ion PO4 3- is called a
phosphate ion
ionic compounds form
crystals
when ionic compounds are dissolved in water, they are
electrolytes
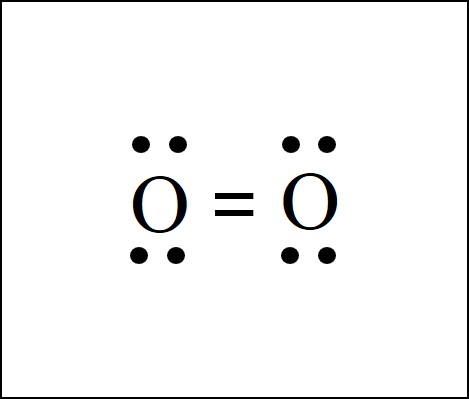
Draw the lewis symbol for an oxygen molecule
Refer to the paper for the answer unless i wasnt lazy and put a picture in here —> remember HOFBrINCl
The measure of an atom’s abilvity to attract a pair of electrons it shares wiwth another atom in a covalent bond is known as its
electronegativity
The rxn 2H2O(l) + O2 → 2H2(g) + O2(g) represents a
Decomposition
the rxn 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l) is
synthesis
The rxn Zn(s) + 2 HCL(aq) _> ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) is
SDR
The rxn NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) -→ NaNO3(aq) + AgCl(s) is
DDR
A solid that is formed as a result of the chem rxn of two aq solutions is called a
precipitate
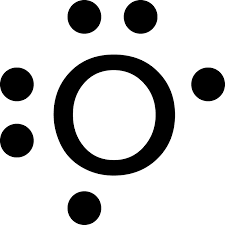
Draw the lewis symbol for oxygen
Refer to the paper for the answer unless i wasnt lazy and put a picture in here
If an anion called selenate has the formula SeO5 3- and is part of an oxyanion series, what would the formula for the hyposelenite ion be?
SeO3 3-
Hypo-ite, Ite, Ate, Per-ate
If XF4 is the correct formula for a metallic fluoride, then the formula for the oxide of X is
XO2
What is the general form of a synthesis rxn
AB + C —> ABC
ionic compounds form
crystals
In lewis structures, shared electrons are shown as BLANK while BLANKS are shown as pairs of dots
dashes, lone pairs
A solid consisting of a number an cation s and anions in a repeating pattern
ionic crystal lattice
a compound that in an aq solution does not conduct electricity
nonelectrolyte
electrons that are lost or gained in the formation of an ion
valance electrons
when ionic compounds are dissolved in water, they are
electrolytes
an atom that as gained extra electrons
anion
an electrostatic attraction that holds anions and cations together
ionic bond
an atom that has lost one or more electrons
cation
an atom that has lost or gained one or more electrons
ion
an ion that has only onen atom
monatomic ion
S/A a) define electronegativity and draw a labeled diagram of the bonding continuum
b) explain how electronegativity can be used to determine if a bond is likely to be covalent or ionic nature
a) Electronegativity is defined as the measure of an atom’s ability to attract e-’s that are part of a chemical to itself, essentially, an atom’s ability to win a tug of war with other atoms over e-. The higher the electronegativity, the more the atom will try and attract electrons.
b) The differences in electronegativity (△EN) can be used to determine whether or not a bond is likely to be covalent or ionic in nature. If the difference between the EN is less than 1.7 (the midpoint) covalent is assumed, and if it is greater than 1.7, ionic is assumed.
**to explain the diagram: F has the largest EN (4.0) nd Fr has the lowest (0.7), so the difference in EN is simply subtraction. The largest △EN is 4.0-0.7= 3.3, the smallest △EN is 0, and the midpoint is 1.7.
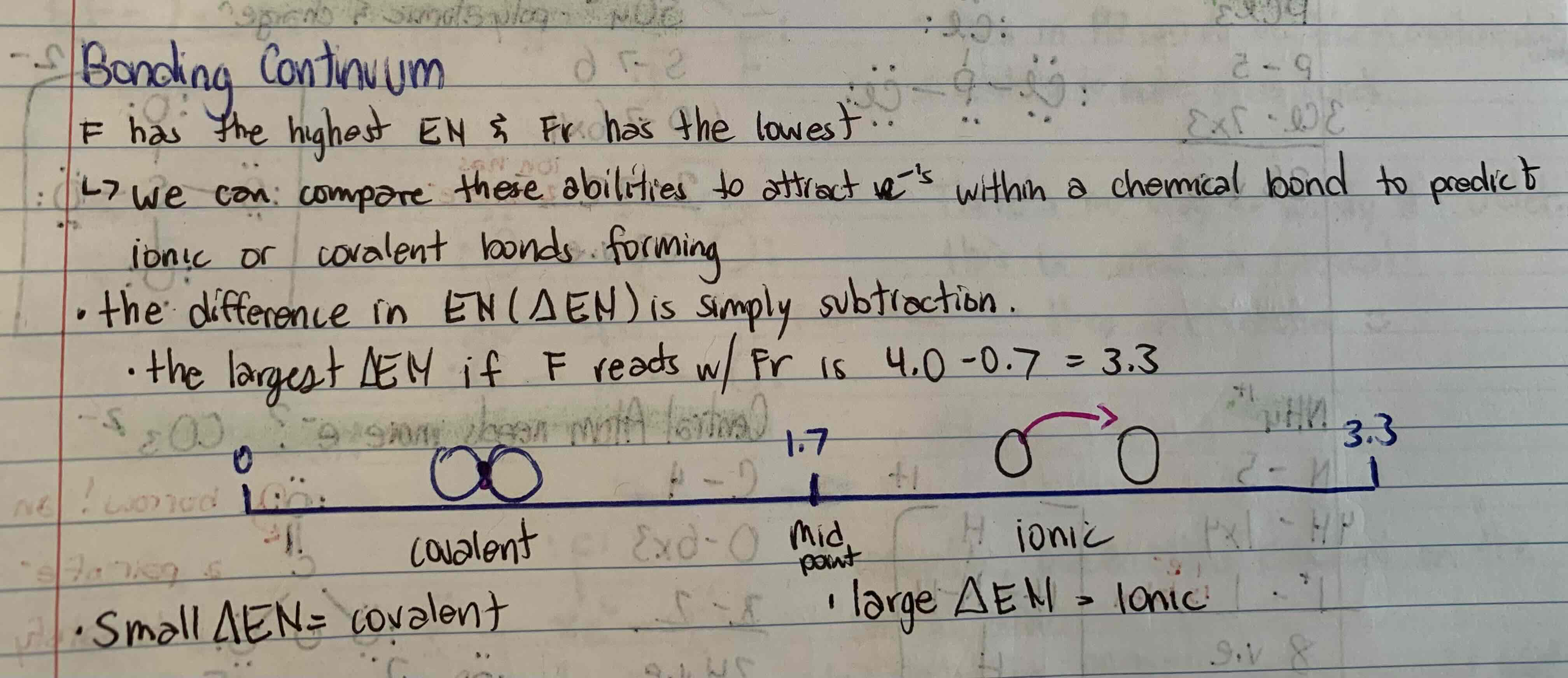
S/A a) explain what the octet rule is and provide three alternative descriptions for it
b) compare and contrast ionic and covalent bonds
The octet rule states that atoms act in such way to achieve a stable octet. This can also be described as
pairing up valence electrons
achieve a more stable electron configuration
fill up valence shells
become isoelectronic with noble gases
achieve a less energetic state
b)
Ionic:
usually metal + nonmetal
has a +ve or -ve charge
transfer of e-
form a crystal lattice structure
solid at room temp
mostly not flammable
Covalent:
two non metals
neutral charge
share e-
form individual molecules
can be a variety of states at room temp
flammable
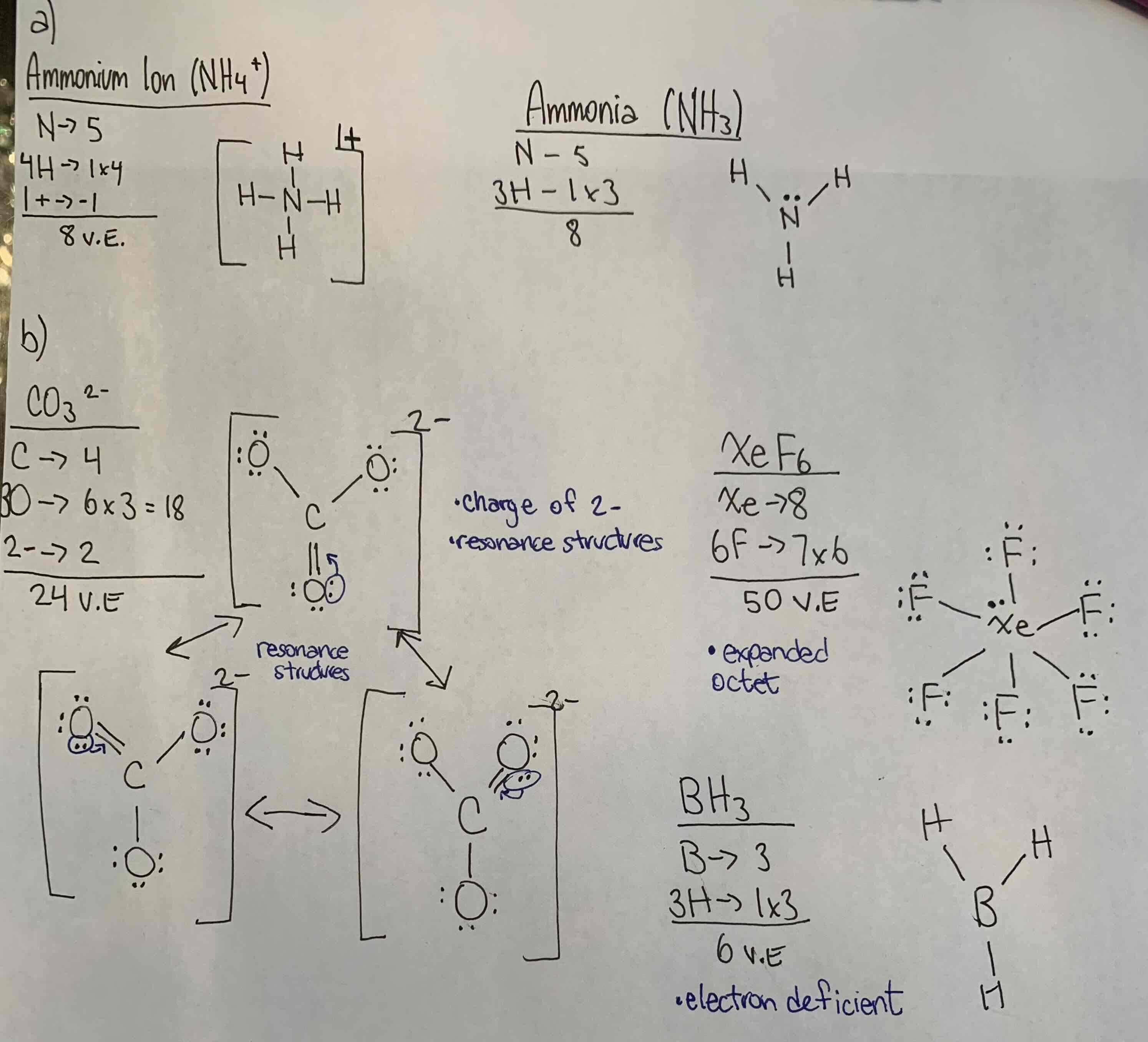
S/A a) Draw the electron dot diagrams for ammonia (NH3) and another for the ammonium ion (NH4+).
b) show al the work and remark on any unique features for the lewis electron dot diagrams for each of the following: CO3 2-, XeF6, BH3
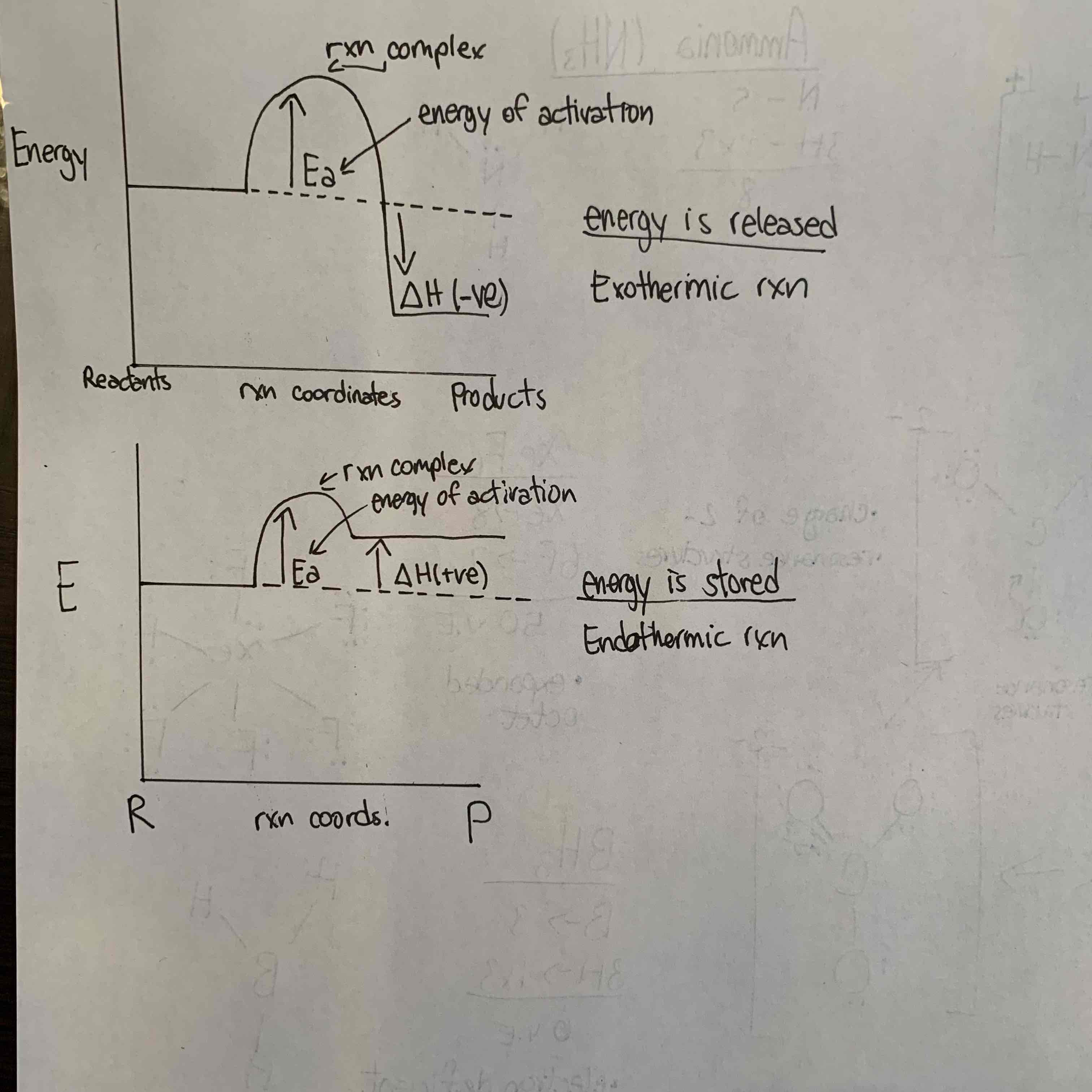
Just mixing two chemicals together is not enough to get them to react. Complete the collision therory for chemical rxns
*Draw and fully label an energy level diagram (energy vs rxn coordinates (time) for an exothermic and endothermic rxn.
*Explain how an exothermic rxn differs from that of an endothermic one (refer to energy)
In order for a chemical rxn to occur, atoms or molecules must
collide with one another
at the right orientation
with sufficient energy to overcome the energy barrier (Ea)
**An exothermic rxn differs from an endothermic rxn because energy is released rather than stored. This means the products of an exothermic rxn have less energy than the reactants, causing negative energy, where as in an endothermic rxn, the products have more energy than the reactants, causing positive energy.
Write the three equations, (balanced overall, complete ionic and net ionic) including states for the rxn when solutions of Iron (III) sulphate and sodium hydroxide are mixed
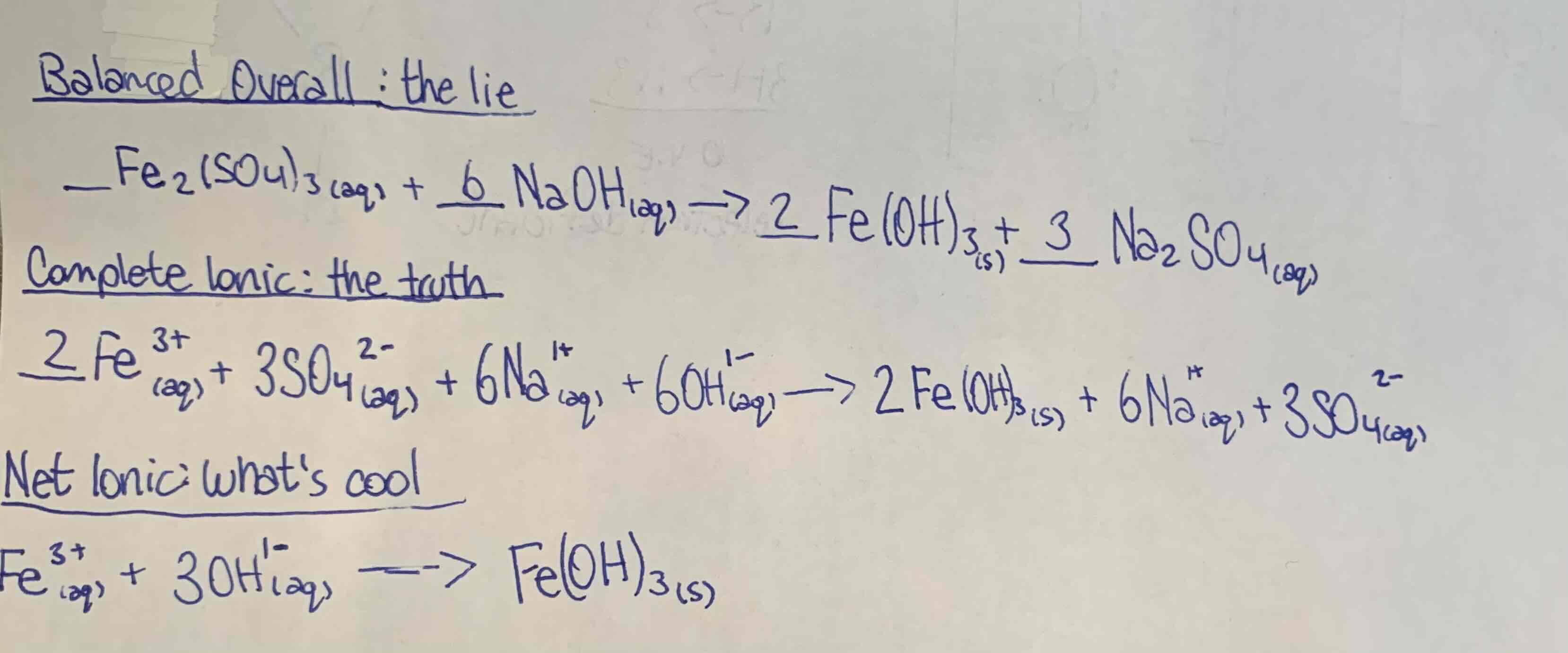
Write the IUPAC names for the following
H2SO3 (aq)
Cu(ClO4)2
Ag
LiHCO3
Mn(NO3)4
NiSO4 • 6H2O
HCl (g)AlH3
N3O5
(NH4)2C4H4O7
Sulphurous Acid
Copper (II) Perchlorate
Siliver
Lithium Hydrogen Carbonate
Manganese (IV) Nitrate
Nickel (II) Sulfate Hexahydrate
Hydrogen Chloride Gas
Aluminium Hydride
Ammonium Tartrate
Write the correct formulas for the following compounds
a) manganese (IV) oxide
b) ammonia
c) lead (II) phosphate
d) bromine monochloride
e) triarsenic heptachloride
f) fluorine gas
g) argon gas
h) vinegar
i) strontium nitrate tetrahydrate
j) ammonium tripolyphosphate
k) perphosphoric acid
a) MnO2
b) NH3
c) Pb(PO4)2
d) BrCl
e) As3Cl7
f) F2 (g)
g) Ar(g)
h) HCH3COO
i) Sr(NO3)2 DOT 4H2O
j) (NH4) 5P3O10
k) H3PO5
For each of the following word equations,
i) predict the products where appropriate
ii) write a balanced chemical equation
iii) identify the type of rxn
a) sodium metal is added to water
b) BaCl2(aq) + Na3PO4(aq)
c) propane gas (C3H8) burns
d) Zn(s) + Mg(NO3)2
e) A hydrochloric acid solution is added to a solution of magnesium hydroxide
f) aq ammonium chloride is poured into a solution of sodium hydroxide
a) SR: Na(s) + H2O (l) → NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
b) DD: BaCl2(aq) + 2Na3PO4(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NaCl
c) C: 2C3H6(g) + 9O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O (l)
d) SR: Zn(s) + Mg(NO3)2 → NR
e) N: 2HCl(aq) + Mg(OH)2(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l)
f) DD: NH4Cl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + NH4OH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + NH3(g) + H2O(l)