Module 14: Cosmic Geometries of the Hindu Temple
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Bodhisattvas
Buddhist priests who achieved enlightenment but remain to guide others
Mandala
A diagram composed of a circle within a square used as a meditative device; became the basis for plans of both Buddhist and Hindu temples across India and Southeast Asia

Vishnu
The preserver; one of the three primary gods of Hinduism
Shiva
The destroyer/creator; one of the three primary gods of Hinduism
Brahma
The creator; one of the three primary gods of Hinduism
Brahman
in Hinduism; the universal consciousness to which all things are connected
Mount Meru
in Hindy cosmology, a mountain of five peaks at the center of the universe surrounded by seven concentric rings of ocean
Naga snake
mythical multi-headed cobra-like snake
Baray
a large man made reservoir
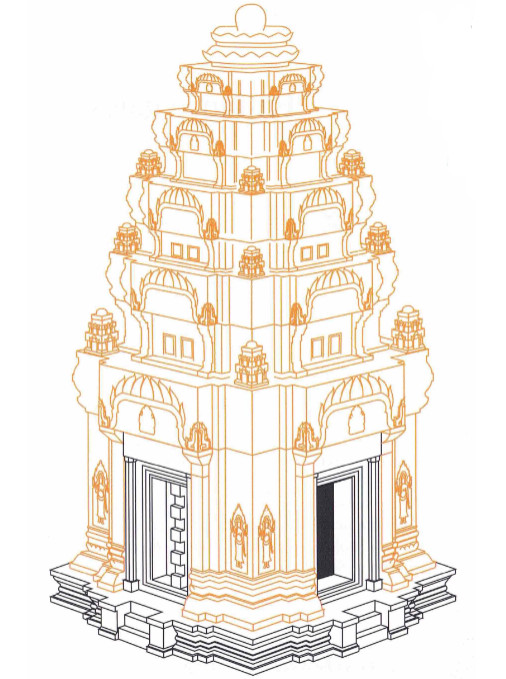
Prasat
a Hindu sanctuary defined by a square cella which housed a statue of a divinity. the cella was accessed by a single door to the east, the sanctuary’s tower rises in five receding levels, the topmost taking the form of a lotus blossom
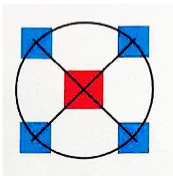
Quincunx
five points arranged in a cross; the basis for the arrangement of sanctuaries in Hindu temples at Angkor
Wat
a Khmer temple
East Mebon
Angkor, Cambodia, 950 CE
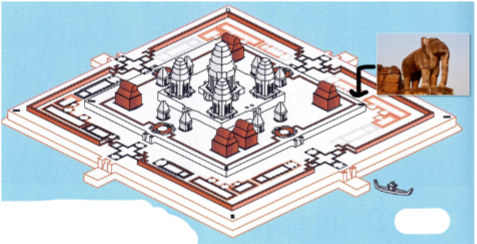
Pre Rup
Angkor, Cambodia, 960 CE

Angkor Wat
Angkor, Cambodia, 1100-1150 CE

Churning of the Sea of Milk
Angkor, Cambodia, 1100-1150 CE

Suryavarman II (r. c. 1113-1150 CE)
Khmer king of the 12th century who commissioned Angkor Wat; his reign marked the height of Khmer power and artistic achievement
Jayavarman VII (r. c. 1181-1218 CE)
Mahayana Buddhist ruler who transformed Angkor into a center of Buddhist devotion and monumental construction, commissioning the walled city of Angkor Thom and the Bayon Temple with its iconic faces
What are the Vedas?
Hindu scriptures and texts; Rig, Ayurveda, Sama, and Atharva
In Hindu philosophy, Brahman represents:
Universal consciousness
What is the Mandala
the cosmological map of the universe; the visual guide to meditation
Describe the center of the universe in Hindu cosmology
the center of the universe is where the gods reside; it is surrounded by 7 concentric rings of oceans
Which empire built the medieval city of Angkor?
The Khmer empire
During whose reign did the Khmer Empire shift its state religion from Hinduism to Mahayana Buddhism?
Jayavarman VII
What are the enigmatic faces on the towers of the Bayon Temple generally believed to represent?
Bodhisattvas
Belief in an immortal soul
Ahtman
Belief in karma
Good/bad actions
Belief in Moksha
Realizing one’s Brahman
Belief in Vedas
Basis of Hindu faith
Belief in Dharma
balance in the universe
What are the parts of a Mandala?
Square outside, circle inside
In the mandala, which shape is symbolic of the spiritual world?
circle
In the mandala, which shape is symbolic of the physical world?
square
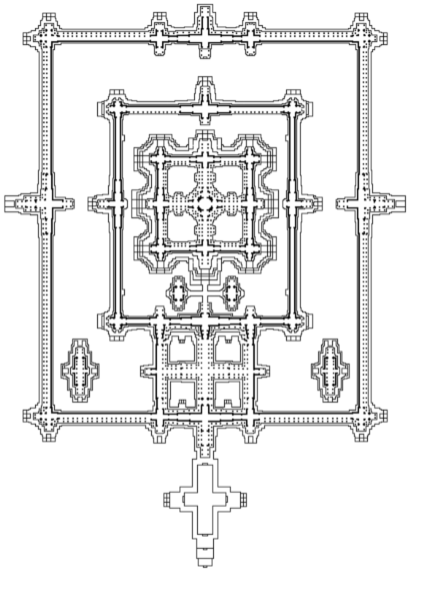
What plan does Angkor Wat have?
Mandala plan
What central belief is shared by both Hinduism and Buddhism?
A cycle of suffering, death, and rebirth from which enlightenment brings release
East Mebon, Pre Rup, and Angkor Wat are examples of the evolution of the ______________ temple type.
mountain
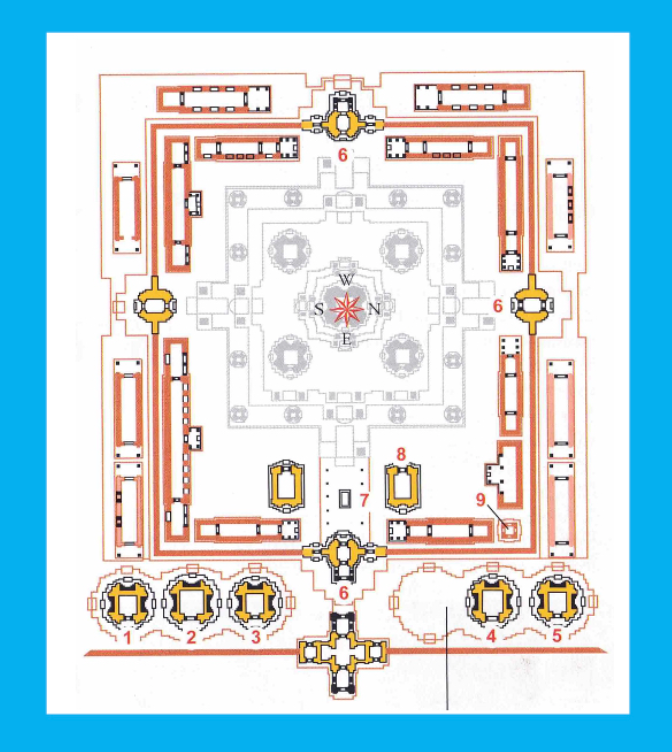
What does the water surrounding the temple symbolize?
the rings of ocean around Mt. Meru