Module 9: Sleep and Dreams
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Sleep
A periodic, natural loss of consciousness (different from unconsciousness resulting from a coma, general anesthesia, or hibernation
Circadian Rhythm
Our biological clock/24 hour cycle; regular bodily rhythms
Examples of Circadian Rhythm
Temperature and consciousness
Ways our circadian rhythm can be altered
Age and experience
Sleeping Brain
Remains active + has its own biological rhythm
REM Sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep; a recurring sleep stage during which vivid dreams commonly occur (other body + brain systems are active during this time)
Other Names for REM Sleep
Paradoxical sleep because muscles are relaxed (except for minor twitches), and R sleep
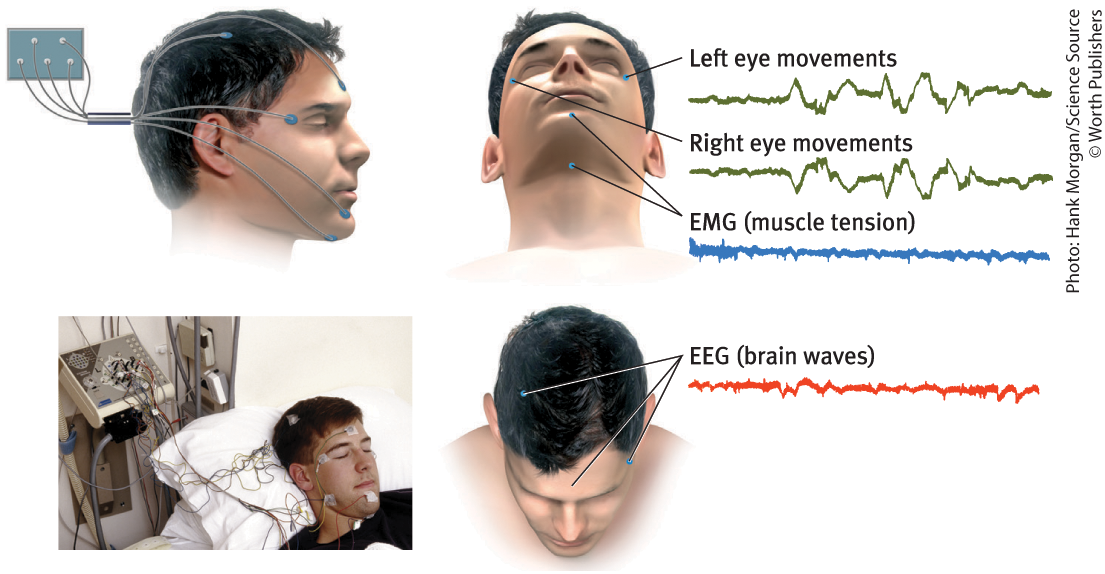
How do sleep researchers measure brain wave activity, eye movements, and muscle tension?
By using electrodes that pick up weak electrical signals
Alpha Waves
The relatively slow brain waves of a relaxed, awake state
Microsleeps
Falling asleep for a few seconds
Hallucinations
Sensory experiences without sensory stimulation, like seeing something when there is not an actual visual stimulus
Hypnagogic Sensations
Hallucinations that occur before falling asleep
Sensations of falling or floating weightlessly before falling asleep are examples of…
Hypnagogic sensations
N2 Sleep
20 minutes of periodic sleep spindles; clearly asleep, but could be easily awakened
Sleep Spindles
Bursts of rapid, rhythmic brain-wave activity that aid memory processing
N3 Sleep
Deep sleep; slow-wave sleep, lasts about 30 minutes; brain emits large, slow delta waves; hard to awaken person
REM Sleep Stage
Occurs an hour after you first fall asleep; for 10 minutes, brain waves become rapid and sharp; heart rate rises, breathing becomes rapid and irregular; eyes dart around every half-minute, protective paralysis occurs, genitals may become aroused
What occurs when eyes dart around every half-minute?
These movements announce the beginning of a new dream
REM sleep tricks the brain into responding to dreams as if they were…
real
Delta Waves
The large, slow brain waves associated with deep sleep
How often does the sleep cycle repeat itself?
Every 90 minutes
Who experiences shorter, more frequent sleep cycles?
Young children and older adults
What happens to the different sleep cycles as the night goes on?
N3 grows shorter and disappears, REM and N2 periods get longer
How does REM offer therapy?
It calms the day’s emotions
Ways sleep patterns are influenced
Genetically, culturally, socially, and economically, and through stress and bright light (tweaks circadian clock)
Insomnia
Sleep pattern that results from DNA; recurring problems in falling or staying asleep
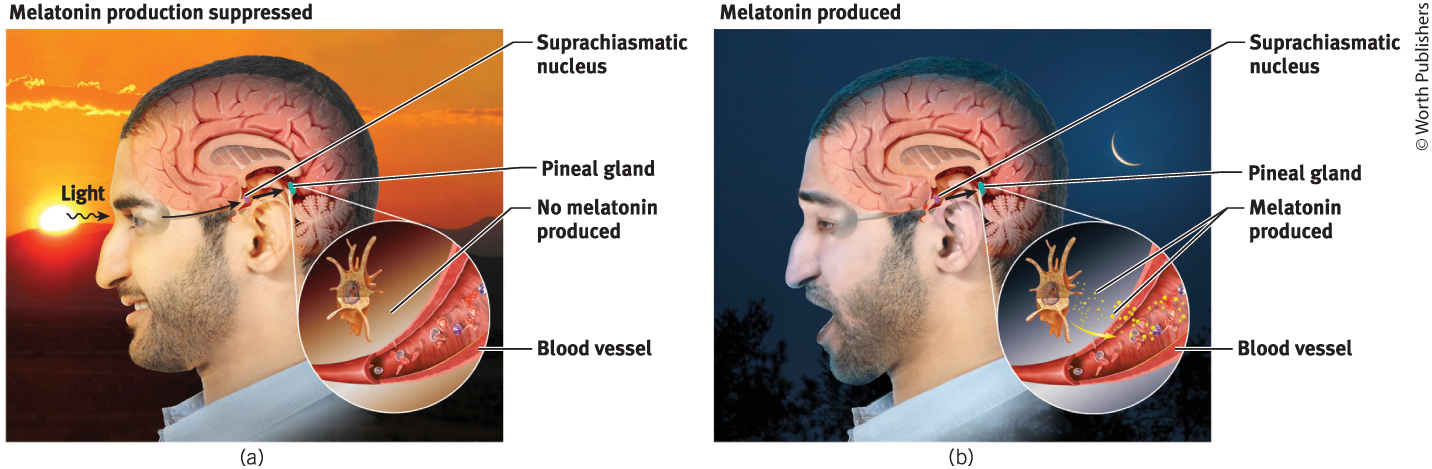
How does bright light tweak your circadian clock?
It activates light-sensitive retinal proteins; these proteins control the circadian clock by triggering signals to the brain’s suprachiasmatic nucleus
No light during the day=
disruption of circadian rhythm
What are the 5 reasons we sleep?
Sleep protects (survival)
Sleep helps us recuperate (repair, rewire, reorganize)
Sleeps helps us restore + rebuild fading memories of day’s experiences
Sleep feeds creative thinking (dreams inspire ideas)
Sleep supports growth
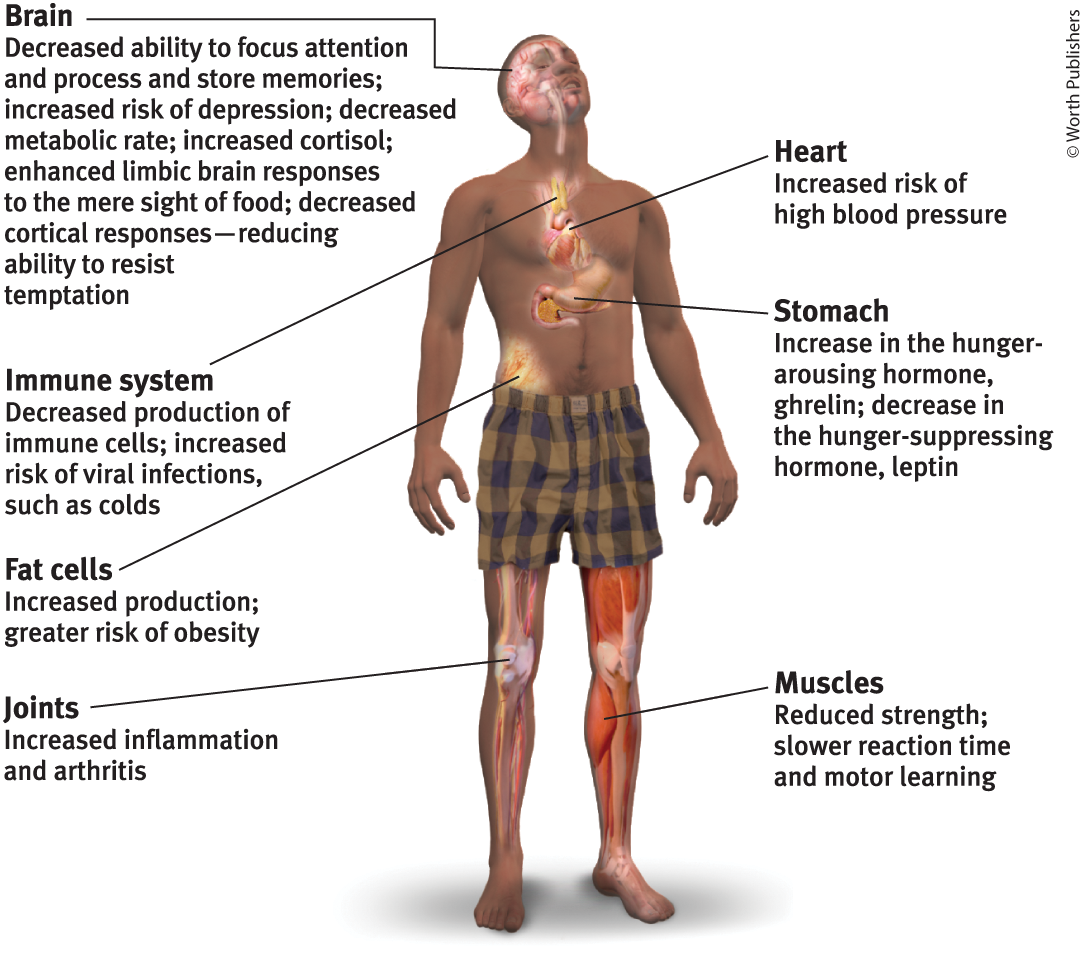
What results from sleep deprivation?
Difference in mood (increased anger, fatigue, depression)
Weight gain
Affects hormones, metabolism, brain’s response to food
Decrease in ghrelin, hunger-arousing hormone + increase in leptin (hunger-suppressing)
Increase in cortisol, stress hormone that stimulates body to make fat
Disrupts gene expression
Enhances limbic brain responses to sight of food, decrease in layers around the cerebellum that help us resist temptation
Narcolepsy
Sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks, sufferer may lapse directly into REM sleep at inappropriate times
Sleep Apnea
Sleep disorder characterized by temporary pauses in breathing during sleep and repeated momentary awakenings
REM Sleep Disorder
Sleep disorder characterized by acting out dreams while sleeping, through physical movements and vocal behaviors
Sleepwalking/talking
Regular activities while asleep; walking occurs during N3, while talking can occur at any stage
Night Terrors
Sleep disorder characterized by high arousal / appearance of being terrified, unlike nightmares, occur during N3 and are rarely remembered
Dreams
A series of images, emotions and thoughts passing through a sleeping person’s mind
What happens to the moments before we fall asleep?
They are lost from memory
What did Sigmund Freud believe about dreams?
Dreams are the key to understanding inner conflicts
Manifest Content
According to Freud, the symbolic, remembered storyline of a dream
Latent Content
According to Freud, the underlying meaning of a dream
Activation Synthesis Theory
The theory that dreams are the brain’s attempt to synthesize (make understanding of) random neural activity
REM Rebound
The tendency for REM sleep to increase following REM sleep deprivation
Cognitive Development Theory
The theory that dream content reflects dreamer’s level of cognitive development (their knowledge and understanding)
Freud’s Wish Fulfillment Theory
Dreams provide a “psychic safety valve”—expressing otherwise unacceptable feelings; dreams contain manifest (remembered) content and a deeper layer of latent content (a hidden meaning)
Information Processing Theory
Dreams help us sort out the day’s events and consolidate our memories
Neurocognitive Function Thoery
REM sleep allows the brain to consolidate (strengthen) memories and process emotional information