APUSH Presidents Review
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
By: Sadie Feingold (Information taken from US History 1 notes, AMSCO, US History 2 notes/CW) Also used: https://www.trumanlibrary.gov/sites/default/files/APUSH-Presidents.pdf
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms

George Washington 👑🇺🇲
1st president, 1789-1797 (VP: John Adams)
Judiciary Act (1789): Congress could regulate the jurisdiction of all federal courts, established judiciary system of 13 federal district courts, 1 chief and 5 associate judges (later becomes 9).
French Revolution (1789): Period of social upheaval that began in 1787 and ended in 1799, sought to change the relationship between the rulers and the governed.
Tariff of 1789: All foreign-owned or built ships paid $0.50 per ton duty to protect trade and raise revenues for the US government.
Whiskey Rebellion (1794): The whiskey tax was the first tax imposed on domestic products by the federal government, leading to violent protests by farmers in the west. Washington sends 15,000 troops to maintain stability and safety and end the rebellion.
Jay Treaty with England (1794): Sought to settle outstanding issues between the US and UK that been left unresolved since American independence.
Pickney Treaty with Spain (1795): Defined the border between the US and Spanish Florida and guaranteed the US navigation rights on the Mississippi River.
Farewell Address (1796): Washington warned Americans about geographical sectionalism and interference by foreign powers in the nation’s domestic affairs.
First Bank (1791-1811): Seen as a way to improve the nations credit and create a common currency, encouraged by Alexander Hamilton
Side note: it was during his presidency that factions began to emerge that would lead to the Democratic-Republicans and Federalists being the first 2 political parties.

John Adams (remember Report Card assignment = B-) 👀🗣🚫
2nd president, 1797-1801 (VP: Thomas Jefferson)
Federalist (supporter of the federal government)
XYZ Affair (1797): A diplomatic incident by US and France that resulted in a Quasi-War (did strengthen the army), where French diplomats tried to bribe US diplomats into ensuring that American ships would not longer be attacked.
Alien and Sedition Acts (1798): Raised the residency requirement for citizenship and allowed the president to deport “aliens” and permitted their arrest during wartime.
Naturalization Act: Limited US citizenship to white immigrants by increasing period of residence required.
“Midnight Judges” (1801): Adams quickly filled the new judicial positions with Federalist lifetime appointees so they continued to have political allies, should have let Jefferson handle this.
Kentucky and Virginia Resolutions (1798): Said that the Alien and Sedition Acts were unconstitutional and helped set a precedent that states could nullify unfair acts passed by the federal gov.

Thomas Jefferson 🗺🔍
3rd president, 1801-1809 (VP: Aaron Burr, Hamilton had been the deciding factor)
Democrat-Republican (Similar to Locke, believed in natural rights, pro-states power, anti-centralized power, wanted a smaller gov, and represented farmers/small guy).
Marbury v. Madison (1803): Marshall established the principal of judicial review, an important addition to the system of “checks and balances” to help prevent one branch from having too much power of the other.
Louisiana Purchase (1803): Encompassed 530,000,000 acres of territory that the US purchased from France for $15 million.
Lewis and Clark Expedition (1804-05): Helped establish a trade network across the US and befriended Indians by exploring more area in the West following the Louisiana Purchase.
12th Amendment (1804): Each elector must cast a vote for president and VP.
Embargo Act (1807): Closed US ports to all exports and restricted imports from Britain following the American Revolution.
Non-Intercourse Act (1809): Lifted embargoes on US shipping except for those bound for UK or France ports.

James Madison 🖋🪖
4th president, 1809-1817 (VP: George Clinton)
Democrat-Republican
Macon Act (1810): Prohibited British or French warships from entering American harbors or territorial waters.
Orders in Council: Established a blockade of part of the continent of Europe and prohibited trade with France, unless American vessels went to British ports for licenses for trade.
“War Hawks” (1811-1812): Desire for war was prompted by expansionist tendencies, they wanted to add Canada and Florida to the US as well as push the frontier farther west despite resistance from Native Americans.
War of 1812: A military conflict fought between the US and Britain over British interference with US trade and impressment of US sailors by the British navy. Strengthened US nationalism, created a cohesive union, encouraged growth of industry in the US.
Hartford Convention (1814): Meeting of new New England Federalists who opposed the War of 1812 to discuss their grievances, leading to the drafting of constitutional amendments to strengthen state controls (EX: 2/3 majority to declare war).
First Protective Tariff (1816): Used to protect US manufactured items from overseas competition rather than just raise revenue for the government.

James Monroe (Era of Good Feelings) 😃🌍
5th president, 1817-1825 (VP: Daniel Tomkins)
Democrat-Republican
McCulloch v. Maryland (1819): Congress has implied constitutional power to create a national bank and individual states can’t tax federally chartered banks.
Gibbons v. Ogden (1824): Decided that the federal government has exclusive power over interstate commerce.
Acquisition of Florida from Spain (1819): Spain gives East and West Florida to the US and the US agrees to assume claims by citizens of the US against Spain.
Missouri Compromise (1820): Allowed Missouri to form a constitution and state government, and admitted Main as a free state so Missouri would become a slave state, also prohibiting slavery in the rest of the Louisiana Purchase north of the 36//30 line.
Monroe Doctrine (1823): US policy toward the Western hemisphere, warns European nations that the US will not tolerate further colonization or puppet monarchs.
“Corrupt Bargain” election (1824): Jackson argues that Henry Clay (Speaker of the House) convinced the House to vote for John Quincy Adams instead.

John Quincy Adams 😠💔
6th president, 1825-1829 (VP: John C. Calhoun)
Democrat Republican
NY Erie Canal: Tranformed NY into the nation’s principal seaport and opened the interior of North America to settlement, allowed Western farmers to ship surplus crops to sell in the North (and the North to send manufactured good to the West).
Tariff of Abominations (1828): A series of tariffs passed by the US Congress intended to protect American industry against foreign competition, however; Southerners argued that it enhanced the interest of the Northern manufacturing industry at their expense.
Calhoun’s Exposition and Protest (1828): Calhoun wrote this and in it he explained how the gov. had exceeded its authority in passing the Tariff of Abominations and that states therefore were not required to follow it.

Andrew Jackson (Old Hickory/Common Man). 🪵😐
7th president, 1829-1837 (VP: John C. Calhoun/ later Martin Van Buren)
Democrat (and first non-Founding father as president, elected in part by Juntos, seen as hero from War of 1812 at the Battle of New Orleans, uses Spoil System “quid pro quo”, expanded federal government - like a veto king,
Jacksonian Democracy: The political movement toward greater democracy for the common man symbolized by the American politician Andrew Jackson and his supporters.
Tariffs of 1832 and 1833: 32- used to remedy the conflict created by the Tariff of 1928 and protect the rapidly growing industry-based economy of the North by imposing heavy taxes on British imports (leads to Nullification Crisis). The Tariff of 1833 reduced high tariff rates slightly.
Second Bank of the US (due to expire in 1836): Would help to regulate the amount of money circulating in the economy, though Jackson wouldn’t renew it, leading banking to be directed by state-charted banks instead. Jackson didn’t trust the bank or Nicholas Biddle, goes well for Jackson surprisingly.
Formation of the Whig Party (1832): Opposed Jackson and thought that the executive branch under him had too much power, supported the 2nd Bank of the US, and higher tariffs (part of the Second party system).

Martin Van Buren 😭
8th president, 1837-1841 (VP: Richard Johnson)
Democrat (very lassiez-faire with economy, believes in limited government)
Panic of 1837: Worst economic recession due to dissolving of the 2nd Bank and falling demand for cotton (primary export of the US), leads to thousands of farmers losing land, unemployment increasing in eastern cities, and inflation.

William Henry Harrison 🥶❄😵
9th president, 1841 (VP: John Tyler)
Whig
Harrison was seen as a war hero and the Whigs blamed Van Buren for the economic crisis, believing Harrison was a simpler man. However, after delivering a 2 hour inauguration speech on a cold day without a jacket, 32 days later he dies of pneumonia and his VP takes over.
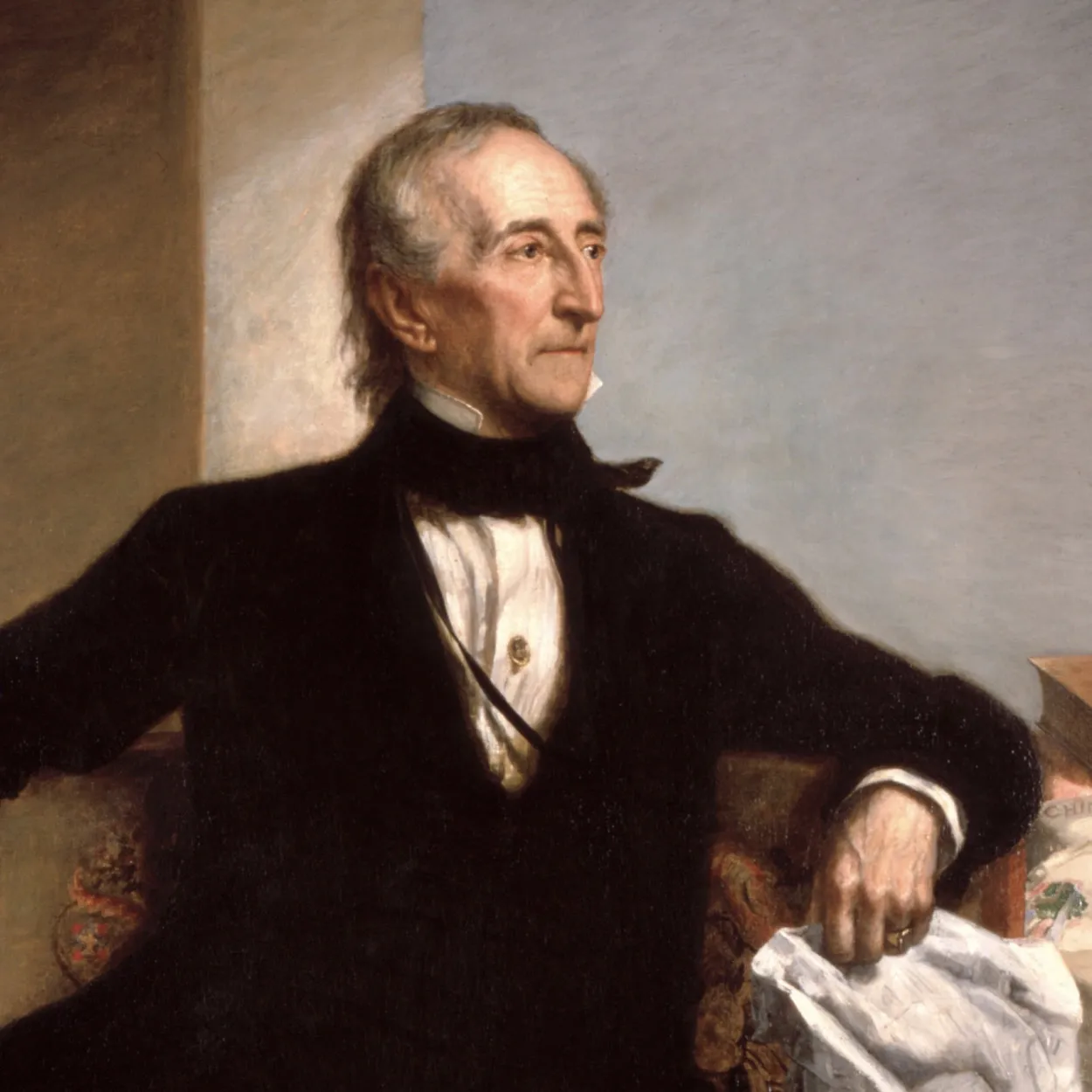

John Tyler 🫠
10th president, 1841-1845
Anti-Jackson Democrat, ran as VP on Whig ticket (only place on ticket to attract Southern voters- from Virginia, own party opposed him, Whigs tried pushing their agenda of a third Bank of the US and higher tariffs, but Tyler sided with the Democrats).
Vetoes Clay’s bill for third US Bank
Canadian border at the 45th parallel (Webster-Ashburton Treaty of 1942 settled the dispute between the ill-identified boundary between Maine and the Canadian province of New Brunswick- which had belong to the British at the time).
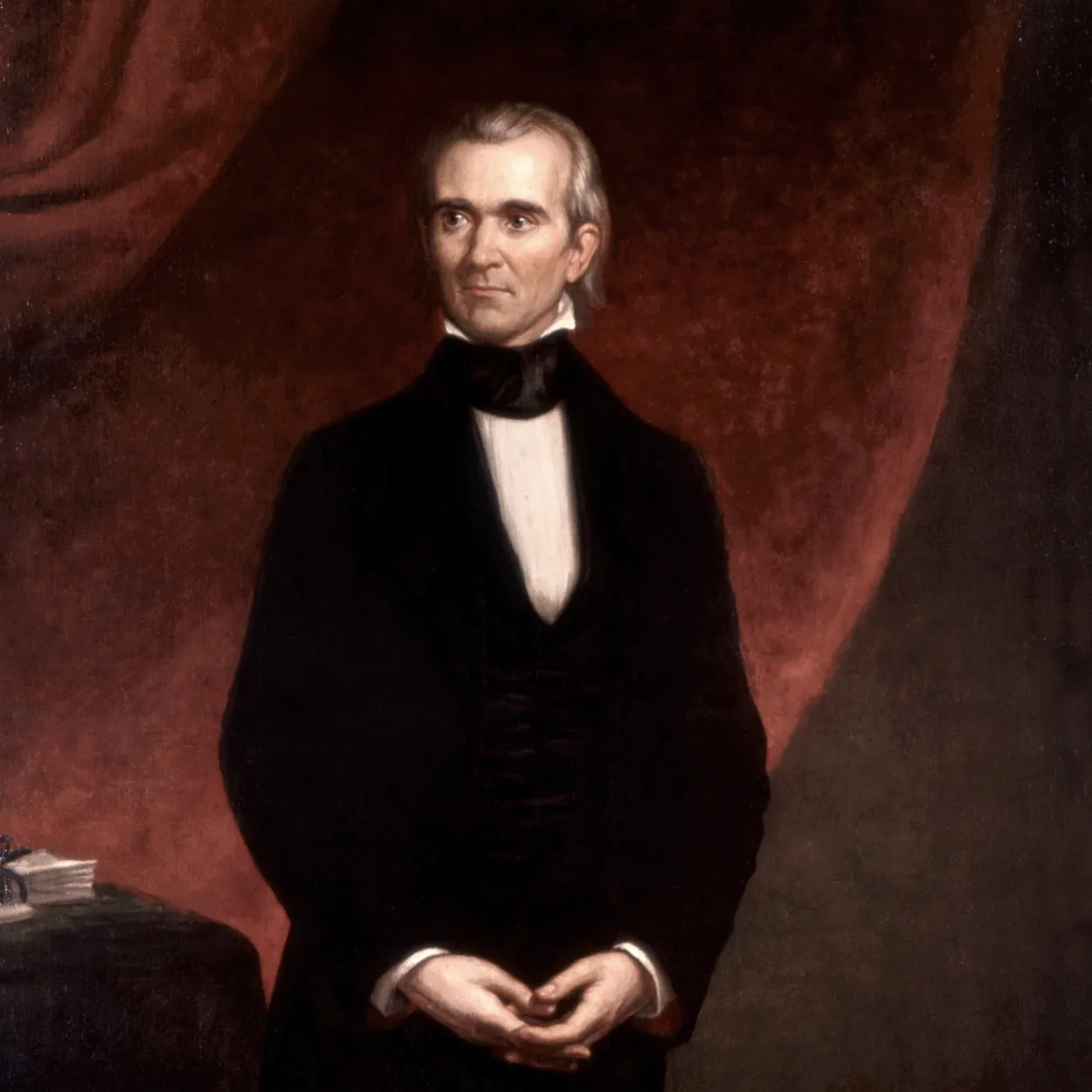

James K. Polk 🥷🗺🇲🇽
11th president, 1845-1849 (VP: George Dallas)
Democrat (favored expansion and manifest destiny, from TN)
Texas = state (1845): Contributes to Mexican-Americans and growing divide over slavery, does help with US expansion/ manifest destiny. Texas had originally belonged to Mexico, but then became independent in 1836 until it was annexed by the US.
Oregon boundary settled (1846): Many Americans had already traveled to Oregon along the Oregon trail following the success of farming the fertile region, but the British also sought the area due to their success in trading with American Indians there. Ends up being split at the 49th parallel.
Mexican-American War (1846-1848): US had wanted to spread democracy and add more land west of the Mississippi, saw that Mexico was politically unstable, and South really wanted to spread slavery. Polk waited till a Mexican army crossed the Rio Grande and captured and killed an army patrol to begin fighting. This led the US to gain 525,000 sq. miles of land at a very cheap price and restored the South’s confidence by the addition of the land. Specifically, the US got California and New Mexico, disrupting free state-slave state balance (escalated tension between the North and South over slavery which ultimately leads to civil war)
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848): Ended the war between the US and Mexico and led Mexico recognizing the boundaries of Texas.
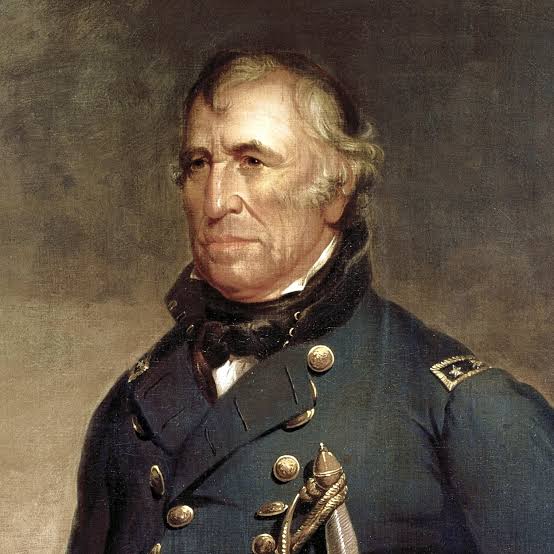

Zachary Taylor 🪖🆓
12th president, 1849-1850 (VP: Millard Fillmore)
Whig
Mexican-American war hero: Helped defeat Mexican troops at Monterrey and Buena Vista.
President Taylor thought that states should be allowed to choose “slave” or “free” (popular sovereignty). He wanted to admit CA and NM as free states but the South refused. Henry Clay “The Great Compromise” ends up drawing up a compromise instead.
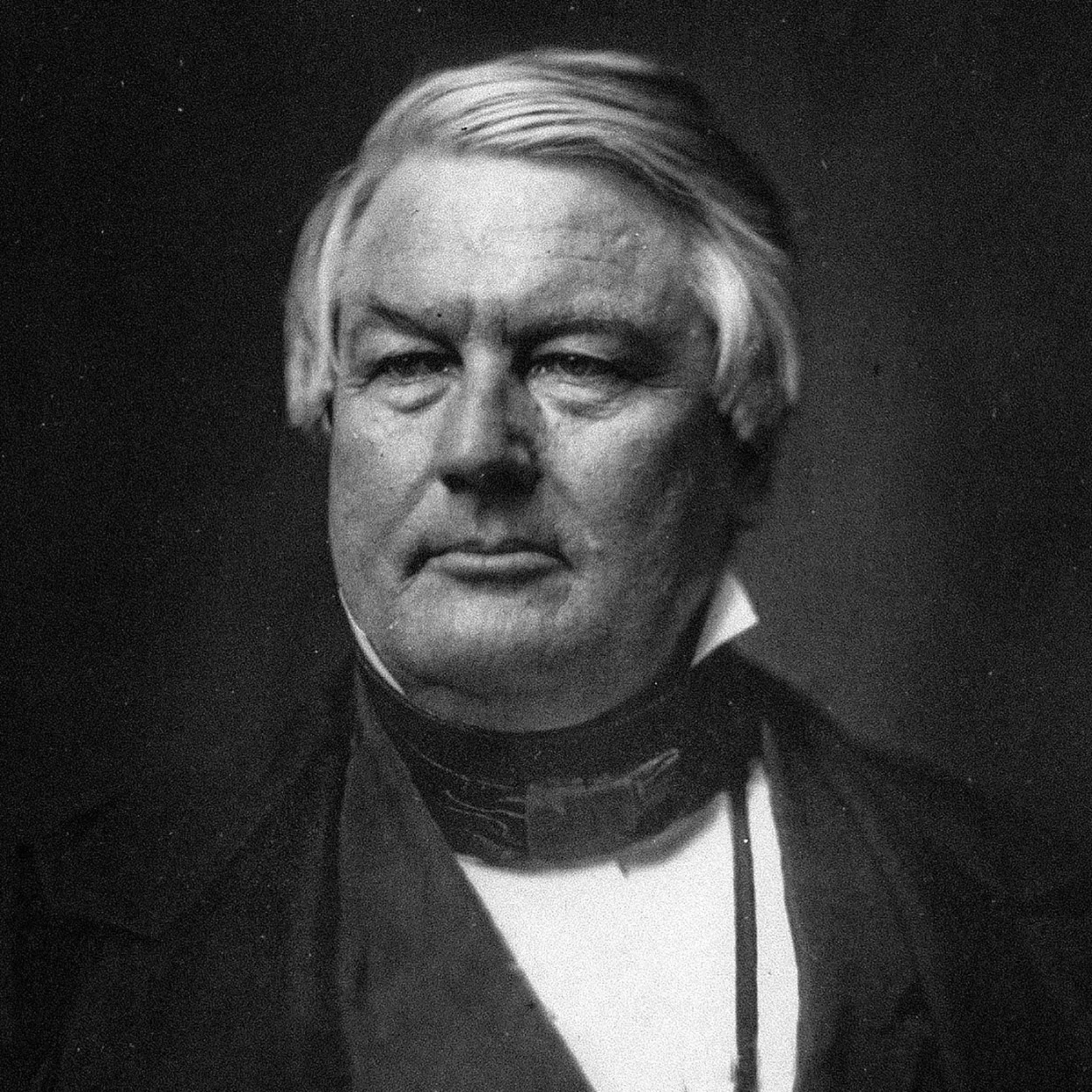

Millard Fillmore 🕙🤝📕
13th president, 1850-1853
Whig
Compromise of 1850: Admitted CA as a free state, giving the North greater political power. It also led to New Mexico and Utah being admitted as “popular sovereignty” (delaying the inevitable by letting states choose), federal government paying off TX debt, abolishing of the slave trade in DC, and the passing of the new Fugitive Slave Act.
Fugitive Slave Act: This law placed fugitive slave cases under the exclusive jurisdiction of the federal gov. and allowed special US commissioners to issue warrants to arrest fugitives. Captured persons who claimed to be free and not runaway slaves were denied the right of trial by jury. People who hid runaways or obstructed enforcement of the law were also subject to penalties. (Legalized human trafficking & turned slavery into a NATIONAL problem that continued to divide the North and the South).
Clayton-Bulwer Treaty (1850): This was made between the US and great Britain that said that both would protect the neutrality of Central America and wouldn’t try to take control over any future waterway.
Uncle Tom’s Cabin is published (1852): About the conflict between an enslaved man named Tom and the brutal white slave owner Simon Legree. Written by Harriett Beecher Stowe (from the North) and while it invigorated Northerners it angered the South by its “untruths”.

Franklin Pierce 🩸🫀😡
14th president, 1853-1857 (VP: William King)
Democrat (From New Hampshire, supported Fugitive Slave Law)
Kansas-Nebraska Bill (1854): Senator Douglas of IL wanted to build a transcontinental railroad (fueled by manifest destiny and desire for western expansionism) but needed to win Southern approval first; so Douglas drafted a bill to split Nebraska into two parts, Nebraska and Kansas, which would be admitted based on popular sovereignty. Both were located north of the 36//30 line, giving Southerners the chance to expand slavery. Repealed the Missouri Compromise of 1820 which had admitted Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a free state, prohibited slavery in all other states (besides Missouri) above the 36//30 line.
Underground Railroad: Fake network of “conductors” and “stations” that was really a lose network of Northern free blacks and courageous ex-slaves and white abolitionists, who helped escaped slaves reach freedom in the North or Canada.
Bleeding Kansas: Abolitionists from Boston send anti-slavery settlers to live in Kansas while pro-slavery Missourians also move to Kansas to vote in determine outcome of the state. However, Missourians vote with guns illegally swaying state to become slave state. Anti-slavery group starts their own gov. in Topeka, KA to oppose pro-slavery gov. in Compton. Leads to groups burning down buildings and printing presses, John Brown’s posse murdering 5 people.
Ostend Manifesto (1854): Secret meeting in Belgium where the US schemed to US purchase Cuba from Spain for $120 million, which angered antislavery members over Cuba becoming a slave state.
James Buchanan 🦆😡😲
15th president, 1857 -1861 (VP: John C. Breckenridge)
Democrat (From Pennsylvania)
Dred Scott v. Sanford (1857): Scott had been held in slavery in Missouri and then taken to the free territory of Wisconsin where he lived for 2 years before returning to Missouri. Her argued that his residence on free soil made him a free citizen, suing for his freedom in 1846. Chief Justice Roger Taney ruled against Scott because Congress couldn’t deprive any person of property without due process of the law & since Framers of Constitution didn’t intend African Americans to become US citizens. Really angered Northerners and delighted Southerners.
Lincoln-Douglas Debates (1858): A series of seven debates between Lincoln and Douglas in the Illinois senatorial race Popular sovereignty, the Lecompton Constitution, and the Dred Scott decision were addressed. Although Lincoln lost, it made him famous nationally and later allowed him to win the Republican nomination for presidency later on.
South Carolina secession (1860): After Lincoln wins in the election of 1860, in the time before he takes office in December 1860 South Carolina votes to secede. Soon after 7 Southern states created the Confederate States of America.

Abraham Lincoln (“Honest Abe”) 🎩🧔👏
16th president, 1861-1865 (VP: Andrew Johnson)
Republican (Born in Kentucky, self-made lawyer, opposed to Mexican-American War and Kansas-Nebraska Act, wanted a UNITED NATION, very moderate in political views- “can’t exist ½ slave and ½ free”). ←1st Republican president
Civil War 1861-1865: Frees 4 million people from slavery (“new birth of freedom”), transforms society by accelerating industrialization and modernization of the North and destroying much of the South. Began at Fort Sumter when Lincoln sent provisions of food there and South Carolina began firing. Since Congress was not in session, Lincoln enabled Lincoln to expand the power of the executive during this time. While the confederates hoped to gain independence, the Union sought to preserve the Union.
Homestead Act (1862): Promoted settlement of the Great Plains by offering parcels of 160 acres of public land free to any person or family that farmed that land for at least five years.
Morill Act: Encouraged states to use the sale of federal land grants to maintain agricultural and technical colleges. (Also creates Freedmen’s Bureau to act a welfare agency to provide food/shelter/medical aid to former slaves and poor whites).
Emancipation Proclamation (1863): A warning issued by Lincoln that enslaved people in all states still in rebellion on January 1, 1863 would be forever free. This only immediately freed 1% of slaves as it only applied to enslaved people residing in Confederate states outside Union control. However, it enlarged the purpose for war (to end slavery). Freed slaves were also used as Union soldiers, bolstering its efforts.
Ten Percent Plan: Lincoln’s plan on bringing states back into the Union where states would be restored after at least ten percent of the population swore an oath of loyalty.
Lincoln's assassination (April 14, 1865) by John Wilkes Booth: Wilkes was a Confederate sympathizer and shot Lincoln at Ford’s Theater in Washington.

Andrew Johnson (foe of reconstruction) ☹🤓👎
17th president, 1865-1869
Republican (White-supremacist Southern Democrat, clashed constantly w/ Congress).
13th Amendment (1865): Lincoln played an active role in the passing of this, though it ended up happening months after his death. The amendment abolished slavery, except for being used as a punishment for crime.
14th Amendment (1868): This amendment declared that all people born or naturalized in the US were citizens and obligated the states to respect the rights of US citizens and provide them with equal protection of the laws.
Amnesty Plan (1865): Gave full pardon to all southerners (except high ranking confederate leaders) who would swear allegiance to the Constitution and accept federal laws on slavery). Leads to 11 Southern states re-entering the Union and many Southerners began to take seats in Congress again.
Military Reconstruction Plan (1867): Divided the South into five military districts governed by previous Union generals. To be eligible for re-admittance to the Union, each Confederate state was required to pass the 13th and 14th amendment and hold new elections.
Tenure of Office Act: Over Johnson’s veto, Congress passed this act, which prohibited the president from removing a federal official or military commander without the approval of the Senate. This law was strictly political, Congress wanted to protect the radical republicans in Johnson’s cabinet (like Secretary of War Edwin Stanton).
Impeachment Trial: After Johnson fired Stanton on his own authority, the House of Representatives charged him w/ "high crimes and misdemeanors”. He became the first president to be impeached, though he was one not short for removal so he ended up finishing out his term.
Formation of the KKK: Group of white Southerners that organized a secret society to intimidate blacks and white reformers. Founded by an ex-confederate Nathaniel Bedford Forrest, the group burned black-owned buildings and murdered freedmen. Proud and weren’t intimidated.
Adoption of Black Codes: Southern state legislatures adopted these laws which restricted the rights and movements of former slaves. It prohibited blacks from either renting land or borrowing money to buy land, placed freedman in a form of semi bondage by forcing them to sign work contracts, and prohibited blacks from testifying against whites in court. (Contract-labor system leads to convict leasing and sharecropping causing them to be re-enslaved).

Ulysses S. Grant 🪖🤑📉
18th president, 1869-1877 (VP: Calfax Wilson)
Republican (Union Army war hero, 500,000 Republican votes for him came from Black Americans fundamentally shifting the Republican party).
First Transcontinental Railroad (1869): The Pacific Railway Act authorized the building of this over a northern route in order to link the economies of CA and the western territories with the eastern states.
15th Amendment (1870): Prohibited any state from denying or abridging a citizen’s right to vote based on race, color, or previous condition of servitude.
Tweed Ring: In NY, William Tweed, the boss of the local Democrat party, masterminded dozens of schemes for helping himself and cronies to large chucks of fraud. Ended up stealing $200 million from NY taxpayers.
Panic of 1873: An economic disaster that left thousands of Northern laborers jobless and homeless. Over speculation by financiers and overbuilding by industry and railroads led to widespread business failure and depression.
Credit Mobilier scandal: Insiders gave stock to influential members of Congress to avoid investigation of the profits they were making from government subsidies for building the transcontinental railroad. Represents the rise of corruption in business and government at the time.
Whiskey Ring: Federal revenue agents conspired with the liquor industry to defraud the government of millions in taxes. Grant’s loyalty to dishonest men around him badly tarnished his presidency.

Rutherford B. Hayes 🥈👿
19th president, 1877-1900 (VP: William Wheeler) —> beginning of Gilded Age.
Republican (Moderate, non-racist, previous governor of Ohio & Union general).
Bland-Allison Act (1878): Passed over Hayes veto and allowed only a limited coinage of between $2 million and $4 million in silver each month at the standard silver-to-gold ratio of 16:1.This did’t satisfy farmers, debtors, and western miners, who continued to press for the unlimited coinage of silver. Was supposed to help the money supply.
Compromise of 1877: Democrats (South) would allow Hayes to become president (close election, electoral votes were contested in 4 states) as long as he would immediately ended federal support for the Republicans in the South and support the building of a Southern transcontinental railroad. As a result, once he became president, Hayes promptly withdrew the last of federal troops protecting African Americans and other Republicans. This brought Reconstruction to an end. (accepts devil’s bargain).
Tried to re-establish an honest government following the corrupt Grant administration & vetoed efforts to restrict Chinese immigration.

James A. Garfield 🫢🫨
20th president, 1881 (March 4- September 19) (VP: Chester A. Arthur)
Republican (Halfbreed, from Ohio and a Union veteran. In his first weeks as president, Garfield was overwhelmed by hordes of Republicans seeking some 100,000 federal jobs. Choose halfbreeds for most offices, provoking a bitter contest with Senator Conkling and his Stalwarts).
Garfield’s assassination by C. Julius Guiteau: Preparing to board a train for summer vacation a deranged officer associated with the Stalwarts short Garfield in the back leading to his death 11 weeks later.
(Mostly politically paralyzed by his own political views and sudden death, not much time to act).

Chester A. Arthur 😃👍⭐
21st president, 1881-1885
Republican (“Stalwart” who replaced Garfield after his assassination, helped end the Spoils System, restart the navy, and attempted to expand trade
Pendleton Civil Service Act (1883): Expanded the number of government employees hired based on their qualifications rather than their political connections. This also create the Civil Service Commission (all helping to reduce the amount of corruption inside the US).

Grover Cleveland ♞🥳
22nd President, 1885-1889 (VP: Thomas Hendricks)
Democrat (Honest, frugal, and uncompromising. Previously mayor of Buffalo and governor of NY. Believed in a limited government
Knights of Labor (1886): A national labor union that began as a secret society in order to avoid detection from employers. Led by Terrence V. Powderly and extended membership to women and people of color. Advocated for worker cooperatives, abolition of child labor, and abolishment of trusts and monopolies. Grew out of control and chaotic.
Haymarket Riot (1886): On May 4, workers held a public meeting in Haymarket Square and as police attempted to break up the meeting, someone threw a bombing (killing 7). Made people think Knights of Labor were radical and violent.
Interstate Commerce Act (1887): Federal government’s first effort to regulate business and monopolies. Required railroad rates to be “reasonable and just” and set up the federal regulatory agency, the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) which had the power to investigate and prosecute pools, rebates, and other discriminatory practices.
Dawes Severalty Act (1887): Designed to break up tribal organizations, which many felt kept American Indians from becoming “civilized” and law-abiding citizens. Divided tribal land into plots of up to 160 acres. US citizenship was to be granted to those who stayed on the land for 25 years.
Washburn vs. Illinois (1886): Supreme Court ruled that individual states could not regulate interstate commerce.

Benjamin Harrison 💲👊
23rd President, 1889-1893 (VP: Levi Morton)
Republican (Stood for high protective tariff and business prosperity, grandson of William Henry Harrison).
Populist Party Platform of 1892: Determined to do something about the concentration of economic power in the hands of trusts and bankers. Called for both political reforms (direct popular election of senators and use of initiatives & referendums) and economic reforms (unlimited coinage of silver to increase money supply, graduated income tax, public ownership of railroads by government, telegraph and telephone systems owned/operated by the government, loans and federal warehouses for farmers to stabilize prices, and an 8-hour work day). —> James Weaver Iowa runs for platform but loses).
North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana, and Washington become states (1889)
Idaho and Wyoming become states (1890)
McKinley Tariff (1890): Raised the price on foreign products to a peacetime high of more than 48% (frustrated rural workers).
Sherman Anti-Trust Act (1890): Prohibited any “contract, combination, in form of trust or otherwise, or conspiracy in restraint of trade or commerce.” Ends up being too vaguely worded to stop the development of trusts in the 1890s.

Grover Cleveland (again- 2nd term) 😟❌
24th President, 1893-1897 (VP: Adlai Stevenson)
Democrat
Panic of 1893: The stock market crashed as a result of over-speculation and dozens of railroads went bankrupt. This continued for 4 years as farms continued to close and unemployment rose. To fix the crisis, Cleveland championed the gold-standard and otherwise a hands-off policy towards the economy.
Venezuelan Boundary Affair (1895): Fighting over Venezuela’s dispute with the UK over a piece of land that the UK claimed as part of their own that Venezuela saw as Venezuelan territory. Used the Monroe Doctrine to make US a mediator in the dispute.
Pullman Strike: Strike of workers living in George Pullman’s company town following a cut in wages and the firing leaders who had tried to bargain for a better deal. This tied up rail transportation across the country leading Cleveland to use the army to keep mail trains running.
American Federation of Labor: Association of 25 craft unions that concentrated on attaining narrower economic goals than the Knights of Labor. Led by Samuel Gompers, the AF of L focused on winning higher wages and improved working conditions through collective bargaining.
Wilson-Gorman Tariff (1894): Provided a moderate reduction in tariff rates, including a 2% income tax on incomes more than $2,000.

William McKinley 💲🇪🇸
25th President, 1897-1901 (VP: Teddy Roosevelt)
Republican (Supported a high protective tariff, considered a friend of labor still. Mark Hanna helped with McKinley’s campaign through the mass media. As he took office, the economy had begun to improve. Gold had been in Alaska helping to increase the money supply. Overall, McKinnley is said to have helped make the US a world power).
New Imperialism: A period of European colonial expansion in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, during which European powers extended their control over territories through political domination and direct rule. The US wanted more raw materials for manufacturing and worldwide markets to sell to.
Spanish-American War (April 1898-February 1899): Expansionists from the South had coveted Cuba since the 1850s. Now, in the 1890s, large American investments in Cuban sugar, Spanish misrule in Cuba, and the Monroe Doctrine all provided justification for US intervention in the area. A combination of yellow journalism, the Cuban Revolt, De Lome Letter, and sinking of the Maine in Havana contributed to American’s push for war. The US ends up winning.
Open Door Policy (1899): Russia, Japan, UK, France, and Germany had all established spheres of influence in China by the 1890s. US wanted to retain access to lucrative trade in China, (made it seem like China was weak aka disgruntled teens that needed a parent) so John Hay (McKinley’s secretary of state) dispatched a note to these other nations asking them to all keep equal trading privileges in China.
Boxer Rebellion (1900): A secret society of Chinese nationalists, the Society of Harmonious Fists (Boxers) attacked foreign settlements and murdered dozens of Christian missionaries. The US quickly responded by crushing the rebellion.
McKinley’s assassination by Leon Czolgosz (1901): Shot by an anarchist and was succeeded by his vice president Theodore Roosevelt.

Theodore (Teddy) Roosevelt 🟫🌳🗺
26th President, 1901-1909 (VP: Charles Fairbanks)
Republican (Young expansionist and hero of the Spanish-American War, previous governor of NY, & an interventionist. Similar to Hamilton & Hobbes: elitist, bottom-up government in which you chose to help the worthy first, pessimist, pro-unions-wanted to regulate big business = NEW NATIONALISM ).
Panama Canal (1903-1914): US wanted a canal through Central America to connect the Atlantic and Pacific oceans to help it hold its newly acquired land from the Spanish-American War. Columbia initially refused, so Roosevelt led a revolt for Panama’s independence. Building the canal took until 1914, later given back to Panama to end bitterness.
“Big Stick” Diplomacy: Roosevelt used the motto “speak softly and carry a big stick” to describe his aggressive foreign policy. By negotiating peacefully (but acting boldly and decisively and having strength in case things went wrong) Roosevelt hoped to continue building up the US as a respected world power. This was a way of intimidating countries without actually harming them.
“Square Deal”: Roosevelt demonstrated that he favored neither business nor labor (unlike other presidents). Came about during the strike of coal miners when Americans feared that if not resolved soon, they’d freeze during the winter. Helped create a 10% wage increase and 9-hour workday for miners (but union didn’t have to be recognized by owners). This encompassed his 3 C’s: consumer protection, conservationism (sets aside 150 millions acres of federal land) & control of corps.
Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine (1904): Said that the US had the right to exercise military force in Latin American countries to keep European countries out. It made sure these countries were paying their taxes so Europe stayed satisfied, which led to poor relations with the Latin America region (Involved in Morocco, Dominican Republic, Venezuela).
Portsmouth Treaty (1905): Teddy creates a diplomatic conference between Russia and Japan in Portsmouth, New Hampshire to end fighting between the imperialist powers. Japan felt that US didn’t give them enough in the treaty.
Gentlemen’s Agreement w/ Japan (1904): Japanese gov. secretly agrees to restrict emigration of Japanese workers to the US in return for Roosevelt to make CA repeal its discriminatory law that made Japanese Americans attend segregated schools (offensive).
Pure Food and Drug Act, Meat Inspection Act, Muckrakers (1906): Muckrakers made the public more informed about the scandalous realities of politics, factories, and slums. In The Jungle, Upton Sinclair described in horrifying detail the conditions of Chicago stockyards and the meatpacking industry —> led to the manufacturing, selling, and transportation of adulterated or mislabeled products being forbidden & requiring federal inspectors to visit meatpacking plants to ensure sanitation minimums are met.
Trustbusting: Roosevelt helps break up the Northern Securities Company, a railroad monopoly. Continues with Standard Oil and 40 other corporations. Wanted to break up companies that stifled completion and harmed the public, but also regulated good ones that worked efficiently and lowered prices.

William H. Taft 😤😕💵👎
27th president, 1909-1913 (VP: James Sherman)
Republican (good-natured, served as Teddy Roosevelt’s secretary of war. Progressive republicans felt that Taft was betraying their cause and had decided to join the conservative wing instead. He was more inclined to avoid conflict and was slow on decision-making). Later on, Taft becomes a Supreme Court Justice.
Paine-Aldrich Tariff (1909): Taft had promised to lower tariffs, but instead, he signed off on this act which actually raised the tariff on most imports.
Pinchot-Ballinger controversy: Progressives respected the chief of Forest Service, Gifford Pinchot, as a dedicated conservationist. They also distrusted Taft’s secretary of the interior, Richard Ballinger (who had tried making 1 million acres of land available for private development). When Pinchot criticized Ballinger, Taft chose to fire Pinchot for insubordination. This made Progressives MAD.
16th Amendment (1913): authorized the US government to collect an income tax. Progressives approved since at first it only applied to the very wealthy.
“Dollar Diplomacy”: Taft adopted a foreign policy that was mildly expansionist and depended more on investors’ dollars than navy battleships. He believed that private American investment in China and Central America would lead to greater stability there and promote US business interests.

Woodrow Wilson 🪖🏦🧨🚢
28th president, 1913-1921 (VP: Thomas Marshall)
Democrat (Previously a teacher, president of Princeton University, & governor of NJ. Wilson was also racist and inflexible. More similar to Jefferson & Locke: believed in a top-down government in which you create a fair playing field by fixing government first then the people- destroy not regulate big business. Twin goals: “Make the world safer for democracy” and “a war to end war”.
Underwood Tariff (1913): addresses Congress in-person (uncommon) about the idea of lowering tariff prices to bring consumer prices down. This act substantially lowered tariffs for the first time in a while (30%), & did also have a graduated income tax.
17th/18th/19th Amendments: traditionally US senators had been chosen by state legislatures but under the 17th Amendment it became required that they would be picked by a popular vote instead. The 18th Amendment declared the production, transportation, and sale of intoxicating liquors illegal. Ratification of the 19th Amendment in 1920 guaranteed women’s right to vote in all elections at the local, state, and national levels.
Federal Reserve System (1913): this would restore confidence in the banks by creating a national (rather than private) banking system w/ 12 district banks supervised by a Federal Reserve Board.
Federal Trade Commission (1914): The FTC would monitor American business, had the power to issue “cease and desist” orders to companies engaging in unfair practices, and aimed to limit business that unfairly limited competition.
Clayton Anti-Trust Act (1914): outlawed certain practices that restrict competition; banned price discrimination where a company would sell a product for a different price from person to person or business to business, gave unions more power, and corrected deficiencies of the Sherman Antitrust Act.
“Moral Diplomacy”: a foreign policy proposed by Woodrow Wilson that only supported countries w/ aligning democratic beliefs with the US. (troops to Nicaragua, Dominican Republic, Haiti, Virgin Islands, & Mexico for this reason).
World War I (1914-1918): Began with a Serbian nationalist assassinating Austrian Archduke Francis Ferdinand, the heir to the throne of the Austro-Hungarian empire. MAIN (militarism, alliances, Imperialism, and nationalism) was also largely at play. The US was first neutral, then in April 1917 the US declared war against Germany.
Lusitania- sunk May 1915: Britain first declared a naval blockade against Germany, leading to Germany torpedoing and sinking British passenger linger, the Lusitania. Many of the passengers were American, pushing the US closer to getting involved.
Zimmerman telegram: a telegram to Mexico from German foreign minister, Arthur Zimmerman, proposed that Mexico receive lost territories (TX, New Mexico, AZ) if it allied itself w/ Germany in WWI.
“Fourteen Points” (January 1917): Wilson presented to Congress this detailed list of war aims designed to address the causes of WWI and prevent another world war. Many of these points surrounded specific territorial questions, recognition of freedom of the seas, an end to secret treaties, reduction of national armaments, self-determination for various nationalities, a League of Nations, & the removal of trade barriers.
Treaty of Versailles (1919-1920): peace conference following the armistice to WWI (where allies won). Many nations there wanted revenge and compensation against Germany. Results: Germany was stripped of colonies in Asia and Africa, forced to admit guilt for the war, & pay lots of money in reparations back to the UK and France. Also created League of Nations, but US never ratifies the treaty or joins.
“New Freedom”: Woodrow Wilson pledged this idea during his election, in which there would be more limited big business and big. government,; bringing about reform by ending corruption and reviving competition by supporting smaller business.

Warren G. Harding ☕😄🤝
29th president, 1921-1923 (VP: Calvin Coolidge)
Republican (Previously a newspaper publisher in Ohio, bad at determining liars which led him to appoint corrupt senators & get involved in the scandals/schemes of the Ohio gang).
Teapot Dome Scandal: Secretary of the Interior Albert B. Fall accepted bribes for granting oil leases near Teapot Dome, Wyoming. Attorney General Harry M. Daugherty also took bribes for agreeing not to prosecute certain criminal suspects. Before the scandal was revealed publicly, Harding suddenly died while traveling in the West.
Washington Conference (1921-1922): Secretary of State Charles Evans Hughes talked on naval disarmament to stabilize the size of the US Navy to that of other nations. The Five-Power Treaty (fixed tonnage issues between the US, UK, JP, France, and Italy —> 5:5:3:1.67:1.67 ratio) , Four-Power Treaty, and Nine-Power Treaty (nations agree to respect Open Door policy in China). are created as a result.
Fordney-McCumber Tariff (1922): a comprehensive bill passed to protect domestic production from foreign competitors by raising tariff rates. Led many European nations to increase their own trade barriers as well. This all increased the price of regular American commodities and made it difficult for European nations to pay back their war reparations.

Calvin “Silent Cal” Coolidge 💬🤑
30th president, 1923-1929 (VP: Charles Dawes)
Republican (previously MA governor who broke up a Boston police strike, believed in a limited government that made war for big business- deregulation, & wanted to limit White House budget).
Dawes Plan (1924): emerging from WWI as a creditor nation, Coolidge continued to insist (along with Harding) that the UK and France pay off their war debts. Charles Dawes created this to be an established cycle of payments flowing from the US to Germany to the Allies. Many Europeans resented the greediness of the US.
Immigration Act of 1924 (National Origins Act of 1924): to reduce the number of immigrants from southern and eastern Europe, this quota act set quotas of 2% based on the Census of 1890, mainly restricting those deemed “undesirable” (in part to due to paranoia following WWI).
Kellogg-Briand Pact (1928): a treaty signed by almost all nations of the world that renounced the aggressive use of force to achieve national ends. This would end up proving ineffective though, because it permitted defensive wars and failed to provide for taking action against violators of the agreement.

Herbert Hoover 😱📉😭
31st president, 1929-1933 (VP: Charles Curtis)
Republican (Protestant, for prohibition, self made millionaire committed to business & volunteerism. Ignored advice from economists that the stock market would crash with government regulation. Previously, Hoover served as Wilson’s Food Administration leader during WWI & as Commerce Secretary for Harding & Coolidge).
Panic and Depression: Great Depression lasted longer, caused more bank failures and unemployment, and affected more people than any preceding period of hard times. Brought on by an increase in consumerism, buying on credit, uneven distribution of income, buying on the margin, and overproduction (among other things).
Stock Market Crash (1929): On Black Thursday there was an unprecedented volume of selling on Wall Street, and stock prices plunged. Then on Black Tuesday, millions of panicky investors ordered their brokers to sell but there were very few buyers. Prices on Wall Street continued to go down and down.
Hawley-Smoot Tariff (1930): set tax increases ranging from 31% to 49% on foreign imports; thus, European countries also began to enact higher tariffs on US goods. Reduced trade for all nations & worsened the depression.
Reconstruction Finance Corporation: federally funded, government-owned corporation created by Congress as a measure for propping up faltering railroads, banks, insurance companies, and other financial institutions. By helping to stabilize big business, Hoover believed these benefits would “trickle down” to smaller ones.
Bonus Army March: 1,000+ unemployed WWI veterans marched to Washington, D.C to demand immediate payment of the bonuses promised to them at a later date. Hoover uses the army to break up encampment, angering many.
20th Amendment/lame-duck amendment: shortened the period between presidential election and inauguration and set the start of each president’s term for January 20th.

Franklin D. Roosevelt 💊🥼🩻🩺⚠
32nd president, 1933-1945 (VP: John Garner, Henry Wallace, Harry Truman)'
Democrat (Born in NY to a very wealthy & spoiled family, Harvard graduate, contracts polio leading him to be paralyzed, previous governor of NY. Greatly expands the role of the federal government). “The only thing we have to fear is fear itself”
New Deal & Alphabet government (AAA, CCC, NIRA, SEC, TVA, etc): focused on the three R’s (relief, recovery, and reform) w/ brain trust to help create this new program. The Agricultural Adjustment Act made available millions of dollars to help farmers meet their mortgages. The Civilians Conservation Corps employed young men on federal lands for reforestation, fire-fighting, flood control, and swamp drainage. The National Industrial Recovery Act tired to guarantee reasonable profits for businesses and fair wages/hours for laborers (ends up failing). The Securities and Exchange Commission was created to regulate the stock market and limit speculative practices. The Tennessee Valley Authority hired thousands of people to build dams, operate electric power plants, control flooding and erosion, and manufacture fertilizer. FOCUSED ON RECOVERY!
Second New Deal (WPA, Wagner Act, Social Security, etc): Works Progress Administration helped create employment on useful projects for Americans. The Wagner Act guaranteed a worker’s right to join a union and a union’s right to collectively bargain. Social Security Act created a federal insurance program based upon automatic collection of payments from employees and employers through a person’s working career. RELIEF & REFORM!!
21st Amendment: ends prohibition by repealing the 18th Amendment.
Huey Long, “Share Our Wealth” program: opponent of the New Deal who preached a program that promised a minimum annual income of $5,000 for every American family, to be paid by taxing the wealthy, instead.
“Court Packing” scheme: FDR proposed that the president be allowed to appoint an additional justice for each current justice over 70 ½ years old (seen as an attempt to tamper with checks and balances of the government).
WWII (1939-1945): US first remains isolationist, but as Hitler (🇩🇪) & Mussolini (🇮🇹) rise in power, shift from neutral to appeasement to being fully involved. Neutrality was first threatened during the Spanish Civil War when General Francisco Franco established a military dictatorship there. The US slowly begins aiding its ally Britain more and more through the Lend-Lease Act and Destroyers-for-Bases Deal as it builds up on preparedness. The bombing of Pearl Harbor is the final push for Americans to enter. Fighting happens in both the Atlantic & Pacific theaters until the launching of 2 atomic bombs officially ends the war. At the Yalta Conference the UN is established and peace is made.

Harry S. Truman 💣🫙💰🚫
33rd president, 1945-1953 (VP: Alben Barkley)
Democrat (previously a Missouri senator, became a decisive leader whose honesty and unpretentious style appealed to many citizens, tried to continue with FDR’s New Deal reforms- wanted to be an idealist but ended up being pragmatist because of Congress and reality. Only sends money to Vietnam). “The Buck Stops Here”
Potsdam Conference (1945): British prime minister Clement Attlee, Stalin, and Truman met in Potsdam, Germany and agreed to demand that Japan surrender unconditionally and to hold war-crime trials of Nazi leaders.
WWII ends (1945): Truman decides to drop atomic bombs in Hiroshima and Nagasaki to end the war after Japan failed to come to an unconditional surrender.
Taft Hartley Act (1947): a pro-business law that was originally vetoed by Truman but still passed under Congress. The act outlawed the closed shop (contract requiring workers to join a union before being hired), permitted states to outlaw the union shop (contract requiring workers to join a union after being hired), outlawed secondary boycotts, and gave the president the power to invoke an 80-day cooling off period before a strike could be called.
Truman Doctrine (1947): Truman asked Congress for $400 million dollars in economic and military aid to assist the “free people” of Greece and Turkey against “totalitarian” regimes. (wanted to stop the TOTAL threat of communism in Europe).
Marshall Plan (1947): an extensive program of US economic aid to help European nations revive their economies and strengthen democratic governments. Specifically, $12 billion in aid was approved for distribution to Western European countries. Helped keep communism out there.
Executive Order 9981 (1948): abolished racial discrimination in the US armed forces and eventually led to the end of segregation in the services.
Berlin Airlift (1948-1949): USSR cut off all access by land to the German city of Berlin. So, Truman ordered US planes to fly in supplies to the people of West Berlin for a while. Helped lead to the division of East and West Germany.
NATO (1949): a military defense pact to protect Western Europe and individual allies from attack, consisting of the US, Canada, and 10 other European nations.
Fall of China to Communism (1949): after a civil war broke out again between Chiang Kai-shek (Nationalists) and Mao Zedong (Chinese Communists), the entire mainland of China ended up falling to communism. Truman doesn’t send in troops.
Korean War (1950-1953): Korea had become dominated by communism in the North & conservative nationalism in the South. After North Korea invaded South Korea, the US sent in troops led by General MacArthur. When MacArthur goes too far, China joins in & then peace is made in 1953.
“Fair Deal”: Truman’s ambitious reform program where he urged Congress to enact national health care insurance, federal aid to education, Civil rights legislation, funds for public housing, and a new farm program. However, most New Deal bills were defeated due to the Cold War and Truman’s political conflicts with Congress.

Dwight D. Eisenhower 🌌🚀🆓🏫
34th president, 1953-1961 (VP: Richard Nixon)
Republican (Raised in Kansas, graduate of West Point, plans Operation Torch in Sicily & helps in D-Day during WWII. Sought to reduce federal scope of power, balance budget, & pro-business polices.Uses the TV to gain attention during election. Big fan of delegating and the chain of command. Doesn’t do anything in Vietnam).
22nd Amendment: determined that no person can be elected to the office of the President more than twice, helping to check the power of the executive.
Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka Kansas (1954): overturned the Plesy vs. Ferguson case, Chief Justice Earl Warren ruled that separate facilities are inherently unequal and unconstitutional and that it should end with “all deliberate speed”. Continued to face opposition in the South.
Montgomery Bus Boycott: as a bus in Alabama took on more white passengers, the driver ordered Rosa Parks to give up her seat, but she refused. Led to the boycotting of city buses by Martin Luther King Jr. and others. Attempted before, but required the most upstanding citizens to carry it out in order to be successful.
Little Rock 9 at Central High School: Governor Orval Faubus in Arkansas used the state’s National Guard to prevent 9 African American students from entering the Little Rock Central high School, as ordered by a federal court. Eisenhower ordered troops to protect black students and let them pass.
Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO): to prevent South Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from “falling” to communism, this regional defense pact was assembled, with all nations agreeing to defend each other in case of attack (US, UK, France, Australia, New Zealand, the Philippines, Thailand, and Pakistan).
Suez Crisis: Egypt asked the US for funds to build the Aswan Dam project on the Nile River, the US refused. The USSR agreed to give limited funding to the project and Egypt sought the rest by seizing and nationalizing the Suez canal. Britain, Israel, and France retake the canal under invasion, which is condemned by the US.
Eisenhower Doctrine: extension of the Truman Doctrine to Middle East
Space Race: increases with the launching of Sputnik I and II into orbit around the Earth, US tries to compete by creating NASA and the National Defense and Education Act (costing billions of dollars all together).
Federal Highway Act of 1956: authorized construction of 42,000 miles of interstate highways linking all the nation’s major cities & to help with national defense. Also helped to create jobs and increase the movement of people to the suburbs.
U-2 Incident: Russians shoot down a high-altitude US spy plane over the Soviet Union, exposing a secret US tactic used for obtaining information, ending thaw in the Cold War created during a presidential retreat to Camp David.
Farewell Address: warns US on dependence on “military-industrial complex” and arms race implications.

John F. Kennedy ☮🆕🪧
35th president, 1961-1963 (VP: Lyndon B. Johnson)
Democrat (charismatic, wealthy, and youthful, previously senator of MA. In the first televised debate JFK comes off as vigorous and comfortable winning him the election, was an idealist. Continues pouring in money and sends in 16,000 advisors- Green Berets- to Vietnam to help train Southern Vietnamese army, but assassinated so couldn’t do more).
Alliance for Progress: promoted land reform and economic development in Latin America.
Baker v. Carr (1962): Supreme Court (w/ Chief Justice Earl Warren) established the principle of “one man, one vote”, meaning that election districts would have to be redrawn to provide equal representation for all citizens.
Peace Corps: an organization that recruited young American volunteers to give technical aid to developing countries.
Cuba- Bay of Pigs Invasion (1961) and Cuban Missile Crisis (1962): JFK approved a CIA mission to use Cuban exiles to overthrow Fidel Castro’s regime —> fails. When US planes discovered that Russians were building underground sites in Cuba for the launching if offensive missiles that could reach the US in minutes. Kennedy responded by announcing a naval blockade of Cuba until weapons were removed —> success.
“New Frontier”: Kennedy called for aid to education, federal support of health care, urban renewal, and civil rights, but these domestic programs withered in Congress (most would be passed later on under LBJ).
Civil Rights Movement Continued: at the March on Washington MLK led one of the largest and most successful demonstrations in US history with about 200,000 people taking part in this peaceful protest in support of the civil rights Bill. During this, King gave his impassioned “I Have a Dream” Speech:
Nuclear Test Ban Treaty: Soviet Union, US, and almost 100 other nations signed this to end the testing of nuclear weapons in the atmosphere. This was offset by a new round in the arms race for developing missile and warhead superiority.
Kennedy’s assassination (November 1963): shot by Lee Harvey Oswald in Dallas, TX.

Lyndon B. Johnson 🌻☮🤜⛑🫨
36th president, 1963-1969 (VP: Herbert Humphrey)
Democrat (From TX, previously a school principal in all Hispanic School, WWII Navy Veteran, 1955 Senate Majority Leader, uses the “Johnson Treatment” to get people to agree to what he wanted. Ironic that a southern president created so much progress in civil rights).
Civil Rights Act of 1964: made segregation illegal in all public facilities, including hotels and restaurants, and gave the federal government additional power to enforce school desegregation. Also set up the the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission to end discrimination in employment on the basis of race, religion, sex, or national origin.
Voting Rights Act of 1965: ended literacy tests and provided federal registrars in areas where blacks were kept from voting. Allowed African Americans in the Deep South to vote for the first time since the Reconstruction era.
SNCC/Black Panthers/Malcolm X: The Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee were influenced by Malcolm X, who advocated for self-defense and black nationalism.
“Great Society” aka War on Poverty: following Michael Harrington’s book on Poverty, LBJ launched an “unconditional war on poverty” which implemented various federal programs that addresses civil rights, education, medical care, urban problems, and transportation. The escalation of the Vietnam War would threaten this.
Medicare (1965): provided health insurance for all people 65 and older.
Medicaid (1965): provided funds to states to pay for medical care for the poor and disabled.
Vietnam War- Gulf of Tonkin Resolution (1964) & Tet Offensive (1968): LBJ uses a naval incident in the Gulf of Tonkin off Vietnam’s coast (North Vietnamese gunboats firing at US warships) to secure congressional authorization for US forces to go in to combat. Gives LBJ all the power to protect US interests in Vietnam. LBJ sends in more troops. On the lunar new year (Tet) the Vietcong launched a surprise attack on every provincial capital and American base in South Vietnam (increasing credibility gap). Go to Pairs for peace in 1968, fails. (See LBJ trying to contain Cold War tensions in Asia).
Assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. and Robert F. Kennedy: MLK is murdered in 1968 & Robert F. Kennedy in the same year (by an Arab nationalist).
Counterculture & hippies: various liberal groups began to identify with blacks’ struggle against oppressive controls and laws, including college and university students. Went hand in hand with a new rebellious style of dress, music, & drug use. Wanted to get rid of unresponsive authority, poverty, racism, and war. Sometimes impatience —> violence (seen as self-destructive).

Richard M. Nixon 🦡🌕🌳🗨😬
37th president, 1969-1974 (VP: Spiro Agnew, Gerald Ford)
Republican (From CA, led the House of Un-American Activities Committee- and Alger Hiss, uses Checker Speech to remain VP under Eisenhower. Supports the “Silent Majority” - labels black people as drug addicts & criminals. Uses dirty under-handed tactics often. Wanted to end Vietnam w/ “peace with honor”). Final Report Card Grade: C. Vietnam War ends.
“Imperial Presidency”: suspicious and secretive by nature this title was given to Nixon, partially due to the large credibility gap at the time.
Moon Landing, July 1969: two American astronauts walk on the moon’s surface, represented an astonishing success for the US space program.
Warren Burger becomes Chief Justice (1969): after Chief Justice Earl Warren resigns, Nixon appointed Warren E. Burger of Minnesota to replace him. Burger Court is more conservative but helps w/ abortion & civil rights still.
Woodstock (1969): gathering of thousands of young people in upper NY State (involves drugs).
EPA (1970): the Environmental Protection Agency was a governmental organization that regulated pollution, emissions, and other factors that negatively influence the environment.
26th Amendment (1971): lowers the voting age to 18 (reflecting the growing voice of young people at the time).
Pentagon Papers (1971): NY Times publishes these documents, which turned out to be a secret history documenting the mistakes and deceptions of government policy-makers in dealing with Vietnam.
Visit to China (1972): Nixon travels to Beijing to meet with Mao Zedong, initiating diplomatic exchanges that lead to US recognition of the Communist government. in 1979 & detente.
SALT (Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty) (1972): Nixon uses relationship w/ China to secure Soviet consent to a freeze on the number of ballistic missiles carrying nuclear warheads, again helping with detente.
Kissinger “Shuttle Diplomacy” (1973-1975): Henry Kissinger was Nixon’s national security advisor and secretary of state during his second term. He helped Nixon conduct secret meetings with North Vietnam’s foreign minister to make plans for peace.
Vietnam (Bombing of Cambodia, War Powers Act of 1973): Nixon’s principal objective was to find a way to reduce US involvement in the war while avoiding the appearance of conceding defeat. In 1970, Nixon actually expanded the war by invading Cambodia in an effort to destroy Vietnamese Communist bases in the country. led to 3,500 secret bombing raids → Congress passed the War Powers Act over Nixon’s veto to require presidents to report to Congress within 48 hours after taking military action & that Congress would have to approve any military action that lasted more than 60 days.
Vietnamization, Kent State Massacre (1970): Vietnamization was Nixon’s plan to gradually withdraw troops from Vietnam and give the South Vietnamese the money, weapons, and training to take full control of the war. (becomes part of Nixon Doctrine which declared that in the future Asian allies would receive US support but without the extensive use of US ground forces). 4 students were killed by the National Guard at Kent State in Ohio after protesting this war.
Wounded Knee, South Dakota (1973): seized by followers of AIM (American Indian Movement) & insisted government honor treaty obligations of the past.
Agnew resigns (1973): previously governor of Maryland & Nixon’s VP. Resigns because he had taken bribes as governor.
Watergate Scandal (1973-1974): sprang from a failed burglary attempt at Democratic party headquarters in Washington’s Watergate Hotel during the 1972 election (Committee to Re-Elect the President was revealed to be involved).
Nixon resigns (August 1974): after being forced to turn in videotapes from Watergate, Nixon is impeached for obstruction of justice, abuse of power,, and contempt of Congress. Decides to resign instead.

Gerald Ford 🚦🪔😳
38th president, 1974-1976 (VP: Nelson Rockefeller)
Republican (first appointed-not elected- president and vice president. Ford had served in Congress for years as a representative from Michigan & as the Republican minority leader of the House. Likable & unpretentious, but many questioned his ability to be president).
Nixon pardon: Ford granted Nixon a full and unconditional pardon for any crime that he might have committed, angered many. Accused of making a “corrupt bargain” but Ford explained that he did so to end the nightmare of Watergate rather than continue to prolong it.
OPEC crisis (1974): for supporting Israel in the 1973 Yom Kippur War, the Arab members of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries places an embargo on oil sold to Israel’s supporters. Created an oil shortage in the US, high inflation rates, and worsened the economy.

Jimmy Carter 🌽💥🫣
39th president, 1977-1981 (VP: Walter Mondale)
Democrat (former governor of Georgia, ran as an outsider against corruption in Washington, very informal-walked to inauguration instead of riding in presidential limo, some felt that he relied too heavily on his politically inexperienced advisers).
Panama Canal Treaty (1977): Senate ratified a treaty that would gradually transfer operational control of the Panama Canal from the US to the Panamanians.
Diplomatic Relations w/ Communist China: US ends recognition of the Nationalist Chinese government of Taiwan to help preserve detente with China.
Three Mile Island Incident (1979): a cooling malfunction of nuclear reactors at the Three Mile Island power plant in PA that led to radioactive gas being released. Made Americans less willing to build additional nuclear power plants in the future.
Egypt and Israel Peace Treaty (Camp David Accords) (1979): Carter invites Egyptian President Anwar Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin to Camp David, Maryland. Helped lead to Egypt becoming the first Arab nation to recognize the nation of Israel.
Iran Hostage Crisis (1979): Iranian militants seized the US embassy in Tehran and held more than 50 members of the American staff as prisoners and hostages . Carter approved a rescue mission but it failed. (all happened after Ayatollah Khomeini and Islamic fundamentalists overthrew the shah in Iran).
“Stagflation”: the combination of economic slowdown and high inflation in the US, which continued to grow under Carter. Carter tried to check inflation with measures working to conserve oil energy , but didn’t work and only increased the federal deficit.
Boycott of 1980 Moscow Olympics: After the Soviets invaded Afghanistan in 1979, Carter did this, along with placing an embargo on grain exports and the sale of high technology to the USSR.

Ronald Reagan 💸💰🧱😉
40th president, 1981-1989 (VP: George H. W Bush)
Republican (Well-known movies & TV actor, previously governor of CA, named names during the Red Scare, master of the media, seen as a likable & sensible champion of the average American).
Rise of Conservatism: a loose coalition of economic and political conservatives, religious fundamentalists, and political actions groups became a big force for change in politics. Opposed big government, New Deal liberalism, gun control, feminism, gay rights, welfare, abortion, and drug use. Jerry Falwell founded the Moral Majority, which financed campaigns to unseat liberal members of Congress.
“Tear Down this Wall”: Directed at Gorbachev by Reagan in front of Brandenburg Gate and the Berlin Wall. Symbol of moving towards the end of the Cold War.
Glasnost & Perestroika/ Mikhail Gorbachev: Gorbachev became the new leader of the USSR and attempted to change Soviet domestic politics by introducing reforms to end political political repression of citizens (openness) and restructuring of the Soviet economy by introducing some free-market practices. Helped lead to the end of the Cold War.
Iran-Contra Affair: the major political scandal of Reagan’s 2nd term that involved an arrangement of selling “arms for hostages” w/ Iran and using some of the money to support the contras in Nicaragua.
NRA: The National Rifle Association lobbied for the continued sale of assault weapons.
Sandra Day O’Connor: Reagan nominated her to become the first woman on the Supreme Court. The court scaled back affirmative action in hiring and promotions and limited Roe v. Wade (more conservative).
Strategic Defense Initiative: represented the Reagan administration’s build in military spending to build new military weapons, such as this ambitious plan for building a high-tech system of lasers & particle beams to destroy enemy missiles before they could reach US territory.
Yuppies: young urban professionals who enjoyed higher incomes from a deregulated marketplace. The standard of the middle class declined though, highlighting the increasing income gap between the rich and poor at the time.
Reaganomics: idea that tax cuts and reduced government spending would increase investment by the private sector, which would increase production, jobs, and prosperity. Referred to as “trickle-down” economics because the idea was that with lesser tax rates at higher incomes, those people invest it back into the economy & everyone in the lower-class would be motivated to work harder to achieve this life style. Changed conversation from what gov. programs should be added to what can be cut and by how much (hurt economy).
Reagan Doctrine: concept of stopping communism before it could attack and enslave a country.

George H.W Bush 🔚🙅😤
41st president, 1989-1993 (VP: Dan Quayle)
Republican (Former ambassador to the United Nations & director of the CIA. He promised not to raise taxes “read my lips- no new taxes”. Sought nothing & wanted nothing from Congress, content.). Cold War officially ends.
Americans with Disabilities Act (1990): Prohibited discrimination against citizens with physical & mental disabilities in hiring, transportation, and public accommodation.
Savings and Loan Scandal (1990): the government’s intervention to save weak savings and loans institutions & to pay insured depositors for funds lost in failed ones cost the taxpayers more money. Led to a recession & more taxes.
Persian Gulf War (1991): Iraq’s dictator, Saddam Hussein, invades oil-rich but weak Kuwait. In the massive operation called Desert Storm, Americans were joined by a military units from 28 other nations. Iraq concedes defeat, boosting Bush’s ratings.
Planned Parenthood v. Casey (1992): reaffirmed the decision in Roe v. Wade prohibiting states from disallowing abortion prior to viability.
AIDS Crisis: Bush doesn't do anything to prevent AIDS or try to promote treatment for it.
27th Amendment: prohibited laws varying the compensation of Senators or Representatives until the next election of the House of Representatives is over.

Bill “Slick Willie” Clinton 🌍📈🚢🍔
42nd president, 1993-2001 (VP: Al Gore)
Democrat (Youthful governor of Arkansas, first baby-boomer president. Biggest period of economic growth in the nation’s history occurred during his presidency- created surplus).
“Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell”: Clinton failed to end discrimination against gays in the military and settled for this policy instead. The policy allowed members of the military to be expelled for being gay, or lesbian, but ensured that they would not be routinely asked or expected to share information about their sexual orientation.
FMLA: the Family Medical and Leave Act allows employees to take unpaid leave to recover from giving birth or after a death in a family.
Health Care Reform attempt: Clinton assigned his wife (Hilary Rodham Clinton) to head a task force to propose a plan for universal health care coverage, but it became overly complicated and ended up failing.
Enron: the large corporation falsified stated earnings and profits with the help of accounting companies. Contributed to the economic bubble that would hurt the economy.
Newt Gringrich: the newly elected Speaker of the House who led Republicans in an attack on federal programs and spending outlined in their “Contract with America”. Confrontation between Congress and Bill Clinton led to 2 government shutdowns.
NAFTA (1994): created a free-trade zone (no taxes/tariffs) with Canada and Mexico.
WTO (1994): the World Trade Organization was established to oversee trade agreements, enforce trade rules, and settle disputes.
Oklahoma City Bombing (1995): a truck bomb killed 169 people in a Federal office building in Oklahoma City. Anitgovernment-militant extremist Timothy McVeigh was convicted for the attack and executed for it. This was done following a standoff in Waco, TX between federal agents & Fundamentalists.
Welfare Reform Act (1996): cut $60 billion out of welfare (cash, rental assistance, food stamps), now can only receive government assistance for up to five years.
Clinton Scandals: in Whitewater, the Clintons were accused of having some involvement in an illegal real estate scheme in Arkansas. President Clinton was also accused of lying under oath about his relationship with Monica Lewinsky. He is impeached because of perjury and obstruction of justice (didn’t go through).
Hopwood v. Texas (1996): ruled that the University of Texas School of Law gave preference to African Americans and Mexican Americans, violating the 14th Amendment’s Equal Protection clause.
Gutter v. Bollinger (2003): upheld the affirmative action admissions policy of the University of Michigan Law School.
Globalization: process by which the US and American businesses developed international influence, leads to US joining G-8, the world’s largest industrial powers.
GATT: General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade reduced tariffs, quotas, and other barriers on trade.

George W. Bush 🚨🚔🛡👮
43rd president, 2001-2009 (VP: Dick Cheney)
Republican (went to Yale, recovering alcoholic, born again Christian).
9/11 Attacks —> Department of Homeland Security: coordinate attacks by terrorists in commercial airliners on the twin towers in the World Trade Center in NYC & Pentagon near Washington. The Department of Homeland Security combined more than 20 federal agencies together to help promote internal safety moving forward. (Used Guantanamo Bay detention centers)
Osama bin Laden/ Al-Qaeda: bin Laden was an Islamic extremist who preached jihad (a holy war against the “Jews and Crusaders” to restore Islamic power from Africa and the Middle East through East Asia).
Bush Doctrine: Bush argued that the old polices of containment and deterrence were no longer effective in a world of stateless terrorism. To protect America, Bush argued that the US be justified in using preemptive attacks to stop to acquisition of WMDs by terrorists and by nations that support terrorism. Lead Bush to launch a War on Terror in an ongoing fight against terrorism (at home, in Iraq, and in Afghanistan) at against the Axis of Evil (North Korea, Iran, & Iraq).
Afghanistan/Taliban: following 911, Bush wanted to track down all Al-Qaeda leaders, which the Taliban refused to do. The movement overthrew the government with bombings, special forces, and Afghan troops in the anti-Taliban Northern alliance. Didn't find bin Laden till later on.
Bush v. Gore: the 2000 election came down to the disputed Florida. The Supreme Court Ruled that varying standards using in Florida’s recount violated the Equal-Protection Clause of the 14th Amendment, leading Bush to win the election.
Fundamentalism: a religious belief that maintains the literal truth of a holy book, influenced the growth of the conservative party during Bush and past administrations.
Great Recession: the worst economic downturn in the US since the Great Depression and was brought on by fraudulent mortgage lending (housing bubble), deregulation of the financial industry, and ponzi schemes. Banks failed and gas prices rose.
Hurricane Katrina (August 2005): hit the Gulf Coast hard and flooded New Orleans, FEMA (Federal Emergency Management Agency) failed both to anticipate and respond to the crisis.
No Child Left Behind: aimed to improve student performance and close the gap between well-to-do and poor students in the public schools through testing of all students nationwide, granting students the right to transfer to better schools, funding stronger reading programs, and training high-quality teachers.
Powell Doctrine: General Collin Powell was Bush’s Secretary of State and the first African American to hold the hob.
Climate Change: Bush supported and signed into law some provisions that helped lower national carbon dioxide emissions.
Bush Tax Cuts: Congress passes a $1.35 trillion dollar tax cut and gives all tax payers an immediate tax rebate. Rather than spend the money people save it, contributing to a decline in the economy.

Barack Obama 👰💒😨⛑
44th president, 2009-2017 (VP: Joe Biden)
Democrat (Junior senator from Illinois, charismatic, became the first African American president, came in during a bad economy & 2 wars in-progress. Tried using drones but some hit homes/hospital, caused some to consider him a war criminal).
Affordable Care Act: aimed to extend affordable healthcare insurance to an additional 25 million Americans through combinations of subsides, mandates, insurance exchanges, and expansion of Medicaid while introducing medical and insurance reforms to control health care costs.
ISIL: in Syria and Iraq the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (also called ISIS) vowed to create a worldwide regime under Islamic law. Led more soldiers being sent to Iraq.
Citizens United (2010): The Supreme Court ruled in this case that corporations were “legal persons” and had the same rights as individuals to buy ads to influence political elections.
Dodd-Frank Act (2010): designed to improve regulations of banking and investment firms to protect taxpayers from future bailouts of “too big to fail” businesses.
Mass Shootings: the mass shooting of 26 children and teachers in CN and the murder of 9 African Americans in a SC church sparked debate over gun rights. The Boston Marathon Bombing (2013) continued to raise questions over gun control and continue to grow fear over terrorism. (Opposition from gun advocates made change difficult for Obama).
Tea Party: a loosely united conservative and libertarian movement that opposed the growing national debt and “Obamacare”. Mostly focused on debt and health care, but some in the group also targeted expanding gun rights, outlawing abortions, & preventing undocumented immigration.
Same Sex Marriage: during Obama’s Presidency Congress repeals “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” and same-sex marriage became protected under the 14th Amendment.
US v. Windsor (2013): ruled that the federal government can’t discriminate against married lesbian and gay couples when determining federal benefits and protections.