(BIO 103) Lesson 2: Central Dogma of Biology
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Transcription
The synthesis of RNA from DNA template
No Thymine (T) in RNA
Thymine is replaced with Uracil (U) in RNA
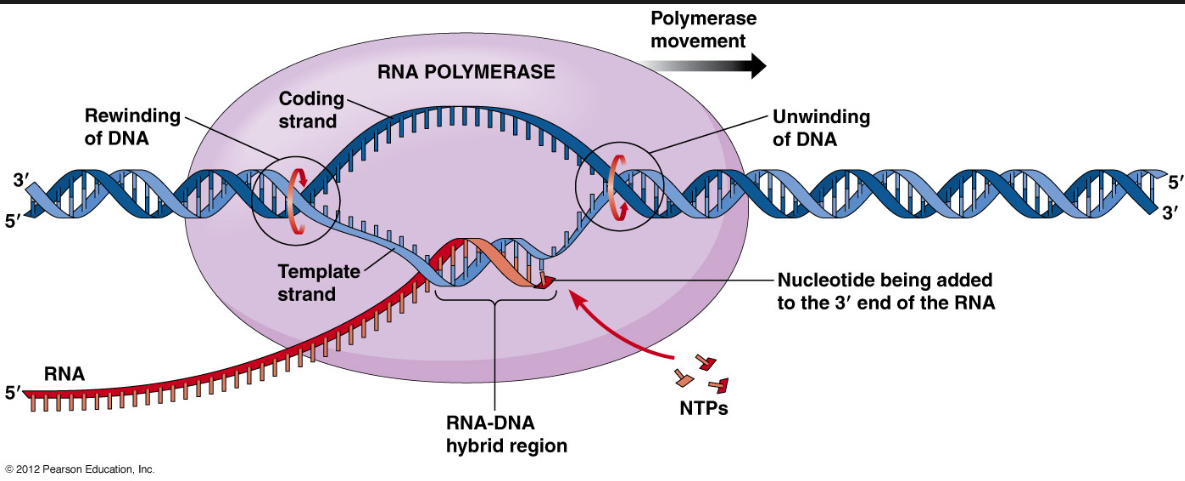
Where does transcription occur?
In the nucleus
Translation
The synthesis of polypeptides made from the mRNA
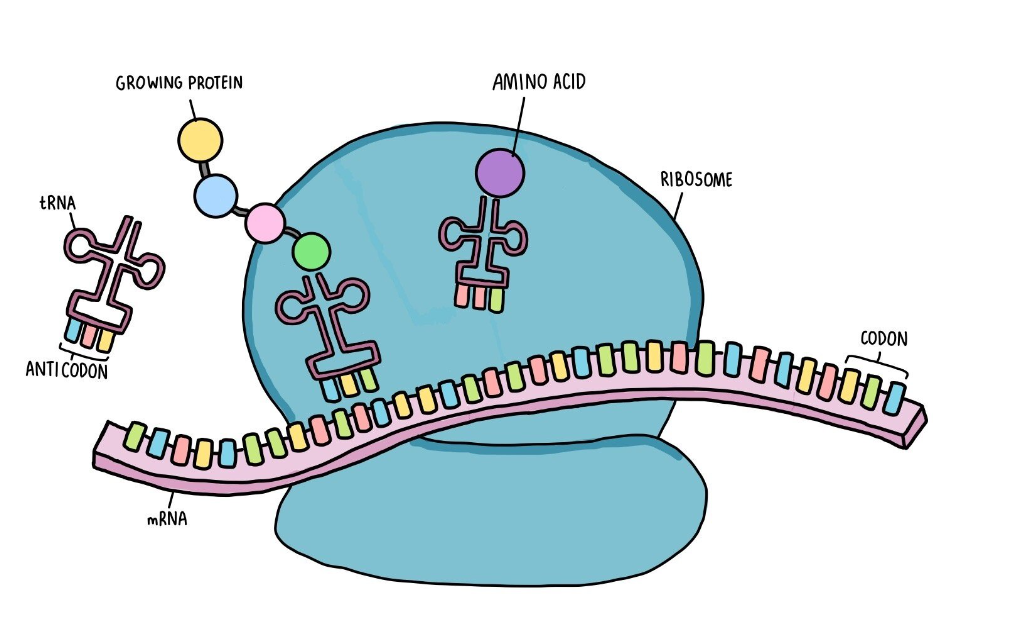
Where does translation occur?
In the cytoplasm by the ribosomes
Steps of gene expression
DNA —> mRNA—>Protien
DNA undergoes transcription to be RNA
The RNA then undergoes RNA processing (occurs in the nucleus)
Where a spliceosome splices (removing from RNA) the introns (in the nucleus)
Exons are kept in this process, causing the RNA to become mRNA
The mRNA undergoes translation to synthesis polypeptides (in the cytoplasm)
Polypeptide eventually becomes mature.
What makes a mRNA mature?
At the 5’ end: there is a 5’-methlyated cap
At the 3’ end: there is 3’ poly A tail
this helps the mRNA to get through membranes and to help with stability.
What is a polypeptide?
A string of amino acids in the order given by DNA and mRNA nucleotide sequences.
What makes a protein (polypeptide) mature?
Folded properly (dictated by primary sequence of amino acids and enviroment)
Amino acids may be +/-
Sugars/chem groups may be added
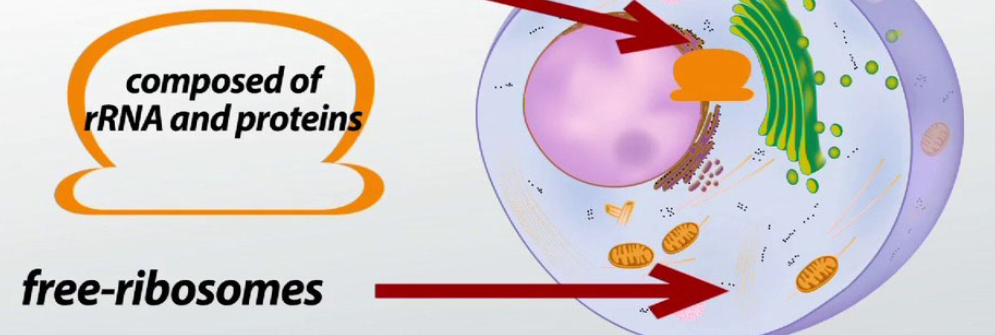
Where do proteins made by “free ribosomes-(completed peptide chains in cytosol)” go?
Remains in cytosol
Nucleus via nuclear pore
Peroxisome
Mitochondria (or chloroplasts)
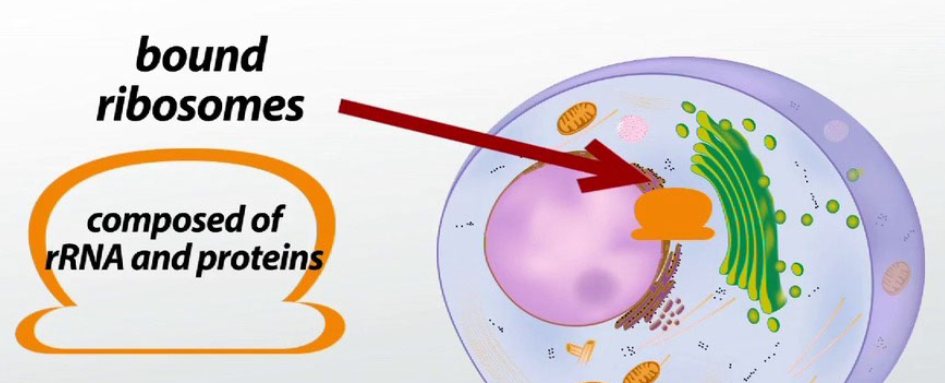
Where do proteins made by “bound ribosomes-(attached to RER (rough endoplasmic reticulum)/completed peptide chains in ER)” go?
Remains in ER
Goes to the Golgi apparatus and either:
Secretory Vesicle (leaves cell)
Plasma Membrane (remains attached to cell)
Lysosome
How does a protein of only amino acids “get told” to go to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and not somewhere else?
The first portion of the elongating polypeptide chain (signal sequence occurs at the N-terminus of the polypeptide). Typical signal sequence about 15 amino acid long
Signal peptide- signal reposition protein (SRP)
What kind of structure does Hemoglobin have?
quaternary structure (there are more than two polypeptides that makes up its structure)
Its quaternary structure is why it can carry O2
Has 4 polypeptides or “subunits”, each subunit hold a hemoglobin group that has a high affinity for binding O2
Normal adult hemoglobin has what genes/subunits?
Has Alpha gene-Alpha subunits and Beta Gene-Beta subunits.
Fetal hemoglobin has what gene/subunits?
Has Alpha gene-Alpha subunits and Gamma Gene-Gamma subunits.
How does the body switch from fetal to adult hemoglobin?
After birth, Bcl11A protiend blocks transcription of Gamma gene
What mutation is in Sickle Cell Disease?
There is a mutation (DNA change) in the Beta gene causing a change in shape.