CUMULATIVE
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
Emergency assessment
ABCDE
Airway
Breathing
Circulation
Disability (LOC, pupils, movementx)
Exposure
comprehensive assessment
health hx + physical assess
head-to-toe
upon admission
focused assessment
more in depth
most important technique for infection prevention
hand hygiene
standard precautions
hand hygiene
PPE w/ infectious material
disinfect material/ instruments
sharp safety
transmission precaution
transmission precaution
source control
social distancing
resp hygiene/ cough tech
appropriate patient placement
standard precaution goal
all waste + contact is potentially infectous
prevent transmission w/ body fluid contact + blood born
wash hands when
visibly soiled
after caring with person w/ infectious diarrhea
C.diff / B. anthracis
inspection
general survey
physical characteristics, behavior, odors
electronic record advantages
enter data quickly
interpersonal data input database for interpersonal communication
legible and time dated. helps identify trends
automated clinical surveillance tools (alerts to data that indicates problems)
high risk errors documentation
inadequate admission assess
failing to record
pertinent health or drug information
changes in pt condition
prior treatment event
failure to notify HCP
failure to follow policy
temperature
36.5-37
>39.5 <35!!!
pulse, resp, o2
60-100; 10-12; 92%
low BP; norm is <120/80
<90 SBP
nociplastic pain
pain w/o identifiable cause
nervous system modification can lead to a phenomenon called ________________________, by which peripheral nociceptors are sensitized to neuropathic pain stimuli.
peripheral sensitization
Result of inflammatory process that creates hypersensitivity to touch or pressure
Peripheral sensitization:
Enhanced response to pain stimulus produced by prolonged pain production
Windup:
(FLACC) scale
Face, Legs, Activity, Cry, Consolability
2m -7y
Central sensitization:
Excitatory process involving spinal nerves produced by continued pain stimuli that can persist even after peripheral stimulation is no longer present
Untreated or undertreated acute pain may lead to chronic pain syndromes, ____________
such as complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS),
Continued painful assault on the peripheral nerves results in transfer of the pain stimulus to the central nervous system.
CRPS
visceral pain
crampy or gnawing
somatic pain
sharp
cutaneous
burning or sharp, such as with a partial-thickness burn
numeric pain scale
0/10/ NPI
7y<
Visual analog scale
line with NPI
cognitive alert but verbally impaired
Mc GIll Pain Questionnaire
verbal descriptors, VAS, present pain intensity rating w/ numbers and words
Brief pain inventory
chronic pain
worst/least pain in past 24, average pain, pain right now
body diagram
functional assess w/ ADL + mood and social
efficacy of pain meds
Pain, Enjoyment, and General activity (PEG)
BPI but shorter
pain on average
how many times pain has interfered with life/ general activity
clinically aligned pain assess (CAPA)
comfort
change in pain
pain control
functioning (ADL)
sleep
FACES
3y<
language communication problem
cal/g
fat 9cal/ g ; protein + carb: 4cal/g
Of the 22 required amino acids, the body can manufacture __ of them from nonprotein dietary sources (nonessential proteins). __ essential amino acids must be obtained through dietary sources.
14; 8
phospholipid
emulsifiers
transport fat soluble across membrane
Vit B (folate)
metabolism + cell synthesis
Vit B12
DNA synthesis, RBC, myelin
vit C
iron absorption
trust vs mistrust
stage I: infant
when uncomfy, caregiver helps
self-efficacy
autonomy vs shame and doubt
II: toddlers
potty train; will learn how to become independent and caregivers will help them distinguish from what is right from wrong
initiative vs guilt
III: preschooler
self-efficancy; actively making plans, setting goals, and performing tasks to feel important. If this is not met, child will have low-self esteem
industry vs inferiority
stage IV: school age
preparing the child to become a worker (integrate to society);
the more time in this stage, the less influence parents have.
School and teachers culture( goals, failures) influence the outcome of child. If not met, child will feel inadequate
identity vs role confusion
stage V: adolescent
group identity, how they appeal to others.
identity and occupational exploration
intimacy vs isolation
stage VI: early adult
fusing their identity to others; not only sexual unions, but close friendships; if not, isolation
generative vs stagnation
stage VII: middle adult
focusing on guiding the next generation; if they have nothing to offer, the stagnation occurs
ego integrity vs despair
stage VIII: late adult
if come to term with their life choices and if not it can lead to despair
Geriatric depression scale
life satisfaction, drop of interests, if happy/mood, memory problems,
National Standards for Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services (CLAS) in Health Care
principle standard: care that correlates w/ diverse needs for all
governance, leadership, workforce:
advance government and leadership that promote CLAS
educate to promote CLAS
communication/ language assist
language assist for no cost
inform of language services
no use of minors as interpreters
easy to understand media in commonly used languages
engagement, continuous improvement, accountability
establish CLAS goals, ongoing assessments, collect data, plan to implement services, and partner w/ community, communicate results to public
chronic hypoxia
clubbing of nails
ABCDE (skin)
Asymmetry
Border irregular
color variety
diameter >6mm
evolution
acne
inflammation of sebaceous glands
comedones, papule, pustule, cyst
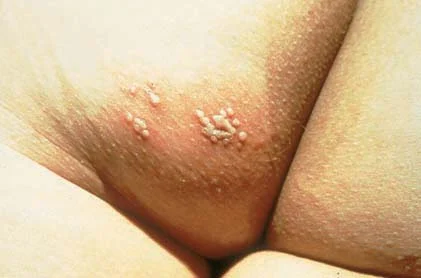
wartz
flesh colored warts
by viruses
rough w/o scale
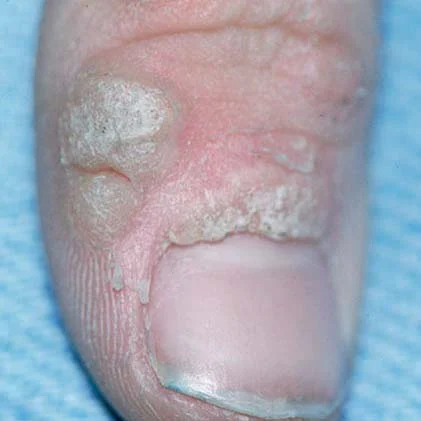
cellulitis
bacterial infection of deep skin tissue
swelling, redness, warmth, tender/pain
impetigo
Staphy aureus or group A strep
vesicle or bullae → honey- colored crust
herpes simplex
cold sores
group vesicles on erythematous base
mouth, genital, and skin
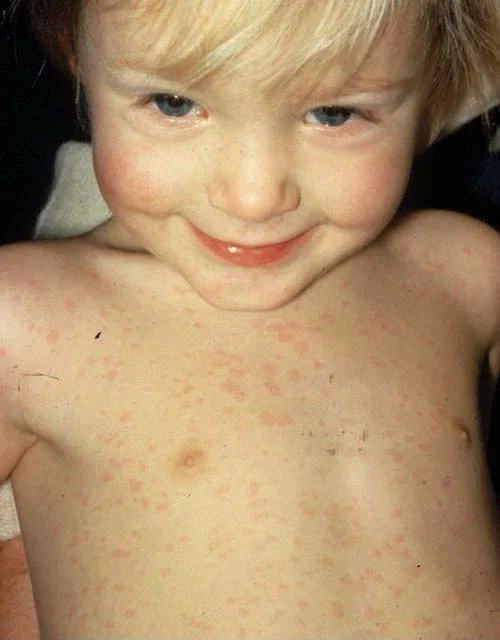
measles
rubeola (virus)
pinkish, erythematous macules and papules from face to caudal spread
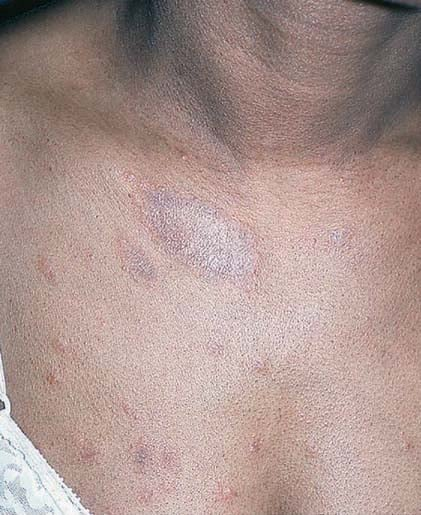
pityriasis rosea
viral herald patch: large oval hyperpigmented lesion w/ fine scale
Christmas tree pattern
rubella
german measles (vaccine)
pink macular and papular rash
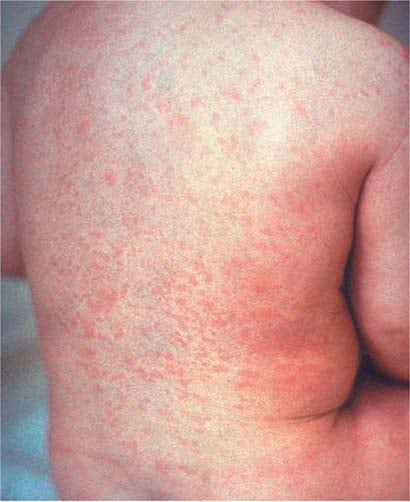
roseola
viral
rash appears as fever resolves
discrete macules and papules
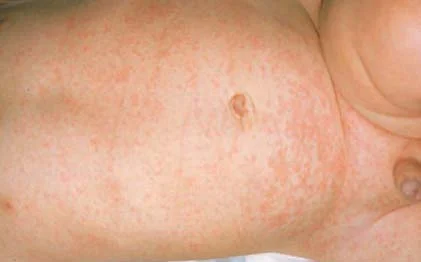
candida
fungus in skin folds
satellite pustules with erythematous macules
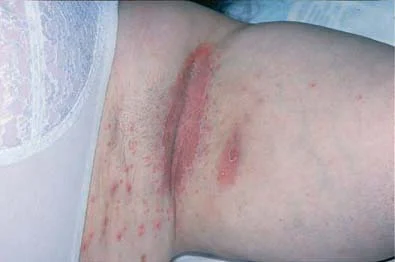
tinea corporis
ringworm
erythema, pruritic, annular lesion w/ raised border and central clearing
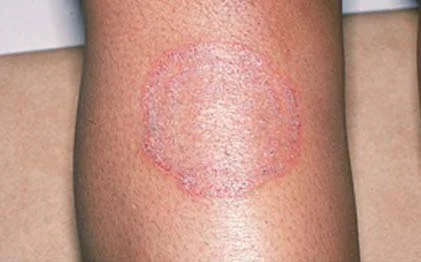
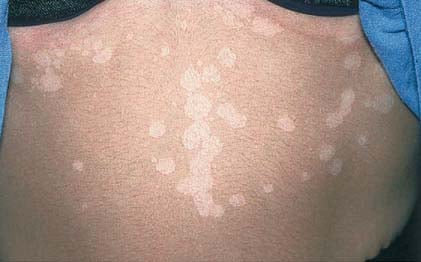
tinea versicolor
by normal skin flora
hypopigmented patchy lesions
upper chest/ back, proximal extremities
_________ are not usually palpable (neck)
thyroid/ parathyroid
unilateral bulging in thryoid
goiter, cyst, or tumor
anterior approach
tilt head slightly back
located thyroid and cricoid cartilage
thyroid crisis
hypermetabolism: tachycardia/pnea, n/v, diarrhea, abd pain, hyperkinesis, fever
hyperthyroid
weight loss, anxiety, palpitation, tachycard, heat intolerance, diaphoresis, muscle weakness
brisk reflex, moist/warm skin
→ thyroid storm
hypothyroid
fatigue, anorexia, weight gain, coarse/brittle hair, cold intolerance
slow speech, cold/dry skin, bradycard, delayed reflex
ptosis
drooping of eyelid
stroke
eye teaching
eye exam Q2y (DM Q1y)
impact of screen time on vision
protective eyewear in occupational
sunlight exposure → cataracts/ conjunctival disorder (sunglasses)
DM control → diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, glaucoma
The ______ refers to what in the environment is visible when the eye fixates on a stationary object.
visual field
static visual field
gross differences in all 4 quadrants
ask them to look at your eyes and put fingers in each quadrant
kinetic visual fields
gross peripheral boundaries
move fingers to periphery until pt becomes aware of target
cataract s/s
halos in eyes
diabetic retinopathy s/s
blind spots
macular degeneration s/s
tunneling in visual field
glaucoma s/s
loss of periphery
CN II
optic nerve: visual acuity/ field
CN III
oculomotor: EOMs, PERRLA, eyelid
cardinal gaze
CN IV
trochlear
cardinal fields of gaze
CN VI
abducens: laterally
cardinal fields of gaze
CN I
olfactory
CN V
trigeminal
chewing + face sensation
clench teeth and ask for pain (trigeminal neuroglia)
CN VII
facial
facial expression
CN VIII
Vestibulocochlear
Hearing + balence
CN IX
Glossopharyngeal
motor
gagging and swallowing
CN X
Vagus
pharynx+ larynx sensation + Swallowing
CN XI
accessory
shoulder shrugging, head rotation
CN XII
Hypoglossal
tongue movement and speech
ear function
hearing
vestibular function: proprioception and equilibrium
conductive hearing loss
when external and middle ear is disrupted
BC x2 AC
cholesteatoma
abnormal growth of cells in middle ear
sensorineural hearing loss
SNHL
inner ear to auditory cortex
presbycusis
sensorineural loss from gradual degeneration of nerves and sensory hair cells of Corti
tinnitus
ringing w/o external sound
meriere disease
vertigo w/ severe n/v and hearing loss
24hr of exacerbations w/ period of remission
otalgia
otitis externa/media
severe pain → relief + drainage = rupture TM
otosclerosis
slow fusion of ossicles
ear infection prevention
cleaning external ear
risk factors:
cigarette smoke
propping baby bottles
bottle feeding in supine position
day care
epitaxis
nose bleed
most common in kiesselbach plexus