Carbonhydrates and isomers
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Carbohydrate
Aldehyde or ketone derivatives of polyhydric (multiple OH groups) alcohols. [C.H2O]n.
Monosaccharides
Disaccharide
Oligosaccharide
Polysaccharide
Monosaccharide
Carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler forms = Basic units.
Water soluble white crystalline solids that have sweet taste.
Trioses
Tetroses
Pentoses
Hexoses
Heptoses
Disaccharide
C12H22O11 (C12H24O12 - H2O)
Two monosaccharide units linked by glycosidic linkage
Difference between Maltose [a(1,4) glycosidic bond] and cellobiose [B(1,4) glycosidic bond]
Maltese = D-glucose + D-glucose a(1-4) glycosidic bonds
Sucrose = D-glucose + D-fructose
Lactose = D-glucose + D-galactose
Cellobiose = D-glucose + D-glucose B(1-4) glycosidic bonds
Oligosaccharide
Carbohydrates that can be hydrolyzed into 3-20 of the same/different monosaccharide units
Fructooligosaccharide (FOS) & Galactooligosaccharides (GOS)
Polysaccharide
Carbohydrates which can be hydrolyzed into more than 20 monosaccharides units
Molecular weight ranges from 1000-150000
(C6H10O5)n
Structural function and storage form of energy
Examples: Starch, glycogen, Cellulose, Chitin, Glycoproteins, Glycolipids, Peptidoglycans, Glycosaminoglycans, Proteo-glycans
Isomer
Molecule that consists of same number and kinds of atoms but differ in their structure or spatial configurations
Structural
Optical (stereo)
Structural isomer
Compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in structural formula
Aldose ketose isomerism
Pyranose-Furanose Ring isomerism
Aldose-Ketose isomerism
When one aldose sugar and one ketose sugar are the same in molecular formula but differ in structural formula
D-Glyceraldehyde/Dihydroxyacetone
D-Glucose/D-fructose
Pyranose-Furanose isomerism
When Pyranose ring and a Furanose ring of carbohydrates are the same in molecular formula but differ in structural formula
D-Glucose (pyranose) & D-Fructose (Furanose)
Haworth projections : open chain forms of aldohexose and ketohexose and soke other sugars react internally to form cyclic hemiacetals and hemiketals
Hemiacetal and Hemiketal formation
Characteristic reaction between aldehydes and alcohols
Characteristic reaction between ketone and alcohol
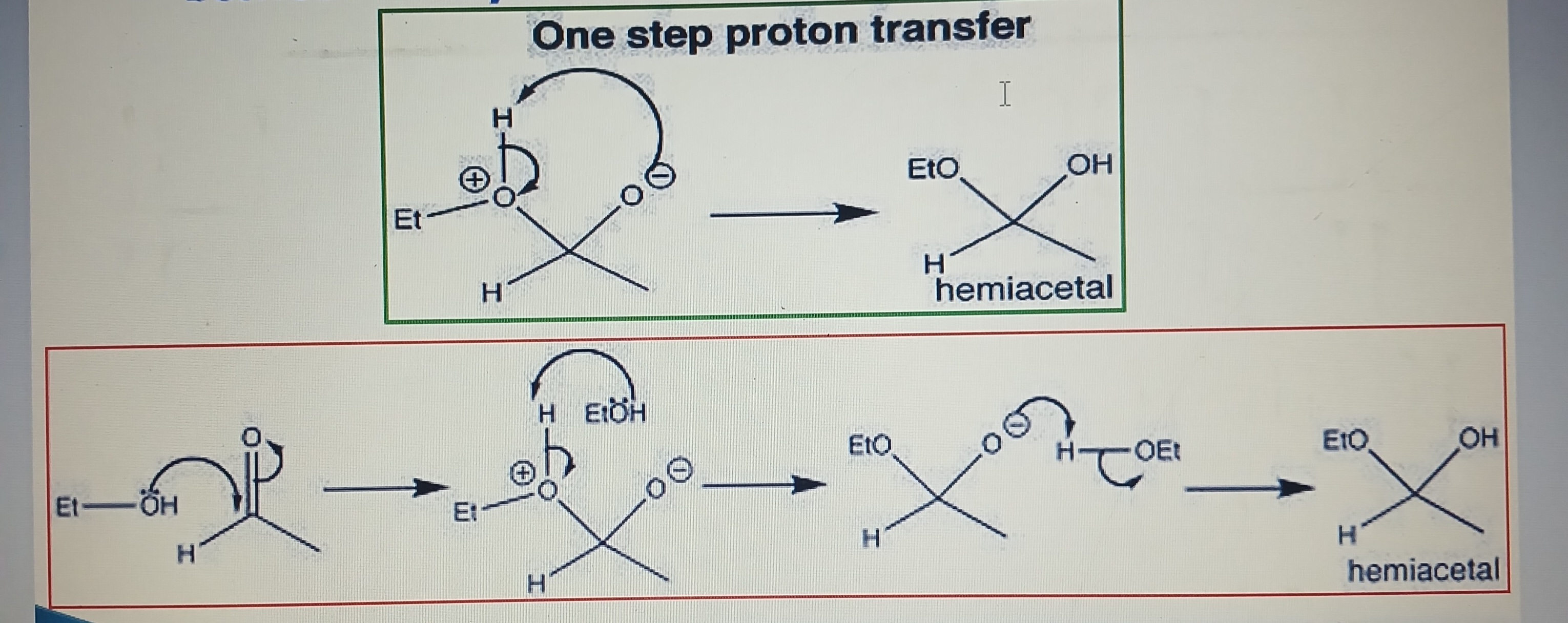
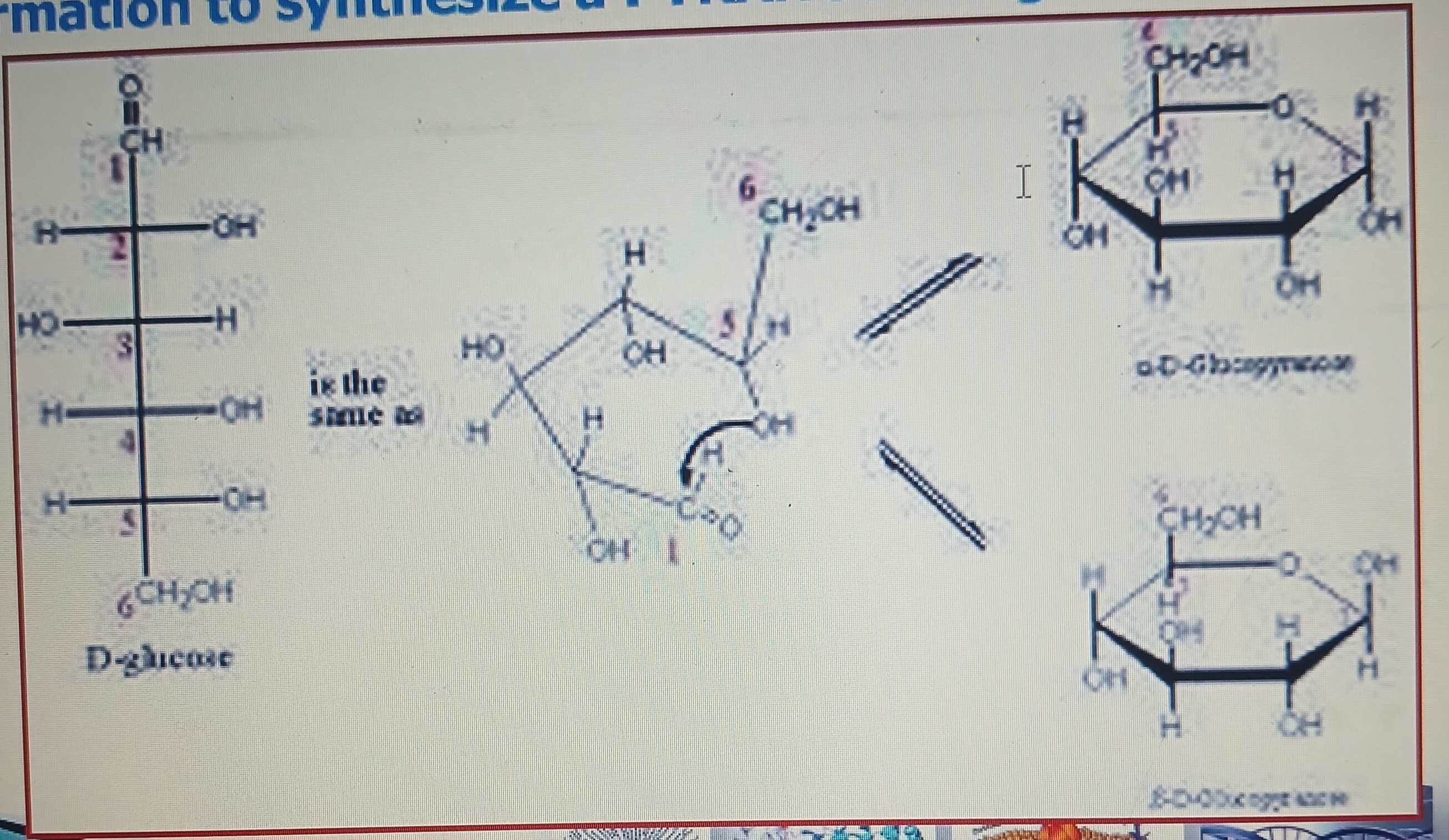
Pyranose ring formation
Aldehyde group (-CHO) at C1 and hydroxyl (-OH) at C5 of a glucose molecule combined together
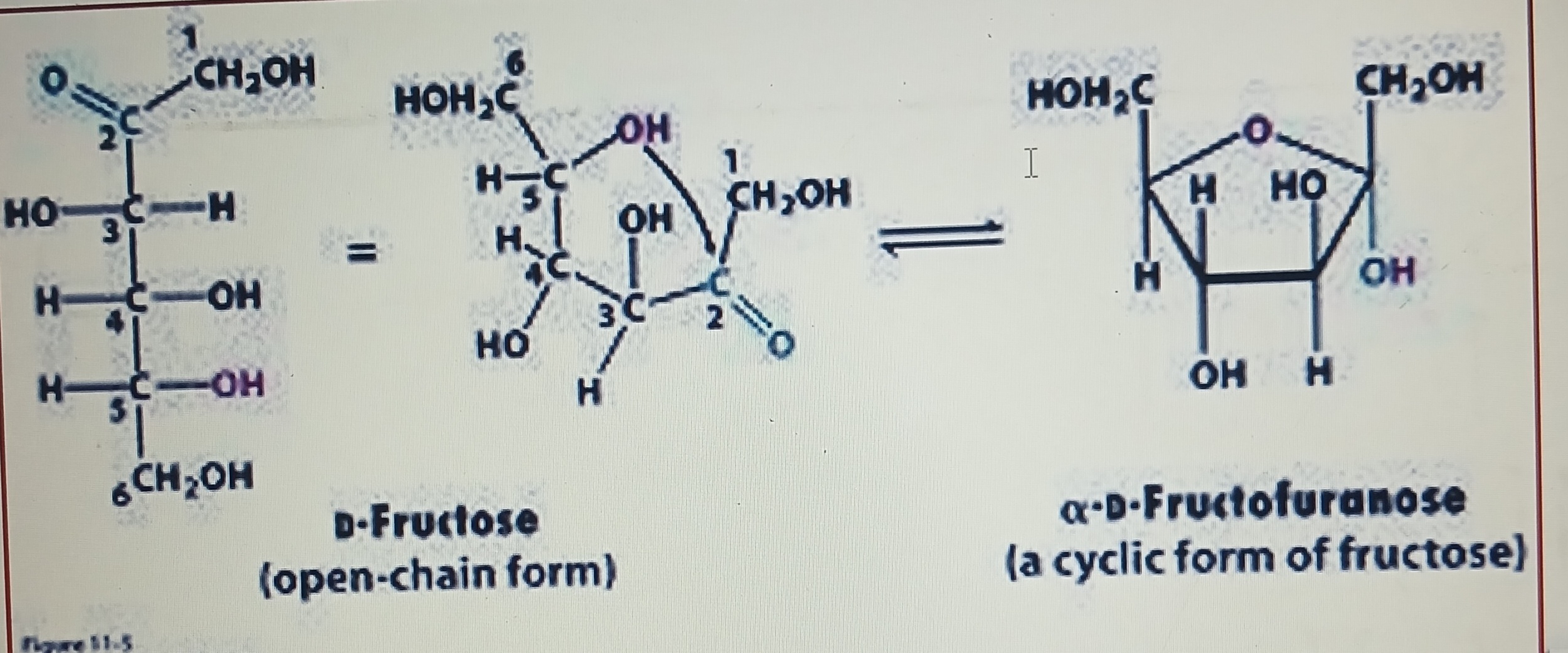
Hemiketal formation
Ketone group at C2 and hydroxyl group at C5 of a fructose molecule combined together to synthesize a furanose ring
Optical/stereo isomer
Compounds that have the same structural formula but different spatial configuration
Form due to presence of asymmetric/ chiral center / chiral carbon atom
Asymmetric/ chiral center
Carbon with 4 different atoms/groups of atoms attached to it
Includes all monosaccharide except dihydroxy-acetone
Think D&L
Enantiomers
Two optical (stereo) isomers are mirror images to each other
D&L
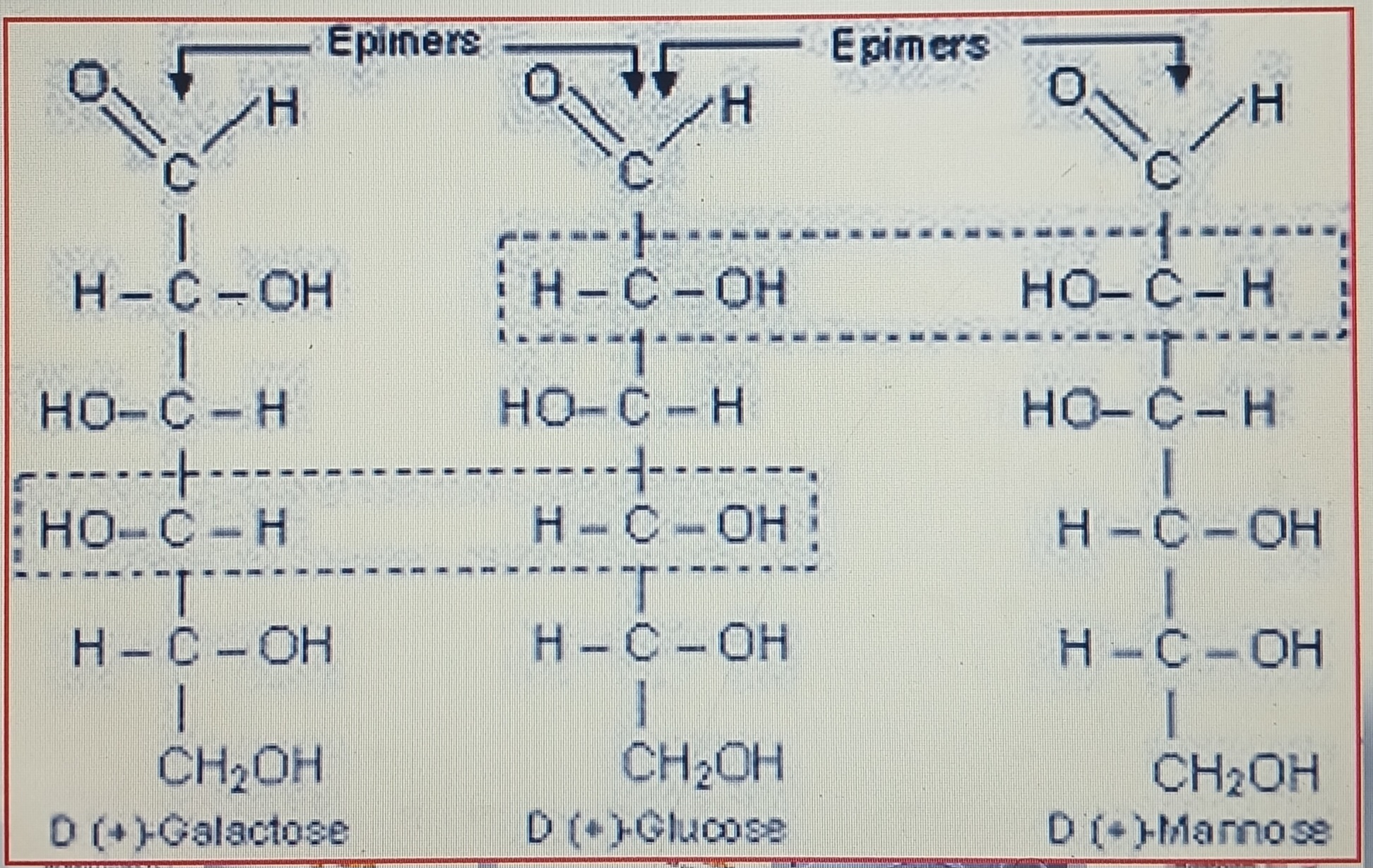
Epimers
Isomers that differ as a result of variation in configuration of the H or OH on a single C atom of a hexose molecule
Glucose: Mannose & Galactose (diastereomers)
Anomers
When monosaccharide cyclases, an asymmetric center is formed. Two different structures are formed based on asymmetric carbon
a-D glucose (OH group is below plane of ring)
Ɓ-D glucose (OH group is above plane of ring)
Anomeric carbon
When 2 oxygen atoms are bonded to a single carbon atom in a ring structure compound
Optical isomers/activity
The presence of asymmetric carbon confers the optical activity on the compound. Optical isomers are also mirror images to each other hence their enantiomers, these compounds have similar properties (same boiling points, same melting points, same solubility) but different optical activity. They names Dextrorotatory and Levorotatory
Dextrorotatory
D(+): when an optically active compound rotates the plane of polarized light clockwise
Levorotatory
L(-): when optically active compound rotates the plane of polarized light anticlockwise
Specific rotation
A specific amount of angle rotates by the plane of polarize light for a particular compound
Standard measure degree of the compound which is D(+) and L(-)
Two enantiomers have equal and opposite specific rotation a-D glucose (+112°) and Ɓ-D glucose (+19°). D-bromobutane (+23.1°) and L-bromobutane (-23.1°)
Mutarotation
The gradual change of optical rotation of 2 compounds which continues until equilibrium is reached.
From the values of specific rotation and mutarotation the composition of the a- and Ɓ form of a given compound in a mixture can be calculated. Sometimes compounds can be separated based on physical features
Maltose
D-Glucose+D-Glucose - a(1,4) bonds
Formed by enzyme action (diastase in plants; ptyalin in animals) hydolysis of starch. Hydrolyzed by maltase. The 2 a-D-glucopyranose components are joined head-to-tail through C1 and C4 with a-1-4-glucosidic linkage.
Reducing sugar
Lactose
Hydrolyzed by dilute mineral acid/ lactase. Monosaccharide units (Glucose+Galactose) joined by a Ɓ-1,4-glycodic linkage.
(a form = infant food and penicillin)
Equilibrium mixture of a- and Ɓ- form = +55°
Cellobiose
Stereo isomer of maltose, Glucose+Glucose - B(1,4) bonds. 2 glucose units joined by Ɓ-1,4-glycosidic bond.
Reducing sugar, mutarotation
Sucrose
C1 of a-D-glucose and OH group of C2 of Ɓ-D-fructose linked by a-1,2-glycosidic bond which can be hydrolyzed by mineral acids or sucrase.
Mutarotation: none; 1,2-glycosidic bond cannot exist in a/Ɓ configuration or in the open chain form (exist only as a solid or in solution)
Non-reducing: potential aldehyde group of glucose and potential keto group of fructose are involved in the 1,2-glycosidic linkage in sucrose
Homopolysaccharide
1 type of monosaccharide unit make up polysacharride
Storage: starch glycogen
Structural: cellulose and chitin
Starch
Made up of Glucose
Amylase (98%): linear polymer of 100-1000 glucose units. Non reducing & reducing ends. Blue in iodine
Amylopectin (2%): highly branched polymer (24-30 glucose units) Purple/red in iodine. Each branch point has a(1,6) glycosidic linkage. Helix form interrupt the colour formation with iodine
Potential aldehyde group of glucose and potential keto group of fructose are involved in 1,2 glycosidic linkage i
Glycogen
Highly branched polysacchiride of glucose linked by a(1,4) and a(1,6) linkages (8-12 units). Non reducing.
Cellulose
Linear homopolysaccharide of D-glucose linked by Ɓ(1-4) glycosidic bonds. Consists of 300-15000 units. Structure of parallel chains linked by H2 bonds lying side by side to form stable fibrous network of intra/interchains hydrogen bonds. Insoluble in water.
Ɓ(1,4) glycosidic bonds resistant to hydrolysis. Exceptions: ruminants- bacteria inside rumen secrete cellulase, a Ɓ-glucosidase, that catalyzed the hydrolysis of cellulose. Termites, digestive tract has parasites that secrete cellulase.
Chitin
Linear homopolysaccharide of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues linked by Ɓ(1-4) linkages.
Also forms extended fibres
Heteropolysaccharide
2 or more different types of monosaccharides present in polysaccharides
Glycoproteins
Oligo/polysaccharide covalently joined to proteins. Carbohydrate part = 80% of total mass, can contain up to 4 branches and O linked to serine or threonine but N linked to asparagine
Glycolipids
Oligo/short chain polysaccharide convalently joined to lipids. Linear polymers lie side by side in bacterial cell wall and in human plasma (5%)
Peptidoglycans
Polysaccharide linked to small peptide. Rigid component of bacterial cell wall.
Alternating Ɓ(1-4) linkage between N-Acetyl-Glucose (GlcNAc) and N-Acetyl-Muramic acid (MurNAc). Linear polymers lie side by side in cell wall and cross linked by short peptides.
Degraded by lysozyme which hydrolyses glycosidic bond between monosaccharides and kills bacteria (present in tears)
Proteoglycan and glycosaminoglycans
Make up extracellular matrix (interlocking network of heteropolysaccharides and fibrous proteins). Acts as porous pathway for diffusion of nutrients and O2 to individual cell
Glycosaminoglycans: linear polymer composed of repeating disaccharides
Hyaluronic acid: alternating units of D-glucoronic acid and N-acetyl glucosamine. Hyaluronidase make tissue more susceptible to bacterial invasion and infection (similar enzyme in sperm)