transfusion medicine
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What determines if patient needs blood transfusion
CS of reduced oxygen provision to tissues (tachycardia, tachypnoea, lethargy, weakness)
If normovolaemic
What % range for deciding transfusion - cats
10-15%
What % range for deciding transfusion - Dogs
15-20%
What to use in blood loss to replace
Whole blood, packed red cells (+fluid therapy)
What to use in haemolysis to replace
Packed red cells
What to use in coagulopathy to replace
Fresh frozen plasma (poisoning), regular plasma, cryoprecipitate (vWD)
Contents of blood products - whole blood
55-65% plasma
35-45% red cells
Contents of blood products - Packed red cells
20-40% Plasma
60-80% red cells
Contents of blood products - Fresh frozen plasma (frozen within 6hrs collection)
99.9% plasma
Clotting factors (I-XII), vWF
Contents of blood products - Frozen plasma (frozen >6hrs since collection)
99.9% plasma
Clotting factors (II, VII, IX, X)
How long can most practices store whole blood
<21d
Where to get canine blood products from + advice + equipment + IDEXX cross matching service
UK pet blood bank (Leicestershire)
What blood type to give if can’t determine patient dog’s (cats must have correct type)
DEA 1 negative
Plasma blood type to give
DEA 1 negative
Which blood types can be given to DEA 1 + dogs without reaction (no naturally occurring ab to RBC)
DEA1+, DEA1-
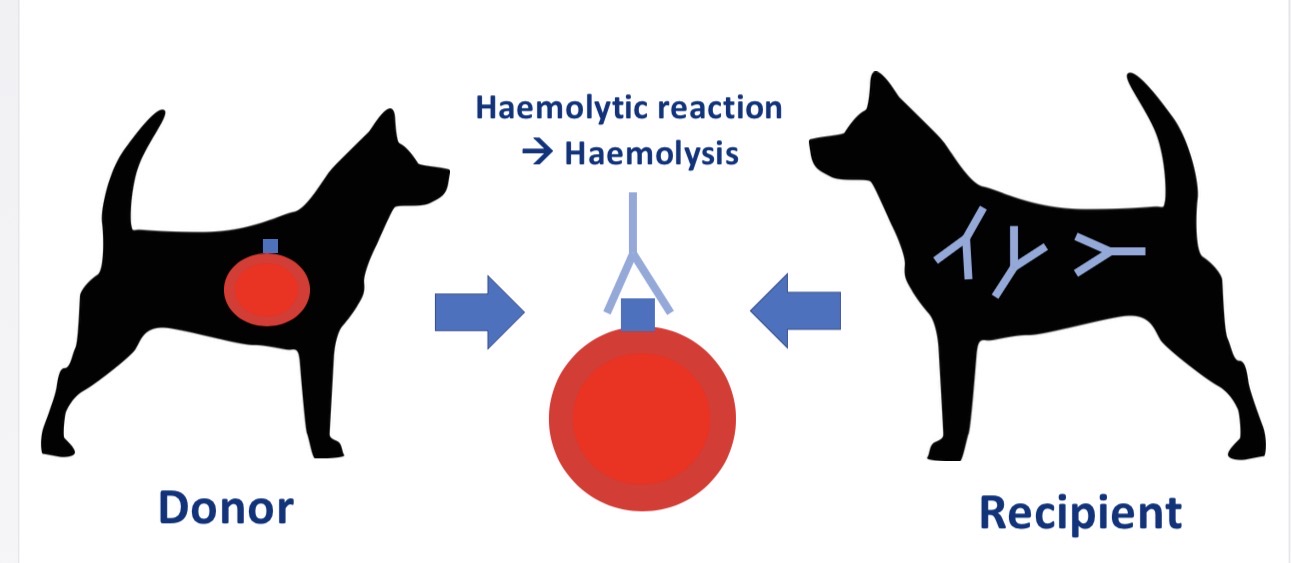
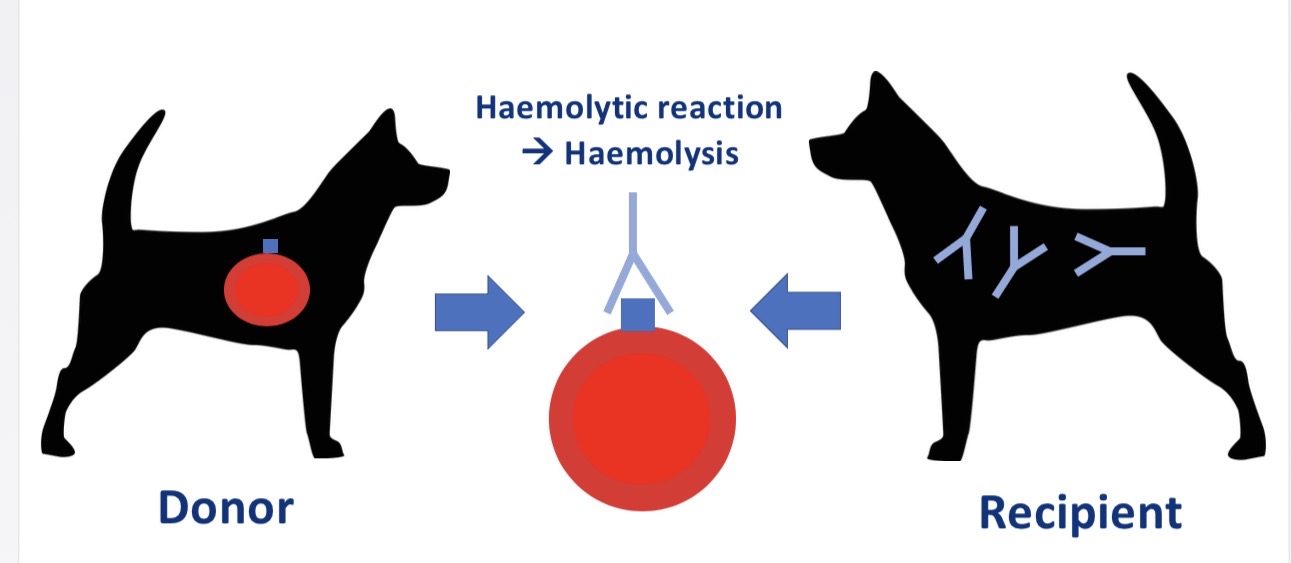
Why does giving DEA 1 - dog DEA 1 + blood produce delayed reaction
No naturally occurring ab (occur from exposure)
Acute haemolytic reaction in subsequent transfusion
Blood type system in dogs
Dog erythrocyte antigen system (DEA)
Blood type system in cats
A/B system
A dominant to B
AB = polygenic
Why is it so important to give type matched blood to cats
Naturally occurring auto antibodies
Fatal acute haemolytic reactions from >1ml incompatible blood
Cat breeds more likely to have type B blood (can’t be given type A blood or severe acute haemolytic reaction)
Devon Rex, British blue
What happens if you give B cats type A blood
BAD - severe acute haemolytic reaction
Strong antibodies
What happens if you give A cats type B blood
Not As Bad - milder delayed haemolytic reaction
Weaker antibodies
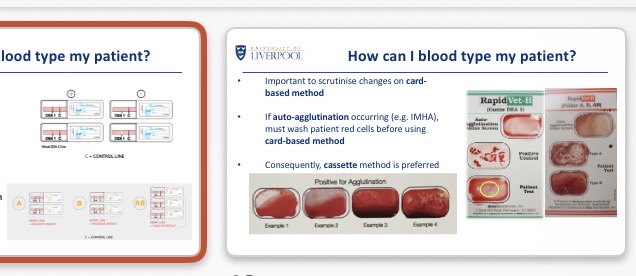
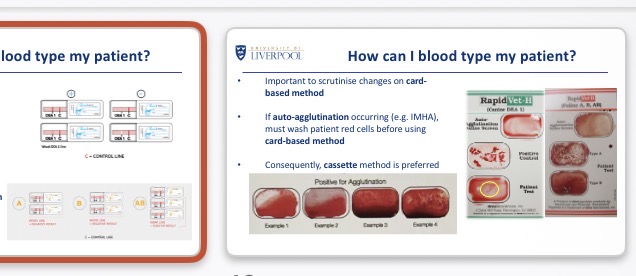
How to blood type patients (DEA, A/B)
External lab (long)
Cassette (using control lines+ positive lines)/ lateral flow tests
Card based method (need to rule out auto agglutination e.g. IMHA → wash patient RBC)
Purpose of cross matching
Detect more haematological incompatibilities (ab-ag, haemolysis) than blood typing (DEA1, A/B only)
Doesn’t detect non ab mediated compatibilities
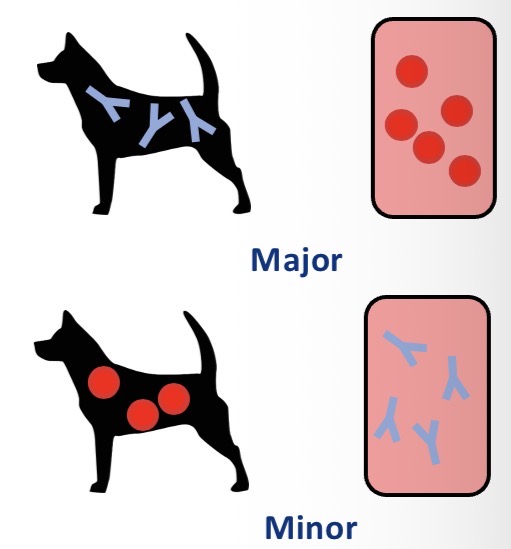
Types of cross matching
Major - recipient ab against donor red cells
Minor - donor ab against recipient red cells
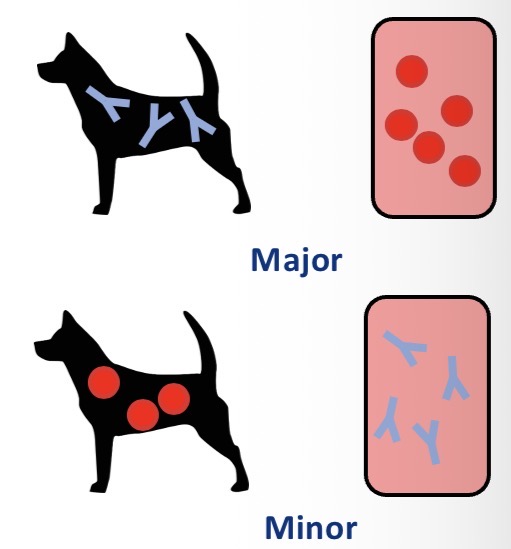
When to cross match
Previous transfusions (unless within 3-5d (not enough time for ab))
Received plasma products
Previous pregnancies
How to cross match (rarely 100% compatible)
External lab (days)
IDEXX + pet blood bank (24hr)
In house gel methods (inaccurate)
Transfusion targets (PCV) - usually give full bags/units
Restrictive = PCV 21-25%, better bone marrow response
Liberal = PCV 35-45%
How to give blood products
IV, intra osseous
Initial Slow rate (dose dependent transfusion reactions)
Sterility
Monitor
Transfusion set with in-line filter
Equipment in giving blood products
Transfusion set with in-line line filter (210 microm, remove debris+clots)
Dogs - drip by drip with transfusion set
Cats - syringe driver
Speed of giving transfusion (inc after 30min)
0.5-1ml/kg/hr (15-30min)
Inc to 4-6ml/kg/hr
Emergency = fast as possible
Within 4hrs
How to flush IV transfusion sets as Ca interferes with anticoagulant + leads to clots
0.9% NaCl (normal saline)
Patient safety during transfusion
Meds in separate line
Don’t actively warm blood- breakdown RBC
Water access
No food access
Don’t disconnect (sterility)
How to monitor patient (what to monitor)
HR, RR, rectal temp, signs of anaphylaxis (swelling, urticaria/ hives, nausea, V)
Types of transfusion reactions
Haemolytic, respiratory, non haemolytic
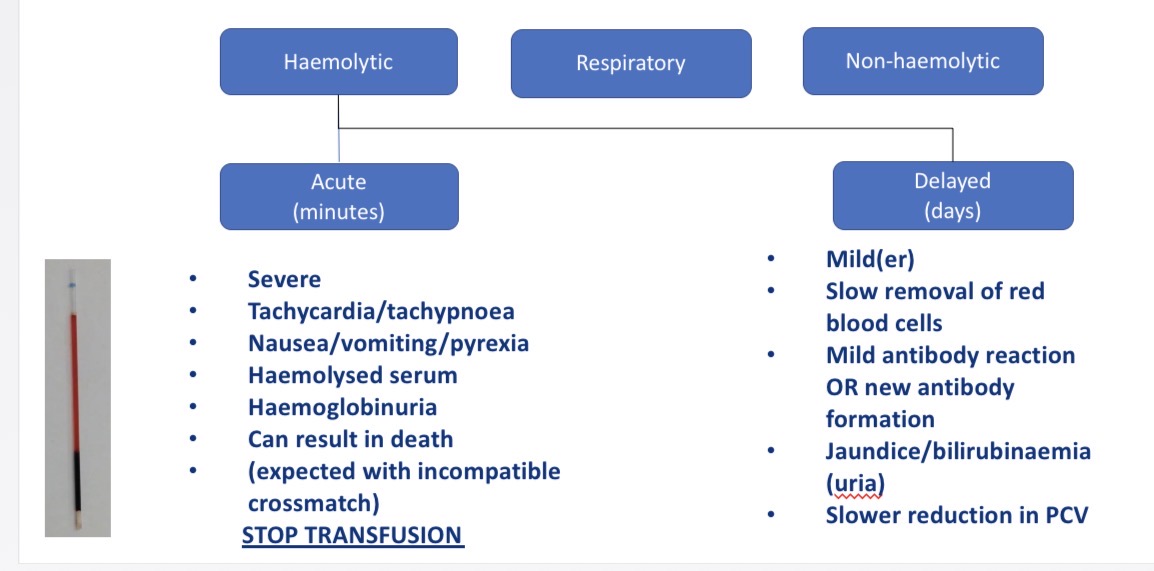
Types of haemolytic transfusion reactions - CS, what to do
Acute (mins)- tachycardia, tachypnoea, nausea, V, pyrexia, haemoglobinuria → check with haemolysed serum (reddish tinge) → stop transfusion
Delayed (days) - mild ab reaction → jaundice, bilirubinaemia, slow dec in PCV
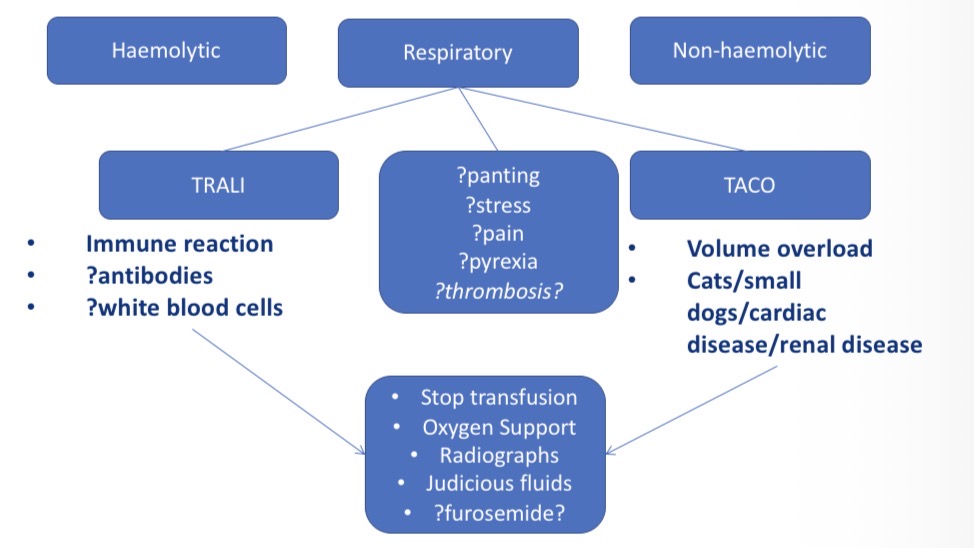
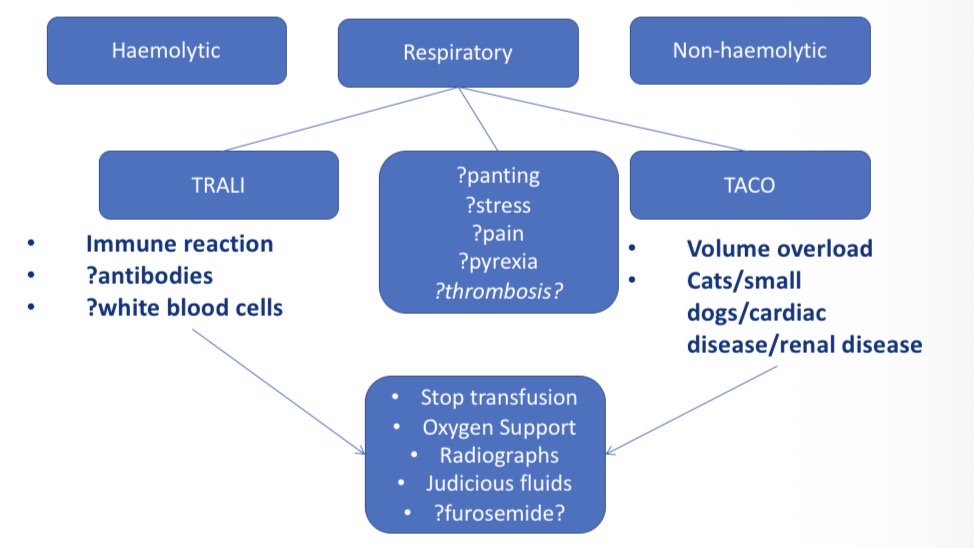
Types of Respiratory transfusion reactions- CS, what to do
Panting, stress, pain, pyrexia, thrombosis
TRALI (transfusion related acute lung injury) - immune reactions
Taco (transfusion associated circulatory overload)- vol overload in cardiac/ renal disease
Stop transfusion, oxygen support, radiographs
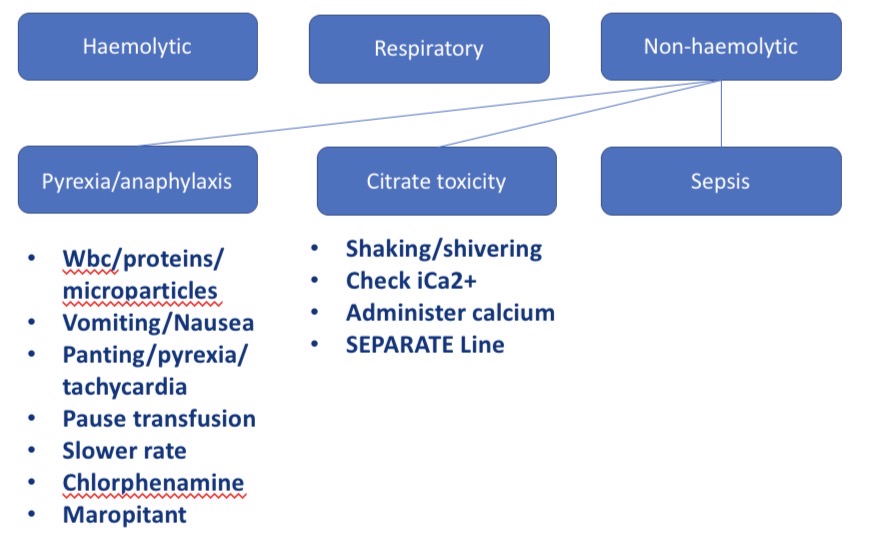
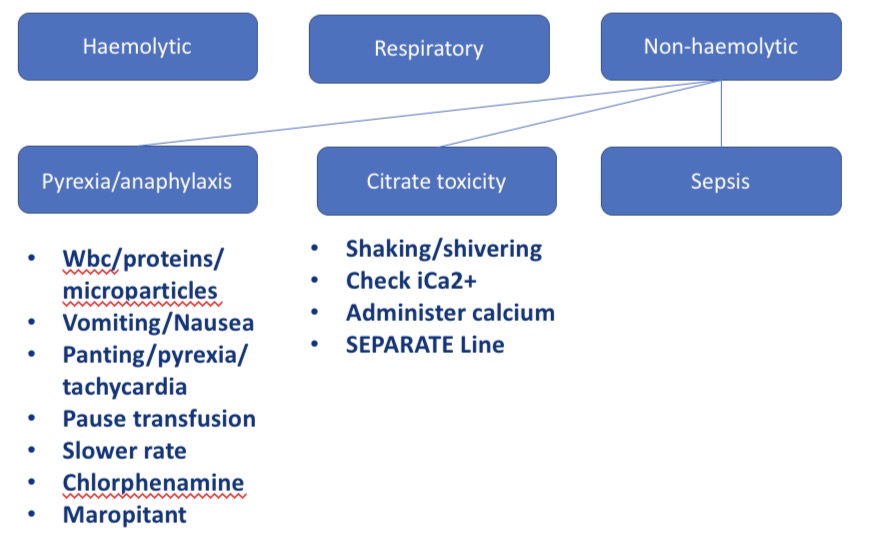
Types of non haemolytic transfusion reactions - CS + what to do
Pyrexia/ anaphylaxis - V, nausea, panting, pyrexia, tachycardia → pause/slow transfusion, chlorphenamine, maropitant
Citrate toxicity - shaking, lower Ca conc in blood → check iCa2+, administer Ca
Sepsis
What to do if concerned about transfusion reaction
15-30min break, restart at slower rate, dont disconnect patient, symptomatic treatment
Common vol blood to give
10-20ml/kg
Most common canine blood type
DEA 1 negative