2 solubility
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
what is molar solubility
amount of substance (mol) that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent dm3
what is Ksp
solubility product
equilibrium constant for dissolution of sparingly soluble salts
dissociation equilibrium for MXn (s)
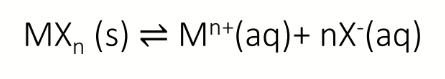
Ksp equation (in terms of concentration) for MXn (s)
what does it represent (ratio)
assumptions?
ratio of soluble ions to insoluble salt (activity of solid = 1)
assume standard conditions and solvent = water with activity 1
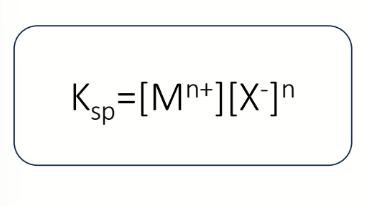
equation for Ksp in terms of activity
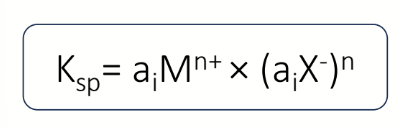
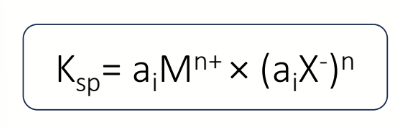
equation to find activity?
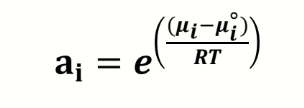
van’t Hoff equation + derivation in terms of Ksp
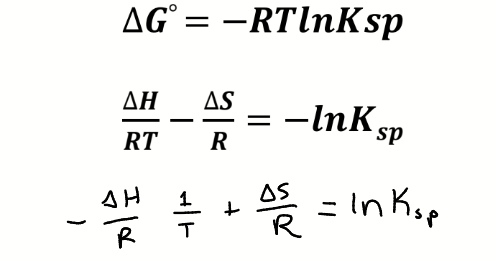
van’t Hoff plot
axes
shape
gradient
intercept
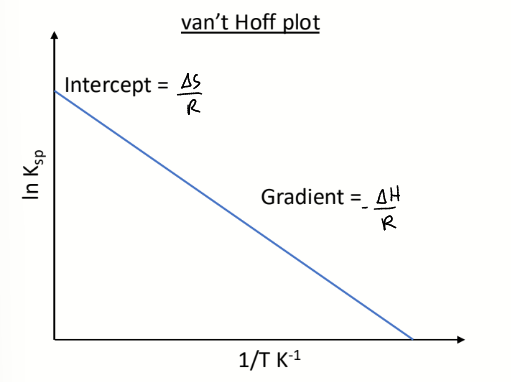
what is electroneutrality
sum of all negative charges in solution = sum of all positive charges in solution
electroneutrality equation for Cz+ and Az-
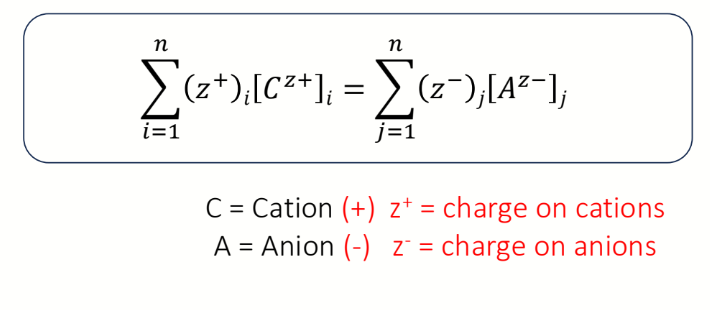
what is charge concentration (for ions)
concentration x charge number
how to write charge balance equation
write sum of cation concentrations on the left, equal to sum of anion concentrations on the right - multiply each concentration by its charge number (not sign)
include H2O, H+ and OH-
what is Formal concentration
the total concentration of a species, in all forms
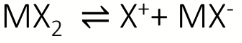
Formal concentration calculation and units for M
Formal concentation of M is the sum of [MX2] and [MX-] at equilibrium in mol dm-3
![<p>Formal concentation of M is the sum of [MX<sub>2</sub>] and [MX<sup>-</sup>] at equilibrium in mol dm<sup>-3</sup> </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f539de2d-e9fb-4922-802b-e95f7d675499.png)
how to write mass balance equation
write formal concentration expressions for the different species
write mass balance equation in terms of formal concentrations using dissolution equation
substitute in expressions for the formal concentrations
how to make an ICE table
if the solubility is x then the concentration of a species is its stoichiometry multiplied by ±x

what is the common ion effect
a salt will be less soluble if ones of its ions is already in solution
Q & K for common ion effect and why
Qsp > Ksp
Ksp is constant at standard conditions so if concentration of ione ionic species is increased the concentration of the other must decrease to oppose the change
how to use ICE table for common ion effect
set initial concentration of the ion to its conc in solution. still add x (or x x stoichiometry)
how to solve common ion effect problems when ICE table gives a cubic equation for x
Le Chatelier’s principle means increasing the concentration of the ion will decrease the solubility of the solid, so assume that the initial concentration of the ion is very close to the equilibrium and that x is small - Ksp << 1
hence x << initial concentration of ion in solution - equation can now be simplified to find x