bio 104 final exam kutztown
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
its so over
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
All aspects of nature were considered fixed and change was inconceivable.
No new species had appeared, and none had disappeared or become extinct.
Strongly thought that if any new species were to appear, it would be through sexual intercourse with multiple different species
Is this a pre or post-Darwinian view?
pre-Darwinian
all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of small, inherited variations that increase the individual's ability to compete, survive, and reproduce.
is this a pre or post-Darwinian view?
post-Darwinian
what scientist claimed “the formation of Earth's crust took place through countless small changes occurring over vast periods of time, all according to known natural laws. His "uniformitarian" proposal was that the forces molding the planet today have operated continuously throughout its history.”
Charles Lyell
what scientist claimed:
“species can change over time
new species come from pre-existing species
all species share a common ancestor
Charles Darwin
Where did Darwin form his theories of natural selection?
The Galapagos islands
Where are the Galapagos islands?
the pacific ocean, off the coast of Ecuador
why are the Galapagos islands significant regarding Darwin theory of evolution?
Darwin’s observation of Galapagos finch species and their differences in adaptation (mainland finches vs island finches) lead Darwin to develop his theory of natural selection (a core component of the theory of evolution)
A species that is only found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country, or other defined zone
Endemic Species
A species that causes ecological or economic harm in a new environment where it is not native.
Invasive Species
What influences organism diversity (in terms of evolution)?
Food availability (what food types are available)
Environmental disturbances (drought, human interaction)
Adaptive radiation
What is adaptive radiation?
a process in which organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment makes new resources available, alters biotic interactions, or opens new environmental niches.
What is natural selection?
The process through which populations of living organisms adapt and change.
Does natural selection make species:
A) More adapted to their local environment
B) Inherently “better”
C) both A and B
A) More adapted to their local environment
What is fitness?
The ability of an organism to produce surviving offspring
What is bio geography?
The study of the geographic distribution of organisms throughout the world
What is the significance of Australia’s marsupials?
Ancestral species migrated to Australia before the last major continental drift event. These marsupials evolved in isolation on the continent and became adapted to its harsh landscape.
What is a homologous structure?
similar features in organisms that share a common ancestor but serve entirely different functions
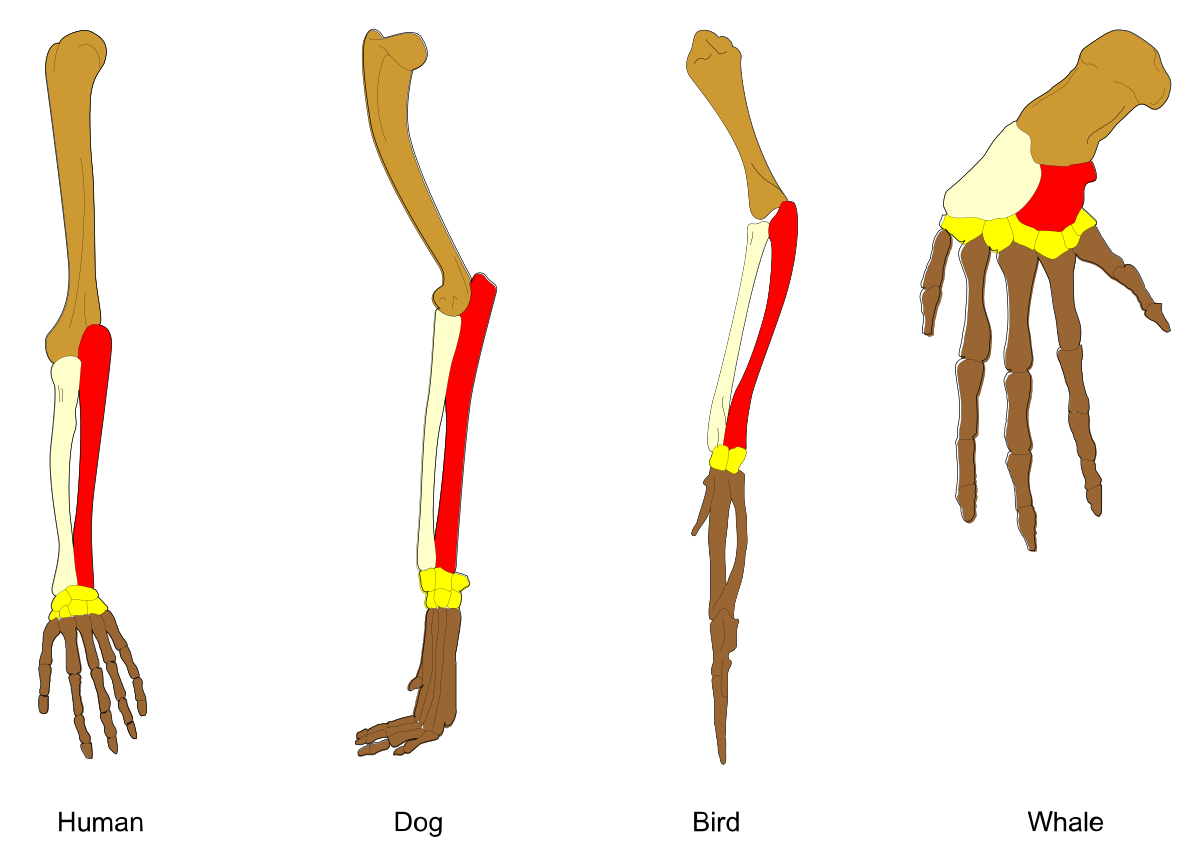
Are these structures homologous, analogous, or vestigial?
homologous
What is a vestigial structure?
A structure that once served a purpose (in an ancestor) that no longer serves the same purpose (in its descendants)
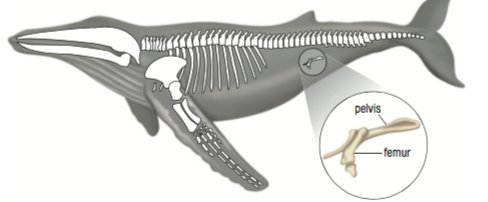
Is this a homologous, analogous, or vestigial structure?
vestigial
What is an analogous structure?
features found in different species that have similar functions; these species do NOT have common ancestors
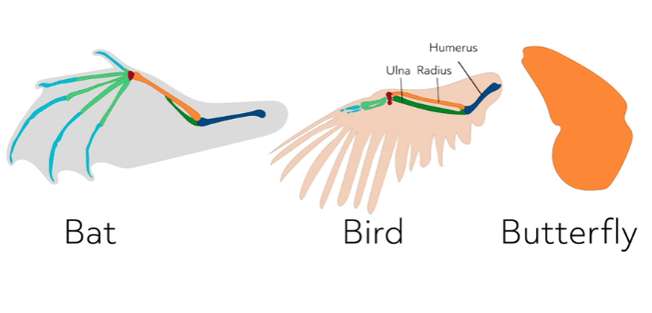
Are these structures homologous, analogous, or vestigial?
analogous
Why do homologous, analogous, and vestigial structures support evolution?
They help indicate presence/absence of common ancestry, and allow for evolutionary origins to be traced.
What is convergent evolution?
evolution where distantly related organisms evolve independently but acquire similar traits
What is the fossil record?
a record of all fossils found and their relative ages.
why is the fossil record significant?
it provides insight into change in species over geological time
what is artificial evolution?
evolution caused by the controlled influence of genetic information
how does biochemical evidence support evolution?
Similarities in DNA parts such as proteins (which are considered biochemical) allows scientists to establish how similar species are, and therefore how/when they evolved.
Did Darwin have access to biochemical evidence?
No, hes old as fuck (biochemical evidence was first analyzed around the mid-1900s).
What is exponential growth?
The unrestricted growth of a population of organisms, occurring when resources in its habitat are unlimited.
how does exponential growth influence evolution?
In situations of exponential growth, it is often true that not all that are born will live to reproduce (natural selection).
What is variation in natural selection?
individuals have traits better suited to an environment than others, enhancing survivability
What is heritability in natural selection?
the proportion of variability transmitted to offspring (more variability = faster trait evolution)
What is reproductive success in natural selection?
Those individual organisms who happen to be best suited to an environment survive and reproduce most successfully, producing many similarly well-adapted descendants.
Do populations or individuals evolve?
Populations. individuals CANNOT evolve on their own; individuals in a population will always have differences. Evolution occurs when a change occurs that influences the entire population.
What is a population?
A defined group of organisms of a single species living together in the same geographic area
What is micro evolution?
evolutionary change within a population
what is population genetics?
the study of population diversity at the genetic level
What is the gene pool?
alleles of all the genes in all the individuals in a population
What is allele frequency?
percentage of each allele in a gene pool
How is allele frequency calculated?
p² + 2pq + q²
p= frequency of dominant alleles
q = frequency of recessive alleles
What is the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A stable, non-evolving state
what is the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
genetic variation in a population will remain constant from one generation to the next in the absence of disturbing factors
What is required for the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium to occur?
-Alleles must not arise by mutation
-Nobody can join/leave the population where it is occurring
-The population is large
-mating is random
natural selection does not favor one genotype
Why is the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium rare?
it is near impossible/improbable for all of its requirements to occur at once
What is genetic drift?
changes in allele frequencies in a population’s gene pool due to chance events (no regard for genotype or phenotype)
What is the bottleneck effect?
Loss in genetic diversity caused by natural disaster, over-hunting, etc. negatively impacts genetic diversity.
What is the founder effect?
A few individuals break away from a population to found a new population.
What is gene flow?
movement of alleles between populations (during migration, gamete flow [plant migration], etc.)
what is a quantitative trait?
A trait that can be measured numerically (such as height)
What is a histogram used for in biology?
Illustrating frequency of alleles?(I think?)
What is sexual selection?
Adaptive change in males/females that leads to increased chance to find a mate
What is the good genes hypothesis?
the hypothesis that females choose mates based on them having traits that improve survival rates
What is the runaway hypothesis?
the hypothesis that females choose traits based on appearance.
How do mutations influence evolution?
they allow for more genetic variation
what is stabilizing selection?
natural selection where the intermediate phenotype is favored
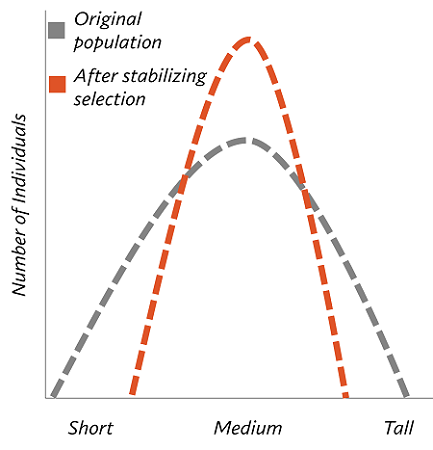
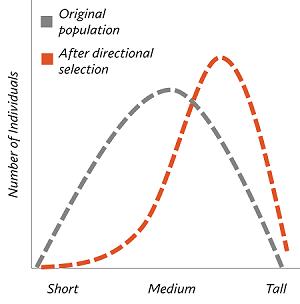
What is directional selection?
Natural selection where an extreme phenotype is favored
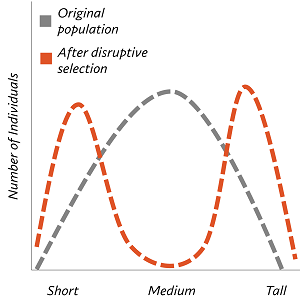
What is disruptive selection?
natural selection where two (or more) extreme phenotypes are favored (avoiding the intermediate)
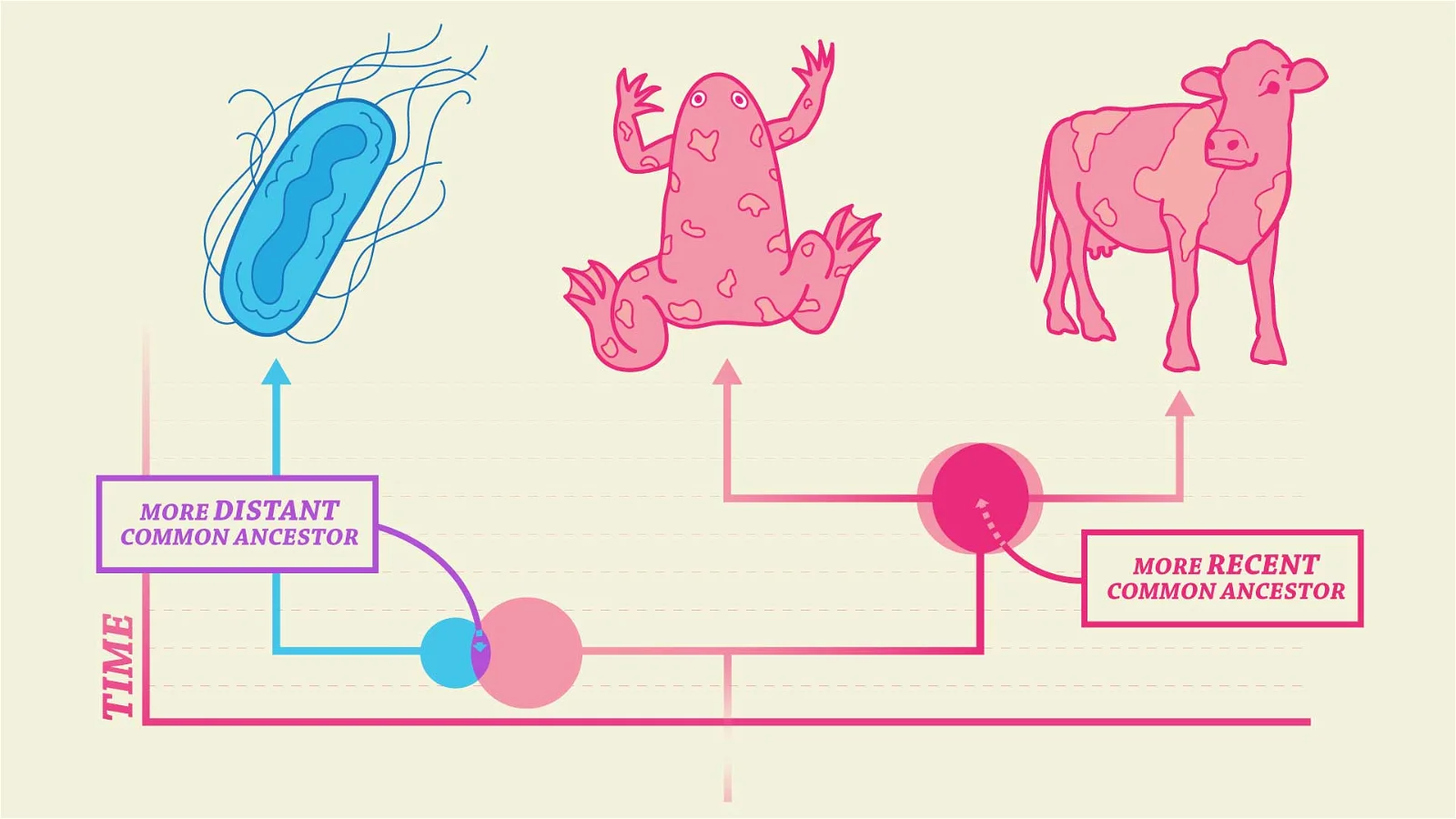
How is common ancestor determined?
DNA testing, characteristic analysis and comparison, etc.
What is a common ancestor
An ancestor shared by two or more descendant lineages
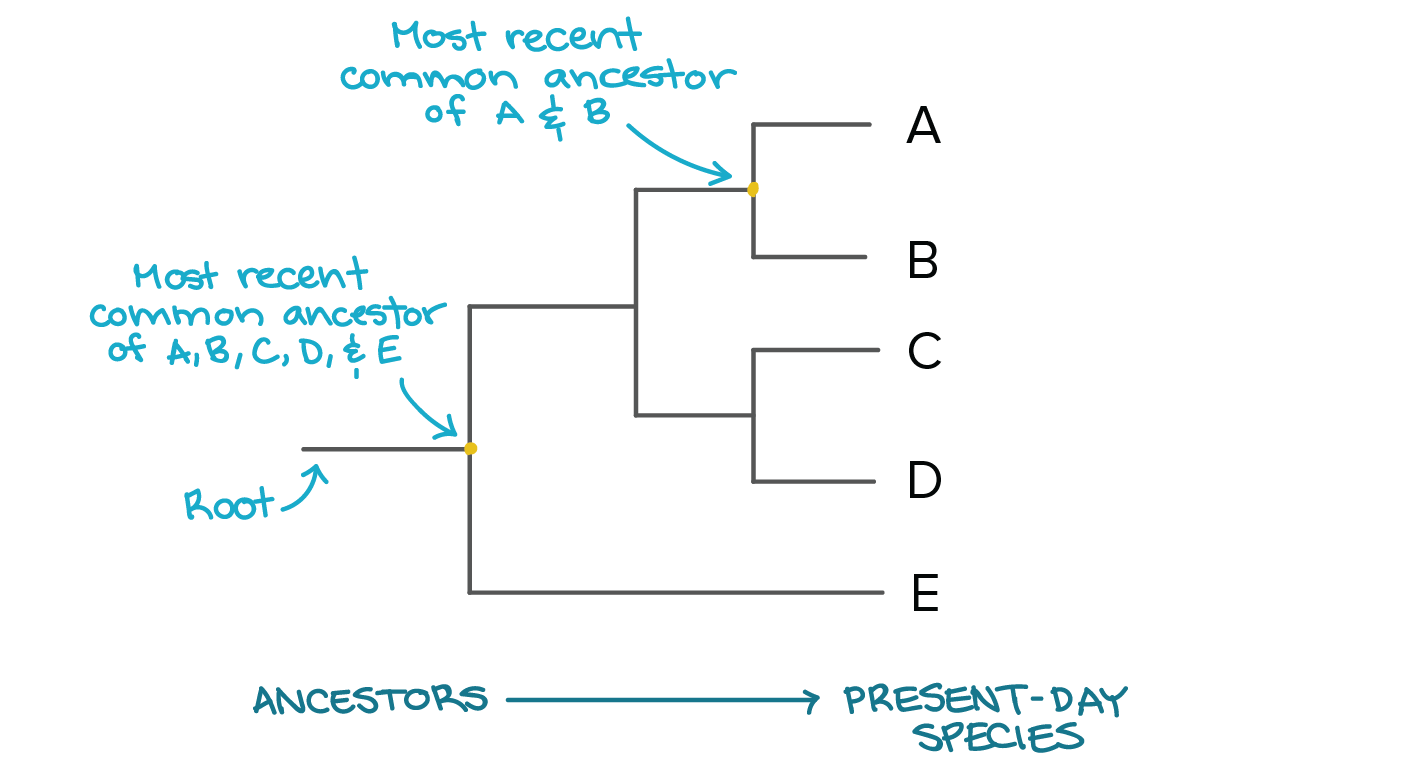
What is a root (in a phylogenetic tree)?
The oldest point in a tree (starting point)
What is a node (in a phylogenetic tree)?
A point where the tree branches out
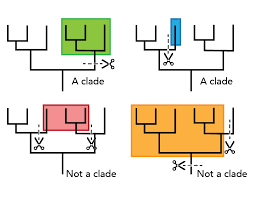
What is a clade (in a phylogenetic tree)?
A group of organisms with a single common ancestor
What is Phylogeny?
the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms (phylogenetics)
What is taxonomy?
the practice and science of categorization or classification of organisms
What is an Ancestral trait?
traits inherited from the common ancestor of two different clades
What is a derived trait
traits that just appeared (by mutation) in the most recent ancestor (the one that gave rise to a newly formed branch)
What is a phylogenetic tree?
a graphical representation of the evolutionary relationships between biological entities, usually sequences or species
What is parsimony?
Use of the simplest traits when constructing a phylogenetic tree
Why is parsimony important?
Fewer evolutionary changes in a tree = better
What is an outgroup (in phylogenetics)?
a more distantly related group on the tree
What is an ingroup (in phylogenetics)?
the group of closely related organisms being looked at on the tree
What is an ionic reaction?
a reaction of ions (cations[+] and anions[-]) where electrons are transferred and + or - ions are formed.
What does hydrophilic mean?
water loving
what does hydrophobic mean?
water hating
What is the difference between polar and nonpolar molecules?
Nonpolar = symmetric, no shared electrons
polar = asymmetric, shared electrons
What is electronegativity?
Measure of an atoms ability to attract shared electrons to itself
What is a high energy state (in an atom)?
a state where electrons are excited
electrons are far from the center of the atom
What is a low energy state (in an atom)?
ground state (lowest)
electrons are close to the center of the atom
what is the phospholipid bilayer?
a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. Acts as a barrier to the passage of molecules and ions into and out of the cell.
What is osmosis?
the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane
What direction does water typically flow in osmosis?
From areas of high to low concentration (water wants to balance out)
What is the endosymbiont theory?
some of the organelles in eukaryotic cells were once prokaryotic microbes
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
entropy constantly increases in a closed system
What is entropy?
the measure of an object’s amount of energy that is unavailable to do work.
What is an enzyme?
A biological catalyst that accelerates a chemical reaction
protein
What is activation energy?
the minimum amount of energy that is required to activate atoms or molecules to a condition in which they can undergo chemical transformation or physical transport
What is an endergonic reaction?
a reaction that requires energy to be driven
What is an exergonic reaction?
a reaction that doesn’t require energy to be driven
What is a redox reaction?
a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of a reactant change
What is photosynthesis?
the absorbance of light energy to create chemical energy
What is the light reaction?
the process of photosynthesis where solar energy is converted into NADPH and ATP
What is the calvin cycle?
light-independent reactions in photosynthesis that form glucose and other carbohydrate molecules
What is the cell cycle?
a series of events that takes place in a cell as it grows and divides.
what is glycolysis?
the splitting glucose into two pyruvate molecules (energy)
what is the prep reaction?
a reaction that converts products of glycolysis to materials that enter citric acid. cycle
What is the citric acid cycle?
the transfer of a two-carbon acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to the four-carbon acceptor compound (oxaloacetate) to form a six-carbon compound (citrate)
What is the electron transport chain?
A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP.
electron gradient
What are the Phases of the cell cycle?
Mitosis, Interphase, G1, S, G2, G0