GI, Liver, Panc, Neuropathology Micro-Anatomy Exam 3
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Define Esophagitis
Inflammation of the esophagus caused by gastric refluxing upward from the stomach
What’s the term for gastric refluxing upward from the stomach
Reflux esophagitis
What is a precursor for Esophageal adenocarcinoma
Barrett esophagus
Where does squamous cell carcinoma arise from in the esophagus
Arise from the lining of the epithelium in the upper esophagus
Where does adenocarcinoma arise from in the esophagus
arise near the gastroesophageal junction
Which disease of the GI tract is associated with adenocarcinoma
GERD
Define Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
chronic reflux of gastric acid into the lower esophagus – incompetence of the lower esophagus sphincter
What change would we see id GERD lead to Barrett metaplasia
epithelial change from squamous to columnar
Special stains for Barretts Esophagus
ABPAS, PAS, Alcian Blue - stains for goblet cells
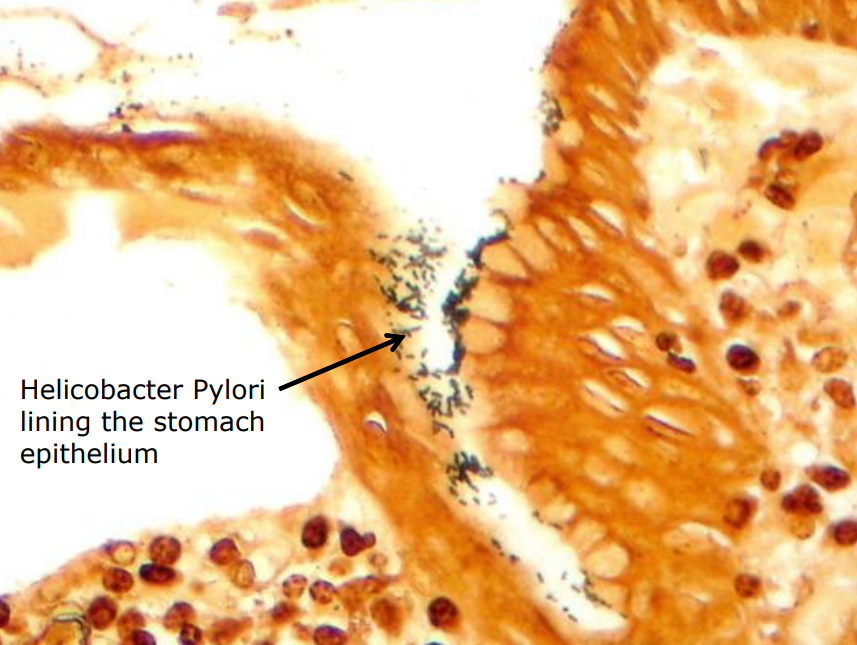
Special stain for H. Pylori
Warthin Starry - silver stain- brown, lining the epi
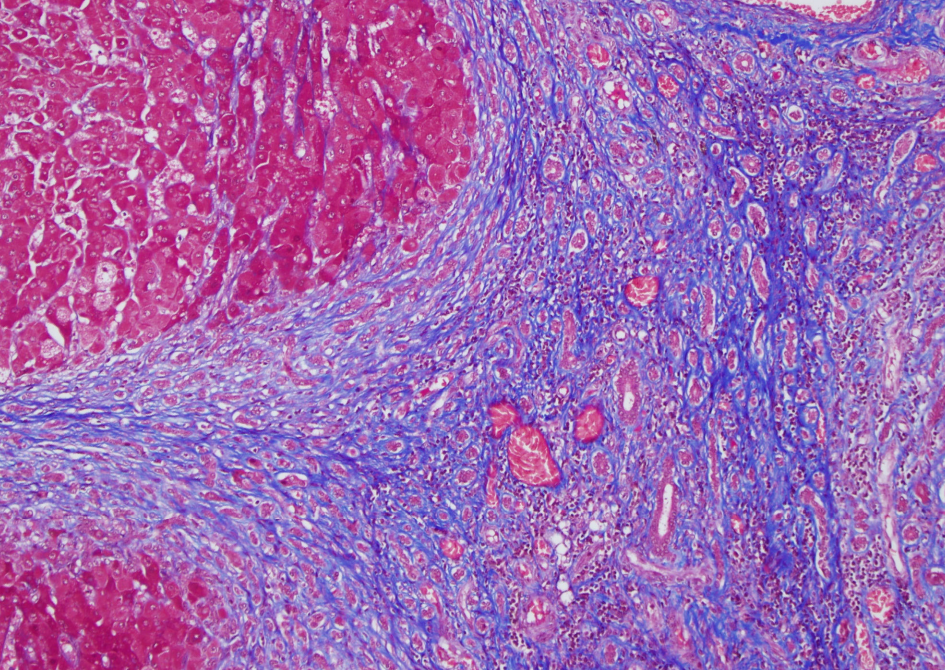
Special stain for cirrhosis
Trichrome- stains for fibrosis (blue)
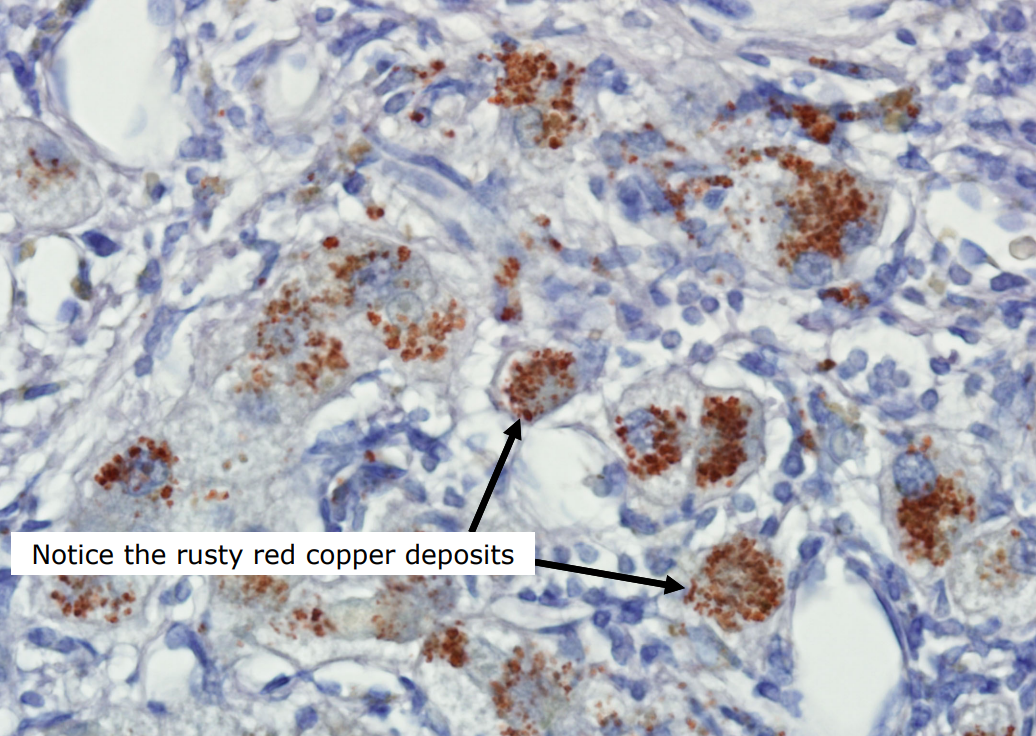
Special stain for Wilsons disease
Rhodanine- stains for copper
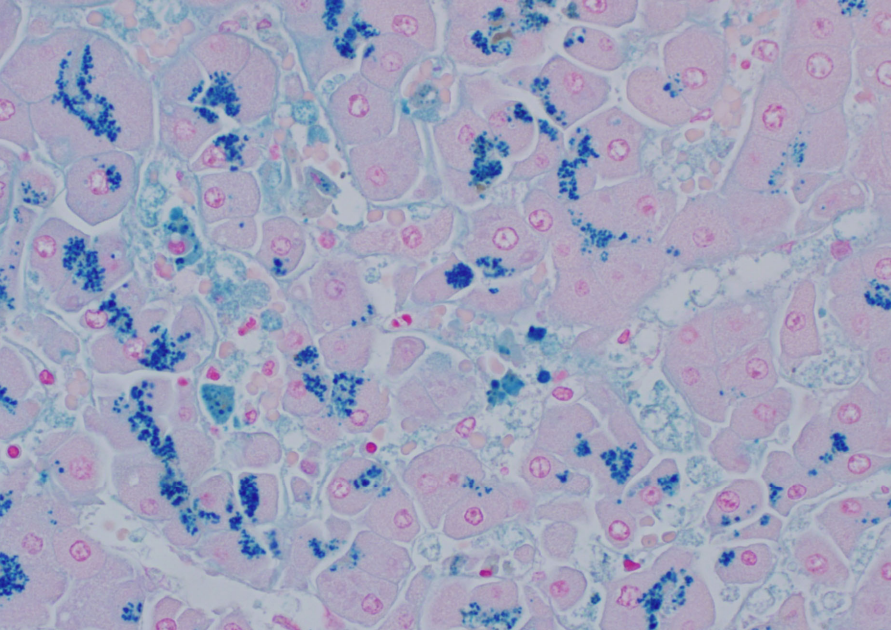
Special stain for Iron disease storage- what diseases does this include?
Prussian blue
Hemochromatosis, hemosiderosis
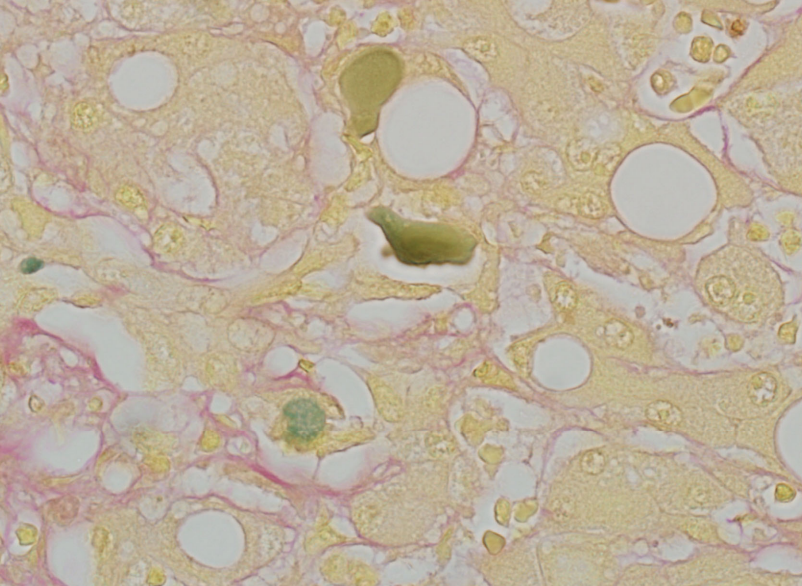
Stains for bile and how does it appear in this stain
H&E- appears brown
Fouchet Hall Bile- olive green
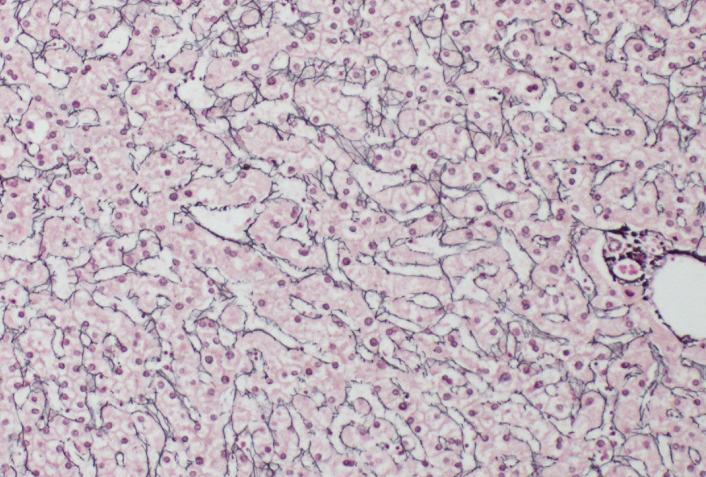
Special stain for reticulin fibers
Retic
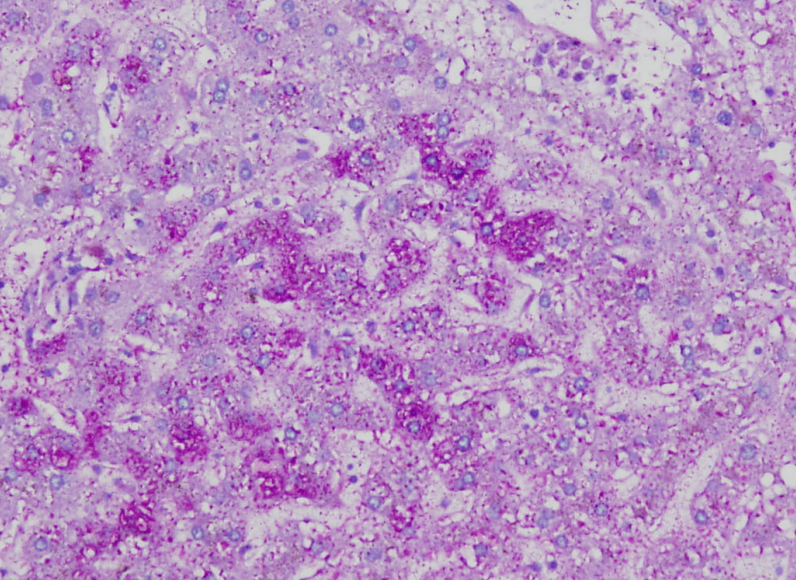
Special stain for glycogen storage
PAS
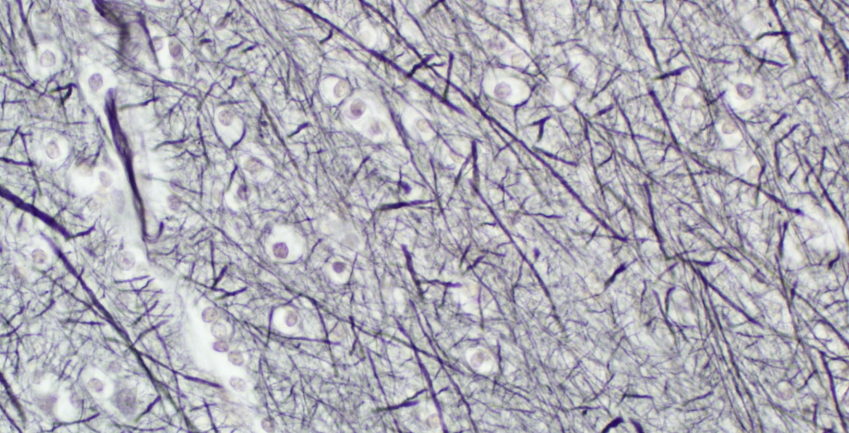
Special stain for neurofibril/ Nerve fibers
Bielschowsky
Stain for Nssl substance
Cresyl violet
IHC stain for neurons, neuronal processes and peripheral nerves
Neurofilaments
Special stain for Myelin
LFB- Luxol fast blue
Special stain for astrocytes
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP)
Alpha B Crystallin
Special stain for microglia
CD68- stains brown
Which organ is host to more neoplasms in the body, other than skin
colon
What pre-existing feature is the precursor for almost all carcinomas in the colon
Preexisting colonic adenomatous polyps
Which -itis is commonly caused from gastric acid refluxing from the stomach
esophagitis
Esophagitis etiology and histology
Etiology- alcohol, smoking, reflux and hiatal hernia
Histology- squamous hyperplasia, reparative epithelium, hyperkeratosis, inflammatory cells
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common malignancy of the esophagus
False- both adenocarcinoma and squamous are 50/50
State two steps that are precursors to INVASIVE esophageal SCC
Dysplasia and carcinoma in situ
Barrett esophagus has an association with gastric reflux
True
Barrett metaplasia is squamous epithelium replaced with _________ epithelium
columnar
Chronic gastritis is usually caused by
Helicobacter pylori
What is the pathognomonic feature of gastric adenocarcinoma
Signet rings
Gluten sensitivity is a characteristic of? What causes it
Celiac sprue- mucosal inflammatory response
What is a characteristic of ulcerative colitis
Wall remains thin
Characteristics of Crohn’s
Inflammation throughout entire wall, skipped areas of disease, small bowel involvement
Growth pattern of colon cancer
polyps
dysplasia
carcinoma insitu
Adenocarcinoma
Metastatic cancer
(Neoplastic/non-neoplastic) ___________ is pre-malignant
Neoplastic
It’s easy to distinguish between neoplastic/non-neoplastic in the colon
false
The most common causes of cirrhosis of the liver
Alcoholism, chronic viral hepatitis, fatty liver disease
Reticulin fibers provide supportive framework for the liver
True- framework for any highly cellular organ
Which of the following is an autoimmune disease?
Hemochromatosis
Primary biliary cirrhosis
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Cholecystitis
Primary biliary cirrhosis
A malignant tumor of hepatocytes that occurs in children
Hepatoblastoma
A malignancy of the bile duct epithelium is called
Cholangiocarcinoma
Stones in the gallbladder
Cholithiasis
The major contributing factor towards acute pancreatitis is
Premature activation of enzymes
There is a close relationship between acute and chronic pancreatitis
True- repeated acute turns into chronic
Pancreatic carcinoma has a low incidence rate and high survival rate
False it has a very low survival rate
A hematoma located beneath the dura mater is called
subdural hematoma
Common fatal Neurological condition
Cerebrovascular disease
Degenerative disease of white matter
Multiple sclerosis
This disease causes over ½ of all cases of adult dementia
Alzheimer disease
Pathological findings of this disease are loss of pigment and lewy bodies
parkinsonism