Chapter 2- Evidence-based Public Health
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Describe what the P.E.R.I.E process is.
1. Problem – what is the health problem?
2. Etiology – what are the contributory causes?
3. Recommendations – what works to reduce the health impacts?
4. Implementation – how can we get the job done?
5. Evaluation – how well does/do the interventions work in practice?
What are the topics that are involved in how the evidence based process works?
Problem
Etiology
Recommendations
Implementation
Evaluation
When describing the problem (first step) -- what defines the occurrence of morbidity and mortality?
burden of disease (Impact)
What is the term for the risk of developing a disease over a period of time (new cases)?
incidence
What looking at the course of a disease to describe the problem-- what are some questions that can be asked?
◦How often it occurs
◦How does it spread
◦What happens when it occurs
◦Incidence and prevalence
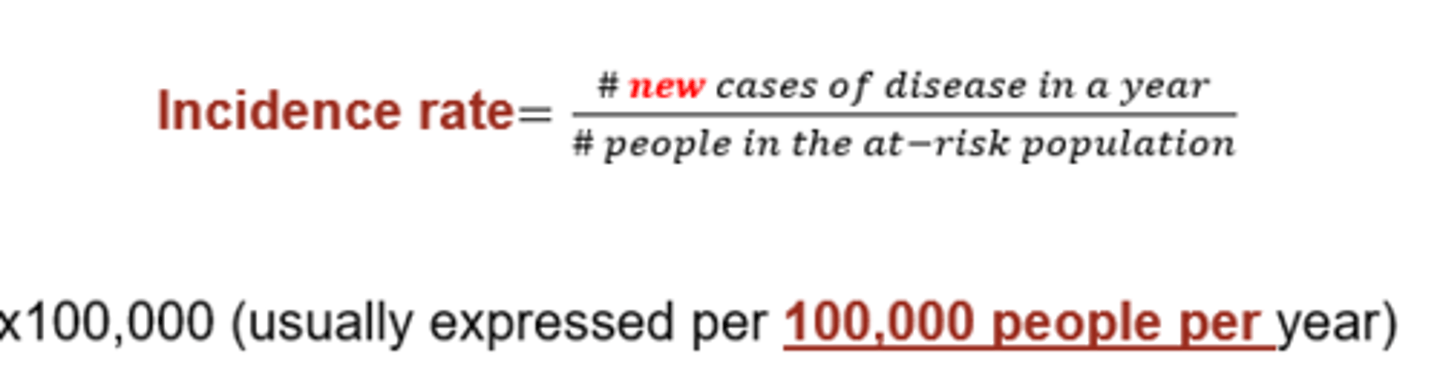
This is the formula for what?
incidence
What is the term for the number of people who have a disease at a point and time (existing cases)?
prevalence

This is the formula for what?
prevalence
How do we establish contributory cause (etiology)?
research
If an infectious disease starts to kill a host quickly but the infectivity stays the same what happens to the incidence and prevalence?
incidence= stays the same
prevalence= decreases
term of a study where you are looking forward (follow into future)
prospective
term of a study where you are looking backwards (in the past)
retrospective
What type of study includes two groups of people (exposed and unexposed) are recruited into the study and "followed up" to see if they develop the outcome?
exposure --> outcome
cohort studies
What type of study occurs with ALTERED intervention group (manipulation)?
randomized controlled trials
What is the term for risk of developing the outcome relative to the exposure (strength of association), with exposure preceding the event?
relative risk
What can be calculated from Cohort Studies and Randomized Controlled Trials?
relative risk
when looking at contributory cause---What is the term for:
•How close are they related
•Relative risk
strength
when looking at contributory cause--- What is the term for:
•Higher levels of exposure, longer duration of exposure increased probability of the "effect."
dose- response
when looking at contributory cause---What is the term for:
•Similar results in multiple locations and populations
consistency
when looking at contributory cause---What is the term for:
•Known biological mechanisms explains cause-and-effect relationship
biological plausibility
These are taken into consideration when looking at what?
•Quality of evidence
• Magnitude of impact
•Benefits, harms, cost
-Effectiveness
recommendations
How do we carry out implementation?
stage of prevention / intervention
What are some questions used to evaluate results?
• Has the intervention been successful?
• How much of the problem was eliminated?
• What problem remains?
RE-AIM Framework for evidence-based interventions
•Reach
•Effectiveness
•Adoption
•Implementation
•Maintenance