Biol 190 Unit 2 Chapter 6
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
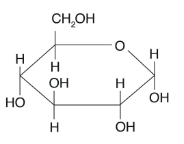
Identify the macromolecule, polymer, dimer, and monomer.
Macromolecule: Carbohydrates
Polymer: polysaccharides (glycogen, starch, cellulose)
Dimer: disaccharide (e.g. sucrose, lactose, maltose)
Monomers: monosaccharide (e.g. glucose, fructose, galactose)
Polymer: polysaccharides (glycogen, starch, cellulose)
Dimer: disaccharide (e.g. sucrose, lactose, maltose)
Monomers: monosaccharide (e.g. glucose, fructose, galactose)
2
New cards
How do we get most of our carbohydrates?
Through eating them
3
New cards
What is the formula for carbohydrates (simple sugars)?
C₁(H₂O) 1:2:1
4
New cards
How do carbon skeletons vary?
Linear structure or ring structure (more stable-\> more common in monosaccharides)
5
New cards
What are hexoses?
Six-carbon sugars; C6H12O6; Ex: glucose, galactose, and fructose are examples of structural isomers
6
New cards
How is a disaccharide formed?
Two monosaccharides link together through a dehydration reaction
7
New cards
What are the covalent bonds between monosaccharides?
Glycosidic linkages
8
New cards
What is the polysaccharide structure and function determined by?
It's determined by its sugar monomers and the positions of its glycosidic linkages
9
New cards
What is the first example of a polysaccharide?
Glycogen: used by animals to store energy and is broken down to release glucose when you need energy
10
New cards
What is the second example of a polysaccharide?
Starch: used by plants to store energy; Potatoes and grains are major sources of starch in our diet
11
New cards
What is the third example of a polysaccharide?
Cellulose:
1\. The most abundant organic compound on Earth
2\. Forms cable-like fibers in plant walls (structural role)
3\. Cannot be broken by any enzyme produced by animals (cannot break the linkages)
1\. The most abundant organic compound on Earth
2\. Forms cable-like fibers in plant walls (structural role)
3\. Cannot be broken by any enzyme produced by animals (cannot break the linkages)
12
New cards
Why do humans consume cellulose?
Fiber (helps clean intestines)
13
New cards
How do cows break down cellulose?
Bacteria in cow's stomach digests the cellulose and gives it to the cow
14
New cards
What are the functions of carbohydrates?
1. Energy (mono and disaccharides)
2. Energy storage: such as starch (polysaccharide)
3. Structural molecule to give shape to organisms (ex. cellulose)
4. Supply carbon: for synthesis of other compounds
15
New cards
Identify the macromolecule, polymer, and monomer.
Macromolecule: Lipids (e.g. TG, PL, Steroids)
Polymer, Monomer: NA (lipids don't covalently link together)
Polymer, Monomer: NA (lipids don't covalently link together)
16
New cards
Lipids are the only class of macromolecules that are \___________
Hydrophobic
17
New cards
What are triglycerides?
Oil and fats; a glycerol molecule joined with three fatty acid molecules via dehydration reactions; stored in adipose tissue
18
New cards
What is the function of triglycerides?
\-storage of energy
\-insulation and protection
\-most common type and storage unit of lipid
\-solid @ room temp= fat ; liquid=oil
\-insulation and protection
\-most common type and storage unit of lipid
\-solid @ room temp= fat ; liquid=oil
19
New cards
How long does it take monosaccharides, polysaccharides, and triglycerides to be used up for energy?
1-2 hours, 24 hours, and months respectively
20
New cards
Fatty acids are a \________________
Hydrocarbon chain
21
New cards
How do fatty acids vary?
\-Saturated: maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible, no double bonds, solid at room temp
\
\-Unsaturated: One or more double bonds, are kinked do not stack, liquid at room temp
\
\-Unsaturated: One or more double bonds, are kinked do not stack, liquid at room temp
22
New cards
Hydrocarbon bonds are...
Rich in energy
23
New cards
In triglyceride synthesis...
3 dehydration reactions join fatty acids to glycerol
24
New cards
What is the covalent bond that holds a triglyceride together?
Ester linkages
25
New cards
Why do fats stick together (aggregate) when placed into an aqueous solution?
Hydrophobic interactions
26
New cards
What are essential fatty acids?
Certain unsaturated fatty acids are not synthesized in the human body; must be supplied in diet (omega-3 fatty acids, required for normal growth)
27
New cards
What are the functions of fat?
1. Energy storage
2. Cushions organs and insulates the body
3. Fat supplies essential fatty acids (EFAs)
4. Carries "fat-soluble vitamins" around the body
5. Necessary for maintaining healthy skin
6. Plays a central role in proper eyesight and brain development
28
New cards
What are trans fat?
Manmade oil to fat through hydrogenation
29
New cards
What is hydrogenation?
1. Adds hydrogen
2. Converts unsaturated fats to saturated fats
3. Makes liquid fats solid at room temperature
4. Increase bad cholesterol levels
5. Will be off the market soon
30
New cards
What are phospholipids?
Composed of three parts: fatty acids, glycerol, polar group; predominant molecule in cell membranes
31
New cards
How do phospholipids differ from triglycerides?
1. Phosphate functional group (polar group)
2. Unsaturated fatty acids (at least one for fluidity)
32
New cards
Are phospholipids amphiphilic?
Yes/ amphipathic
33
New cards
What happens when phospholipids are added to water?
Phospholipid bilayer forms spontaneously
34
New cards
What are the hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions of phospholipids?
Hydrophobic: fatty acid tails; Hydrophilic: Polar phosphate heads
35
New cards
What is the structure of steroids?
Carbon skeleton of four fused rings
36
New cards
What is the function of steroids?
Steroids vary in the functional groups attached to this set of rings, which in turn affect their function
37
New cards
What is the most common steroid in humans?
Cholesterol:
\-gives structure to cell membranes, keeps them "fluid"
\-Precursor to steroid hormones (reproductive hormones)
\-gives structure to cell membranes, keeps them "fluid"
\-Precursor to steroid hormones (reproductive hormones)
38
New cards
Do steroids contain fatty acids/ provide energy?
No
39
New cards
Are steroids soluble in water?
No, all lipids are insoluble in water
40
New cards
Do we make sex hormones?
No, we create it by eating cholesterol