AP BIO unit 2
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
types of cells
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic Cell
- no nucleus, no membrane-bound organelle
- single-celled
in bacteria and archaea
Eukaryotic
membrane bound organelles, nucleus, compartmentalized
found in plants, animals, fungi, protist
similarities between the types of cells
cell membrane, ribosomes, and genetic material
Ribosome
made of protein and ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Read messenger RNA(mRNA) to synthesize proteins
Free-floating or attached to rough ER
Smooth ER
synthesizes lipids/hormones
detoxification of waste/poison
hold calcium
Rough ER
highly folded
packages proteins and send them to Golgi Apparatus vis transport vacuole
continuous with the nucleus and has ribosomes spotted
Golgi Apparatus
"post office of the cell"
Helps fold/modify proteins and package them into vesicles.
Sends the vesicles to their intended destination
Lysosome
Bubble full of hydrolytic enzymes that break down/digest macromolecules or waste
Also involved in apoptosis - releases enzymes that break down parts of the cell and ensure that cell dies in a controlled way
Peroxisome
lipid hydrolysis
use catalase to break down hydrogen peroxide
Vacuole
A sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area
(vacuoles in plants are large and help maintain plant cell shape: turgor pressure )
Take in food (endocytosis. phagocytosis)
Take in liquid(Pinocytosis)
take in hormones and proteins (Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis)
Protein Secretion
REGular VIdeo Chat
R: Ribosomes on Rough ER synthesize proteins
Round ER helped fold the protein and package them to Golgi Apparatus
Golgi Apparatus packages protein into Vesicles
Vesicles transport to the cell membrane
Cell membrane - vesicles fuses and allow protein to leave
Mitochondria (structure)
made of inner/outer membrane, matrix (inside cristae/gel like), and cristae (inner membrane folded)
Mitochondria function
ATP production/Cell Respiration
How does mitochondria make ATP
some in glycolysis (start) , some in matrix(Krebs/Citric cycle), most in Cristae (through Electron Transport via oxidative Phosphorylation)
Central Vacuole (function and where)
stores molecules, waste products, and water - big and enable growth
maintain proper water pressure (turgor) by filling up with water and pressing against wall
Contractile Vacuole
controls balance of water levels in cell by taking in/out water
found in protists
Chloroplast (structure)
"poker chip" = thylakoid
"stack of chips" = granum
fluid outside the granum = stroma
thylakoid membrane
Where do the light dependent and independent reactions take place, what do they do?
Light dependent: thylakoid (chlorophyll, and use photosystem)
Independent (Calvin/Dark Cycle) : stroma
what does chlorophyll in thylakoids do
convert light to chemical energy
store energy by carrying chemical energy that is used in calving cycle to make glucose
where does citric acid cycle take place
in the matrix
where does electron transport chain take place in cell respiration
oxidative phosphorylation in the inner membrane (cristae)
Where does the electron transport chain in photosynthesis take place?
thylakoid membrane
what does the electron transport chain do
Convert electron to ATP energy
Where is ATP synthesized in photosynthesis?
thylakoid /granum
SA:V ratio SA/V
the larger the SA: V ratio the better
High SA for more nutrients
Low V for better efficiency
Increase in SA affects V how ?
cell increase in size, the volume increases more, leading to a lower ratio
8How can a cell increase surface area without increasing the volume?
Folding, compartmentalization, and Microvilli which are structures that increase SA
How can an increase in surface affect heat exchange?
greater surface area = better aids in regulating temperature by improving staying cool or staying warm
Easily get heat because of SA or easily lose heat
Cell Membrane what is it made of
Phospholipids, Proteins, Carbs(exterior), Cholesterol (scattered within bilayer (in between phospholipids)
types of proteins in cell membrane
Integral - partially EMBEDDED in the membrane
Peripheral - attached the the inside or outside SURFACE
Transmembrane - all the way through the membrane
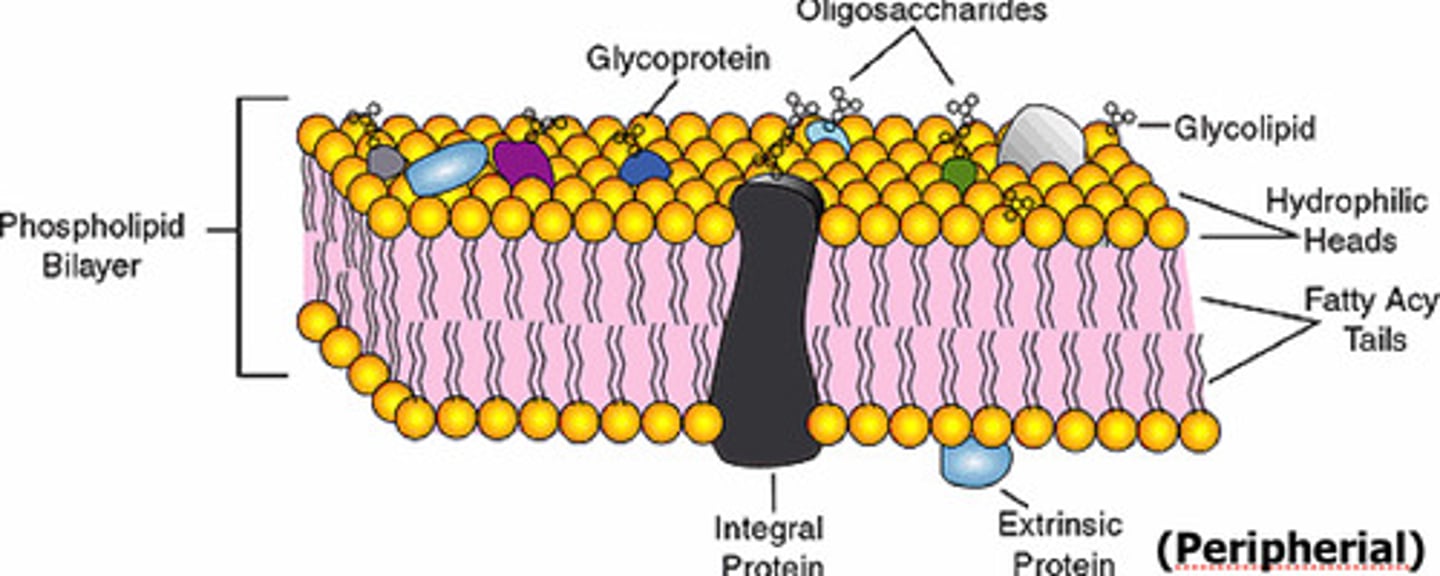
glycolipid and glycoprotein
carbs that are connected to phospholipid or protein
orientation of cell membrane
Head - hydrophilic/polar = outside
Tail - hydrophobic/nonpolar = inside
How does the phospholipid bilayer maintain the internal environment of a cell?
Selective permeability - only lets in small, nonpolar, and steroid hormones molecules to go in (without any help)
function of membrane proteins
transport, cell signaling, holding cell in place
define fluid mosaic model
made of many components
fluid (move laterally side to side)
What is the function of steroids in the plasma membrane?
Regulate membrane fluidity in response to temp changes
Stability
Rafts
What is the function of glycoproteins in the plasma membrane?
Allow cross-linking of cells which gives the tissues strength
Cell recognition
Carbs Attached to the phospholipid protein
What is the function of glycolipids in the plasma membrane?
Facilitate cell-to-cell adhesion and recognition
Attached to a phospholipid
Cell-to-cell recognition (ID)
What types of materials can easily pass through the membrane?
small, nonpolar, small steroid hormones
Why does this type of material easily pass through the membrane?
properties match the membranes inside (of bilayer)
What types of materials require a protein to pass through the membrane?
why ?
- large, polar molecules, or ions (charged)
They are larger, can't interact with hydrophobic interiors, and some ions need energy.
True or False? Any molecule can use any transport protein.
F
What types of materials require a vesicle for export or a food vacuole for import?
bulk transport or larger material
what is cell WALL and what type of cells have the m
rigid structure made of complex carbs
Plants, fungi, and bacteria
How does the cell wall maintain cell structure?
interconnected network of cellulose fiber, proteins, and polysaccharides.
How does the cell wall protect the cell from hypotonic solutions?
the cell wall creates rigid structure to maintain lysis
or
Turgor pressure - as water goes into the cell, it fills the central vacuole, pushing the membrane against the cell wall. (keeping it upright)
How do materials pass through the cell wall?
Diffusion, endocytosis, transport protein, channels and pores
What composes the cell wall of a plant?
Cellulose
What composes the cell wall of a fungi?
chitin
What composes the cell wall of a prokaryote?
Peptidoglycan
passive transport
diffusion and facilitated diffusion : things move across cell membrane without energy (going with concentration gradient )
active transport
things moving across cell membrane with the help of energy ADN membrane protein (transport protein) - go against concentration gradient
example of active transport
potassium sodium pump - 3 sodium ions out, 2 potasium in
What is a concentration gradient?
regions along which the density of a substance increases or decreases.
How does concentration move
oncentration will move from high to low concentration until reaches equilibrium (or it could also move from low to high via active transport)
What causes a concentration gradient?
When a solute is more concentrated than in one area than another. - a membrane separates two different concentrations of molecules
3 endocytosis
Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis, Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis (taking in hormones, and proteins)
How do large amounts of water pass through the membrane?
aquaporins (channel protein)
How do charged molecules or ions pass through the membrane?
membrane proteins - active transport OR passive transport (depends on which way of the concentration)
How do the passage of ions affect the membrane potential?
it affects membrane potential by altering the distribution of charges. For example, sodium entering will make it more positive, while potassium entering will make it negative
How does the Na+/K+ ATPase maintain the membrane potential?
Active transport 3 sodium ions out, 2 potassium ions in
Concentration gradient higher Na outside, higher K in side
hypotonic
less solution, more water
hypertonic
more solution, less water
which way does solution move
hypo to hypertonic
in other words high water to low water
water potential
high to low
osmoregulation
The control of water balance.
regular diffusion vs facilitated
regular - nonpolar, small
facilitated - larger but still small, POLAR, charged, with membrane protein
active transport. /
need energy more polar and large (+ ions)
things like exo/endocytosis
endosymbiosis theory
a previously free-living (photosynthetic or anaerobic) prokaryote was engulfed by another cell through endocytosis. After living together, instead of digesting, it was mutually beneficial The once free-living prokaryote lost its independent functionality and became mito and chloro
Eukaryotic cells developed when ancient cells engulfed free-living prokaryotic cells, which then became important parts of the eukaryotic cell, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts.
endosymbiosis evidence
double membrane, DNA, ribosomes, autonomous/reproduce on own
what organelle synthesizes cytolisc proteins
free ribosomes
what evidence do we have the chemosynthetic prokaryotes engulfed first
all eukaryotes have mitochondria but not all eukaryotes have a chloroplast
why are eukayotic cells larger
they compartmelaized membrane bound organelle which allow for the increased size of the cell
waht binds to the small subunit of ribosome
mRNA
what do cholesterol do for cell membrane
temp buffer
keep it togther
waht binds with ribosomes to start translation
mRNA
what binds with thje large subunit of ribosome
tRNA
how to find water potential
solute potential + pressure potential
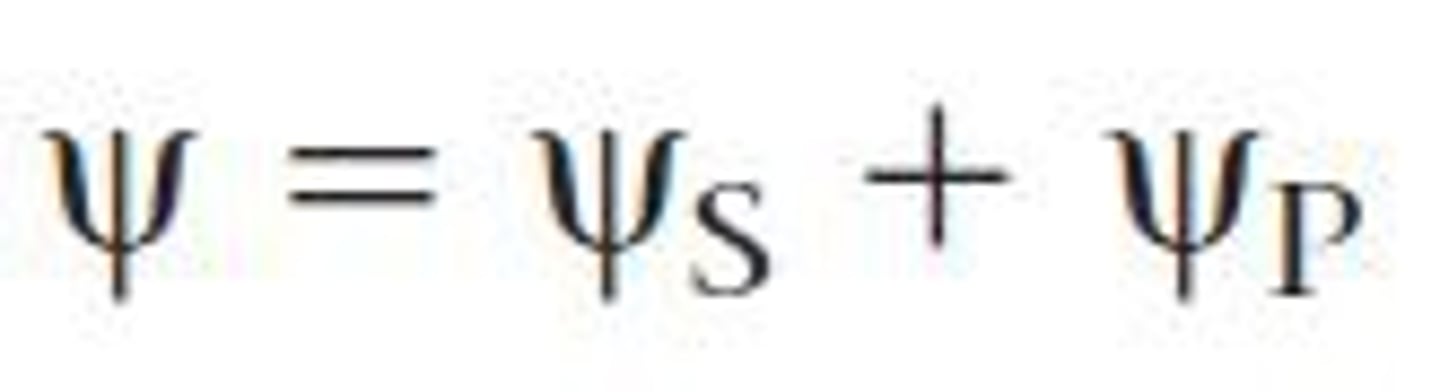
How to find solute potential
-iCRT
i = ionization constant (how many ions a substance dissolves into
C = molar concentration (M)
R = pressure constant = 0.0831
Temp (K) = (Celsius + 273 )
Pure Water solute = 0
Sugar solute = 1
Salt solute = 2