Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System (gtallo)
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
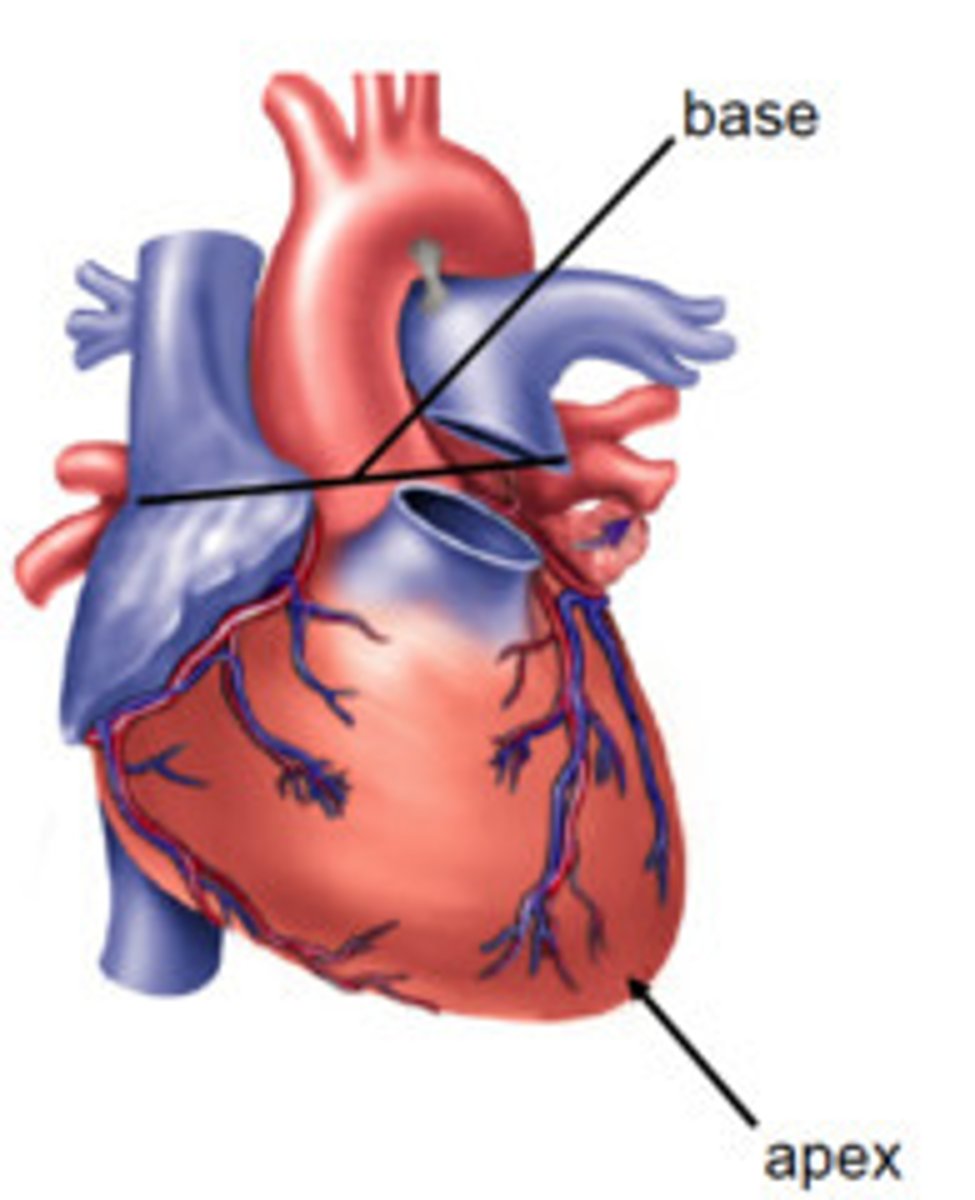
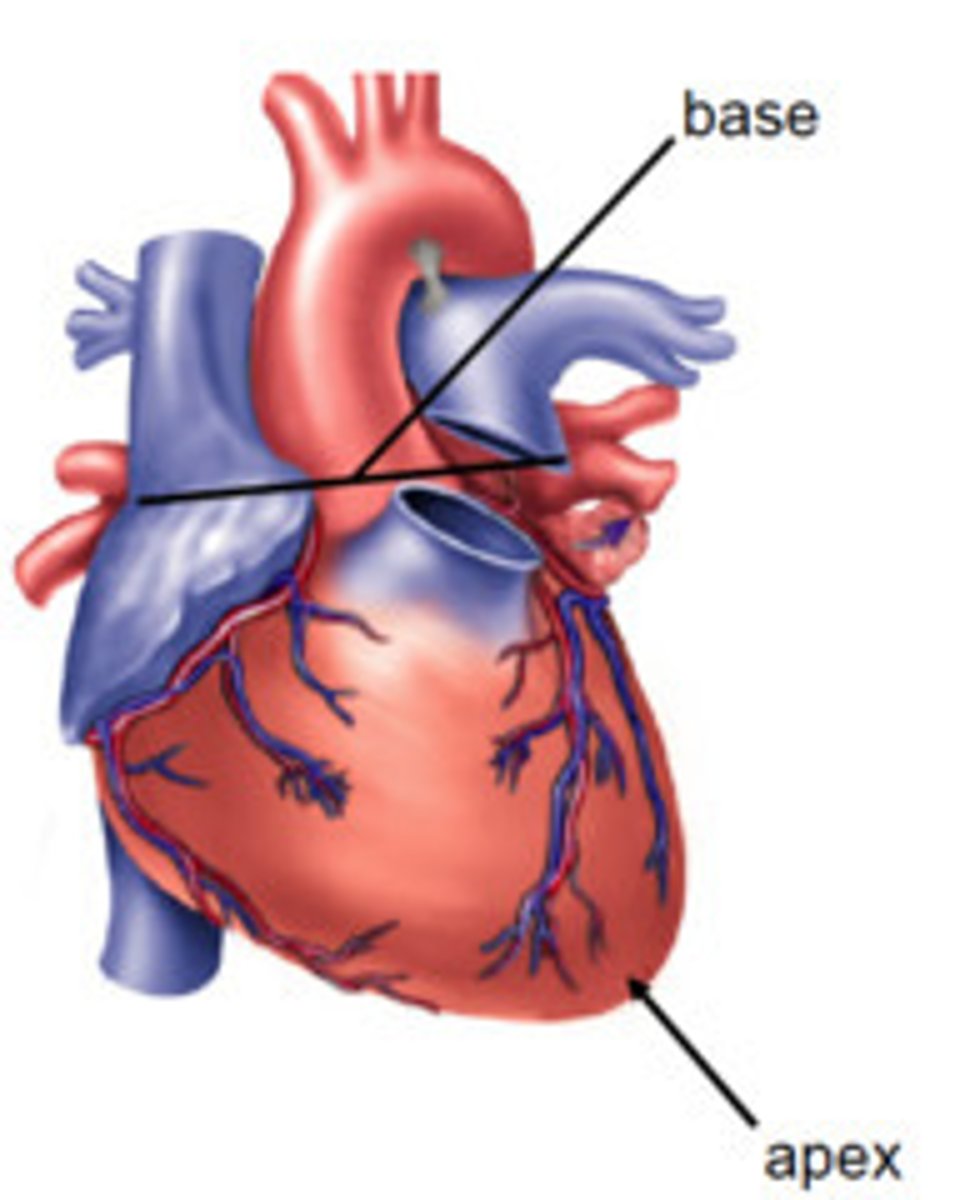
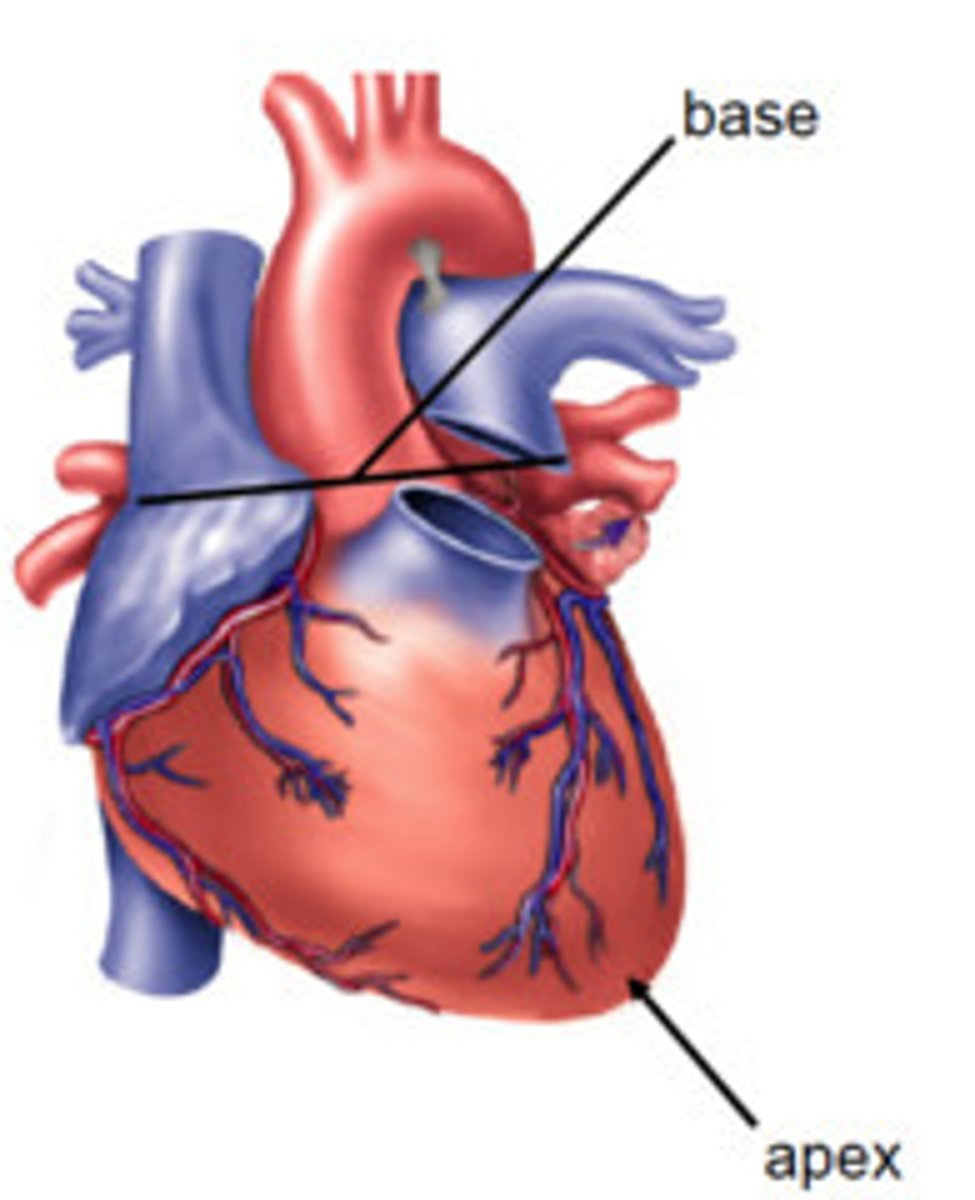
apex
The bottom of the heart
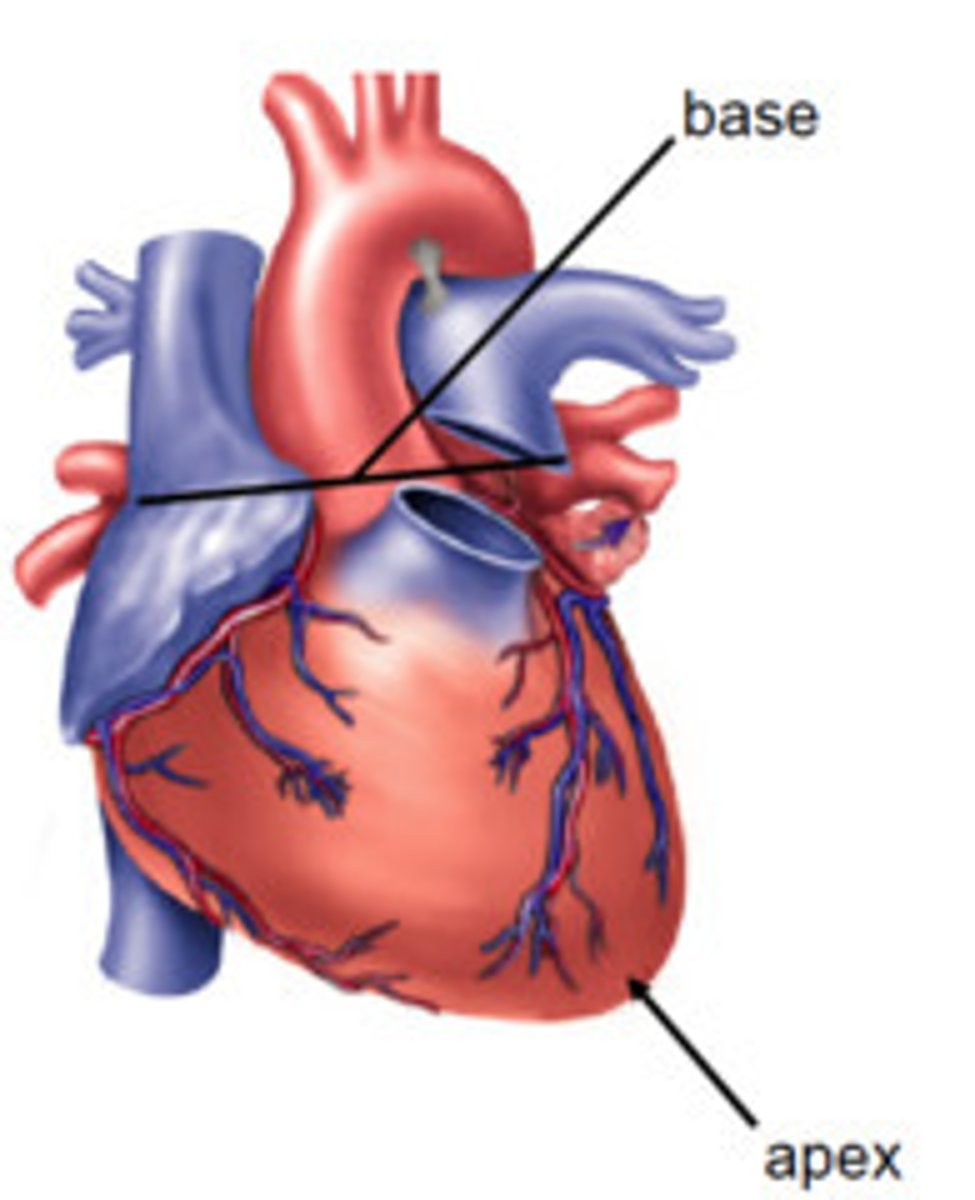
base
The top of the heart
4
-endocardium, myocardium, epicardium, and pericardium
How many layers does the heart consist of?
precordium
The area on the anterior chest wall that covers the heart.
left atria
This chamber pumps oxygenated blood to the left ventricle.
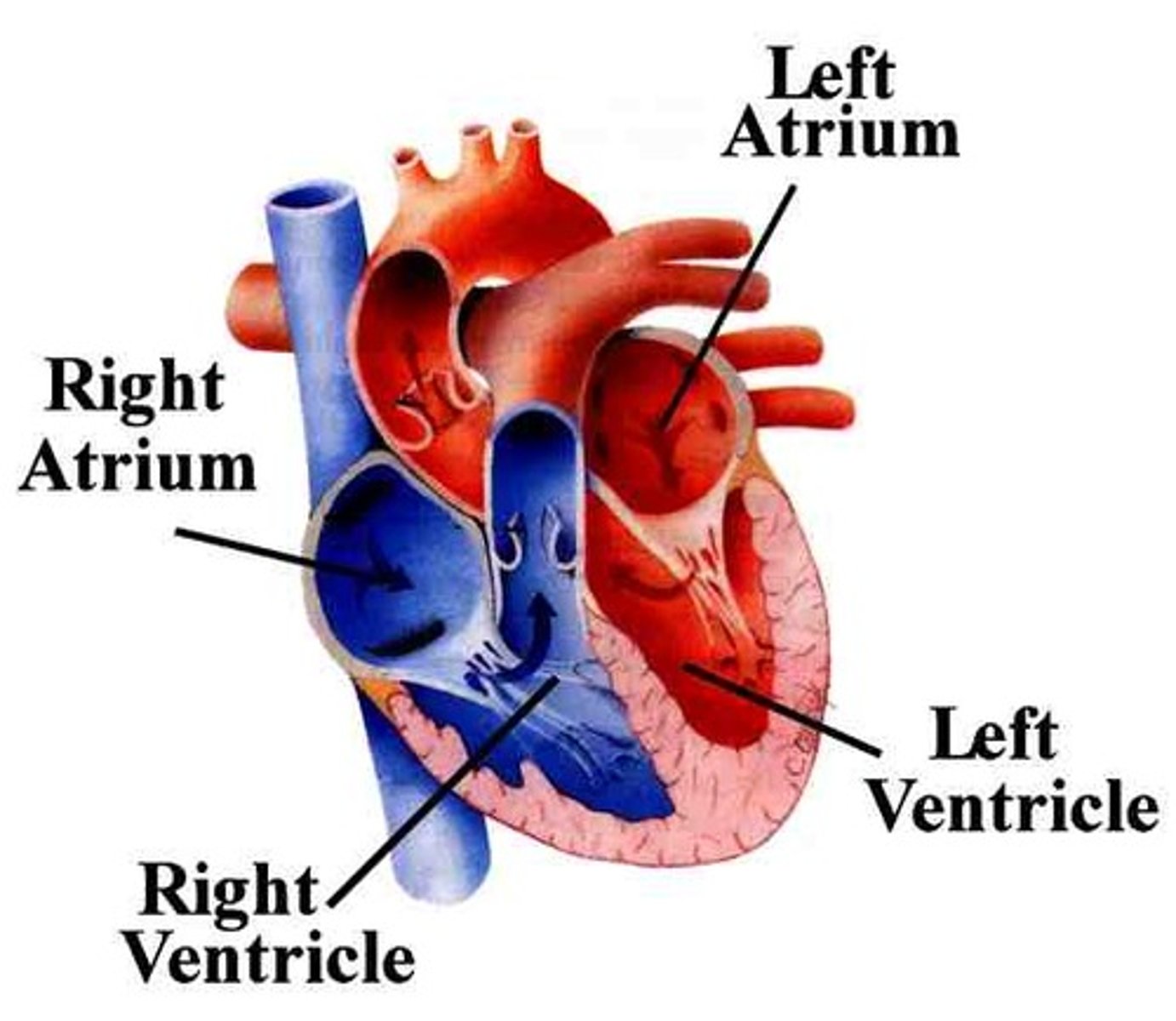
right atria
This chamber receives deoxygenated blood and pumps it to the right ventricle.
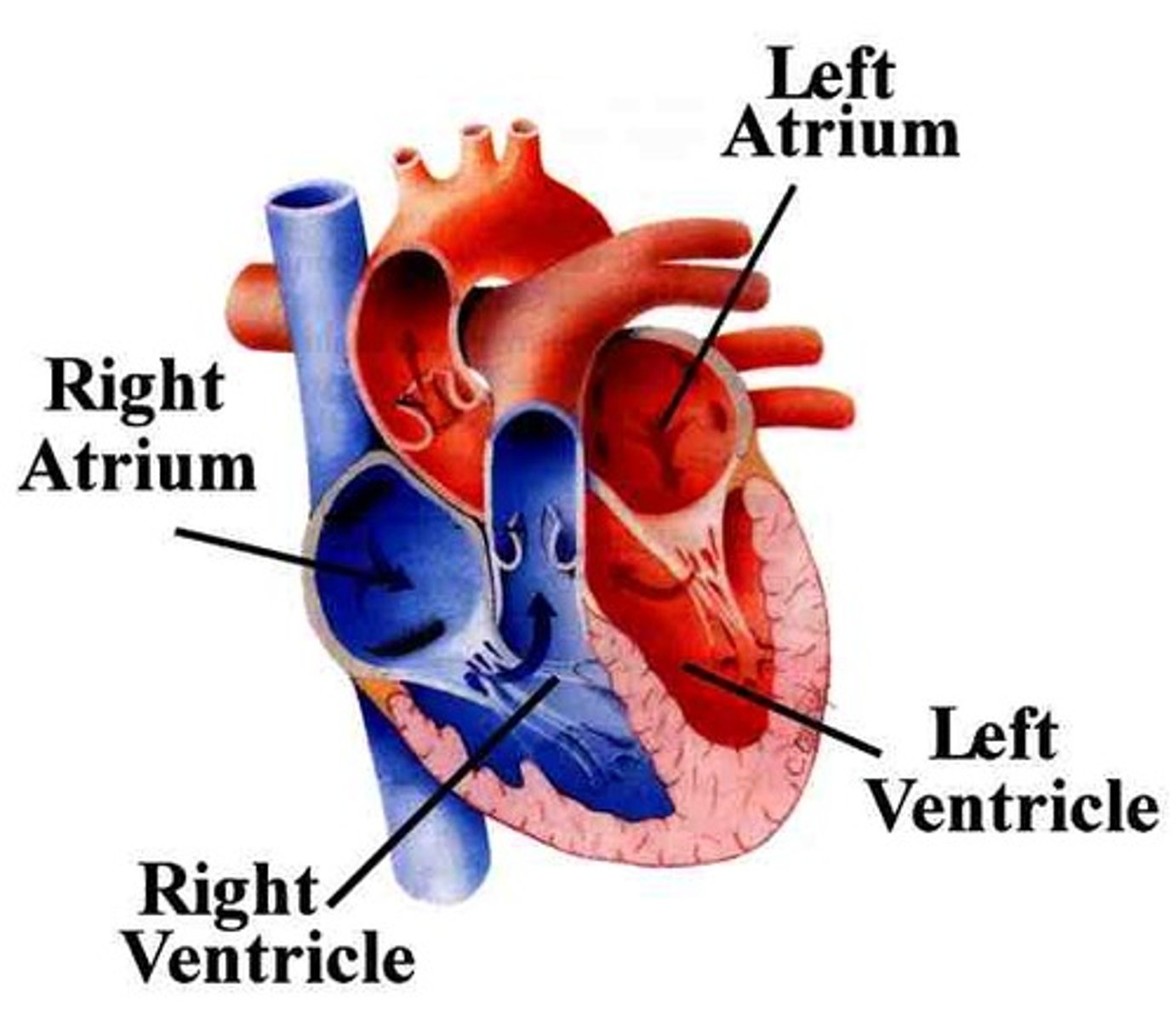
left ventricle
This chamber pumps oxygenated blood to the aorta.
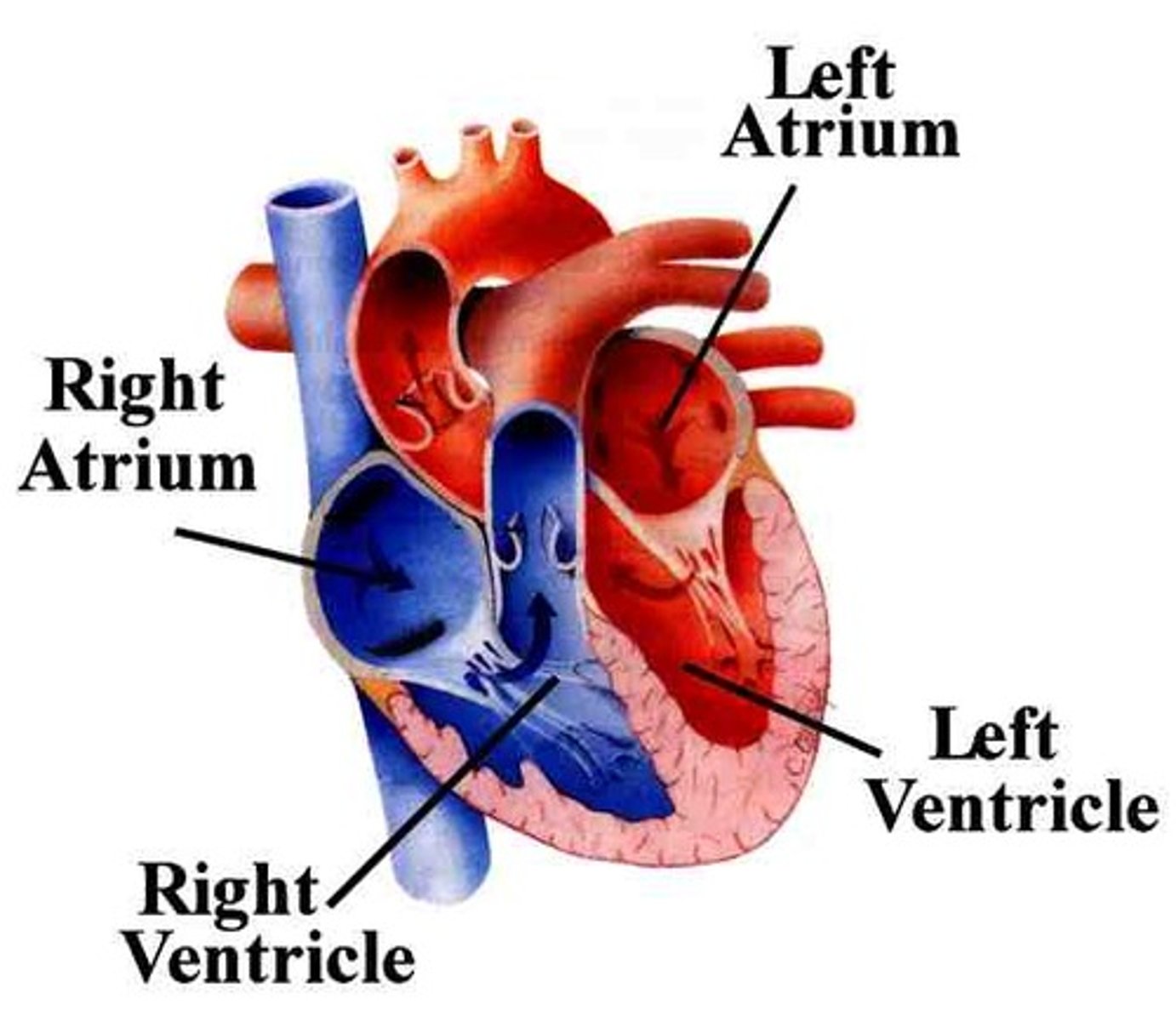
right ventricle
This camber pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
antrioventricular valves
Separates the atria and ventricles; includes the mitral and tricuspid valves:
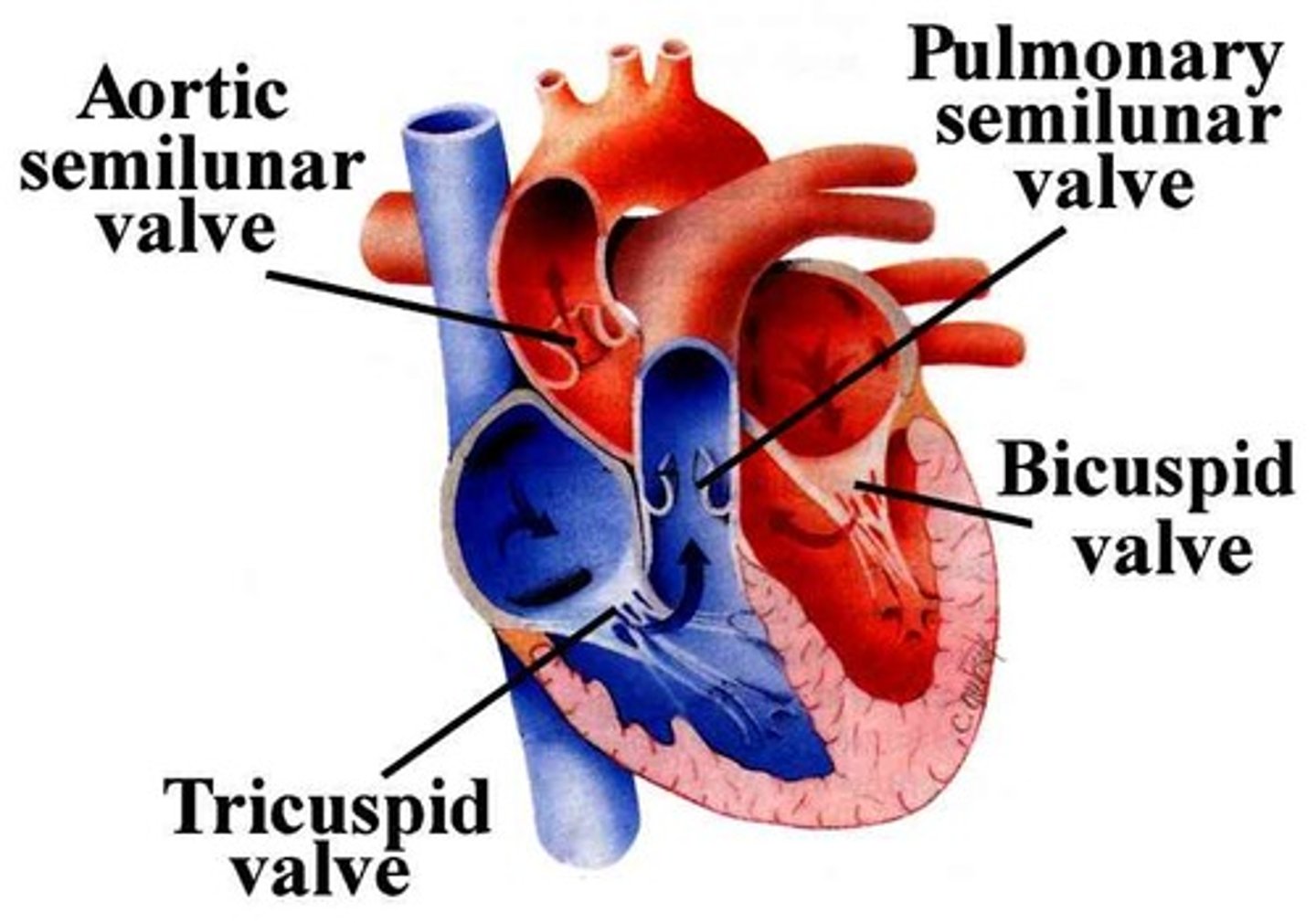
semilunar valves
Separates the ventricles from the pulmonary artery and aorta;
includes the pulmonary and aortic valves:
cardiac cycle
A complete heartbeat consisting of contraction and relaxation of both atria and both ventricles.
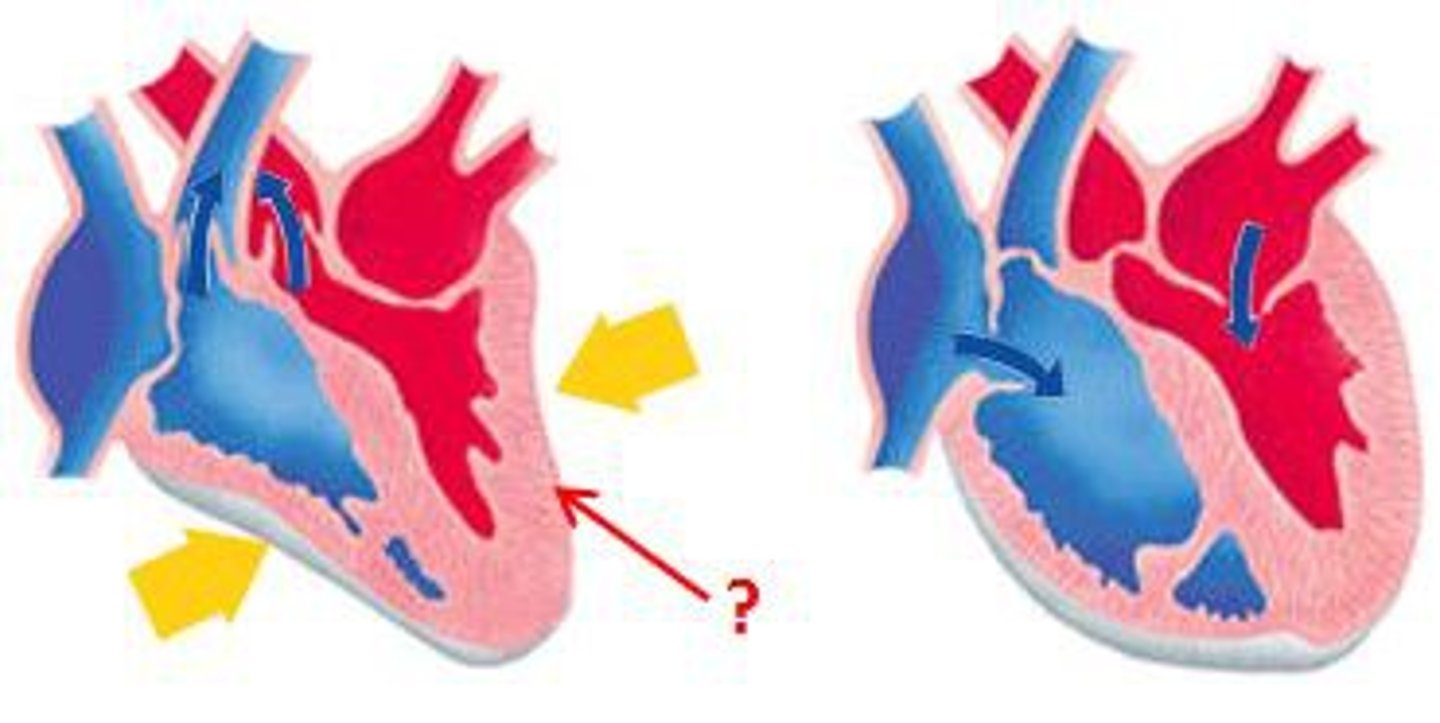
systole
Contraction of the heart
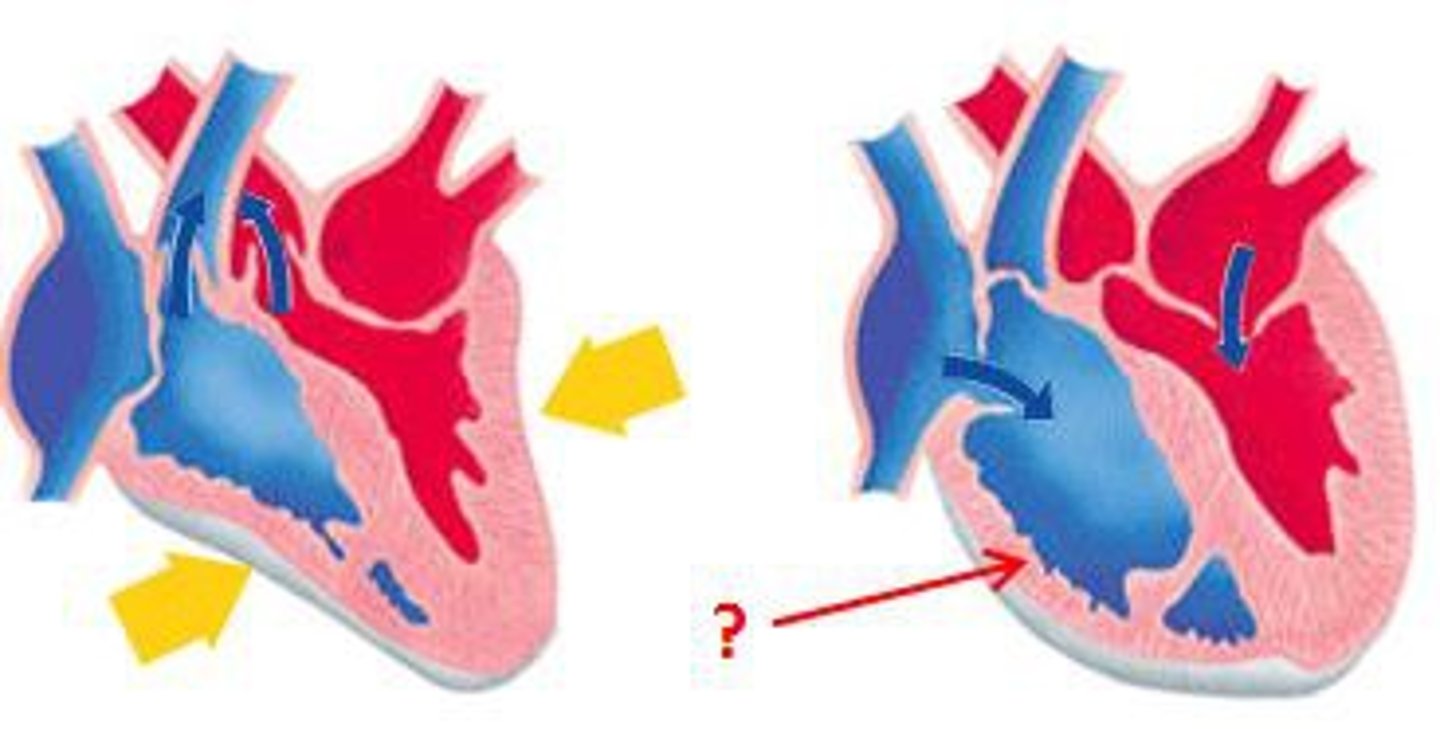
diastole
Relaxation of the heart
6L per minute
What is a normal cardiac output?
pacemaker; it initiates electrical impulses
Sinoatrial (SA node) is known as the _______.
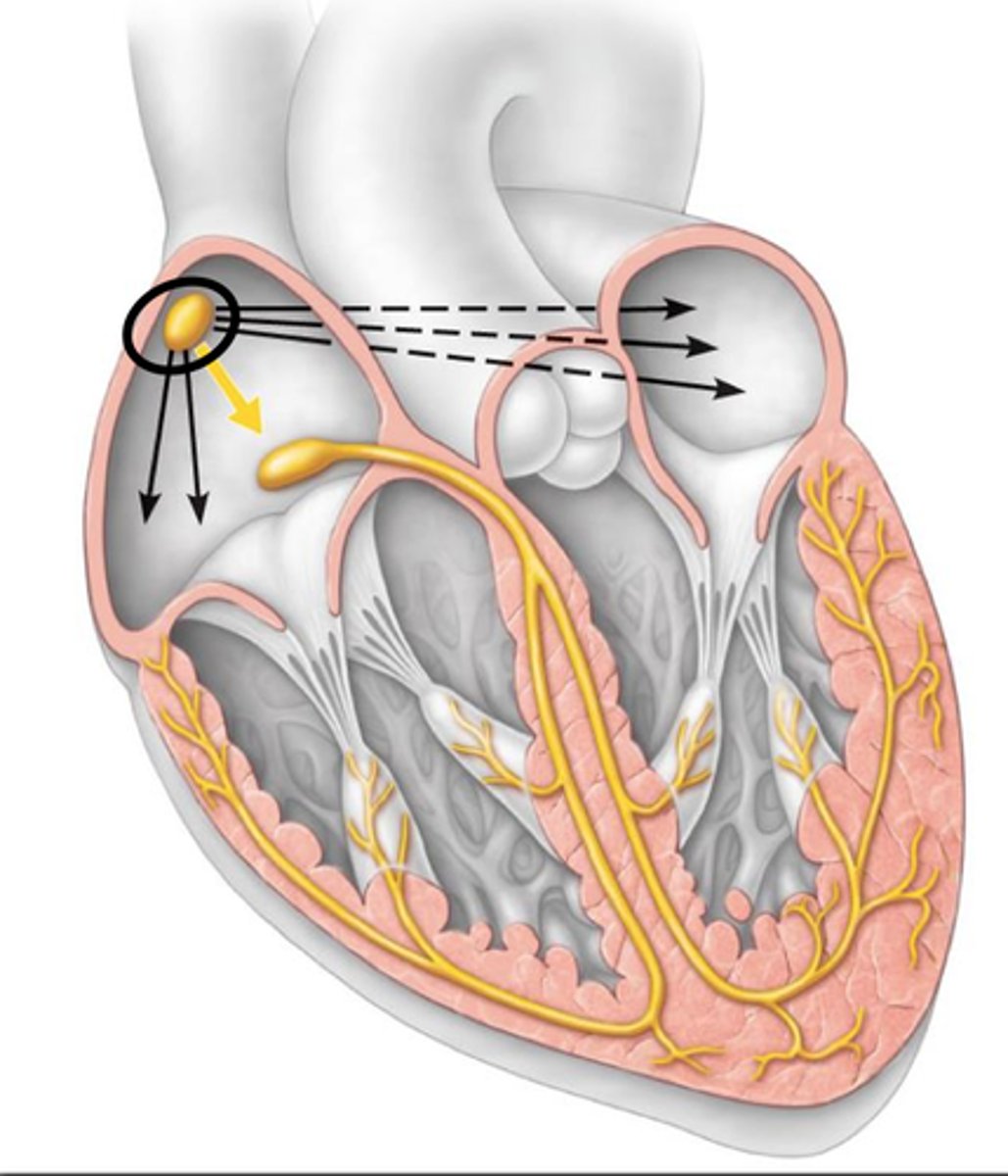
depolarization
Ions move from a negative to positive charge which allows the heart to contract.
Repolarization
The cells return to their normal charge after depolarization.
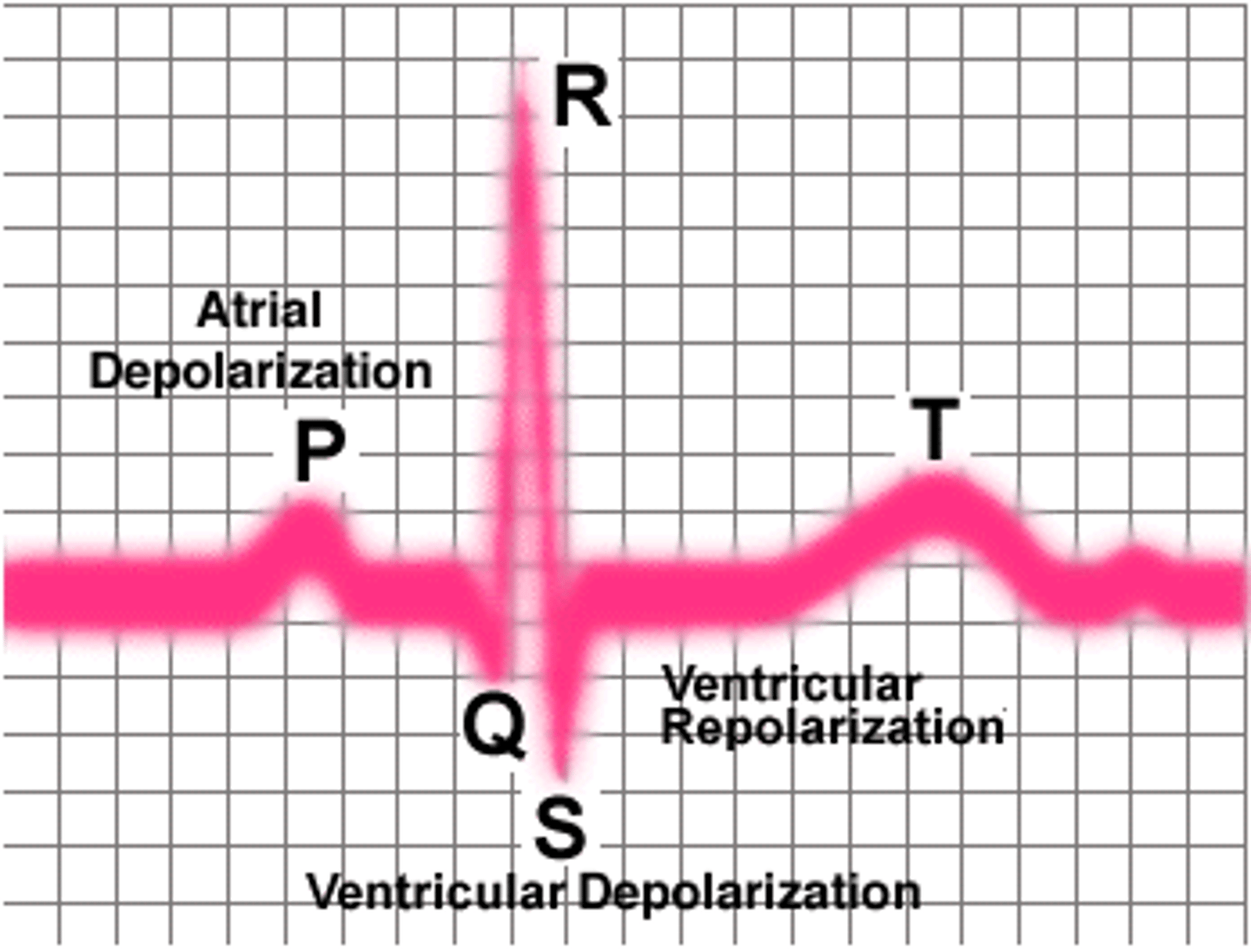
P wave
Atrial depolarization wave
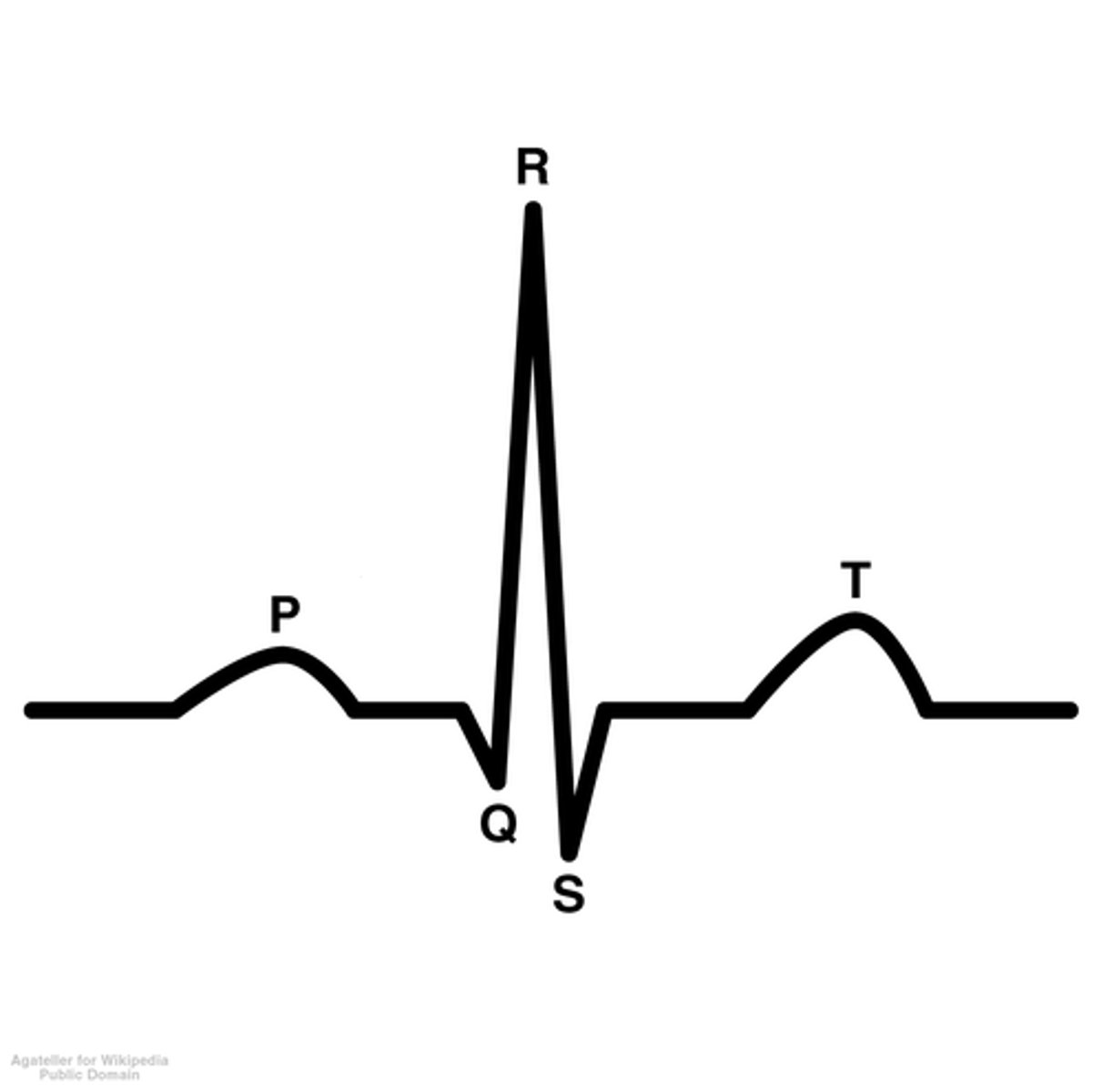
QRS complex
Ventricular depolarization wave
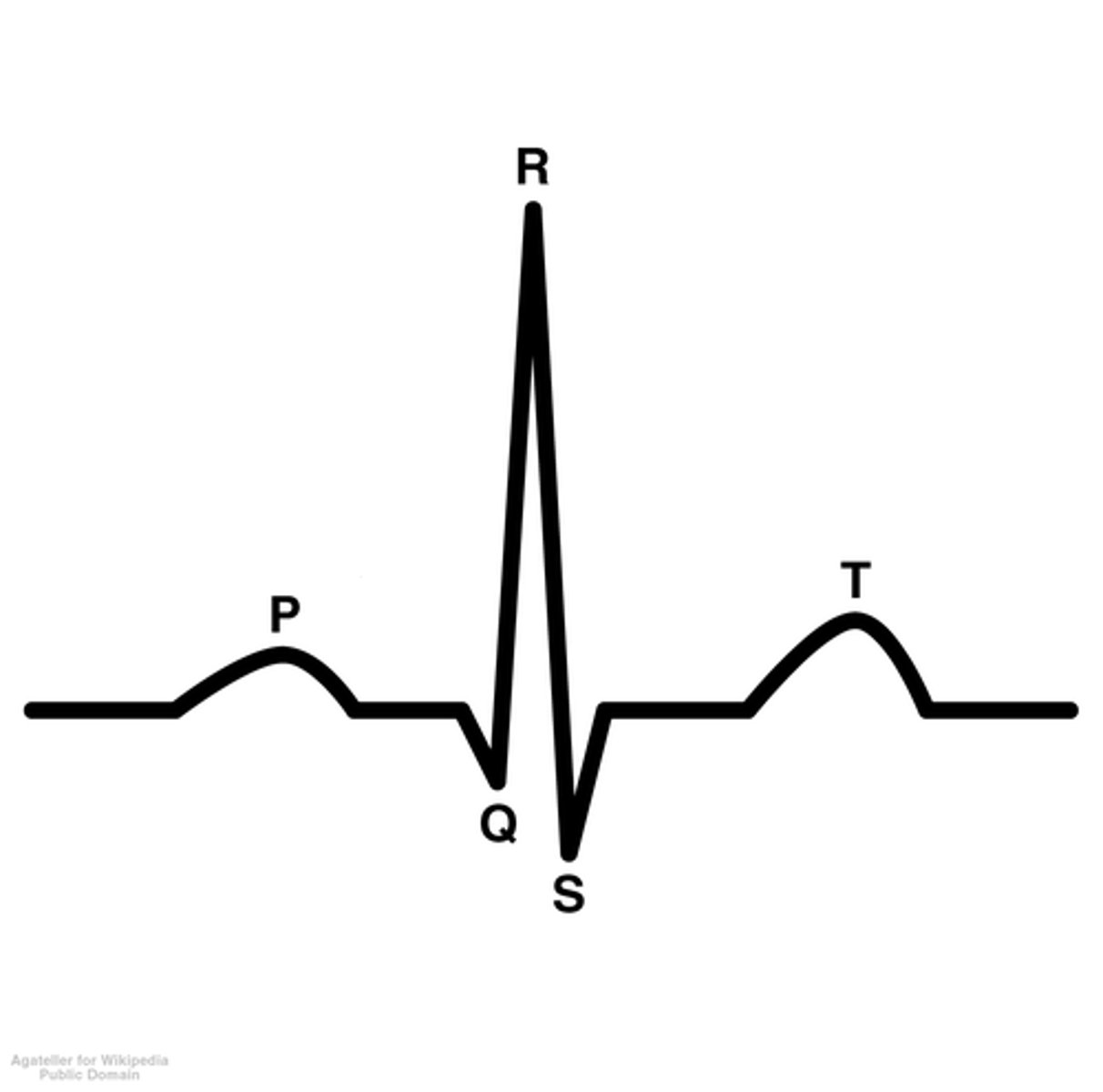
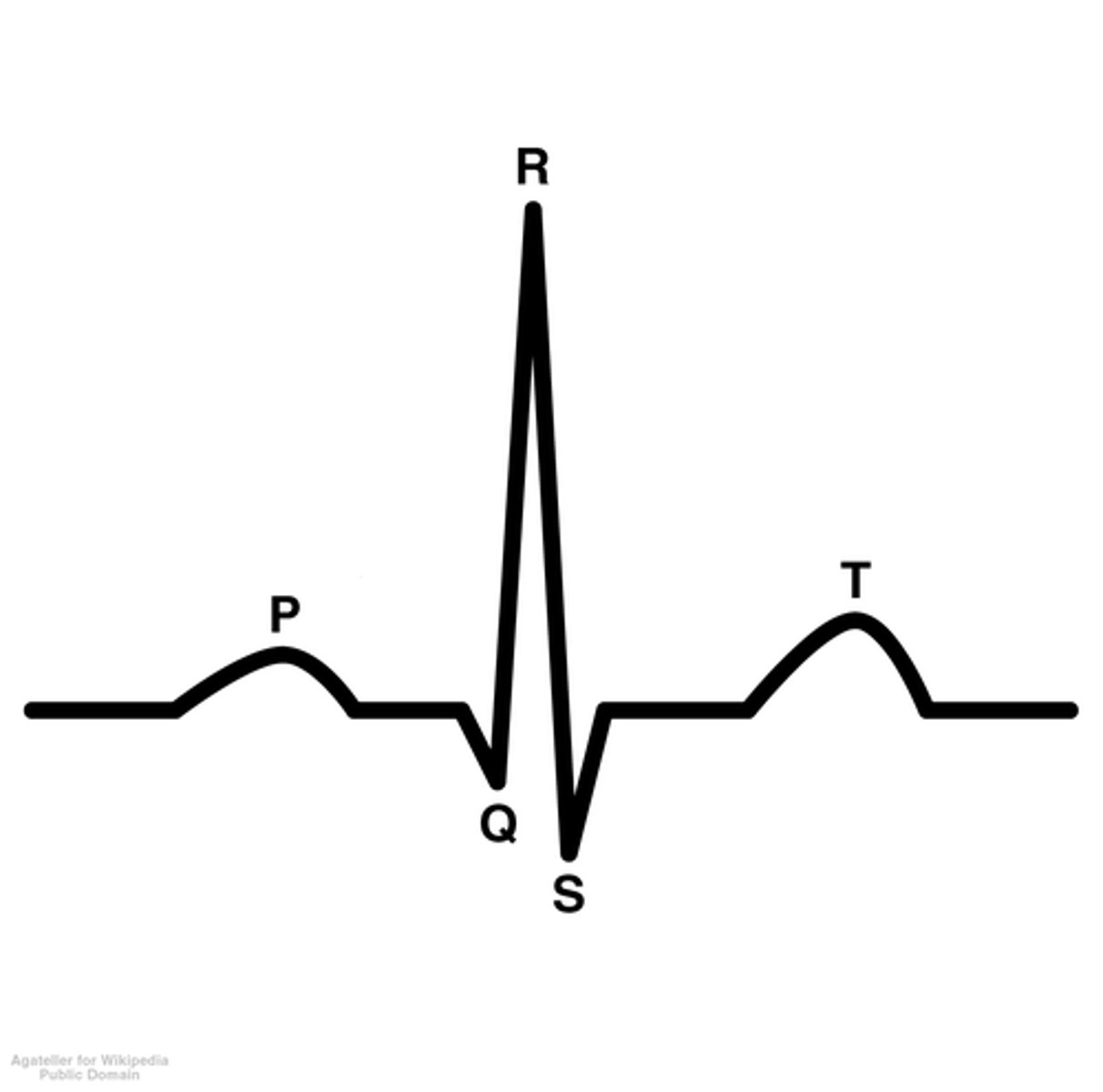
T wave
Ventricular repolarization wave
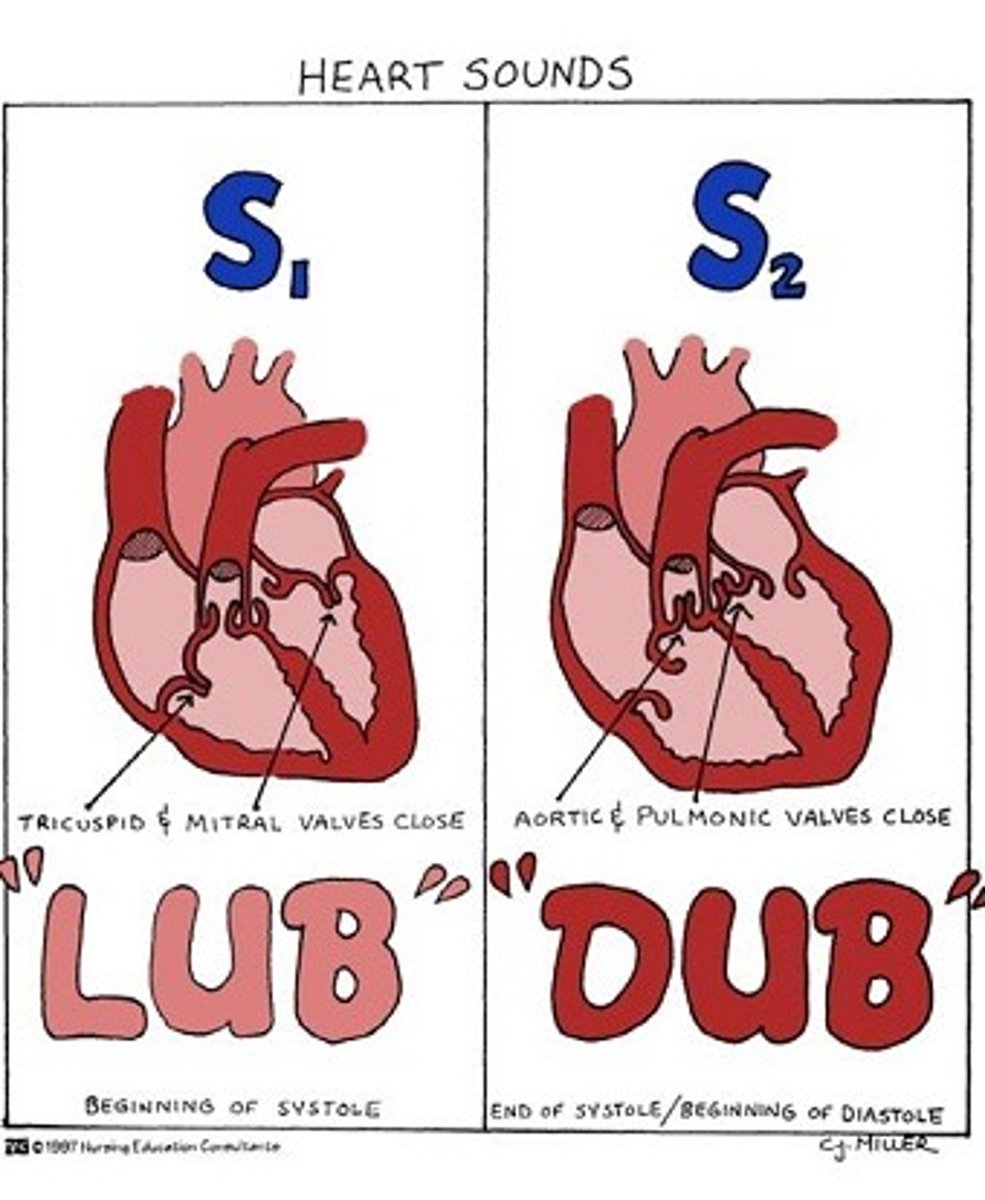
valve closure
How are heart sounds created?
Closure of the atrioventricular valves
How is the s1 "lub" sound created?
apex of the heart (bottom)
S1 sounds are louder at the:
Closure of the semilunar valves
How is the s2 "dub" sound created?
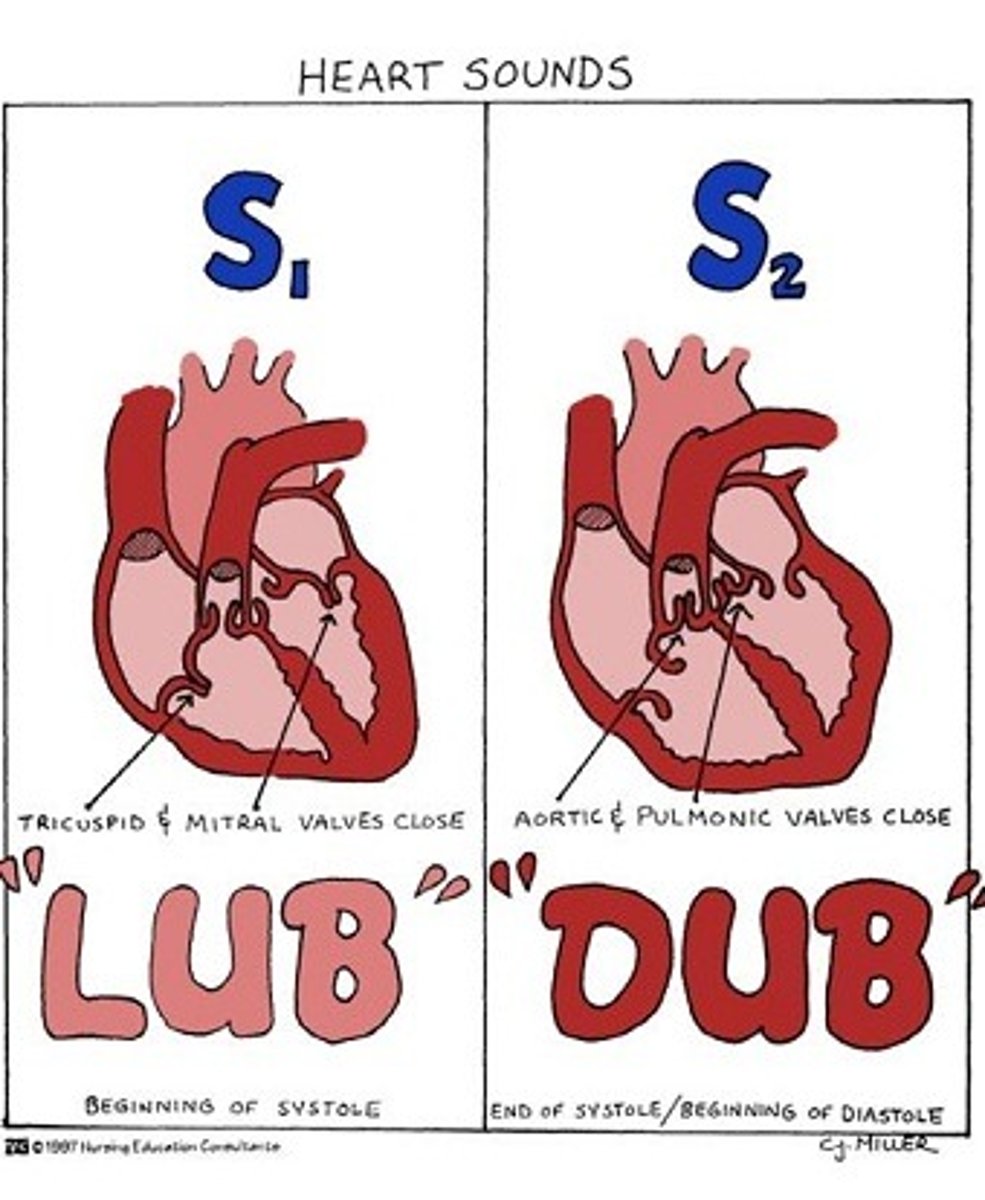
base of the heart (top)
S2 sounds are louder at the:
S3
An extra heart sound that occurs early in diastole (after s2)- is related to the deceleration of blood against the ventricles
"ventricular gallop"
S3 is also known as:
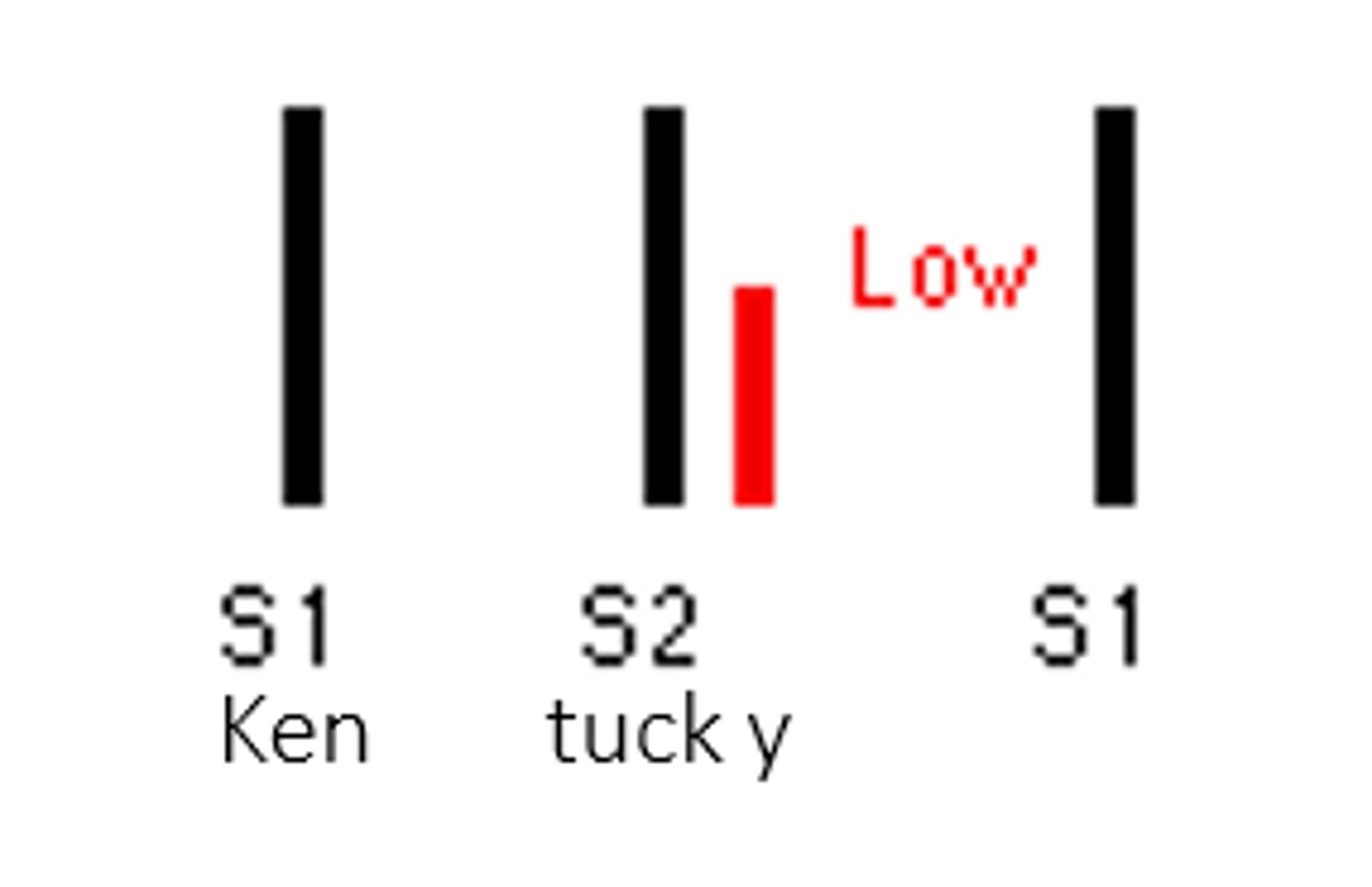
40 years of older
-can be a sign of heart failure
S3 can be normal in young adults and athletes but is abnormal in the age group of:
S4
An extra heart sound that occurs at the end of diastole (before s1)- is related to the atria working hard to contract
"atrial gallop"
S4 heart sound is also known as:

heart murmurs
A swooshing sound that are caused by turbulent blood flow in the cardiovascular system
-can occur anywhere in the cardiac cycle
-can be cognitional or developed
innocent/physiological murmur
A murmur with no symptoms, not caused by a heart problem. Typically, it occurs from extra blood flow in the heart.
abnormal/pathological murmur
A murmur from age-related changes. Heart disease, or a structural problem are the causes.
palpitations and SOB
Patients with an abnormal murmur may experience:
I-IV (6 grades) in order from lowest to highest
How many grades are on the heart murmur grade scale?

The sound it produces from the amount and thickness in the blood.
What determines the intensity of a heart murmur?
crescendo
Stars soft and gets louder:
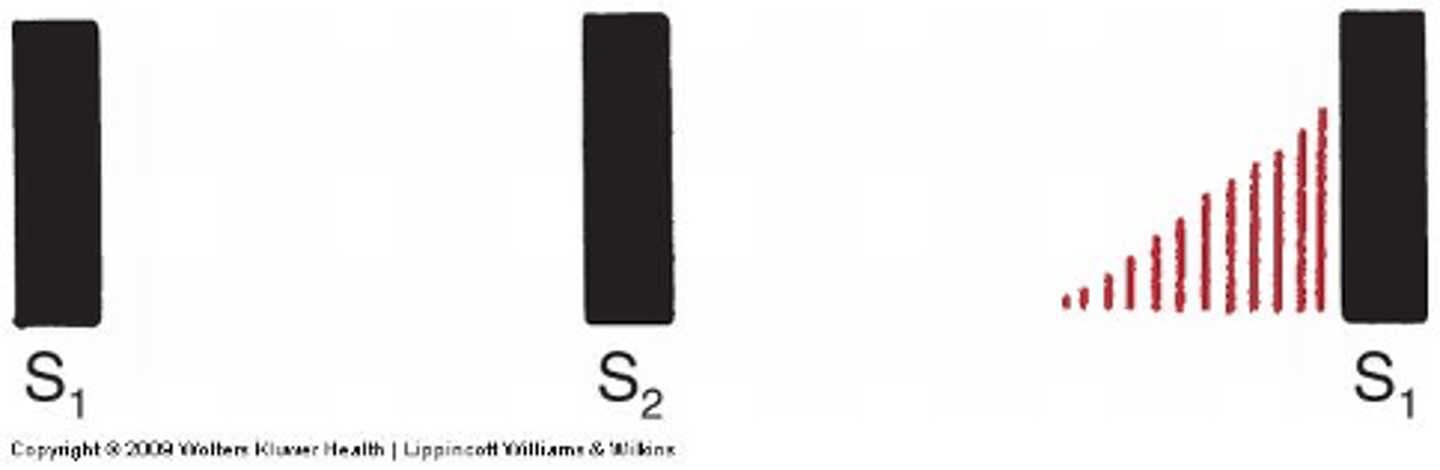
descrendo
Starts soft and gradually fades away:
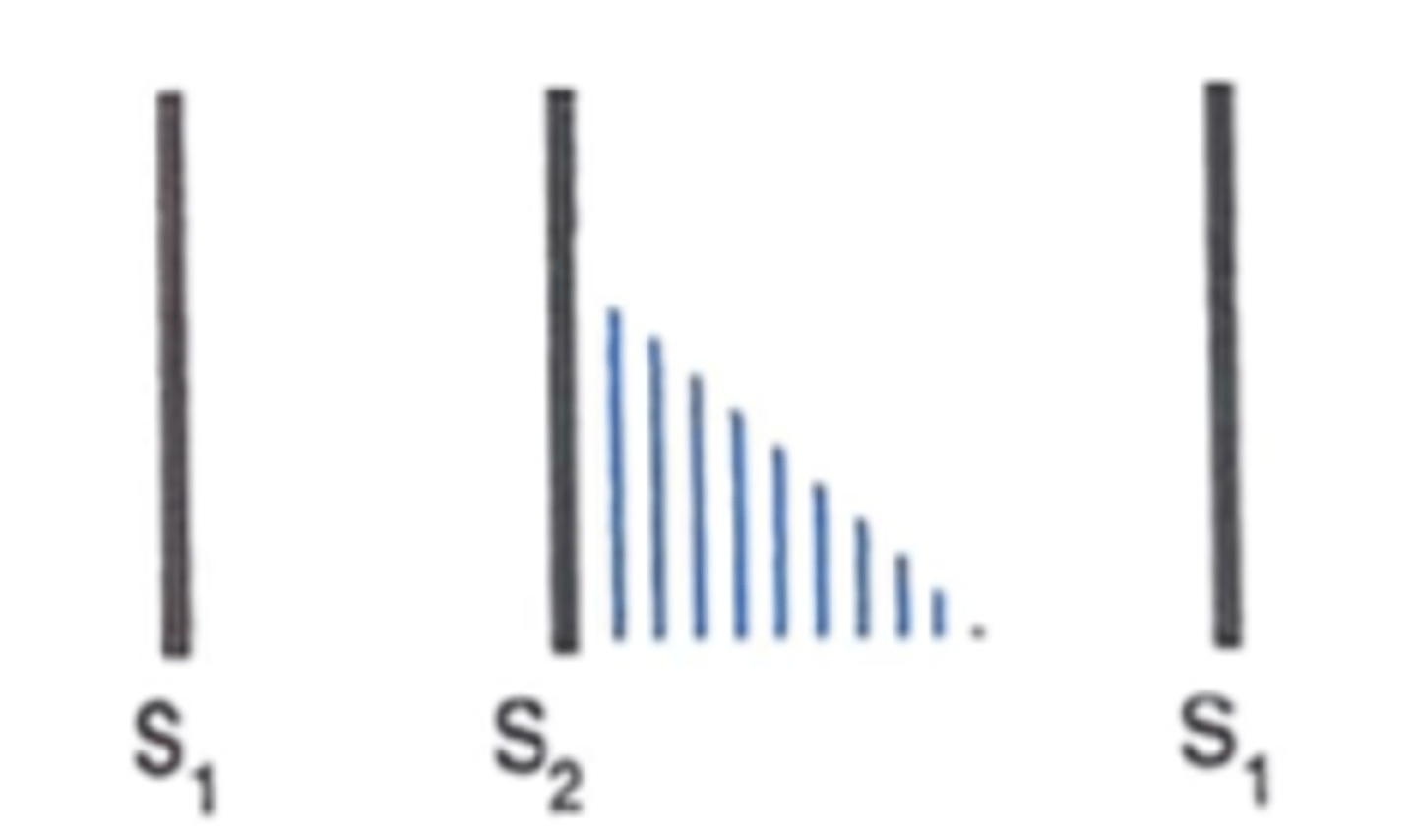
plateau
Same intensity configuration of a murmur:

ejection clicks
High-pitched sounds that occur at the moment of maximal opening of the semilunar valves.
-reflective of cardiac output
-typically heard after S1
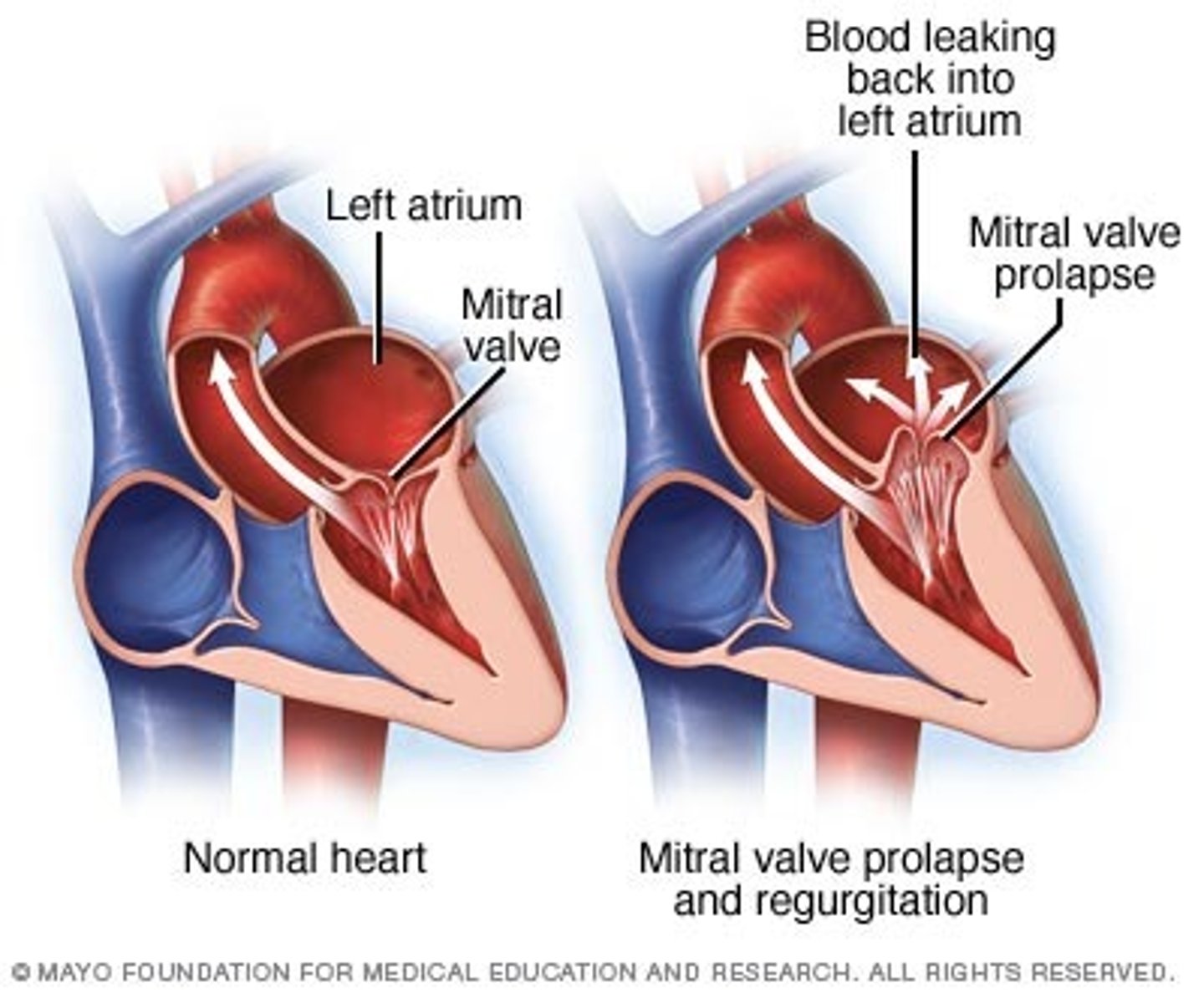
mitral valve prolapse
A midsystolic ejection click is a cardinal finding of:
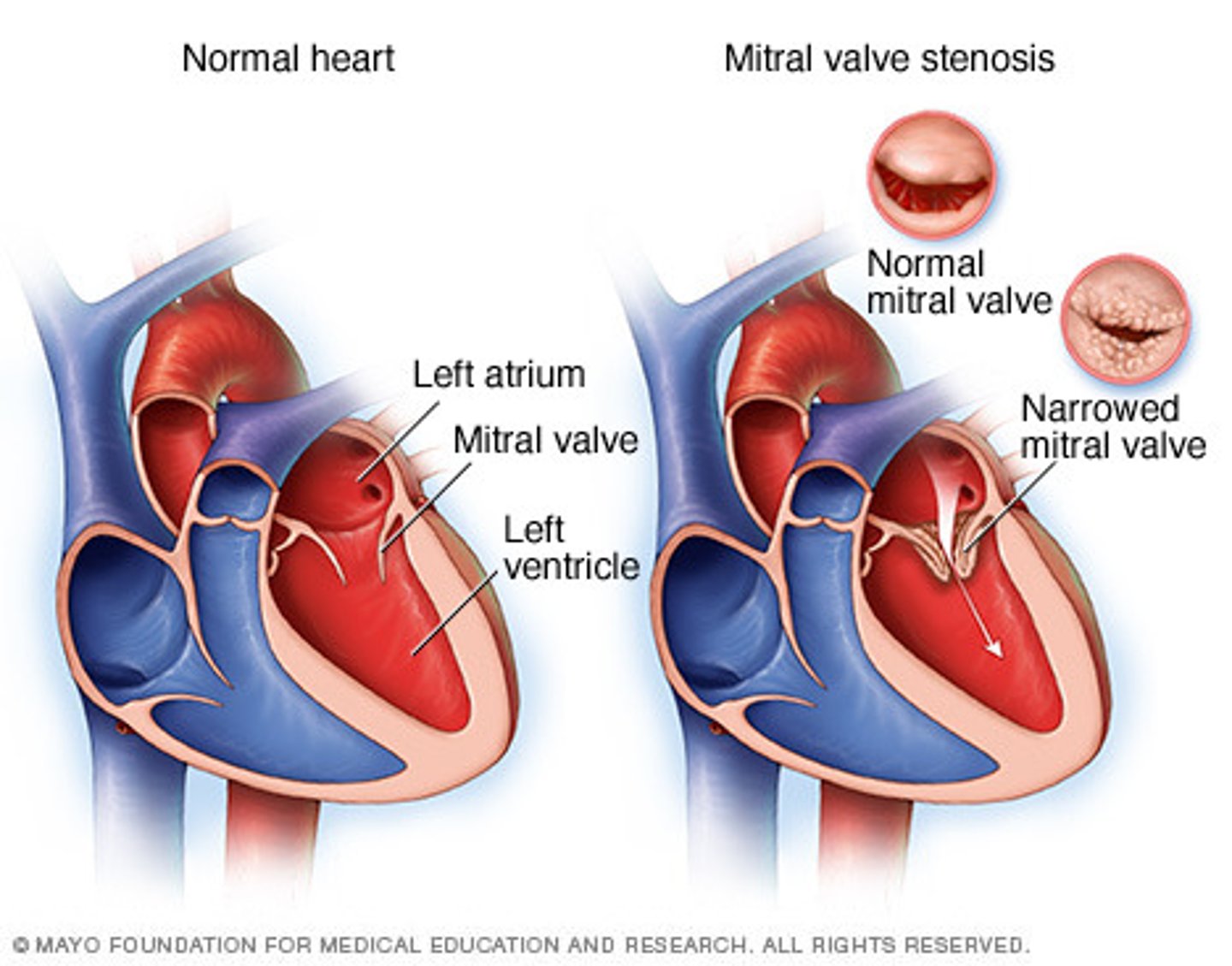
opening snap
Loud, high-frequency found from a stenoic valve opening.
pericardial friction rub
Friction of the visceral and parietal layers
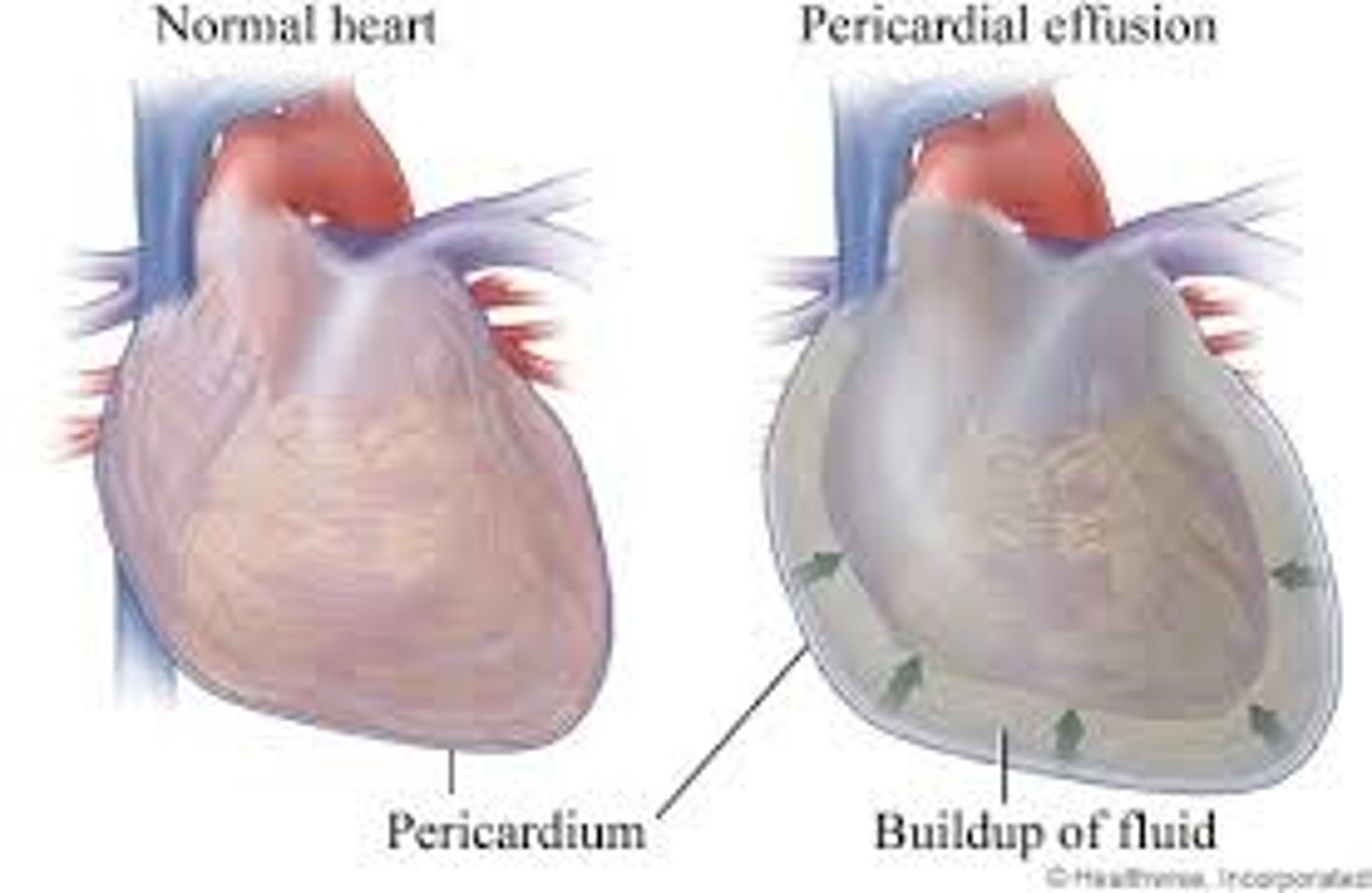
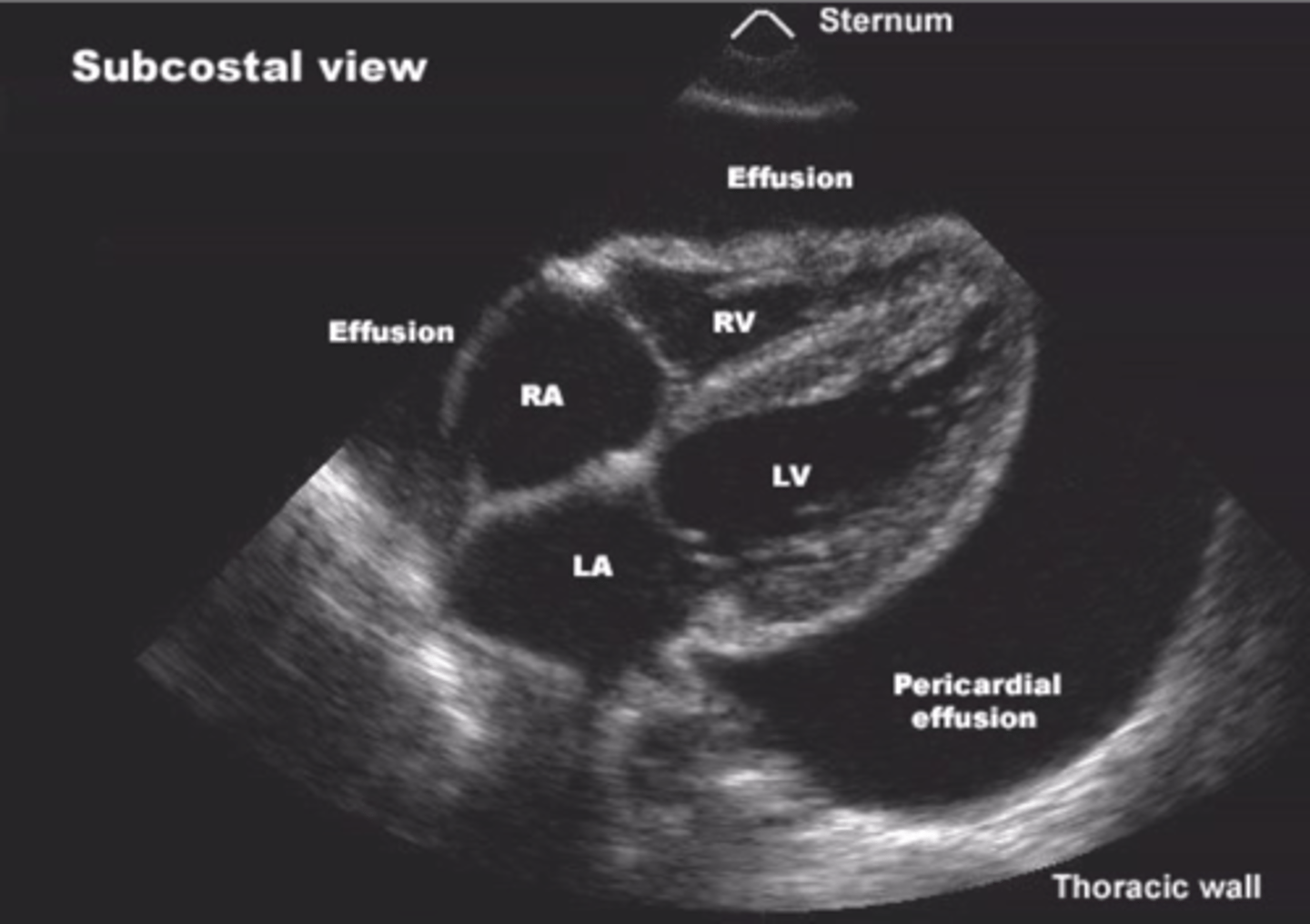
pericardial effusion
A collection of fluid between the pericardial sac and the myocardium.
lipid profile
Blood test used to measure HDL and LDL.
good cholestrol
High density lipoprotein (HDL)

Bad Cholesterol
Low density lipoprotein (LDL)
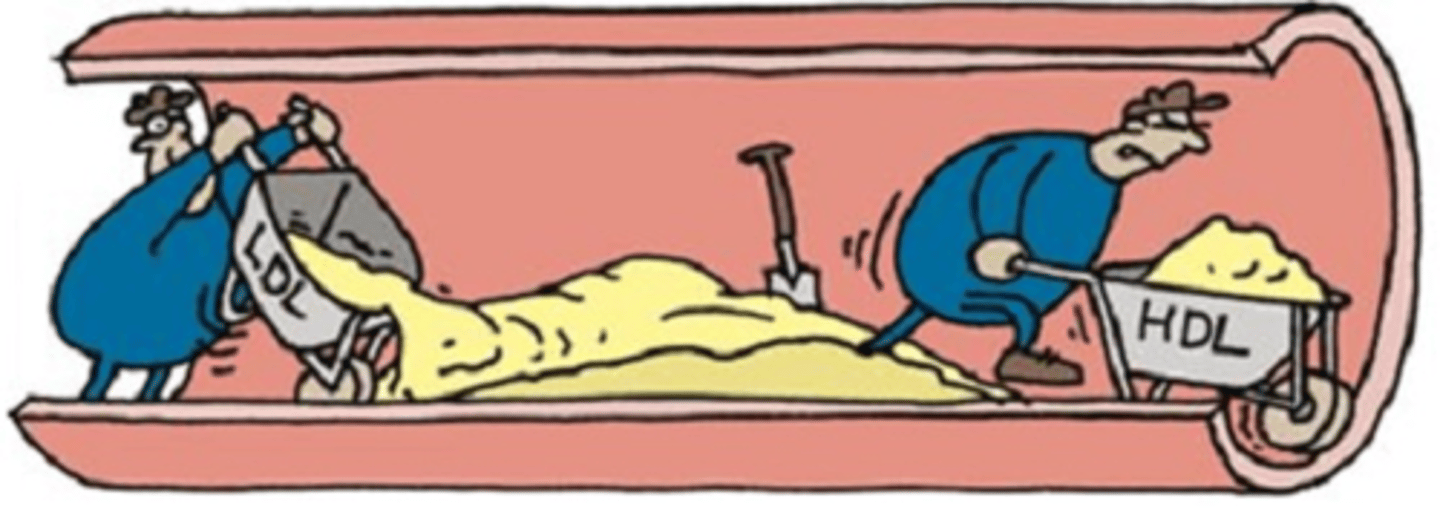

coronary artery disease
Atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries; predictor for strokes
<200 mg/dL
Normal total cholesterol level:
creatine kinase
An enzyme that will increase when it detects damaged cardiac tissue due to decreased oxygenated.
4 to 6 hours
The creatine kinase level will rise ______ after someone experiences chest pain.
troponin
A protein in the cardiac muscle that is released when there is heart damage.
3-4 hours
Troponin is released ______ after damage.
electrocardiogram (EKG)
A measurement of heart electrical activity.
echocardiogram
An ultrasound of the heart.
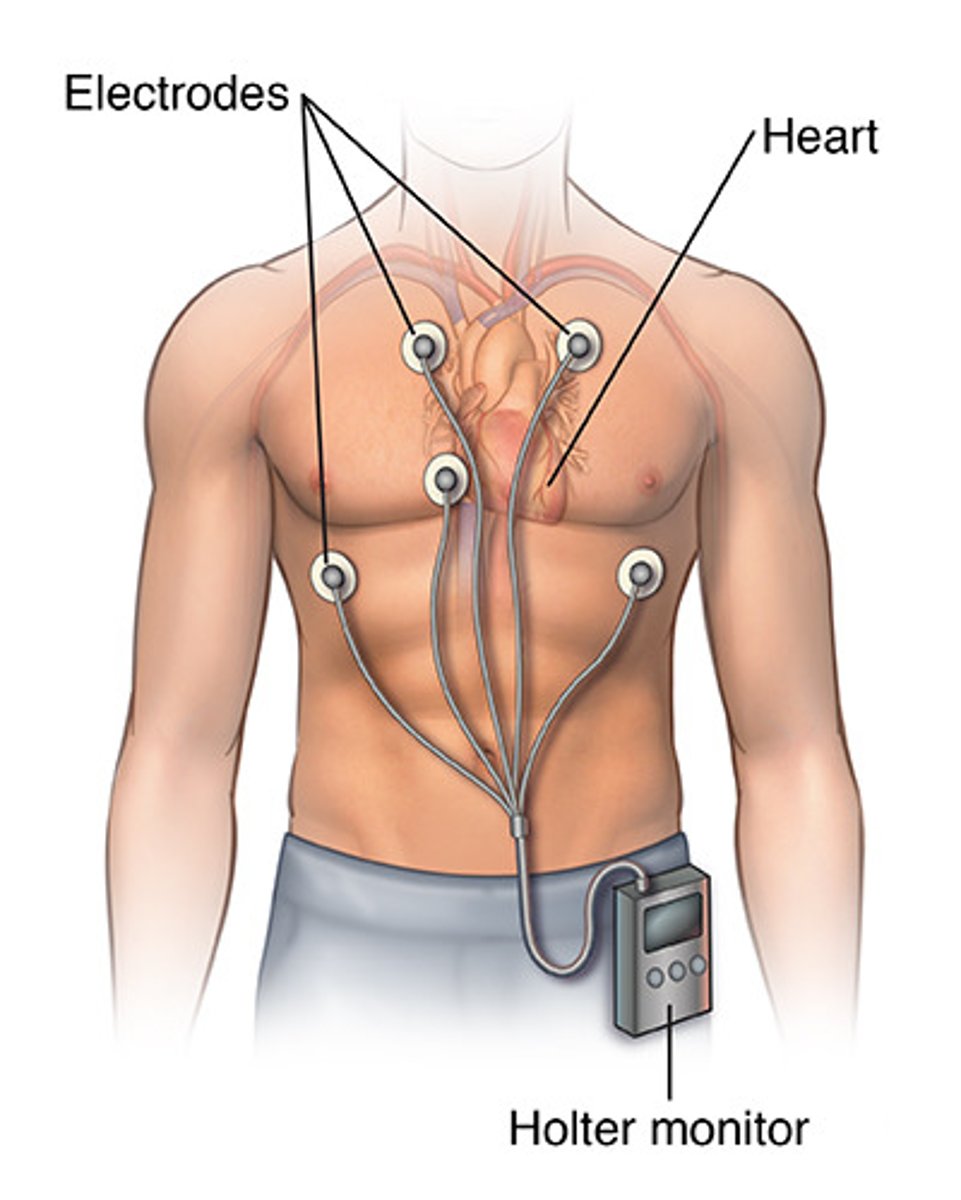
Holter monitor
A portable electrocardiograph that is worn by an ambulatory patient to continuously monitor the heart rates and rhythms over a 24-hour period.
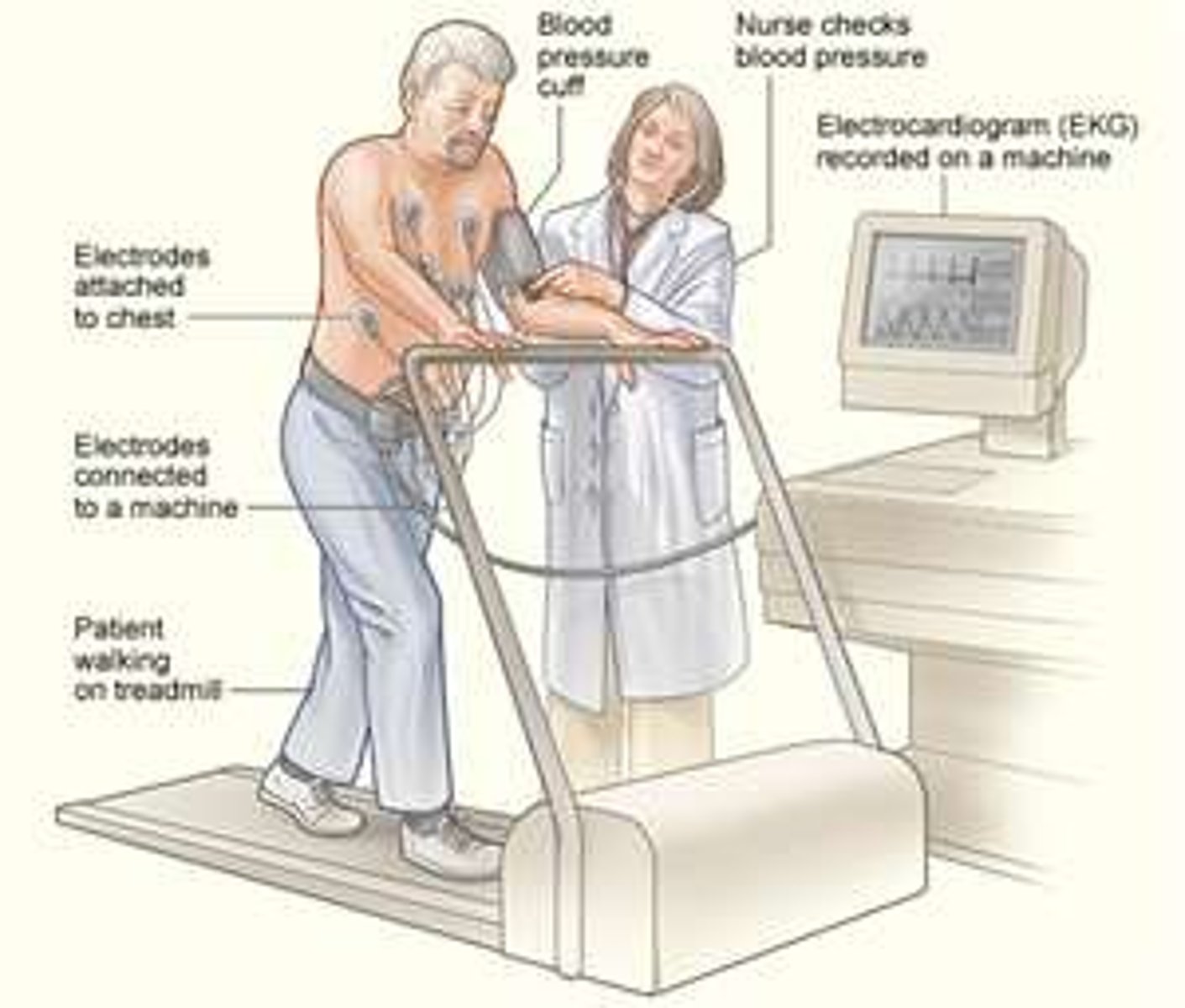
Exercise stress test
Study that evaluates cardiac function during physical stress by walking on a treadmill. Cardiac function is monitored during this study.
rheumatic fever
Untreated strep throat that can damage the heart
Smoking, diet, exercise, hygiene, obesity
Modifiable cardiac risk factors:
genetics, age, sex
Non-modifiable cardiac risk factors:
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
The #1 cause of death in women:
1 out of 3 women die from this
heart-healthy diet
A diet that includes fruits/vegetables, whole grains, lean meat, low sodium and lowfat. Eliminating unsaturated fats such as greasy foods.
at least 20 mins 3x a week
What amount of exercise lowers the risk of CHD?
angina pectoris
Chest pain
Onset
Location
Duration
Characteristics
Aggravating/Alleviating Factors
Related Symptoms
Treatment
Severity
OLDCARTS to assess a symptom
Severe chest pain often described as an elephant sitting on the chest
Most classic symptom of a myocardial infarction:
heart palpitations
Increased awareness of the heart beating; known as a "fluttering" or racing feeling
central cyanosis
Cyanosis of the mucous membranes such as the tongue, conjunctiva, lips, and skin.
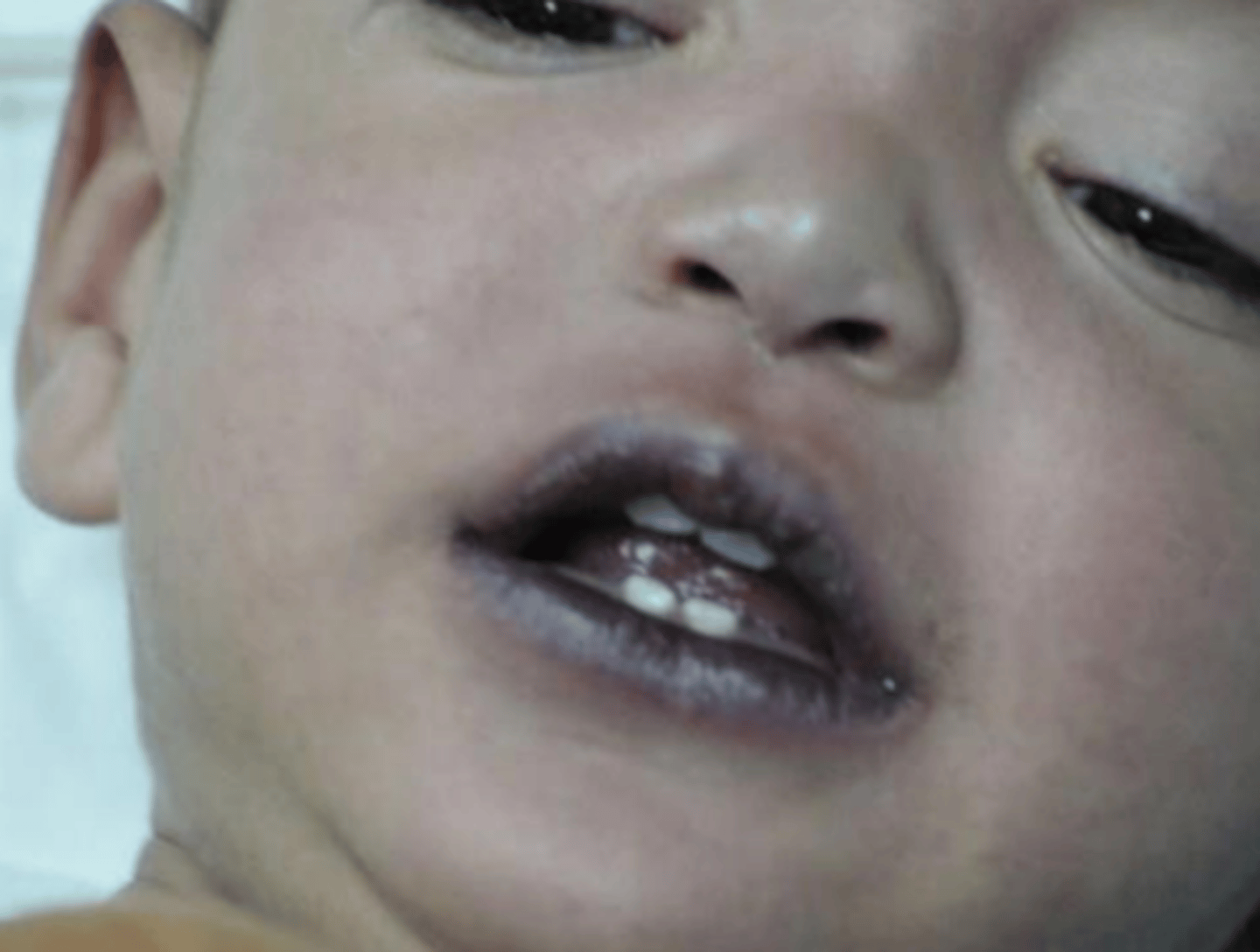
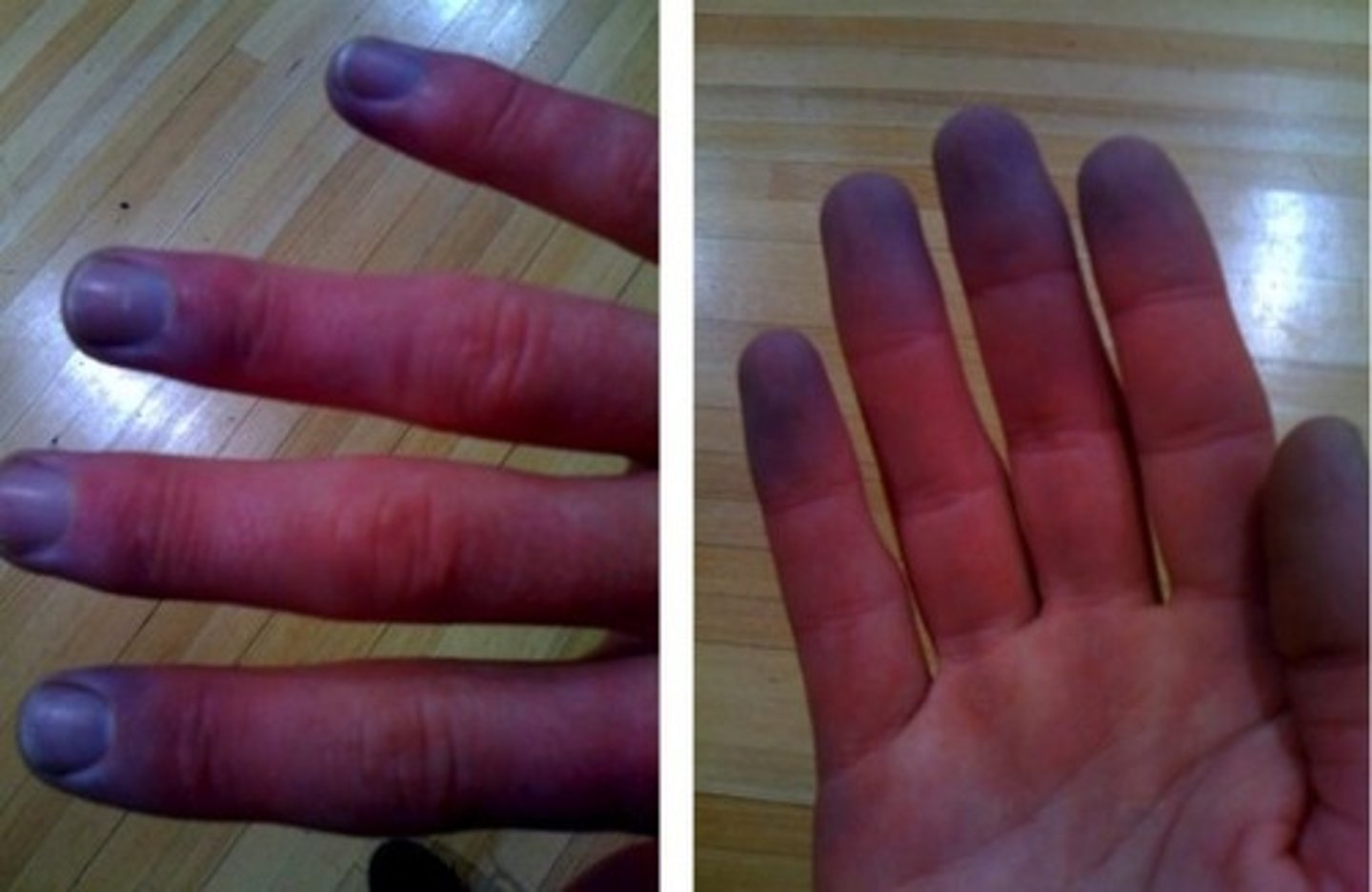
peripheral cyanosis
Cyanosis of the peripheral extremities such as the nailbeds, palms, soles, and tips of ears.

nocturia
-can be a symptom of CHF
Excessive urination at night.
diaphoresis
Profuse or excessive sweating.
30 degree
The HOB should be at a ______ angle when completing a cardiac assessment.
mitral
What is the point of maximal impulse?
heaves or lifts
Sustained, forceful, outward thrusting of the ventricle secondary to increased workload.
apical
Sometimes, you can see the _____ pulse at the 5th ICS mid-clavicular line.
at the apex
Where would you see a left ventricular heave?
at the sternal border
Where would you see a right ventricular heave?
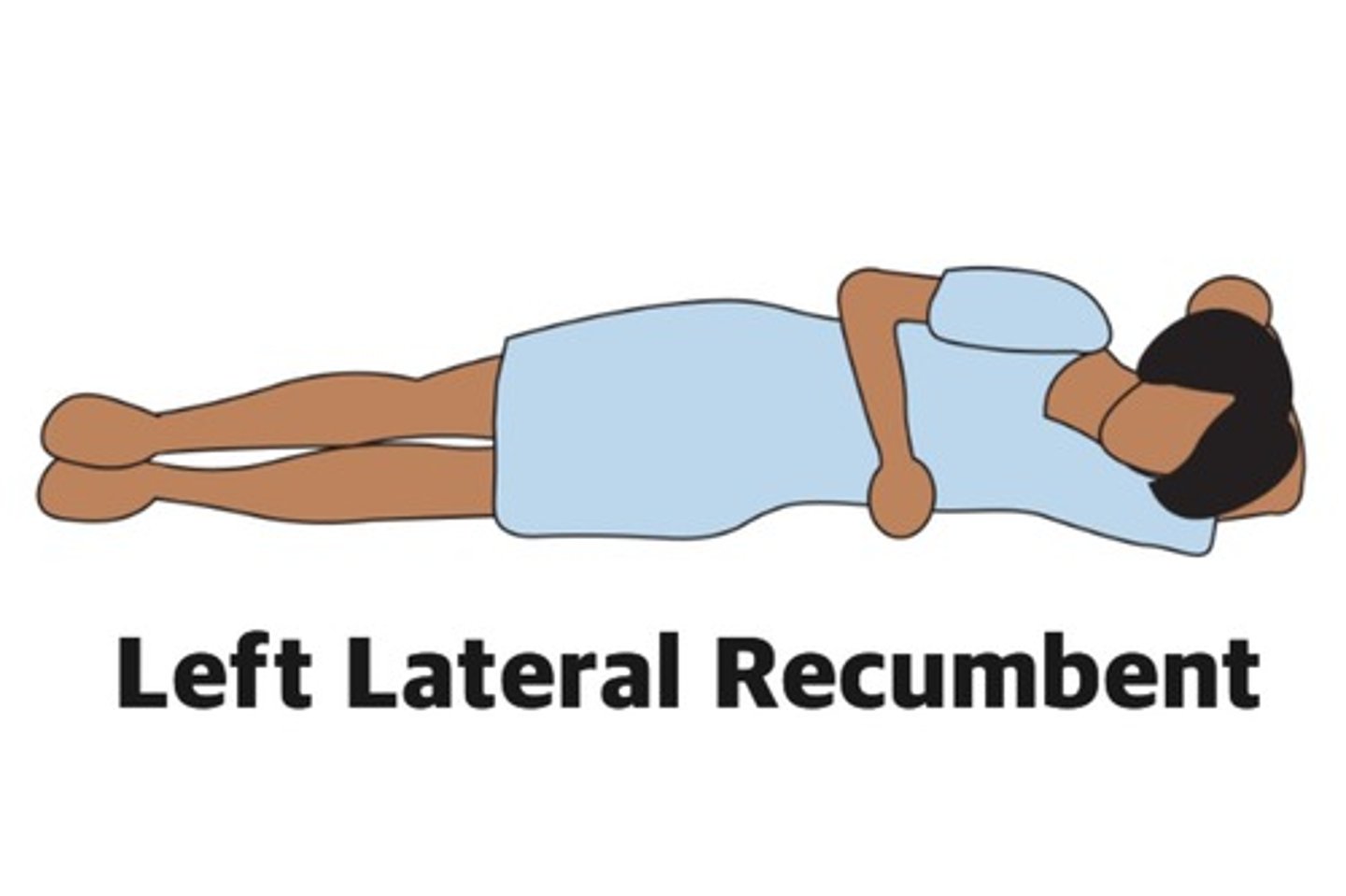
left lateral recumbent position
What position is best when palpating the apical pulse?
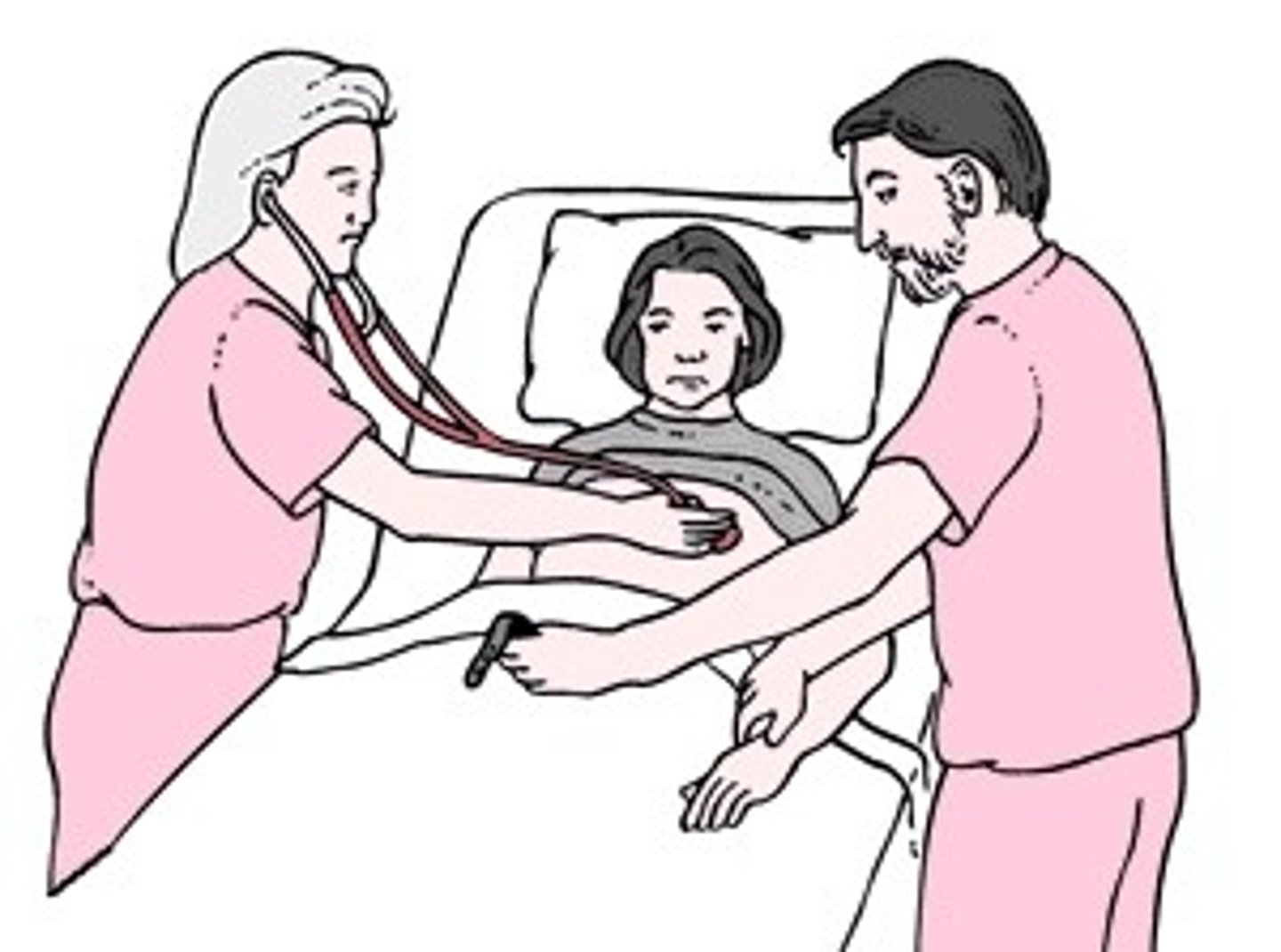
Palpate the carotid or radial pulse to compare
While auscultating the apical pulse, what do you do with your other hand?
pulse deficit
Difference between the apical and radial pulse rates; is concerning if it is greater than 10
high-pitched sounds
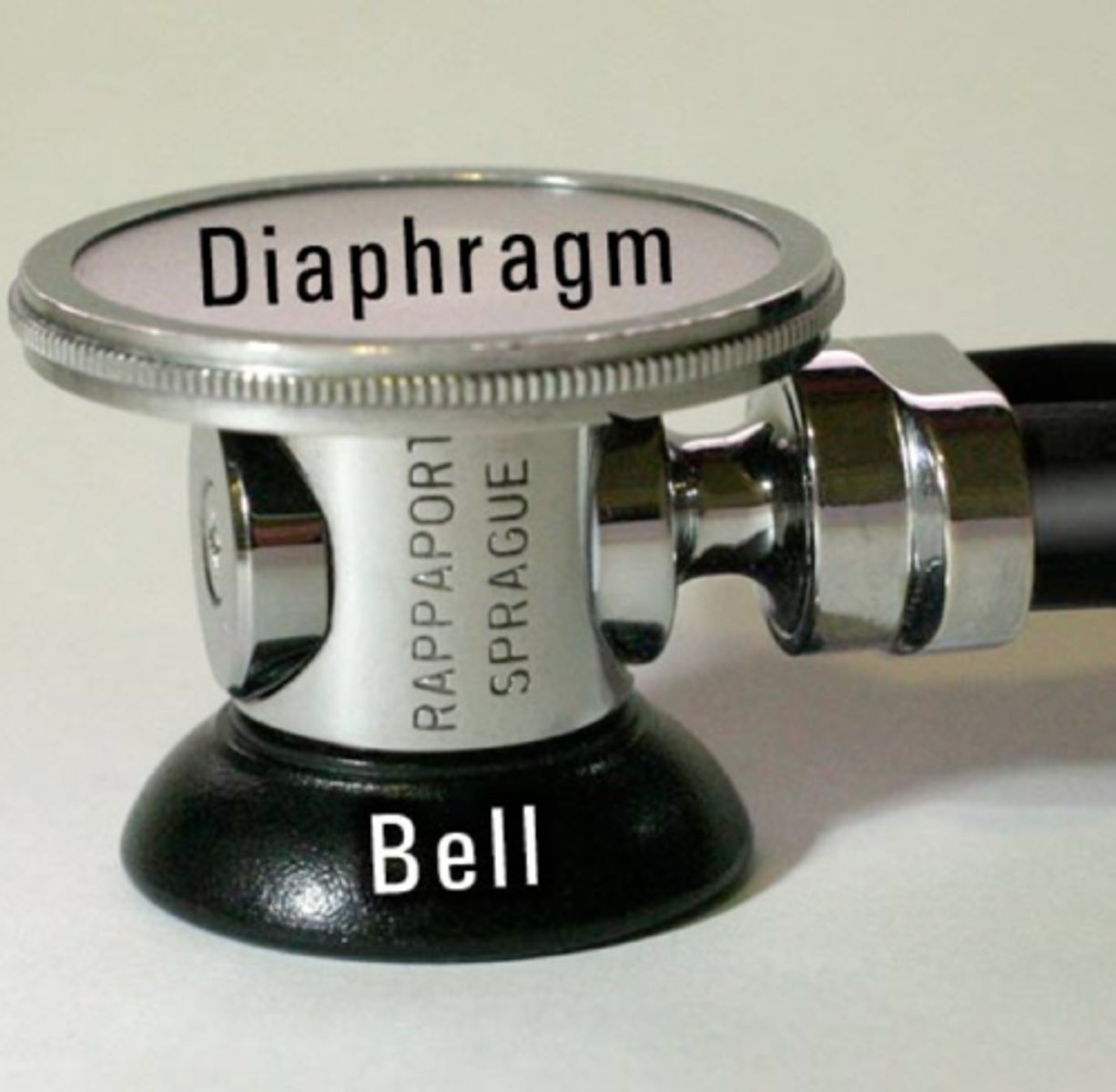
Use the diaphragm to listen to:
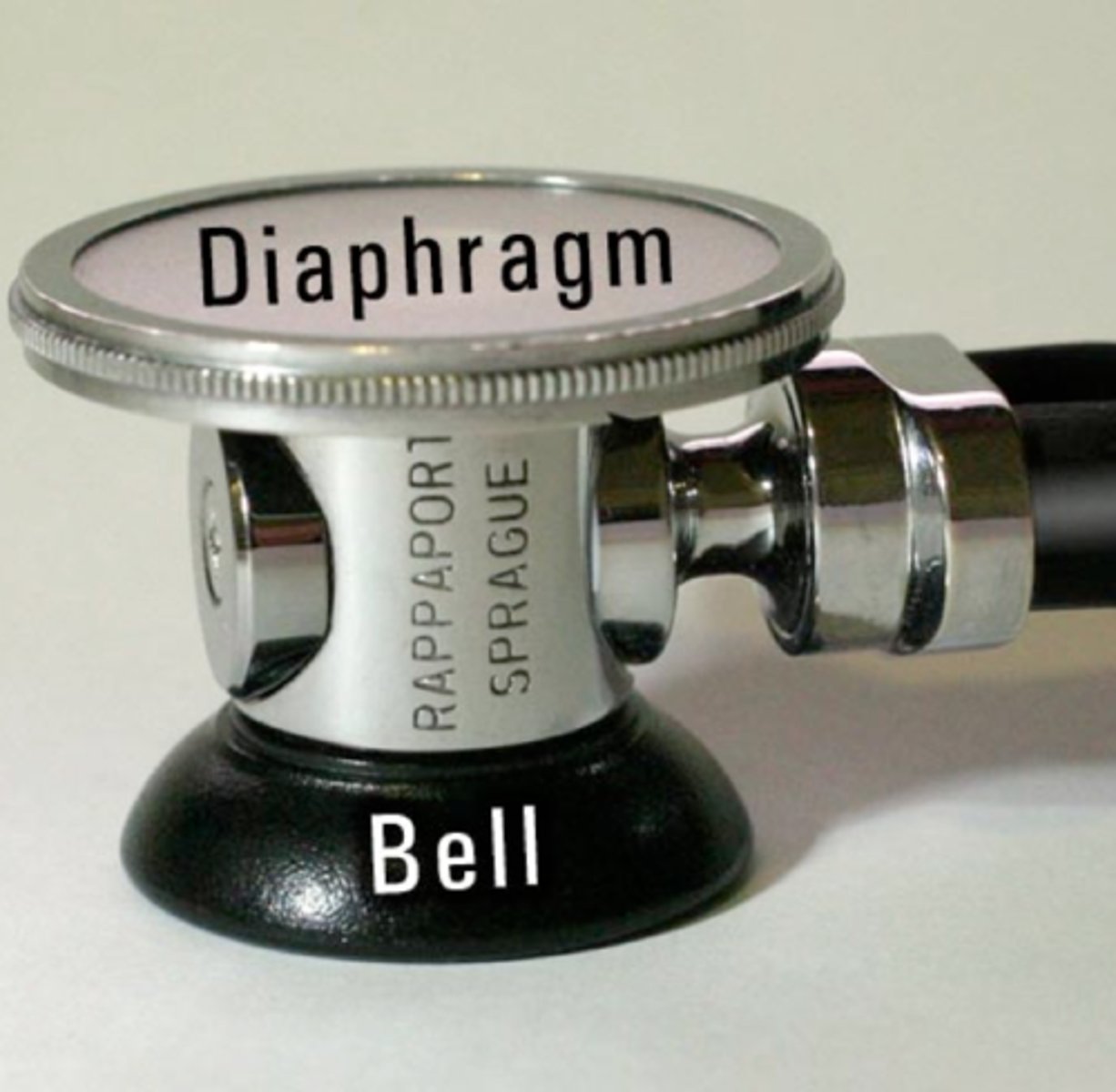
low-pitched sounds
Use the bell to listen to:
Ask them to hold their breath.
What do you instruct your patient to do when listening to the carotids?
Split s2
Normal heart sound that affected by respirations.
reduce deaths from HD and strokes
Main cardiac goal of healthy people 2030:
-low levels of HDL
-high levels of total cholesterol and LDL
The US Preventative Services Task Force recommends that the risk factors for HD are:
Every 4 to 6 years
The American Heart Association recommends all adults aged 20 or over have their cholesterol checked how often?
cholesterol and cancers
Red meats can put an individual at risk for _______.
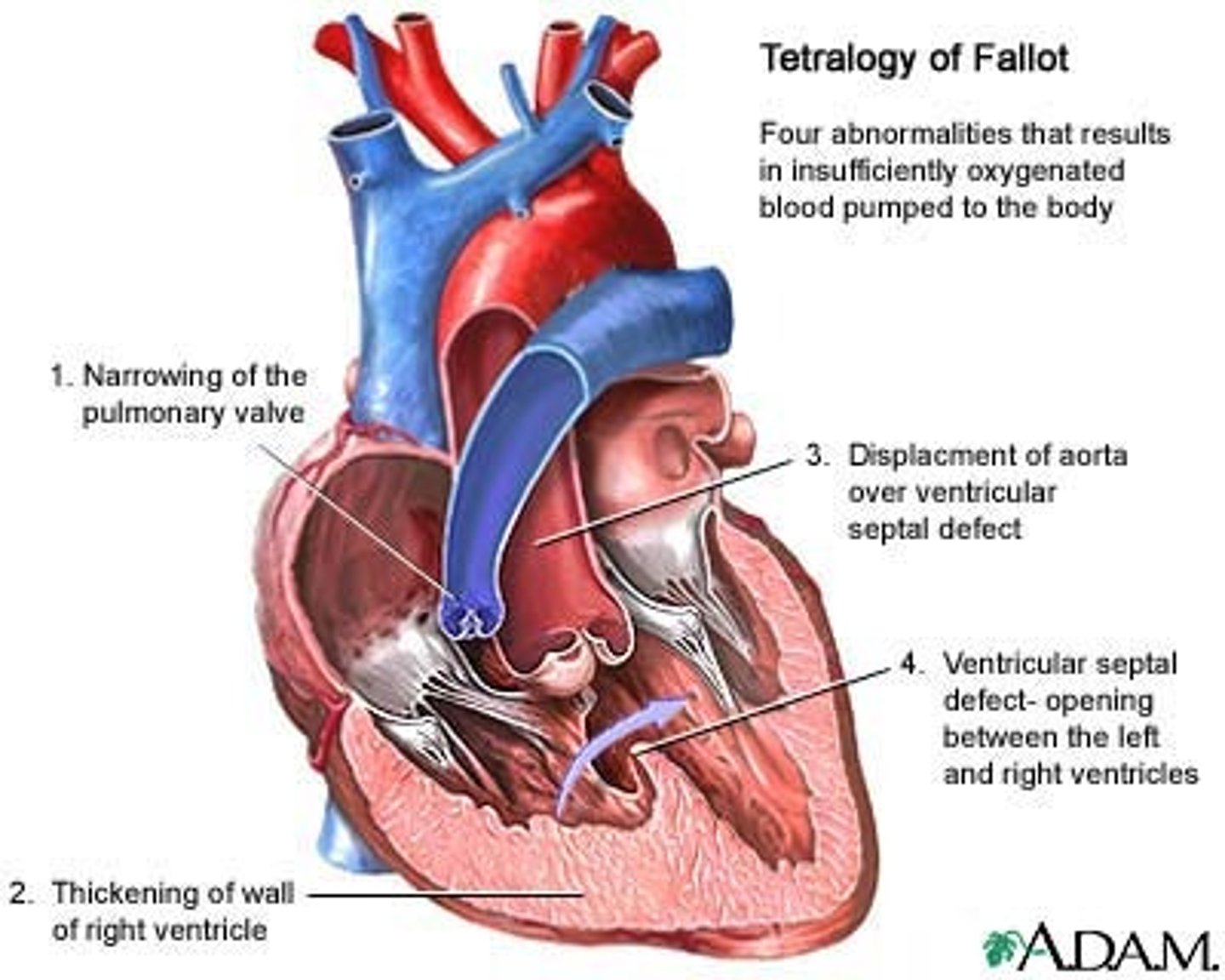
tetralogy of fallot
Congenital malformation is commonly seen in infants
turning blue or extreme fatigue
A key sign of cardiac malfunction in infants or children:
extreme fatigue or changes in ADLs
A key sign of cardiac malfunction in eldery: