AP Biology Chapter 9: Cell Reproduction (Mitosis) - Majoros
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Cell cycle
series of events in which a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form two daughter cells
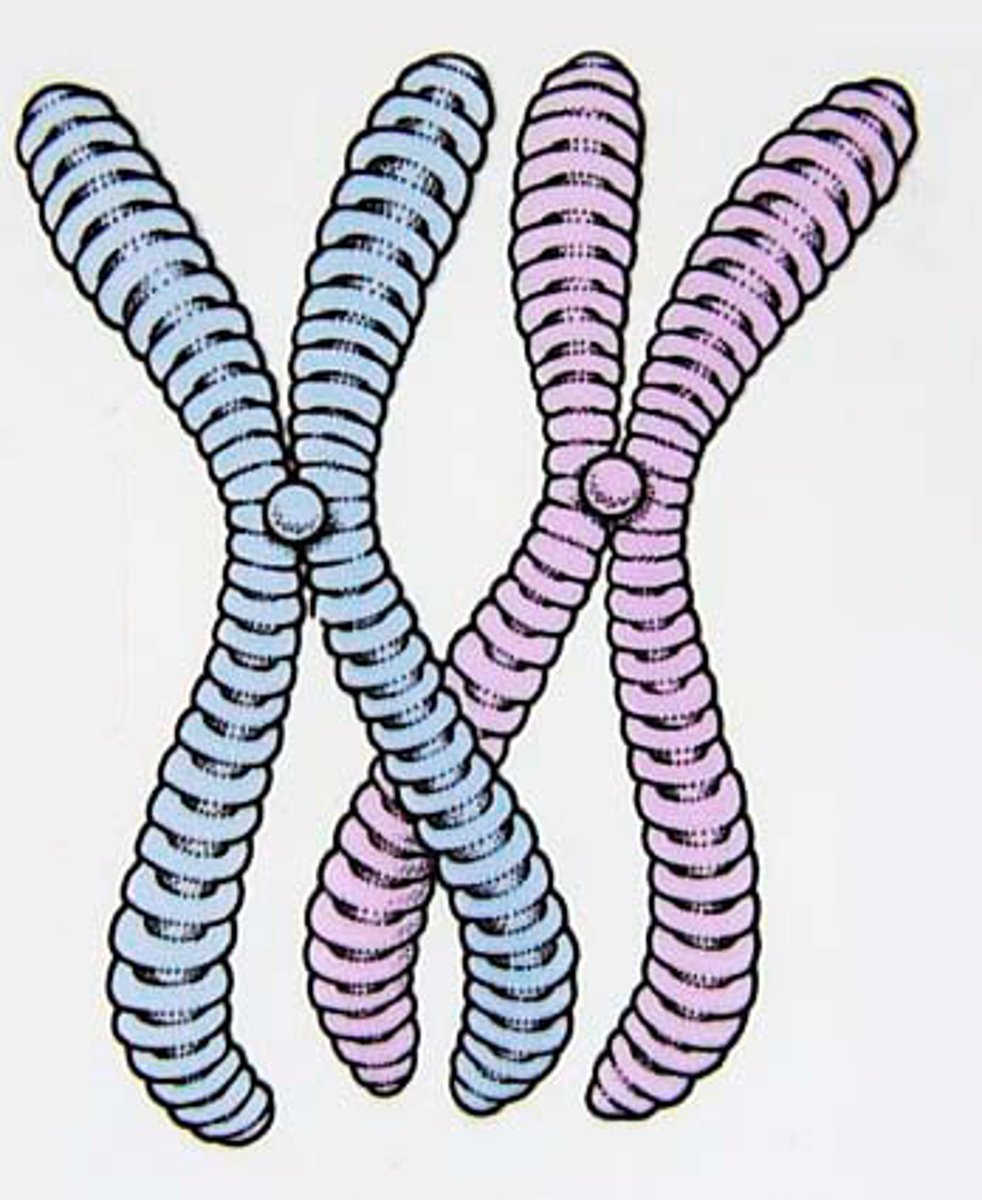
chromosome
Each chromosome consists of one very long DNA molecule and associated proteins; contains thousands of genes
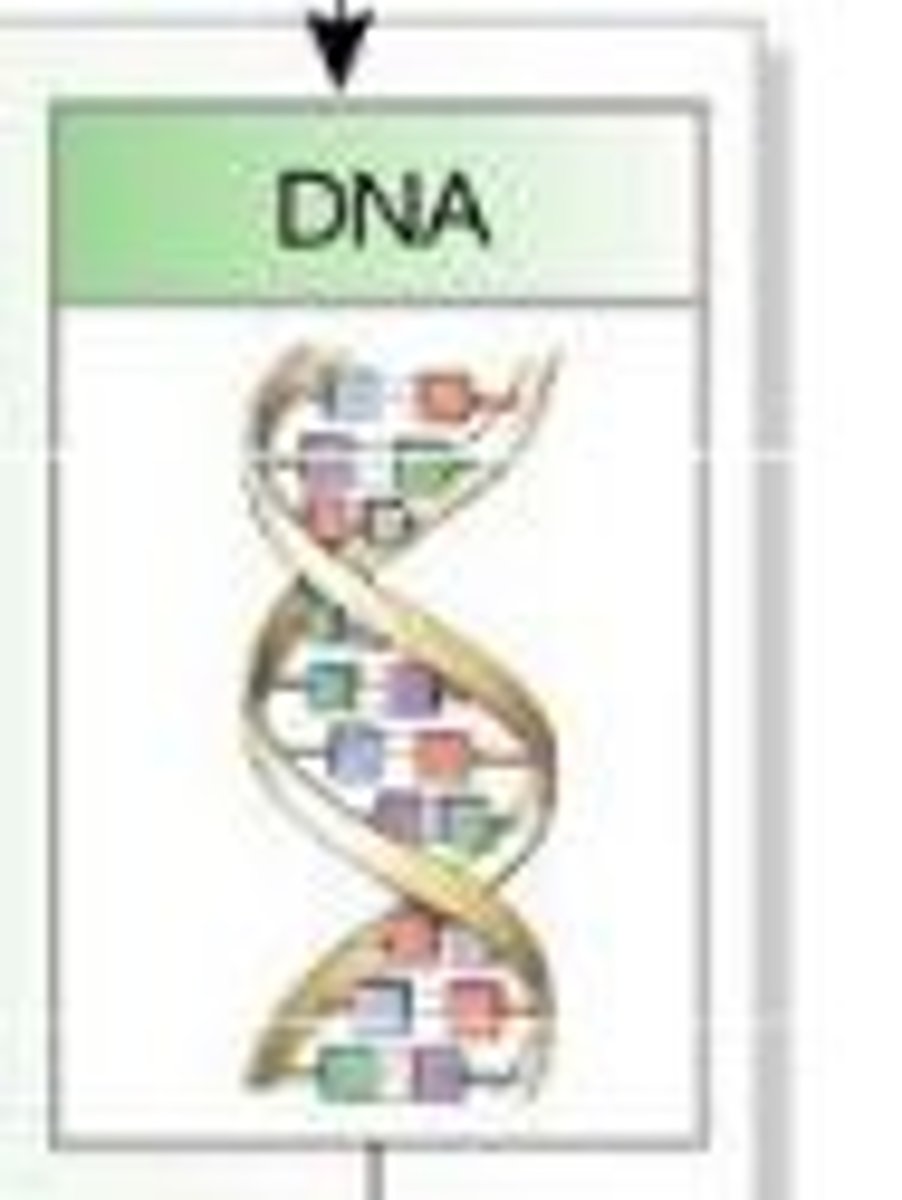
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
A complex macromolecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes; instructions to make proteins
binary fission
type of asexual reproduction in which a prokaryote replicates its DNA and divides in half, producing two identical daughter cells
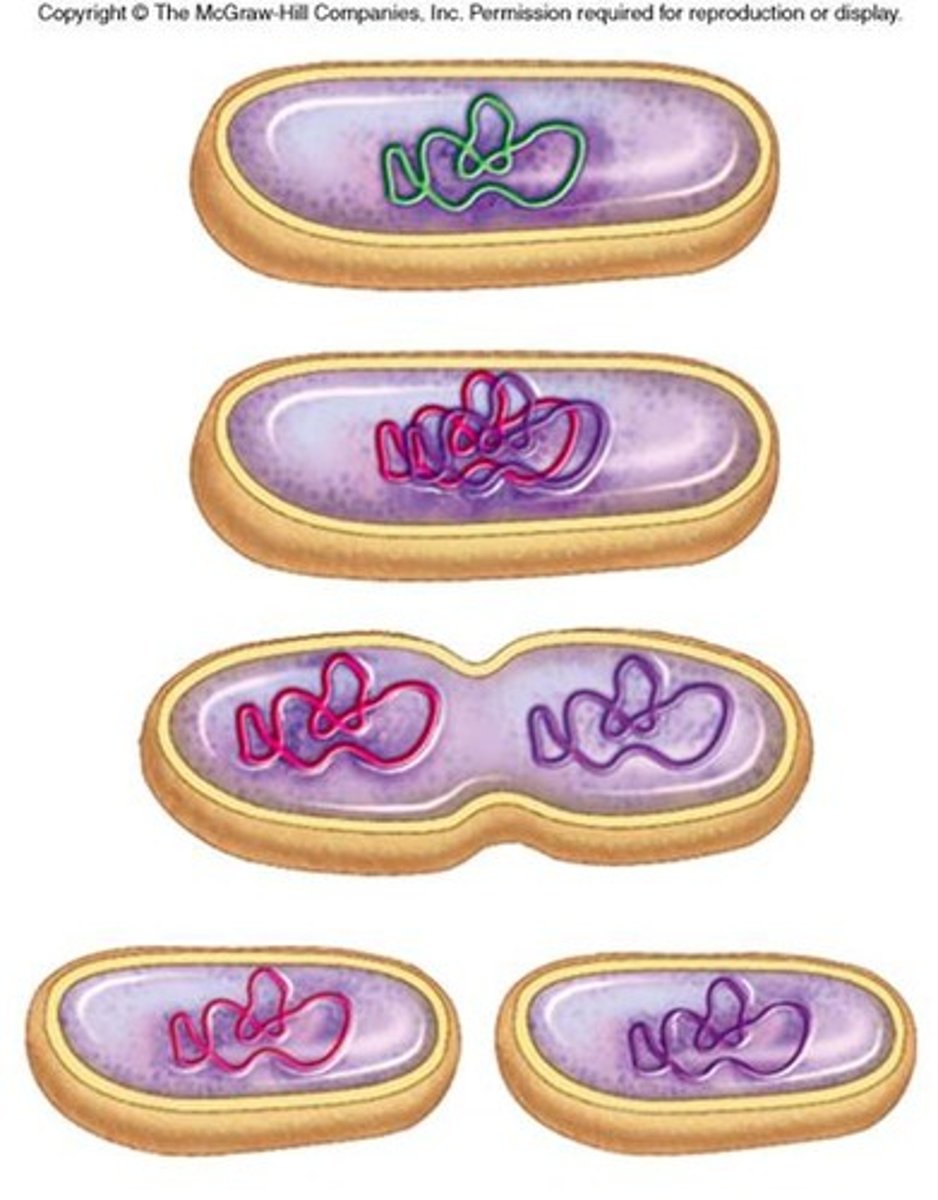
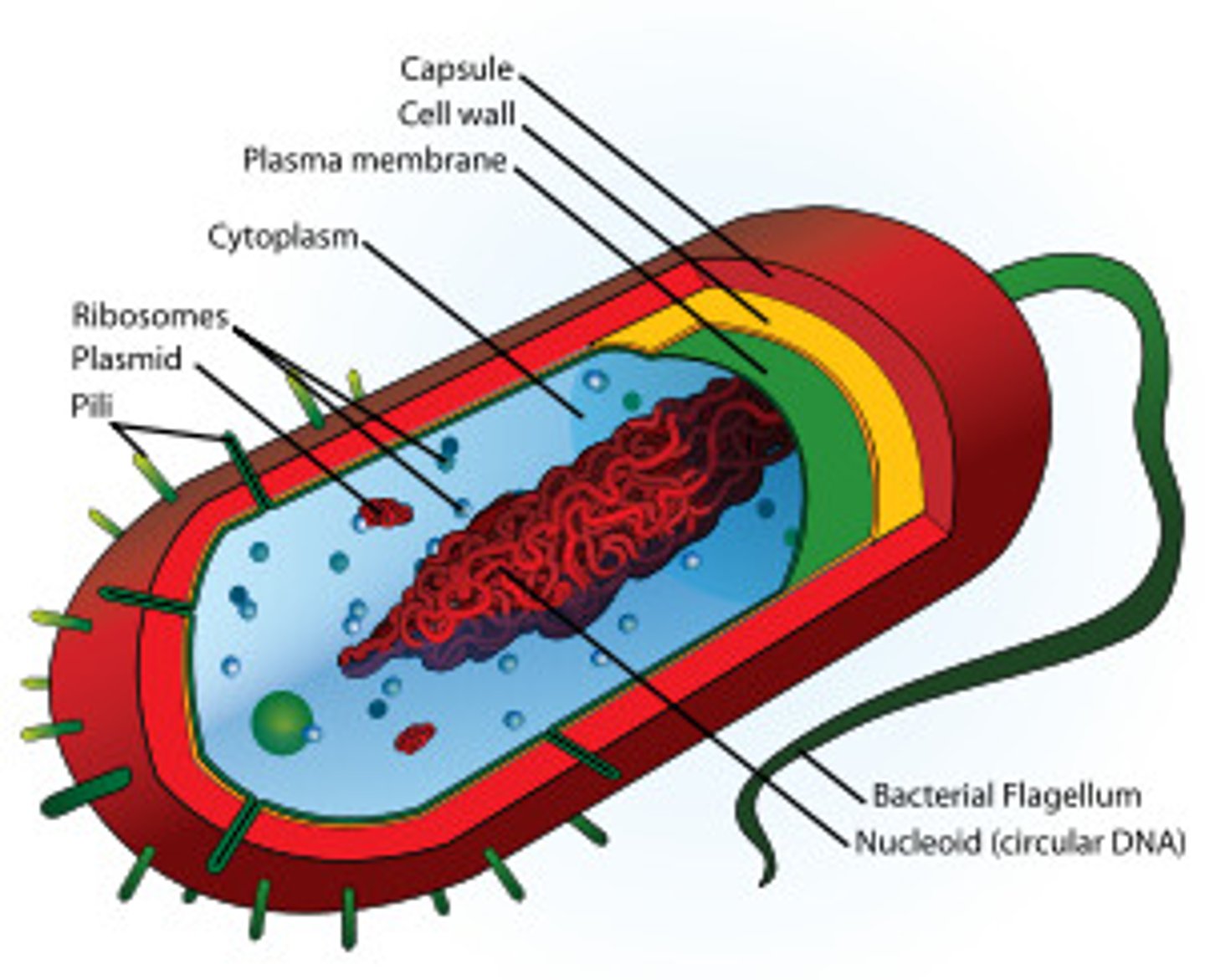
Prokatyote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles; ex. bacteria
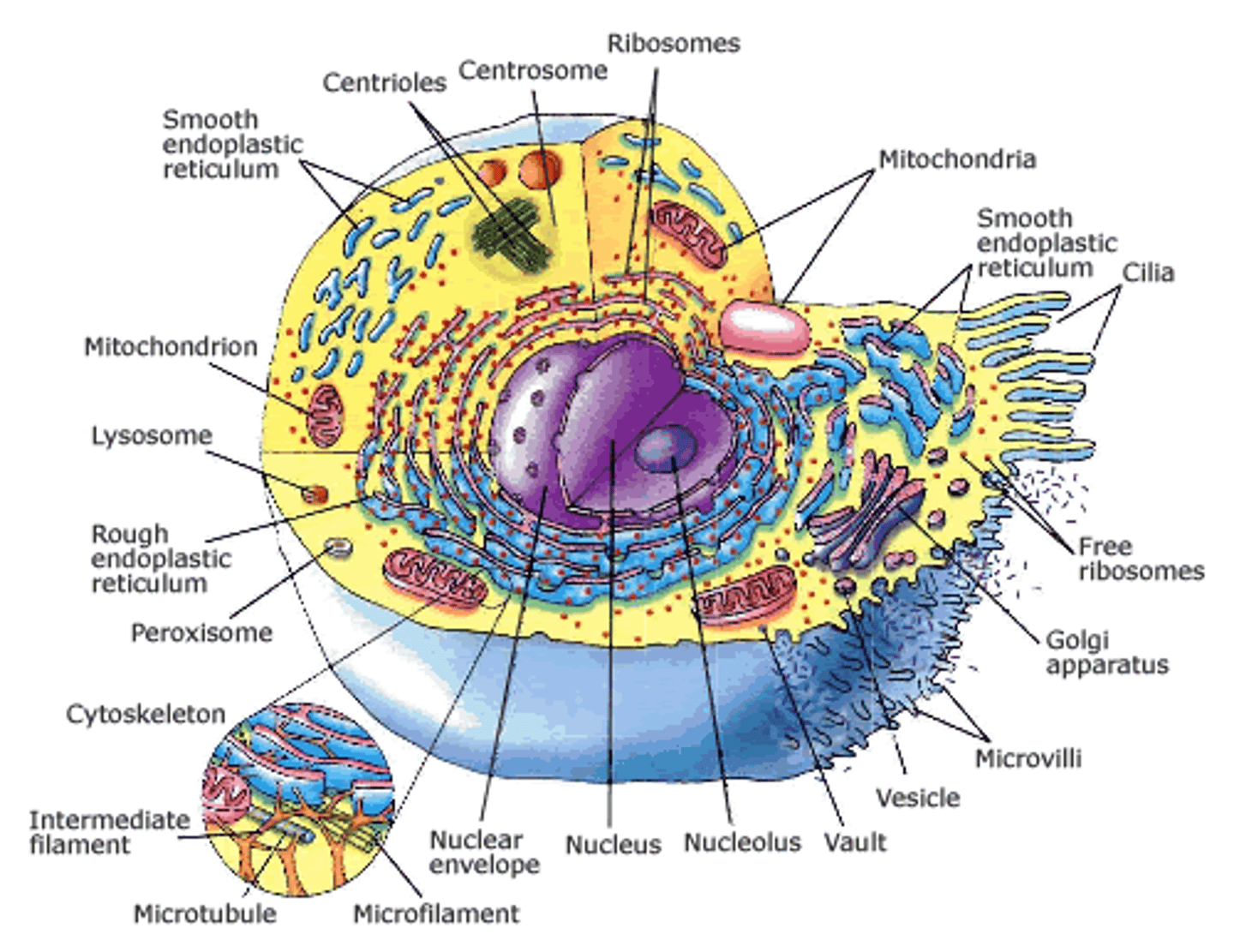
Eukaryote
organism whose cells contain a nucleus and membrane bound organelles; ex. plants, animals, fungi, YOU
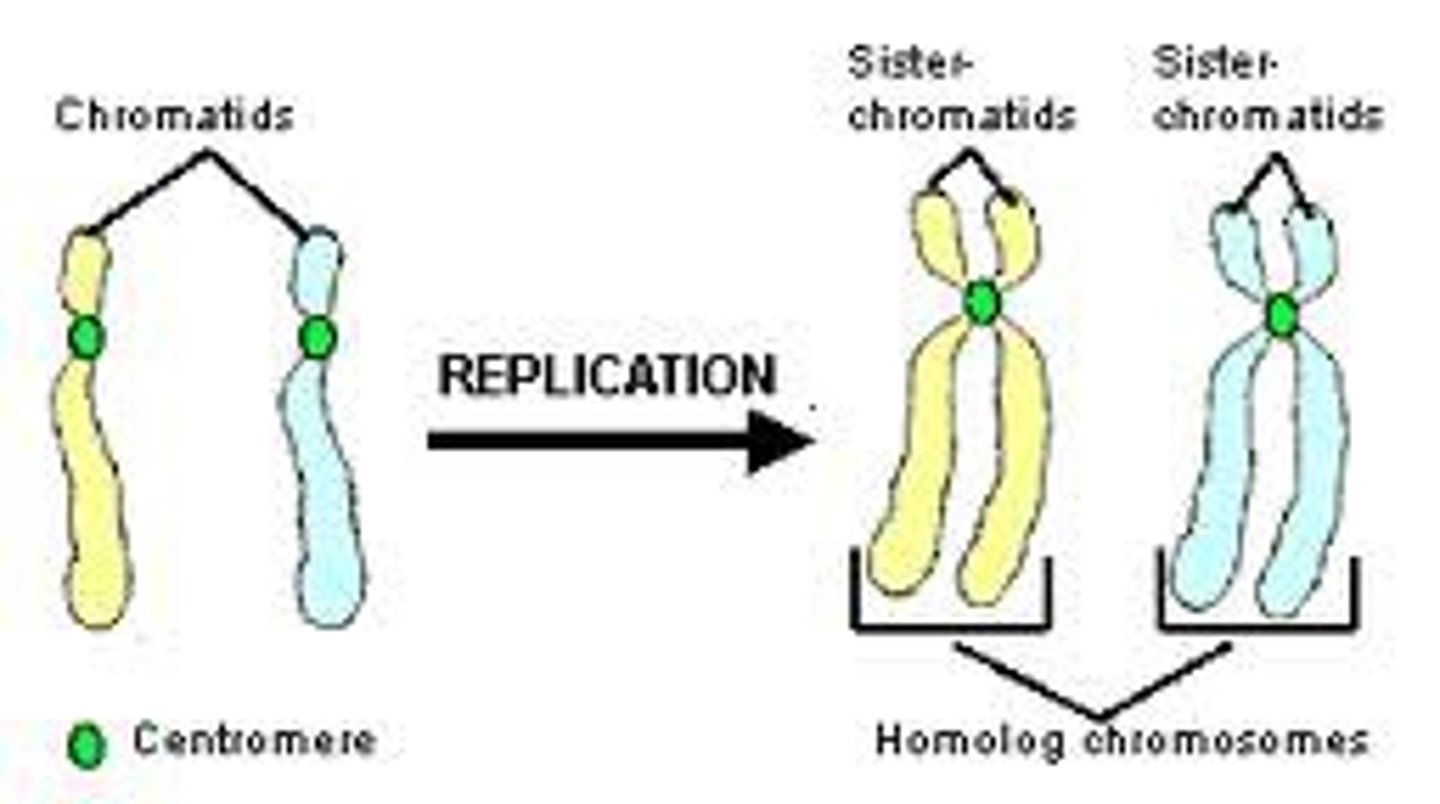
homologous chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes that are the same size, same appearance and same genes.
Chromatid
thick condensed DNA; how DNA is stored during Mitosis to keep it organized; one half of a set of "sister chromatids"
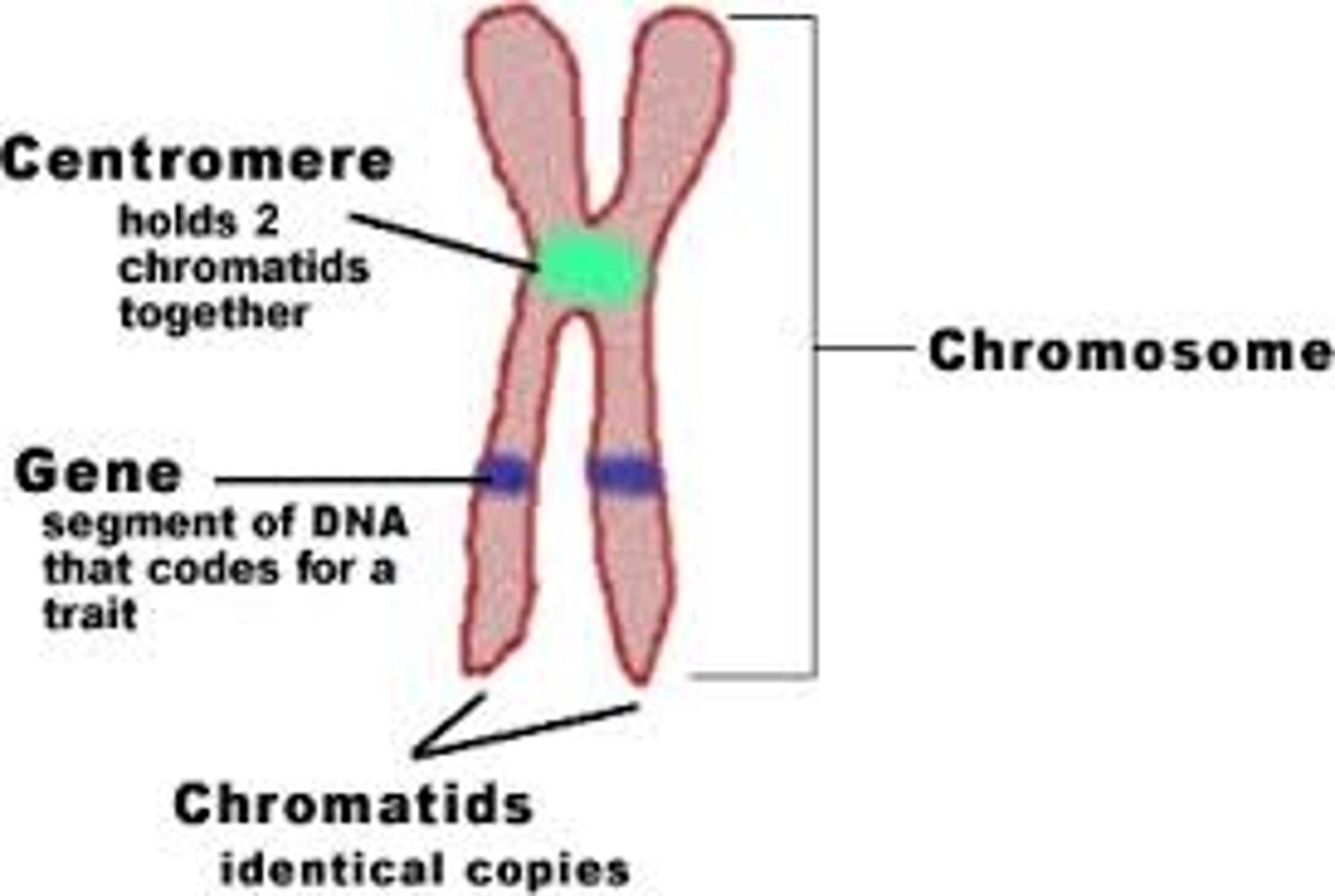
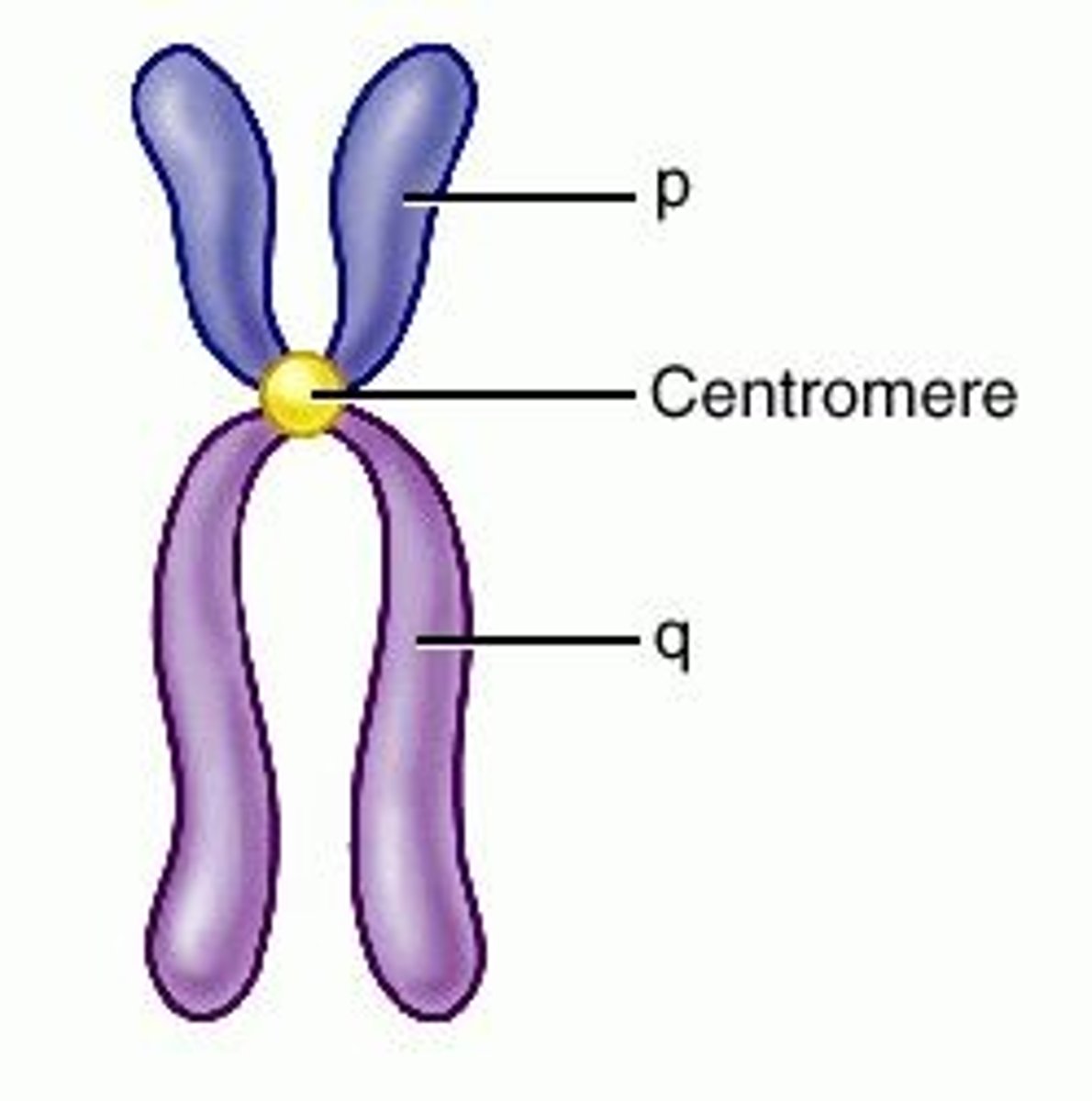
Centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
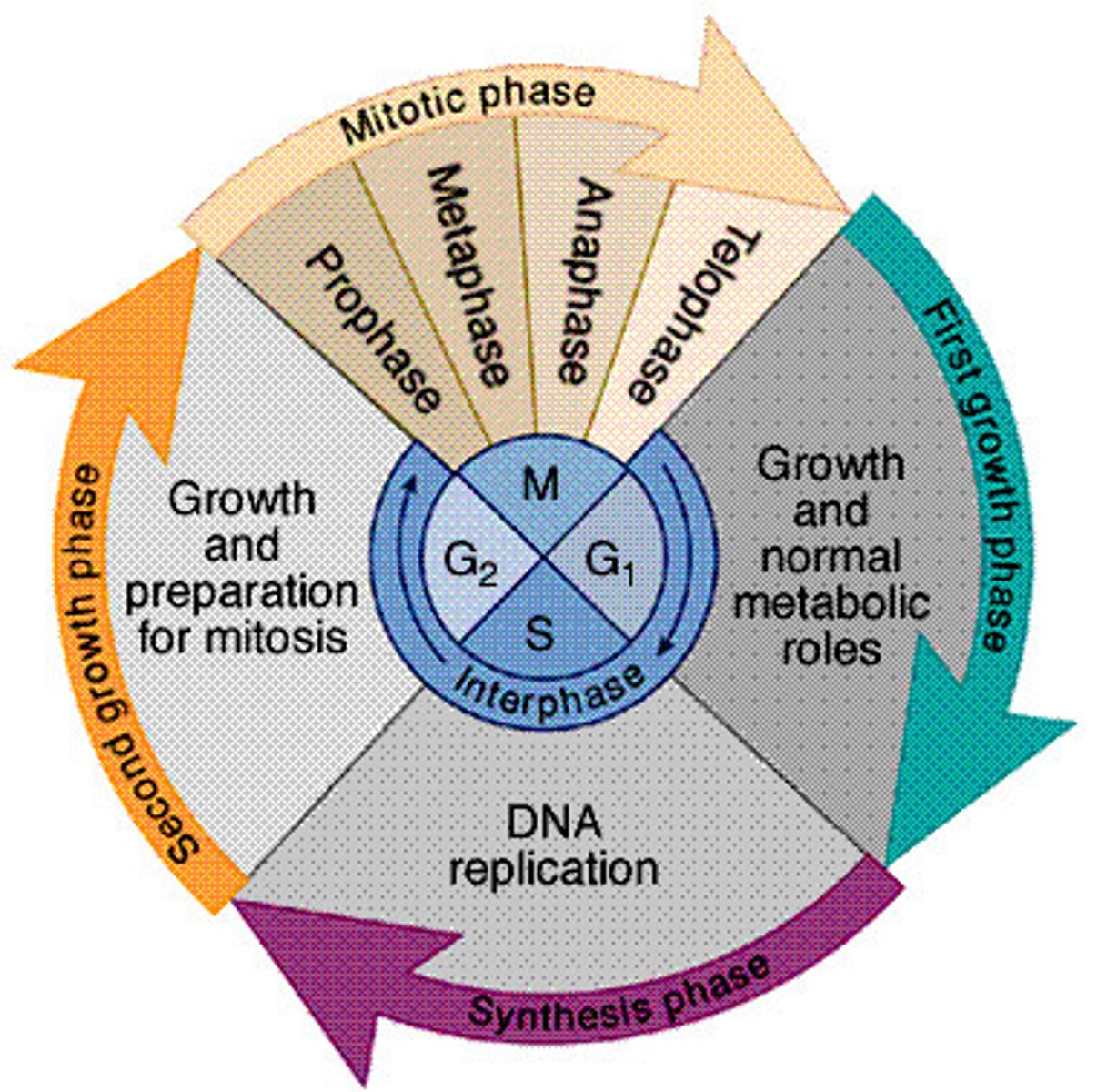
Mitosis
part of eukaryotic cell cycle during which cell divides
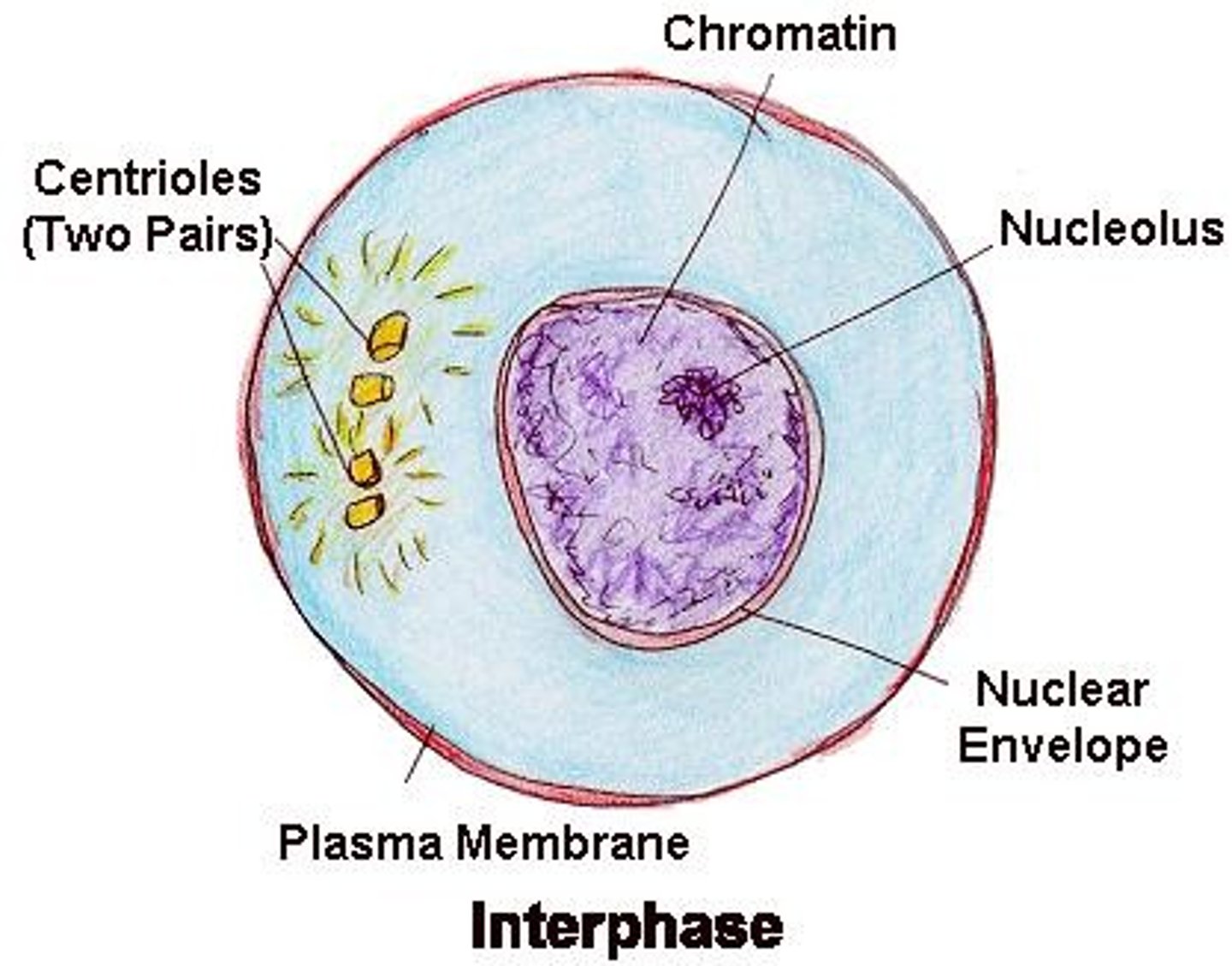
Interphase (Mitosis)
The "normal" growth phase of the cell, when DNA replication happens
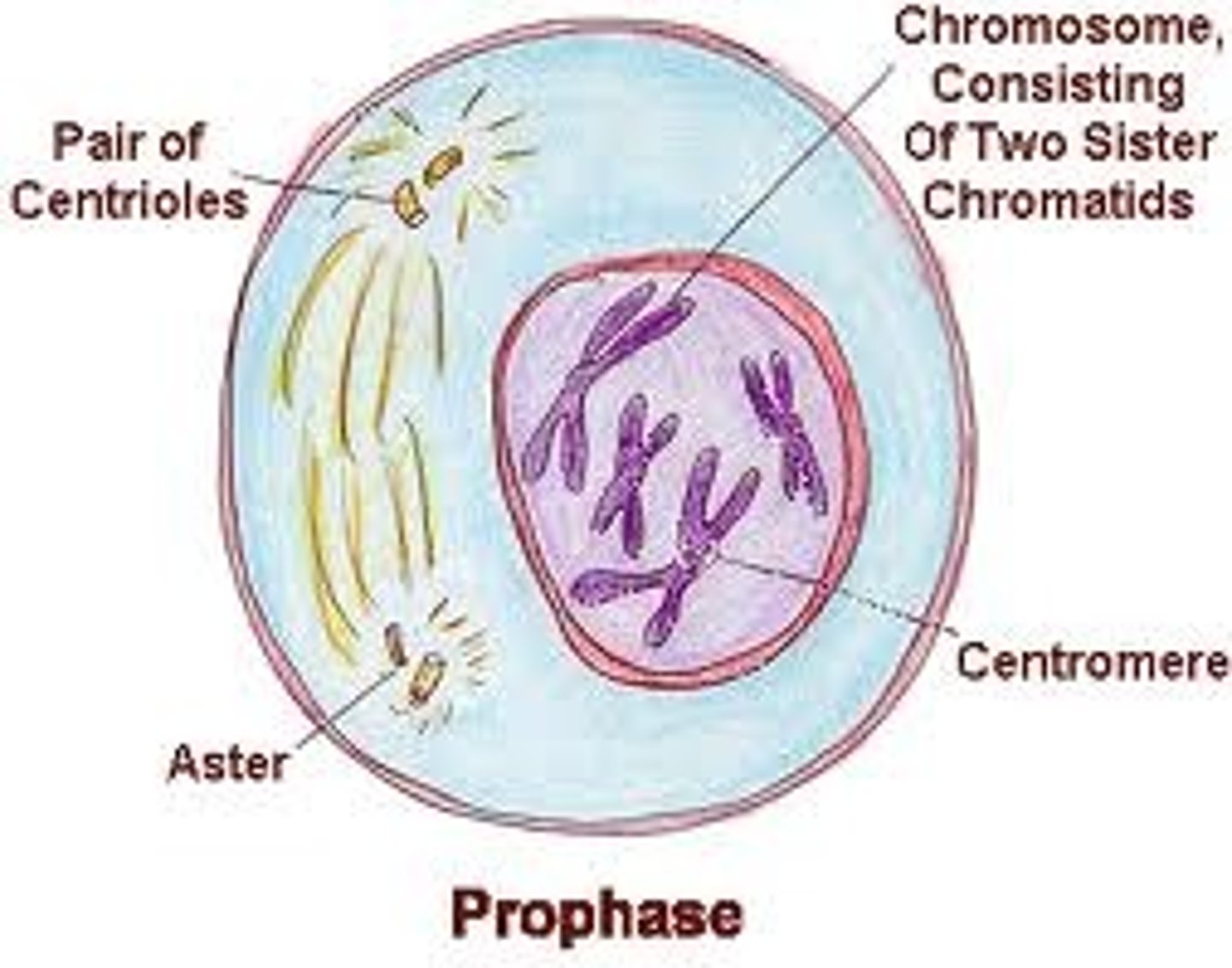
Prophase (mitosis)
chromatin condenses into chromosomes, centriole moves to poles, nuclear membrane dissolves
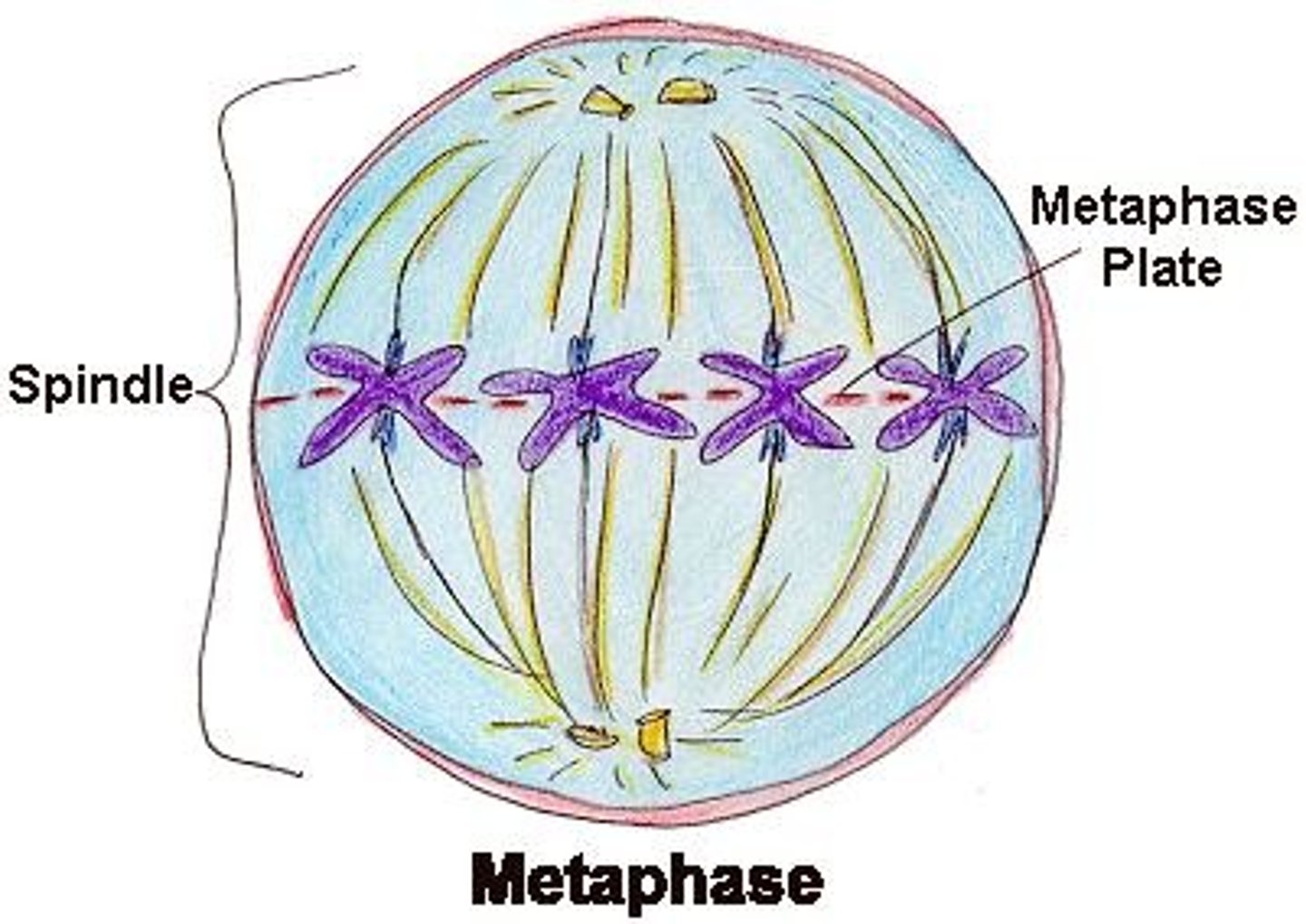
Metaphase (mitosis)
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
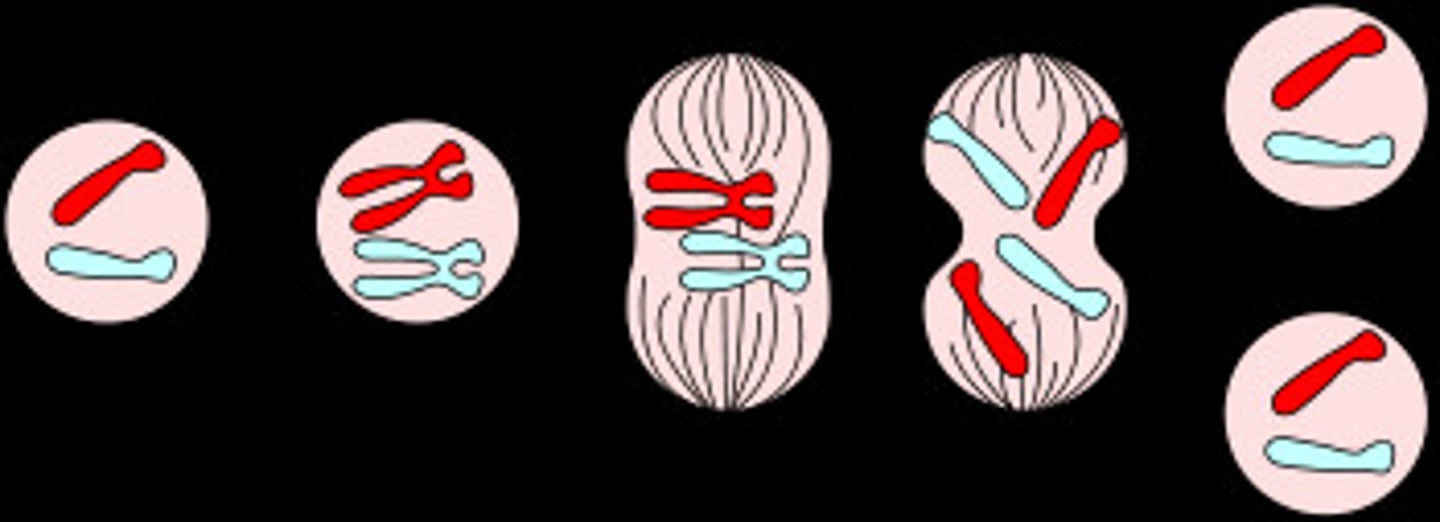
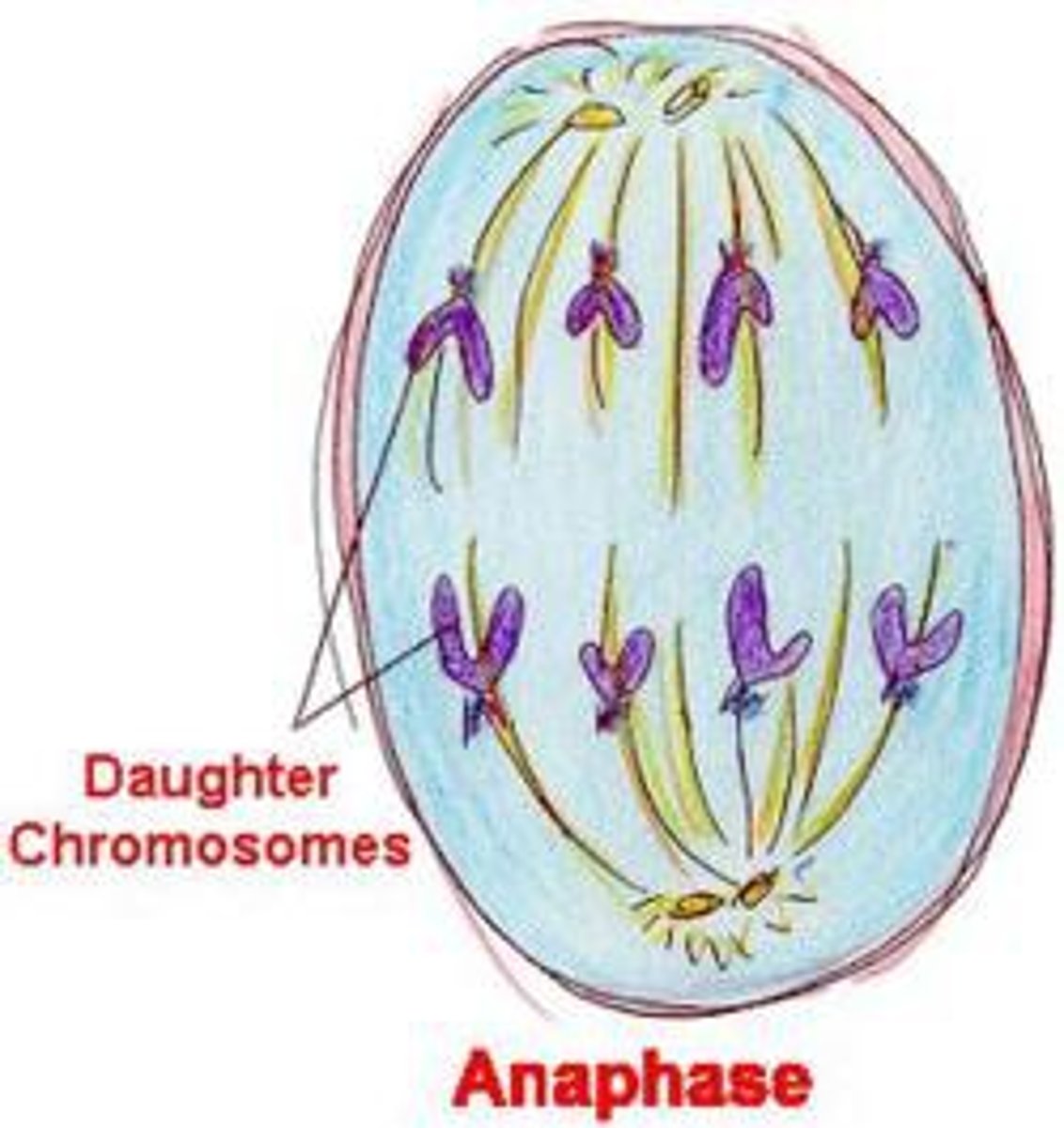
Anaphase (Mitosis)
sister chromatids are pulled apart
Telophase (mitosis)
Nuclei begins to reform around separated chromosomes
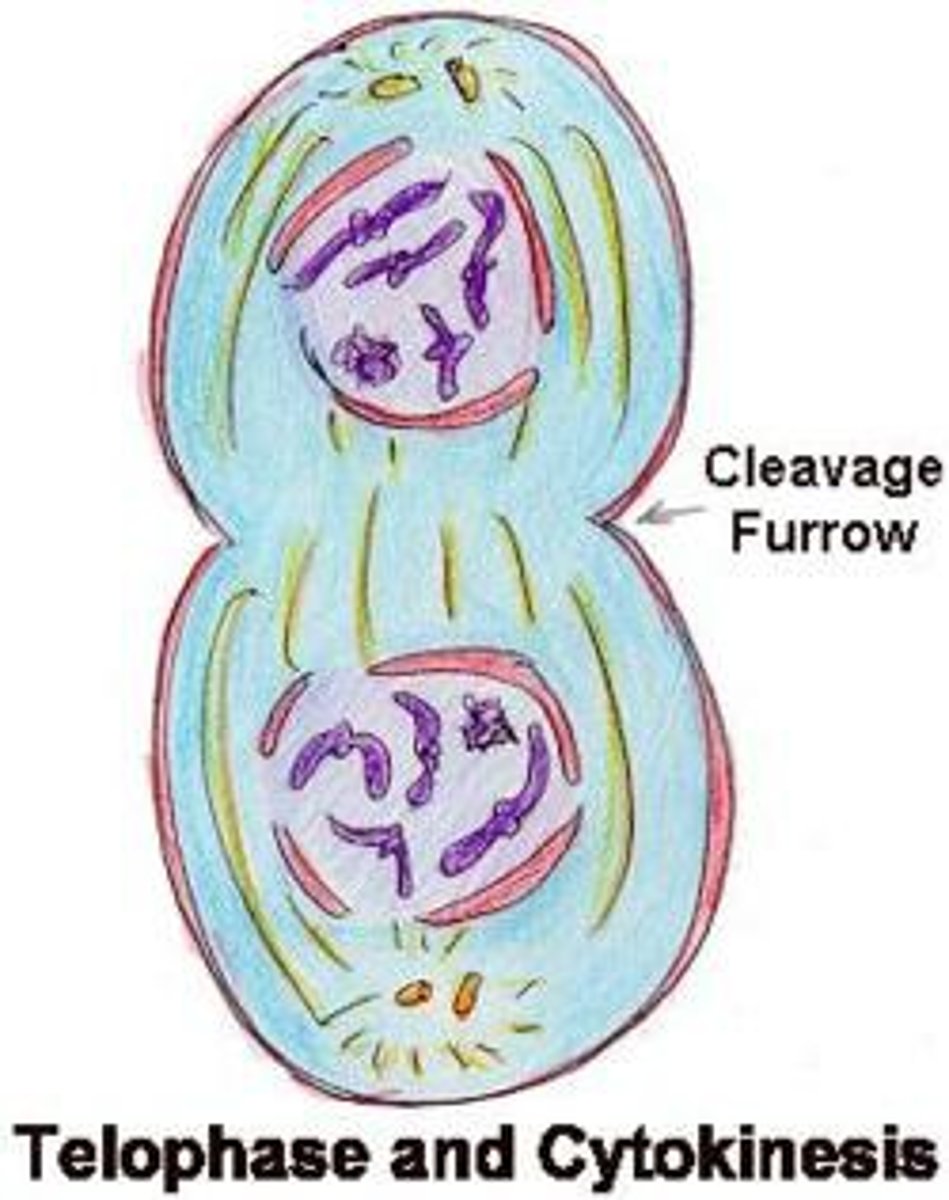
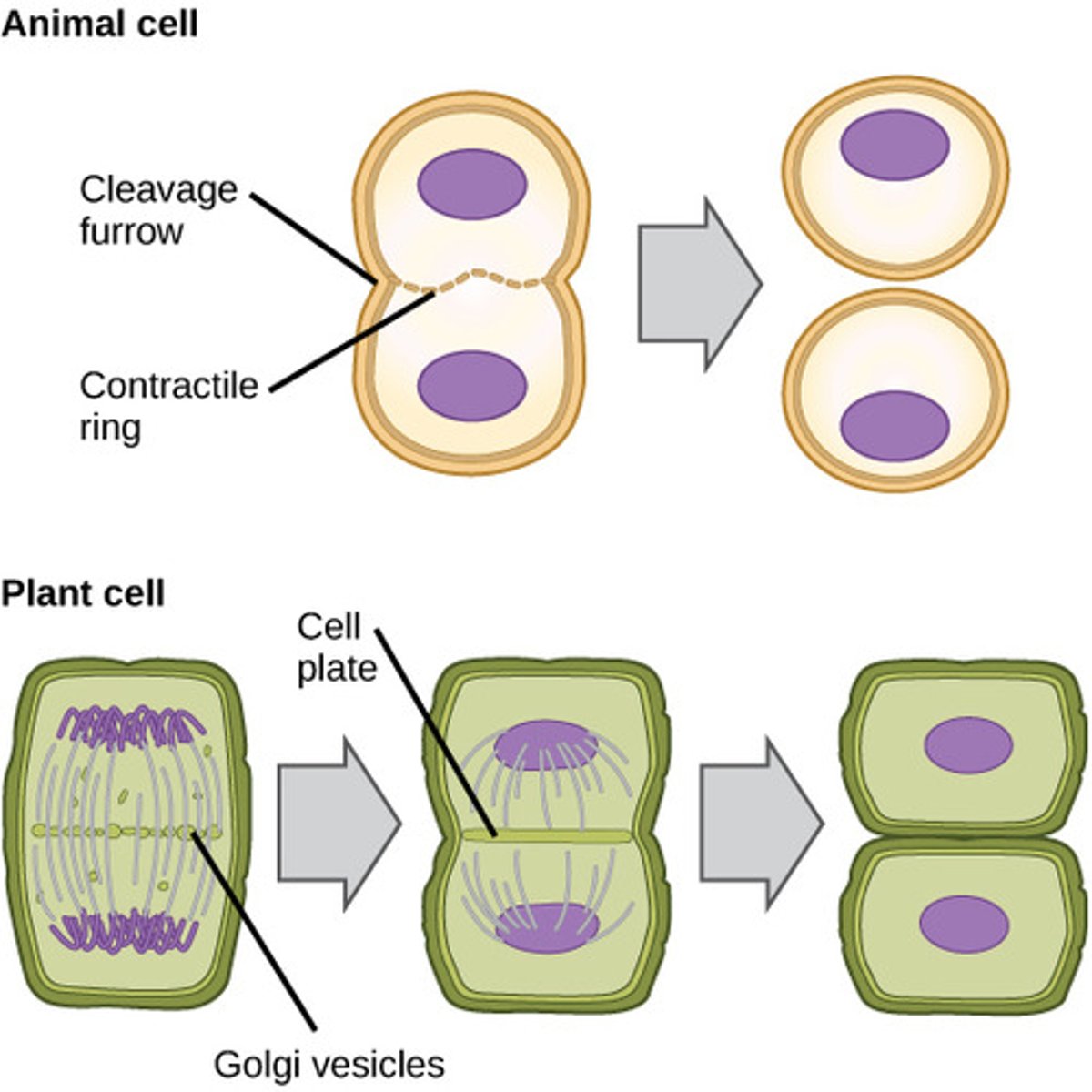
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
Centrioles
a minute cylindrical organelle near the nucleus in animal cells, occurring in pairs and involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division.
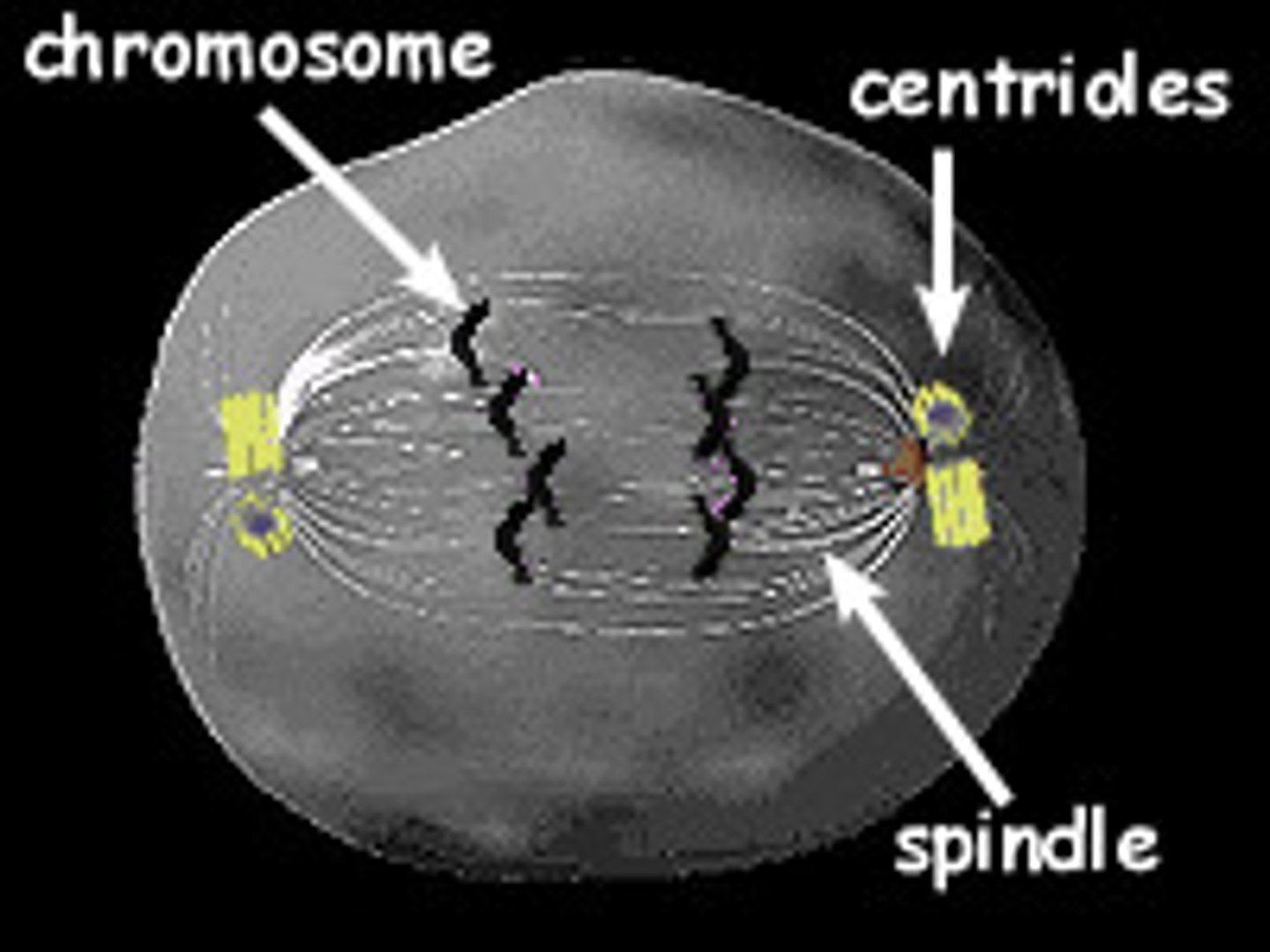
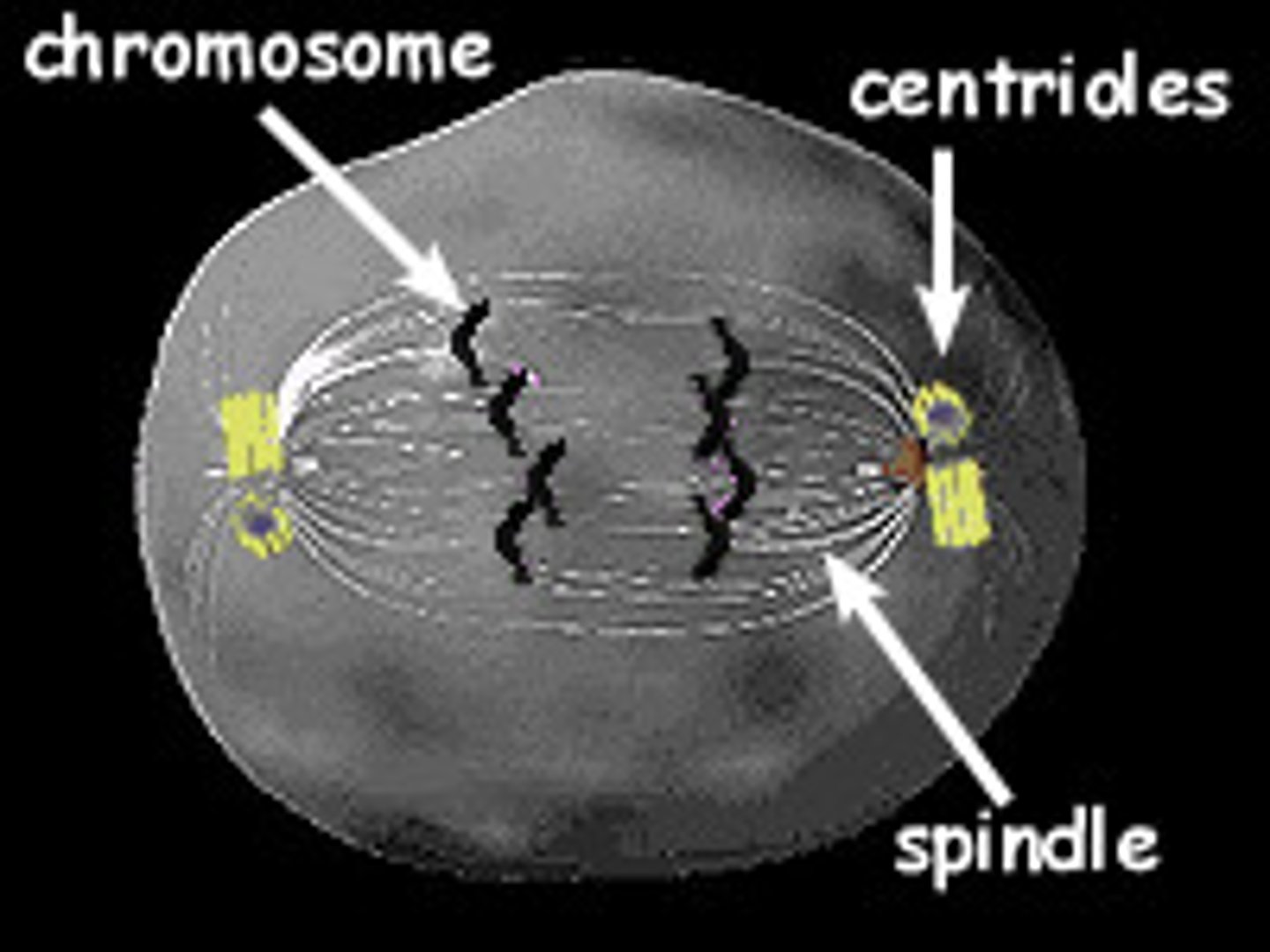
Spindle Fibers
Protein structures the comes from the centrioles which move the chromosomes during cell division.
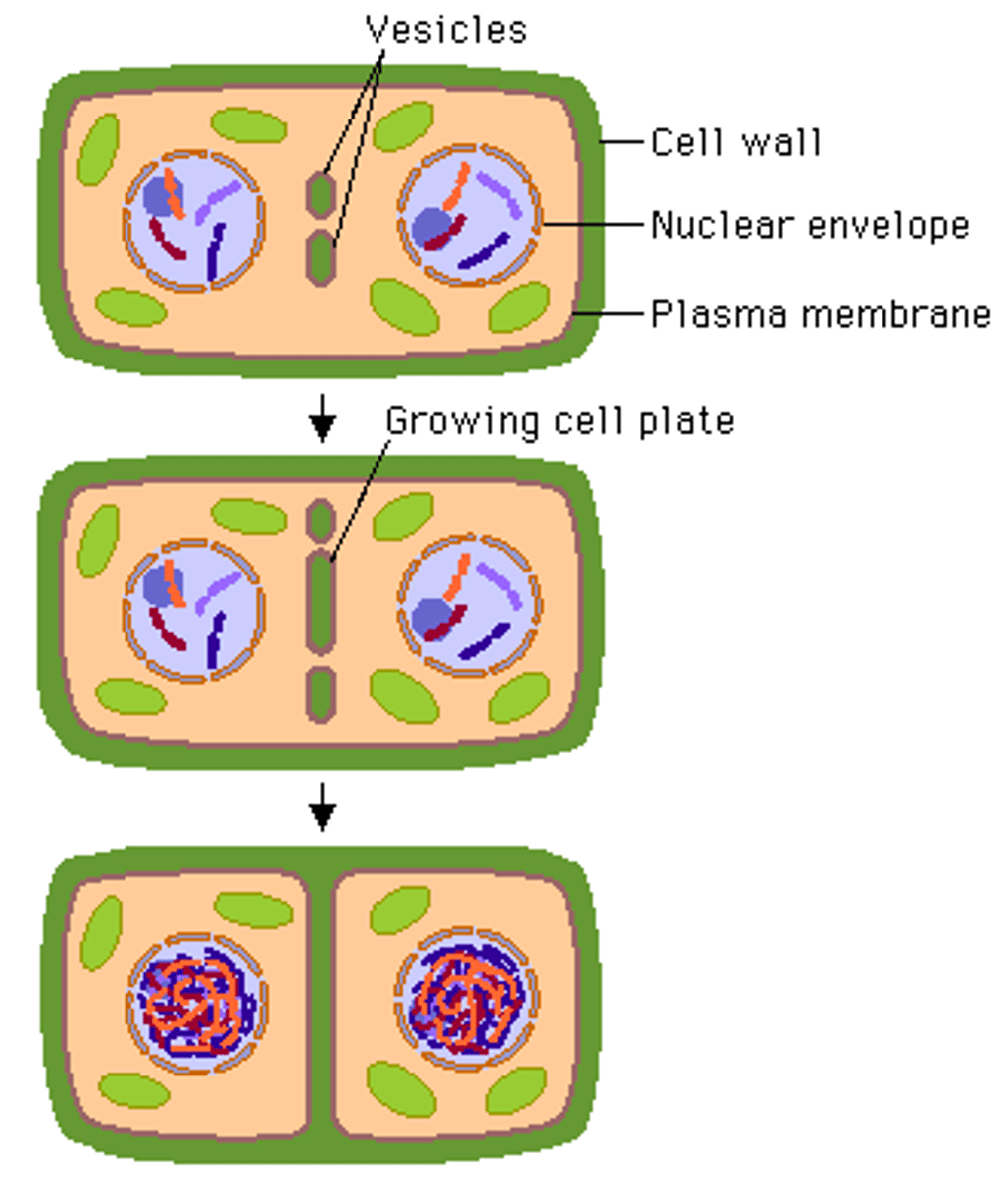
cell plate
In a plant cell, midline of dividing cells. Becomes the cell wall eventually.
Organism
An individual living thing
asexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves only one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent.
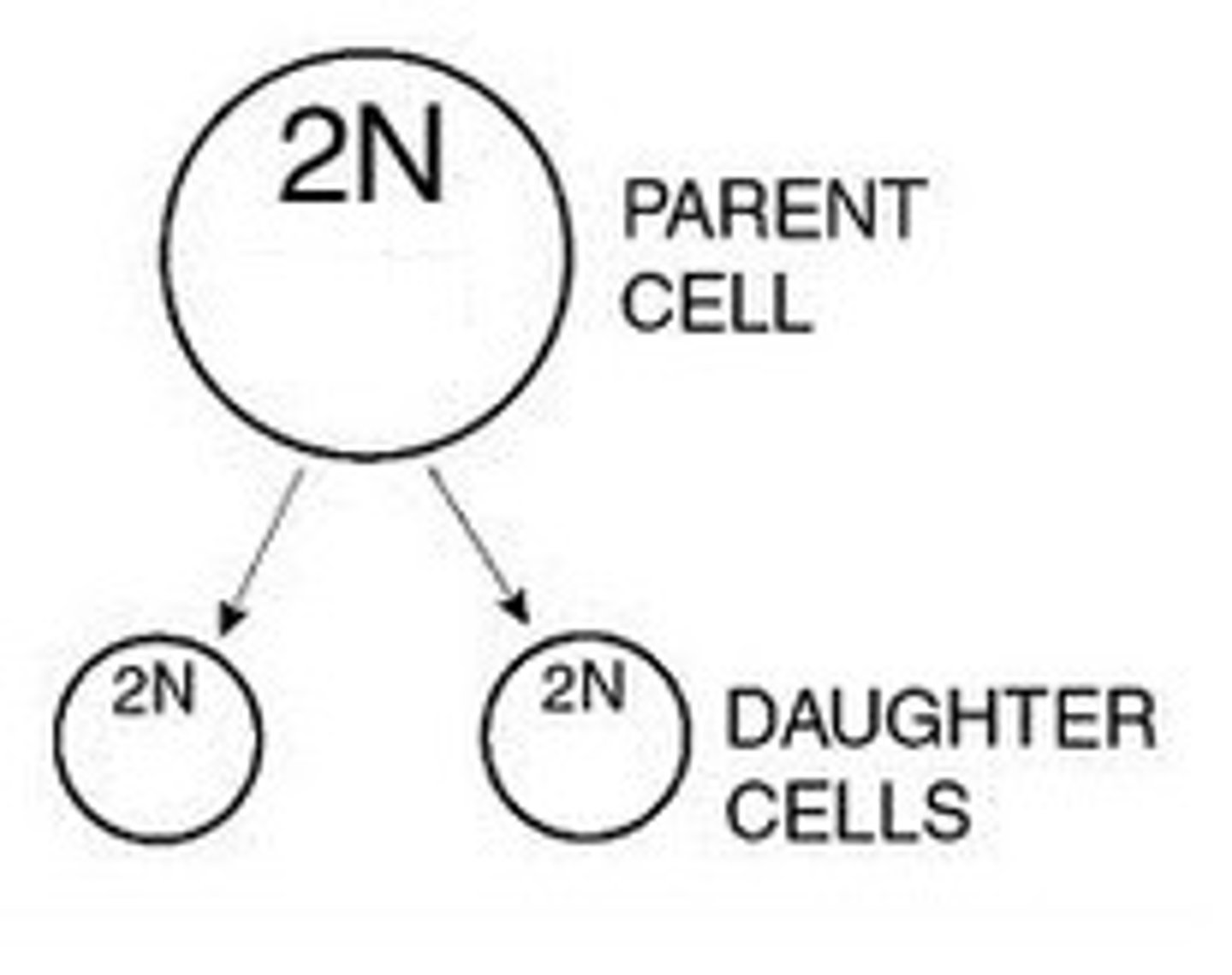
parent cell
original cell before cell division
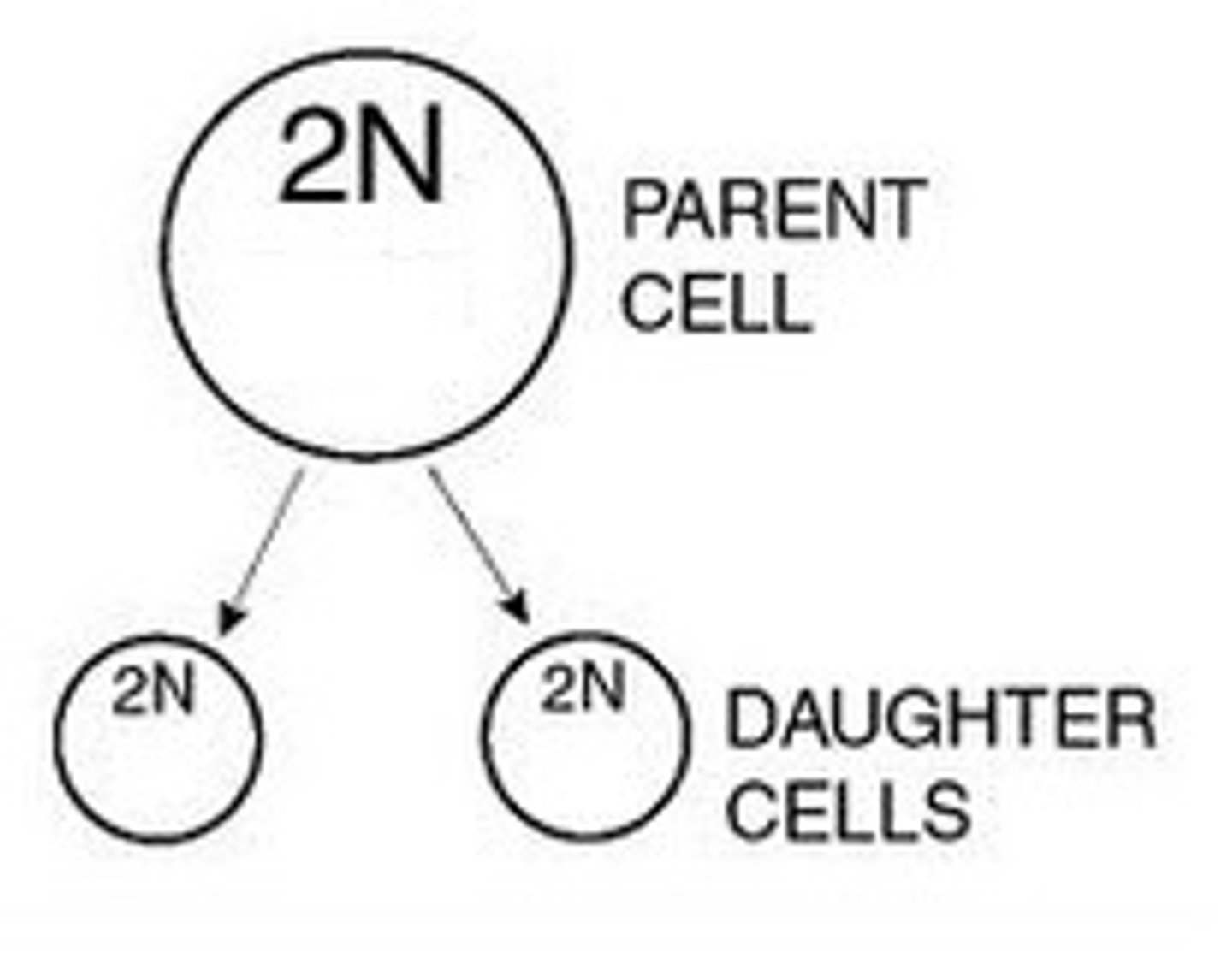
daughter cell
The cells that are produced as a result of mitosis. These cells are identical to each other, and also to the original parent cell.
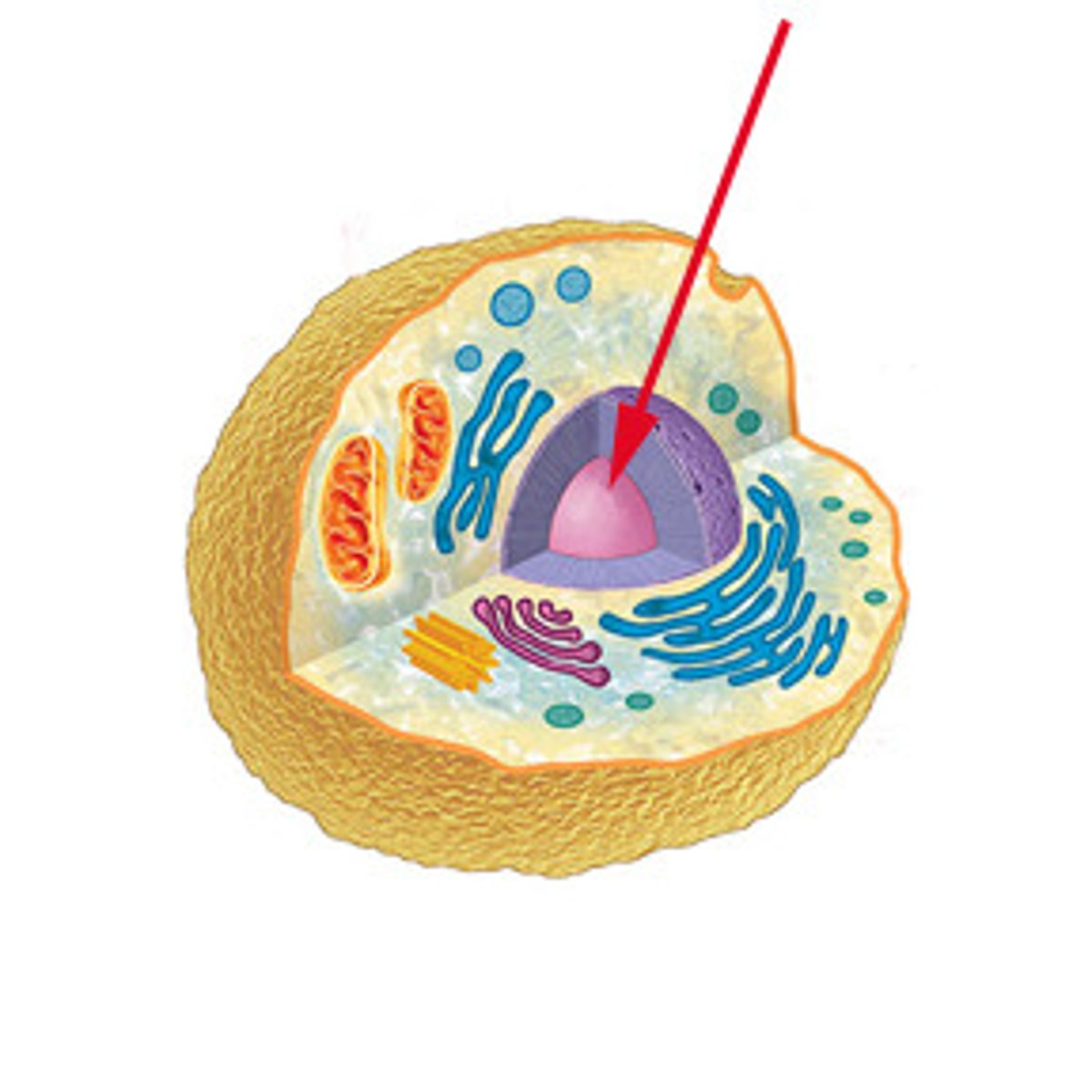
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
Chromatin
thin, threadlike DNA; how DNA is during interphase
Replication
process of copying DNA prior to cell division; making an identical copy
Life Functions of Mitosis
Growth & Repair, reproduction of single cells
Growth
The function of mitosis that allows multicellular organisms to get larger; more cells are dividing than dying
Repair
The function of mitosis that allows multicellular organism to maintain and repair itself by replacing damaged cells; same number of cells made as are dying
Cancer / Tumor
uncontrolled cell division; many more cells are being made than are dying
Reproduction
A function of mitosis in which one cell makes two identical daughter cells
Prometaphase (Mitosis)
The nuclear membrane disintegrates. Spindle microtubules attach to chromatids at the kinetochores.
G1 checkpoint
checks for cell size, nutrients, growth factors and DNA damage
G2 checkpoint
asses if DNA replication has occurred, go ahead signal triggers mitosis
M checkpoint
cell monitors spindle formation and attachment to kinetochores
cleavage furrow
The area of the cell membrane that pinches in and eventually separates the dividing cell
Cyclins + CDKs → activate MPF
Promote cell division.
Kinetochores
protein complexes associated with centromeres
p53
Protein that halts cell division when DNA damage is present, allowing time for repairs.
Proto-oncogenes
normal genes that play essential roles in regulating cell growth, division, and differentiation
oncogenes
mutated versions of proto-oncogenes that promote uncontrolled cell growth and division, leading to tumor formation.