2.3 weather and climate
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
weather
day to day conditions in the atmosphere
climate
average weather conditions based on averages of 40years of data
temperate climate
a climate that isnt too hot or too cold and has 4 clear seasons
describe coldest and warmest seasons in UK
coldest=jan-feb
warmest-july-aug
where are sunshine hours greatest in UK
south coast of england
which part of UK has shorter winter days and longer summer days
Scotland as it is further north
where is it wettest in UK
west
Snowdonia in Wales-3000 mm of rain a year
which are the driest areas of UK
Parts of the east, such as East Anglia, receive less than 700 mm a year.
describe average temperature in UK
Average temperatures in UK are warmer at lower latitudes and colder at higher latitudes.
which area is mostly affected by severe weather in UK
Scotland
average daily temps in summer in UK
The average daily maximum temperature at Glasgow in July is 19°C compared with 22°C in London.
Scotland is 3°C colder than UK
what factors affect UK climate
altitude
distance from sea
air pressure
latitude
influence of global circulation model
how does latitude affect UK climate
as latitude increases, av temp decreases
affects how much sun the UK gets during diff seasons
the further away from equator, the cooler the area
how does altitude affect UK climate
altitude=height above sea level
locations at higher altitude have colder temps
temps decrease by one degree every 100m
mountain areas are cooler than sea level areas
how does prevailing wind direction affect climate
prevailing wind=min wind that blows most the time
everywhere gets lots of diff winds from diff directions
the temp and wetness of winds can be affected by what wind travels over
how does global atmospheric circulation affect UK climate
where the air is warm, moist air leads to low pressure weather systems which is poor weather i.e rain and wind
when the air sinks, this leads to drier weathers
how does distance from sea affect UK climate
oceans heat up and cool down much more slowly than land
coastal areas tend to be cooler in summer and warmer in winter than inland places at the same latitude and altitude
global circulation model
a theory that explains how the atmosphere operates in a series of three cells each side of the equator t
what impact does global circulation model have on world
affects climate across world
leaves tropical areas with little rain
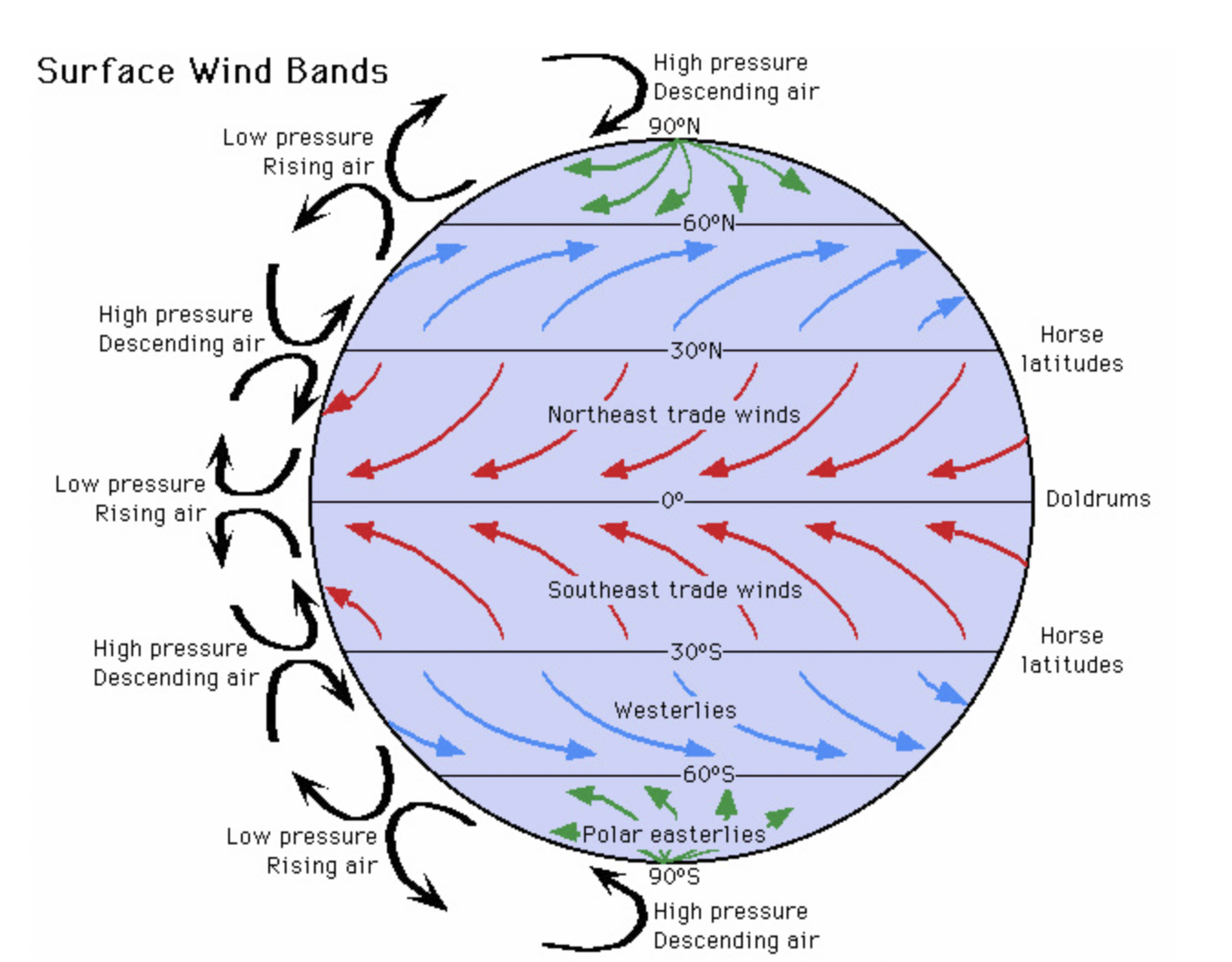
three cells of global circulation model
Hadley cell(0-30 degrees N and S of equator)
Ferrel cell(30-60 degrees N and S of equator)
Polar cell(60-90 degrees N and S of equator)
Hadley cell location and role
located near equator
involves warm, moist air rising leading to frequent rainfall and low pressure
when air reaches 30 degrees N and S air cools and sinks , it moves towards higher latitudes, descends and creates dry, high pressure zones(deserts)
Ferrel cell location and role
between Hadley and polar cells
air on surface is pulled towards poles , forming warm south westerly winds in northern hemisphere and north westerly winds in southern hemisphere
these winds pick up moisture as they travel over sea
at around 60 degrees N and S, they meet cold air
the warmer air from tropics is lighter than dense cold polar air it rises as two airs meet
this causes low pressure and unstable weathers
polar cell locations and role
at the poles, air is cooled and sinks to form high pressure
it then flows towards lower latitudes
at 60 degrees N and S the cold air mixes with warmer tropical air and rises causing low pressure
overview of climate zones on earth
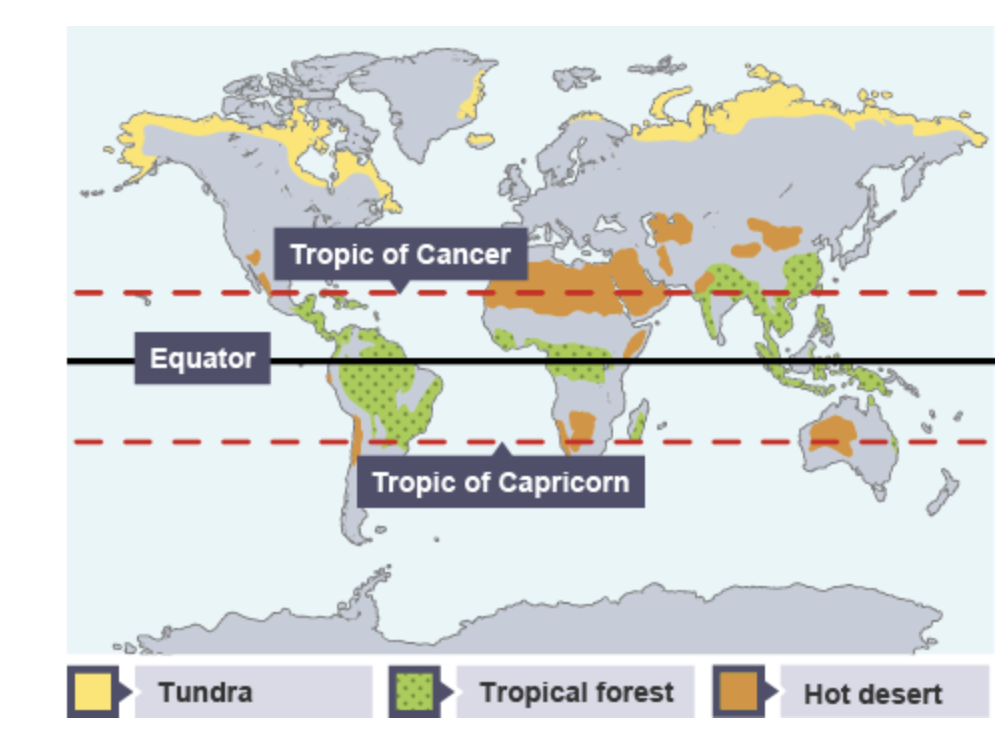
location of semi-arid grasslands
found mostly in Africa but also Asia, South America and oceania
between tropics
close to equator so warm and away from low pressure so dry
temperatures in semi arid grasslands
reach as high as 30°C during the summer months with intense sun, while winter temperatures may drop to around 0°C with frost
vegetation in semi arid grasslands
baobab trees-stores water in trunk
long grass-stores water in roots to survive in fire
acacia trees-long roots to reach water, thorns
animals in semi arid grasslands
zebra-migrates to fresh grass, camouflages
giraffe-long neck to reach fresh leaves, tail to swish flies
lion-camouflages, large teeth and claws to kill
places with semi arid grassland climate
australia
ghana
central asia
sicily
tropical rainforest location
belt around equator, between Tropic of Cancer and Capricorn
south and central America , Africa and Southeast Asia
temperatures of tropical rainforest
stays around 20-25 degrees
highest temps in January
highest rainfall in October
long wet seasons
vegetation in tropical rainforest
liana vines-spread from tree to tree to reach sun in canopy
drip tips- help rainwater drain quickly to roots
buttress roots-large roots supporting tall trees to help absorb nutrients
animals in tropical rainforest
poison dart frog-poisonous
jaguar-camouflage
spider monkey-long tails to swing
places with tropical rainforest climate
ecuador
india
Cameroon
central africa
how are areas of high pressure created by global circulation
-air, which is heated at the equator and rises, cools and sinks at around 30° north and south of the equator, creating high-pressure zones associated with dry conditions.
how are areas of low pressure created by global circulation
through the rising of warm, less dense air, which occurs at the equator and in other regions where solar radiation is intense, leading to unstable weather conditions.
why is it hot at equator and cold at poles
less atmosphere to pass through t equator so more heat makes it to the surface
equator faces sun all year
depressions are
low pressure
anticyclones are
High pressure
global pressure systems
typical weather in low pressure areas
summer=prolonged rainfall, cloudy skies, storms
winter-storms, snow, heavy rainfall
typical weather in Hugh pressure areas
summer-calm, long sunshine periods, thunderstorms
winter-extensive fogs, very cold nights, cloudless skies
extreme low pressure weather
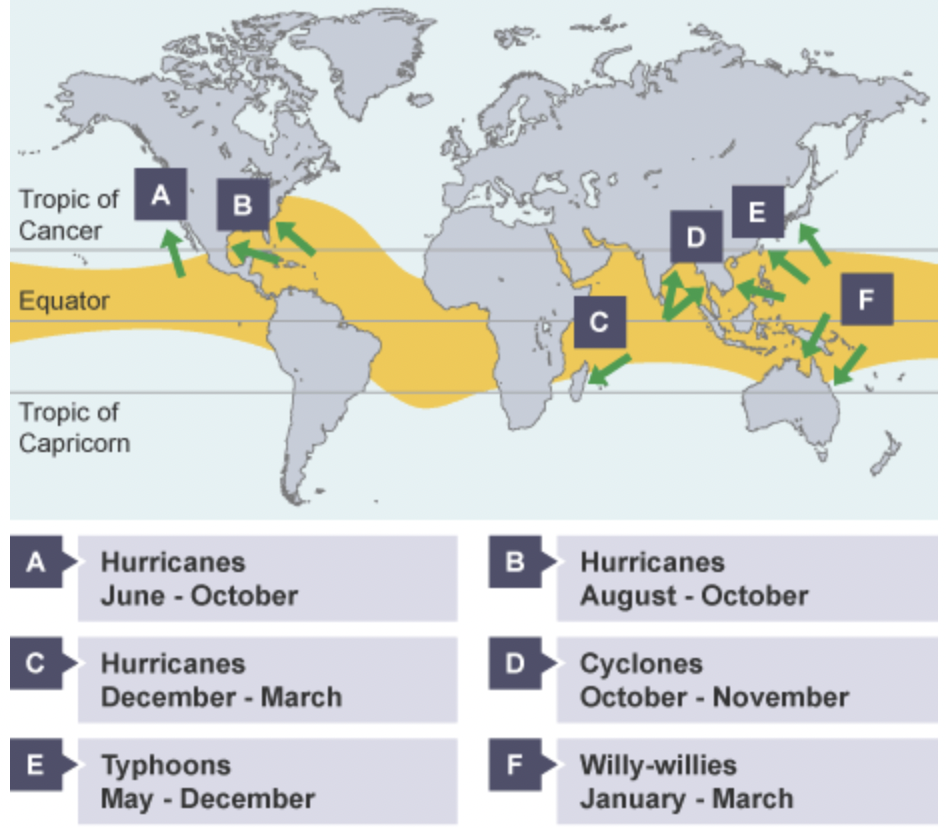
tropical cyclones-large rotating storms over oceans in tropical areas
cyclones-violent tropical storms over India ocean
hurricanes-violent tropical storm in caribbean region
typhoon-violent tropical storm over Pacific Ocean
extreme High pressure weather
drought and heatwaves -prolonged dry periods of weather
global distribution of cyclone/hurricanes
often occur at start of American summer from end of June to October
how do cyclones form
sea temps must be 27 degrees weeks prior
warm air rises rapidly, creating low pressure
leads to condensation and development of towering cloud and torrential rain
warm moist air moves in to replace the rising air and spirals upwards toward atmosphere
high pressure case study
California drought
low pressure case study
hurricane Haiyan in philipines