1.3 market failure
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
define the term marginal private benefit (MPB)
refers to the additional benefit received by an individual or firm from consuming or producing one more unit of a good or service.
define the term “Marginal external benefit” MEB
is the additional benefit to third parties from the consumption or production of one more unit of a good or service.
Define “marginal social benefit” MSB
is the total benefit to society from the consumption or production of one more unit of a good or service, including both private and external benefits.
define "Marginal private cost" (MPC)
refers to the additional cost incurred by a producer or consumer from producing or consuming one more unit of a good or service.
Marginal External Cost (MEC)
refers to the additional cost imposed on third parties or society from the production or consumption of one more unit of a good or service, not borne by them
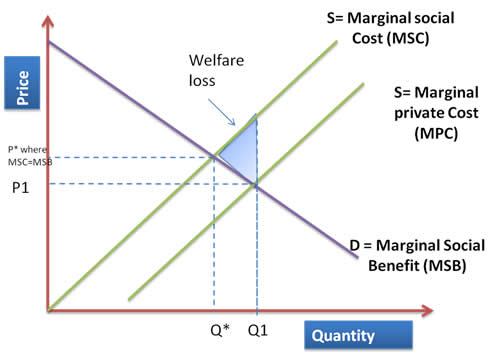
Marginal Social Cost (MSC)
is the total cost to society of producing one more unit of a good or service, including both the Marginal Private Cost (MPC) and the Marginal External Cost (MEC).
define the concept "third party"
refers to any individual or group that is not directly involved in an economic transaction but is affected by its outcomes. they experience externalities
differences between a consumption externality and a production externality
A consumption externality occurs when the consumption of a good affects third parties (e.g., secondhand smoke or the benefits of education).
A production externality occurs when the production of a good affects third parties (e.g., pollution from factories or technological advancements).
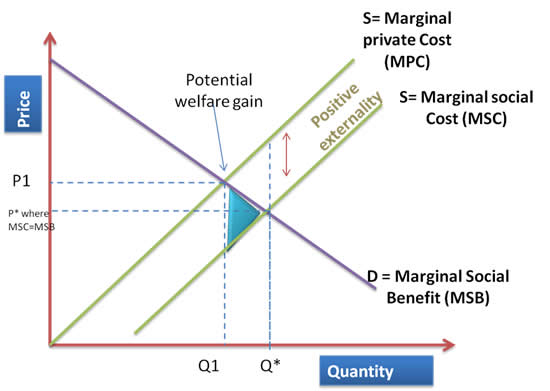
Define the term "Positive externality"
When a good causes external benefits to a third party from the consumption or production of it
Define the term “Non-rival”
"Non-rival" refers to a good or service where one person's consumption does not affect another person's ability to consume it.
Define “non-excludable”
"Non-excludable" means that no one can be prevented from using a good or service.
difference between a private good and a public good
A private good is both excludable and rivalrous, meaning people can be prevented from using it, and one person's use reduces its availability to others (e.g., a sandwich).
A public good is non-excludable and non-rivalrous, meaning everyone can use it, and one person's use doesn't reduce its availability to others (e.g., clean air).
Explain the free rider problem
The free rider problem occurs when people can benefit from a good or service without paying for it, leading to underproduction or underfunding of that good since there's little incentive for individuals to contribute.
Indirect taxes
a tax on consumer expenditure
Used to correct negative externalities
Effect: Increase private cost → reduce output
Diagram: Shift in MPC → closer to MSC
Evaluation:
Inelastic demand → ineffective
Can be regressive for lower income individuals
Revenue for government
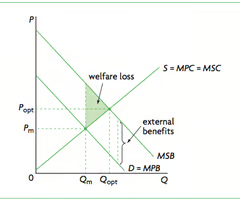
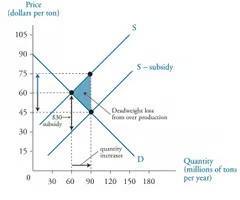
Subsidies
A payment made by the government to producers to reduce the cost of production and/or encourage the consumption or production of a good or service.
Used to encourage positive externalities
Lowers cost of production → increase consumption
Diagram: Shift MPC rightward toward MSC
Evaluation:
Expensive
Government failure possible
what is government failure
When intervention worsens resource allocation
Leads to greater net welfare loss
real world examples
Sugar tax (UK)
Congestion charge (London)
COVID vaccines (positive externality)
Smoking bans (negative externality)
asymmetric information
Asymmetric information occurs when one party in an economic transaction has more or better information than the other.
evaluation of government intervention
Effectiveness: Depends on PED, government knowledge
Efficiency: Is it value for money?
Equity: Who gains/loses?
Long-term vs short-term effects
market failure
Market failure occurs when the free market fails to allocate resources efficiently, leading to a net welfare loss.
why arent public goods provided by the free market
Public goods are not provided by the free market because of the free rider problem – individuals can benefit without paying, so firms have no incentive to supply them as they can’t make a profit.
information gaps
An information gap occurs when consumers or producers lack full knowledge to make rational decisions.
How can indirect taxation help correct market failure from negative externalities?
Indirect taxes (e.g. on cigarettes or petrol) increase the private cost of consumption or production reducing output to the socially optimal level and internalising the externality.
why may a subsidy lead to government failure
Subsidies may lead to government failure if they are misallocated (e.g. to inefficient firms), create dependency, or if the opportunity cost is too high.
negative production externality
positive production externality
what are subsidies
a sum of money granted by the government to assist an industry or business so that the price of a commodity or service may remain low or competitive.
positive consumption externality
what is VAt in the UK
20%
government failure
£9.3 million granted to wind turbines to slow down their production as the network was unable to cope with the amount of electricity
london deaths due to pollution
284 - (guardian, 2023)
invisible hand
Prices allocate scarce resources among competing consumers
Price changes act as a signal to show where resources are required and where they aren't
Prices serve to ration scarce resources when market demand outstrips supply
Price increases incentivise firms to increase supply
subsidy diagram
demerit goods
Goods that are considered to be undesirable for consumers and are over-provided by the market, maybe due to the good having negative externalities.
consumer surplus on a graph
below the demand curve and above the price (the top one)
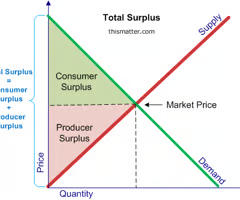
what is producer surplus
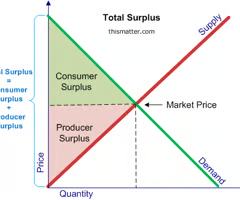
quasi public goods
Public goods which take on some of the characteristics of private goods
why would public goods not be introduced in a free market
Suppliers cannot stop consumers from accessing these goods and therefore they will not produce them (free rider problem)
why ma the government have to pay for flood defenses
individuals may refuse to pay but still use services due to the free-rider problem (if the flood services were provided by private sector) leading to insufficient funds to build flood defences. Therefore the government will do this via taxation.
why did Marx hate the free market
He believed it created prosperity for few and poverty for many. Exploited the proletariat / it would break down because owners of business made huge profits at the expense of workers
economies of scale
when the average cost of producing a good or service falls as the quantity produced increases