Physics Electrostatics quiz
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Coulombs Law
Inversely proportional to the square of the separation between the two particles and is along the line joining them as well as proportional to the product of the magnitudes of the charges q1 and q2 on the two particles, KE= |q1||q2|/r²
Types of Charges
proton (+ charge), electron (-charge), e=1.6×10^-19C
Conductors
materials in which the electric charges move freely, copper, silver, aluminum
Insulators
materials in which electric charges do not move freely, glass, plastic, rubber
Semi-conductors
the characteristics are between those of insulators and conductors, germanium, silicon
Charging by Conduction
a charged object is placed in contact with another object
Charging by Induction
an object is connected to a conducting wire or pipe burned in the earth, it is said to be grounded
Van De Graaff Generator
a machine designed and built by Robert J. Van de Graaff that is designed to teach students how static electricity works. When touched, the generator sends electrons through someone’s body that causes their hair to become static.
electron
the electron is a subatomic particle that is found in all atoms. Unlike protons, neutrons, or the nuclei of atoms, electrons are elementary particles
Proton
a positively charged particle that is found in the nucleus of every atom. One of the three basic subatomic particles that make up atoms along with electrons and nuetrons
Nuetrons
Subatomic particles found inside the nucleus of every atom. They have a neutral electric charge (neither negative nor positive) and have slightly more mass than positively charged protons
Electric Field of a Charge
Describes the region of space where a charged particle experiences a force due to the presence of another charge
What will happen to two objects with the same static charge?
they will repel each other
What machine is used by teachers to show static electricity?
Van de Graff Generator
What are all substances made from?
atoms
What happens to an atom if it gains an electron?
it becomes negative
Which is an example of the build-up of static electricity?
lighting
Which part of atoms causes static electricity?
electrons
Units on electric field are__
newtons/Coulomb
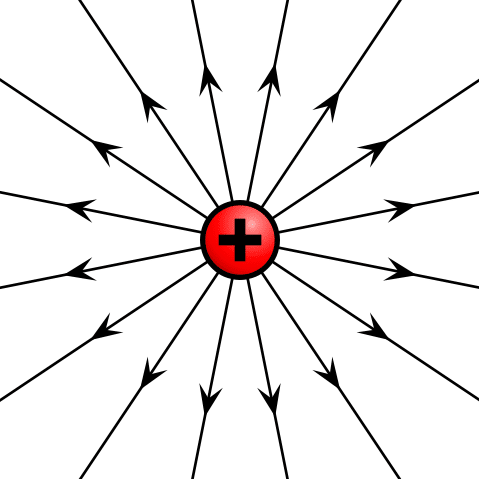
Positive Negative or Neutral
Positive
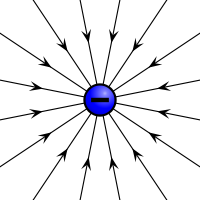
Positive Negative or Neutral
Negative
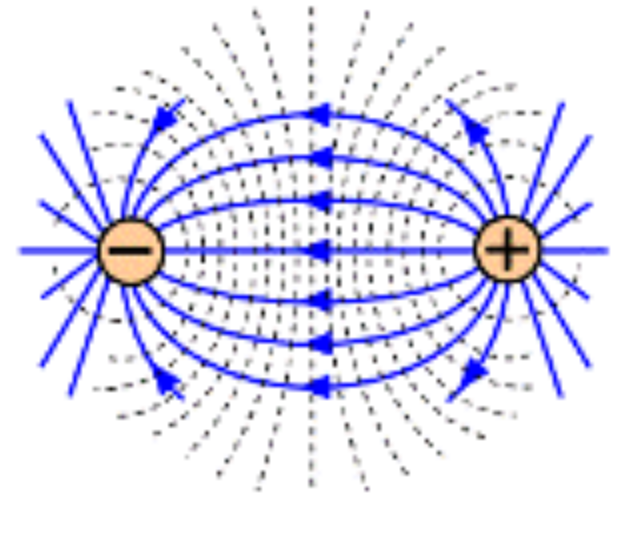
Positive negative or neutral
neutral
What is the charge on a proton?
1.6×10^-19 C
True or False: Carbon is more conductive than pure water
True
A neutral hydrogen atom has one proton and one electron; if you remove the electron, what will be the leftover charge?
Positive
A charge distribution has electric field lines pointing into it. What sign is the net charge?
negative
If you double the distance between 2 point charges, by which factor does the force between the particles change?
1/4
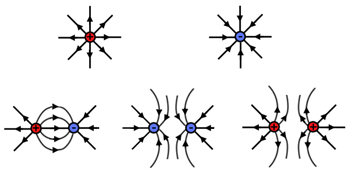
This is???
Electric Field Pattern
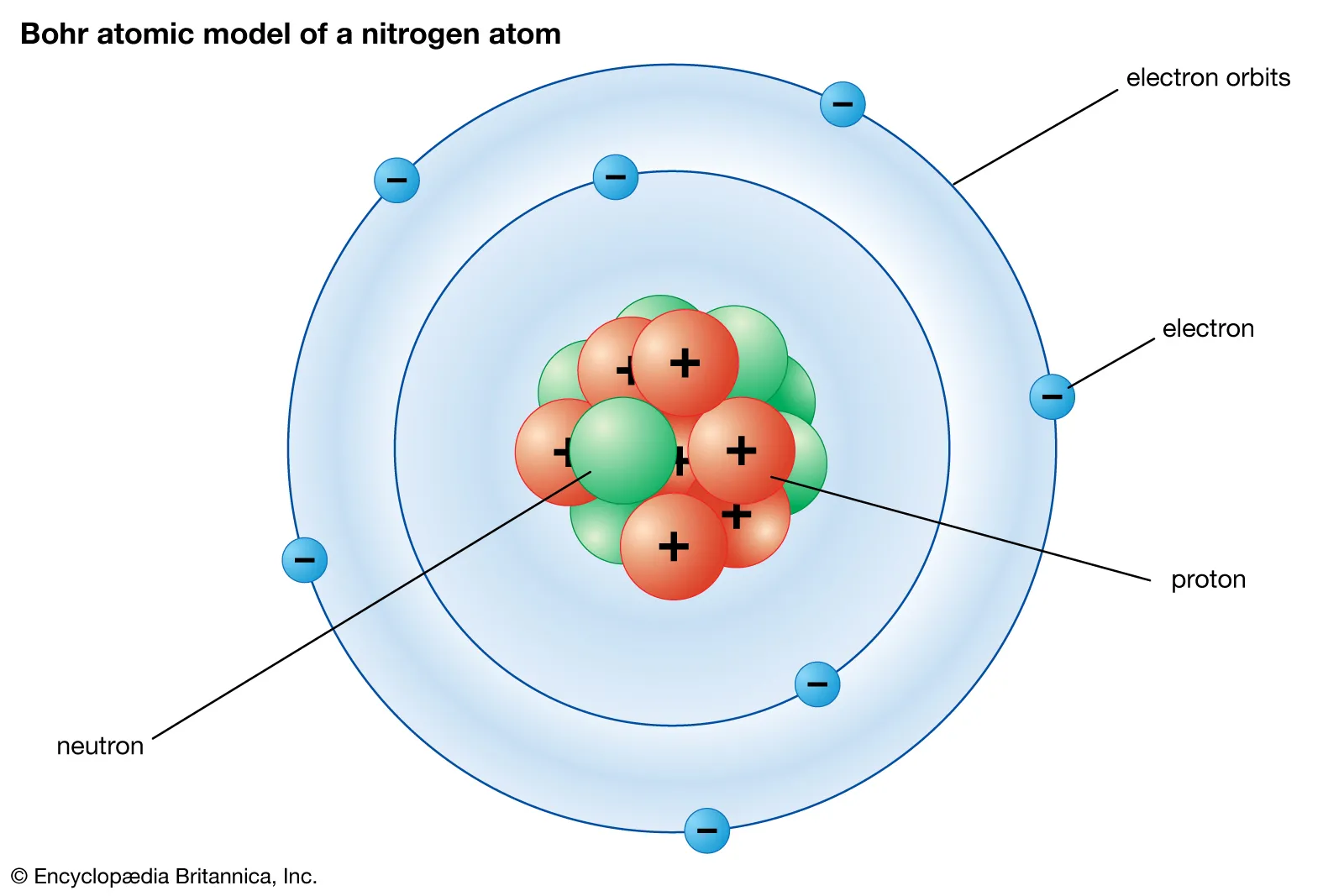
This is??
Proton
Names of Scientists
William Gilbert (1600), Charles Coulomb (1785), Hans Oersted (1820), Michael Faraday, James Clerck Maxwell (1865-1873), Hertz