Music Technology: Key Terms and Concepts
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
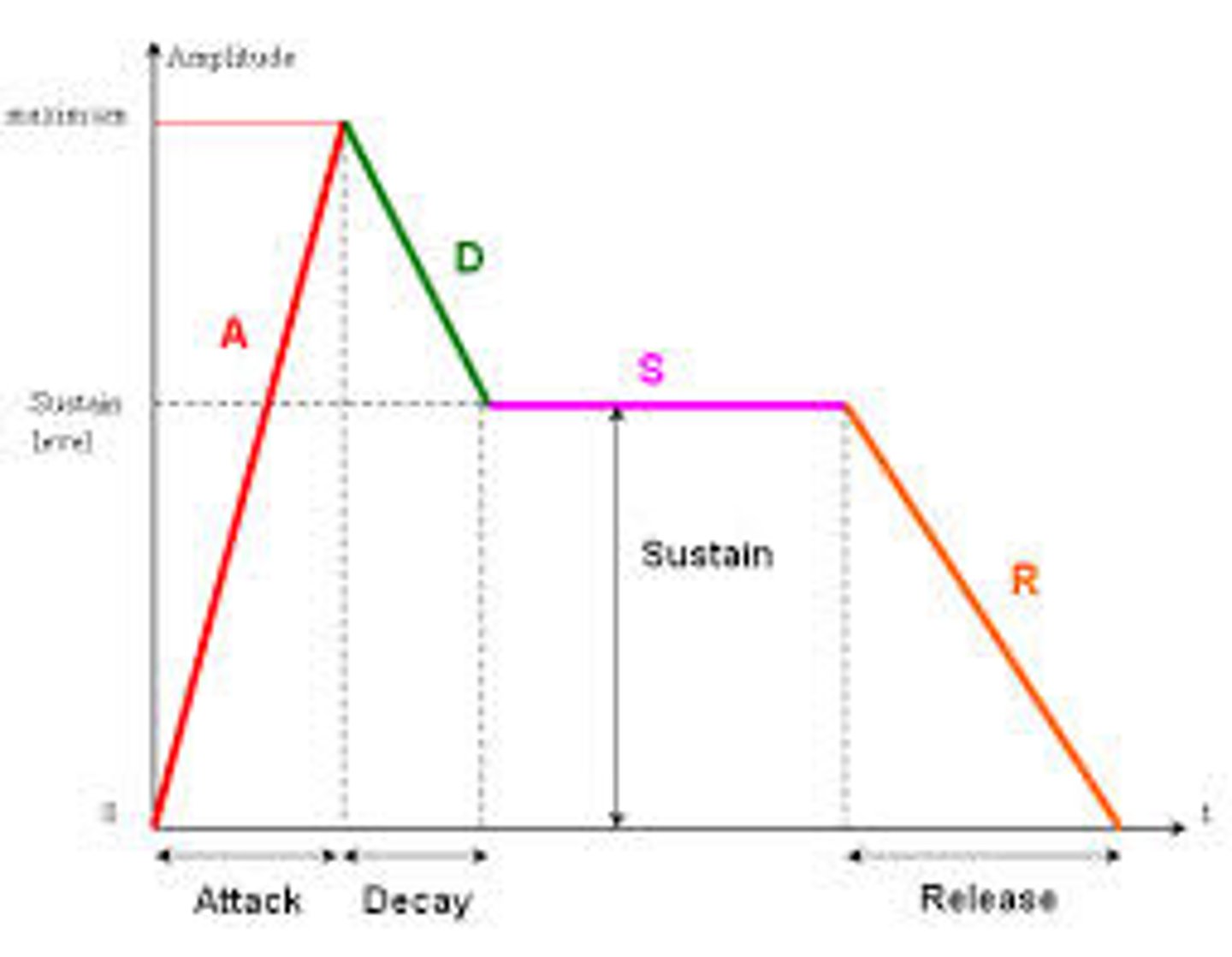
Attack, Decay, Sustain, Release
The four stages of an envelope that shape the dynamics of a sound.
Amplifier (Amp)
A device that increases the strength of an audio signal.

Analog Synthesis
Sound synthesis using analogue electrical signals, often found in vintage synths.
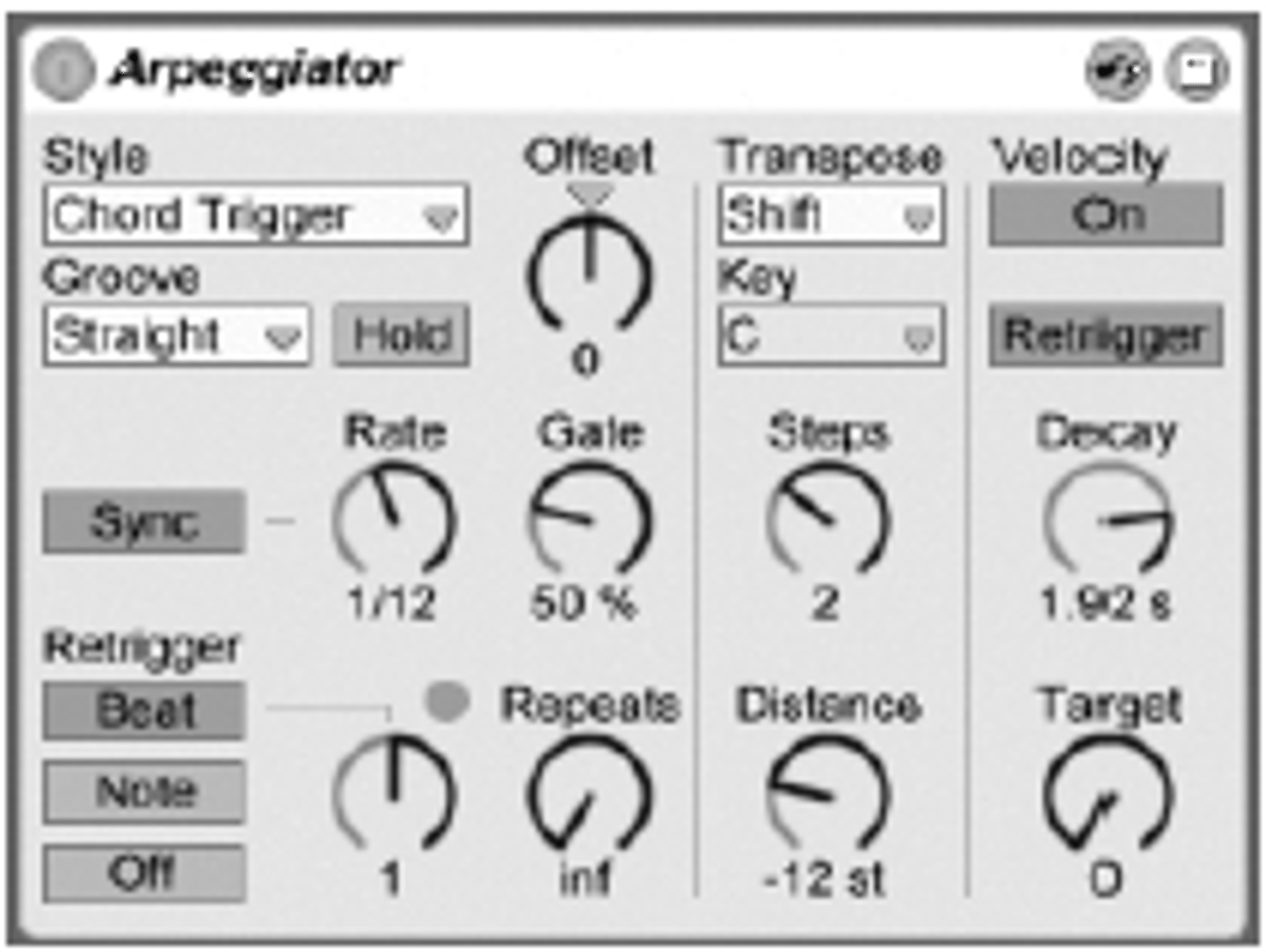
Arpeggiator
A function that automatically plays a sequence of notes in a set pattern.
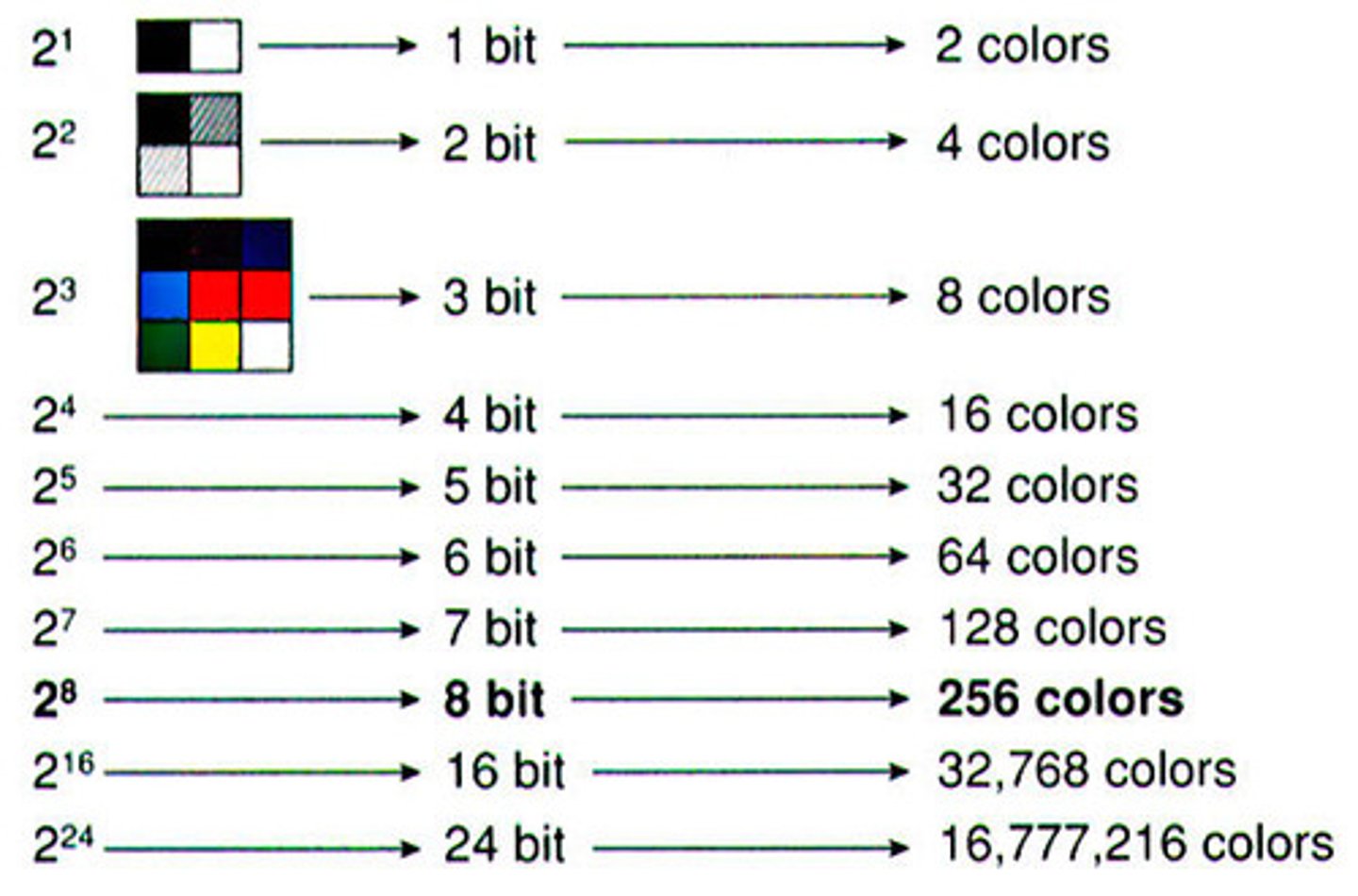
Bit Depth
The resolution of digital audio, determining dynamic range (e.g., 16-bit, 24-bit).
Bus
A signal path that allows multiple tracks to be routed together for processing.
Buffer Size
Determines the amount of latency in a digital audio workstation (DAW); smaller sizes reduce latency but increase CPU load.
Bypass
A mode that disables an effect without removing it from the signal chain.
Clipping
Distortion caused when an audio signal exceeds the maximum level.
Compressor
A dynamic processor that reduces the difference between loud and quiet sounds.
Crossfade
A gradual transition between two audio signals or tracks.

Cue Mix
A separate audio mix used for monitoring, often for performers during recording.
DAW (Digital Audio Workstation)
Software used for recording, editing, and producing music (e.g., Logic Pro, Ableton Live).
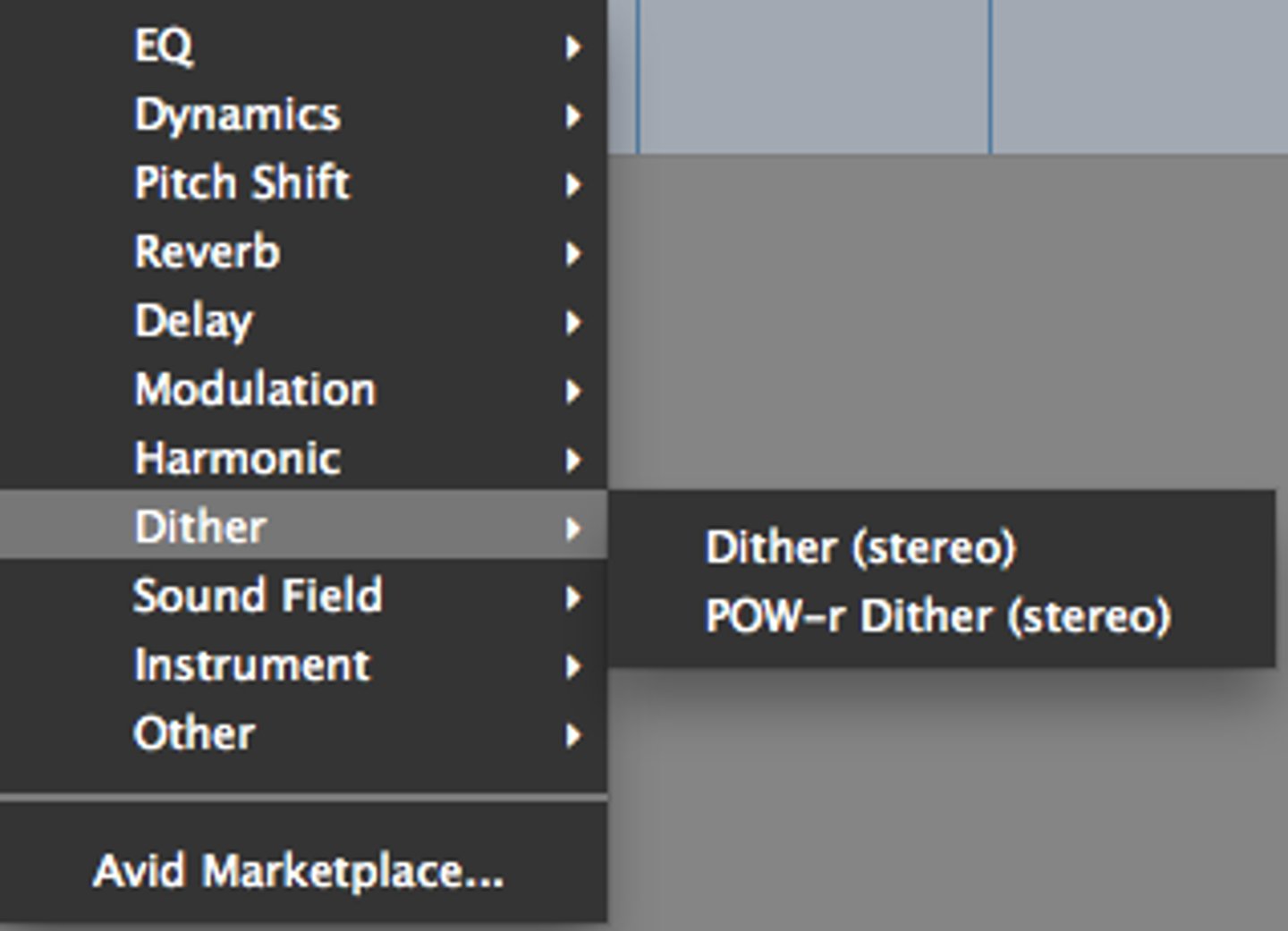
Dithering
A process that adds low-level noise to reduce quantisation errors when converting audio bit depth.
DSP (Digital Signal Processing)
The manipulation of audio using digital algorithms.

Distortion
An effect that alters a signal to add harmonic content, often used for guitar and synth sounds.
EQ (Equalisation)
The process of adjusting the balance of frequency components in an audio signal.
Envelope
A control signal that shapes a sound's evolution over time (see ADSR).
Export (or Bounce)
The process of rendering a final mix into a file format such as WAV or MP3.
Fade In/Out
A gradual increase or decrease in volume at the start or end of a track.
Feedback
A loop where an output signal is fed back into an input, often used in delay and reverb effects.
Filter
A tool used to remove or emphasise specific frequency ranges.
Gain
The amount of amplification applied to an audio signal.
Gate (Noise Gate)
A processor that mutes audio below a set threshold.
Glitch
A digital audio effect that introduces artefacts like stutters and errors for creative effect.
Harmonics
Overtones that accompany a fundamental frequency, affecting timbre.
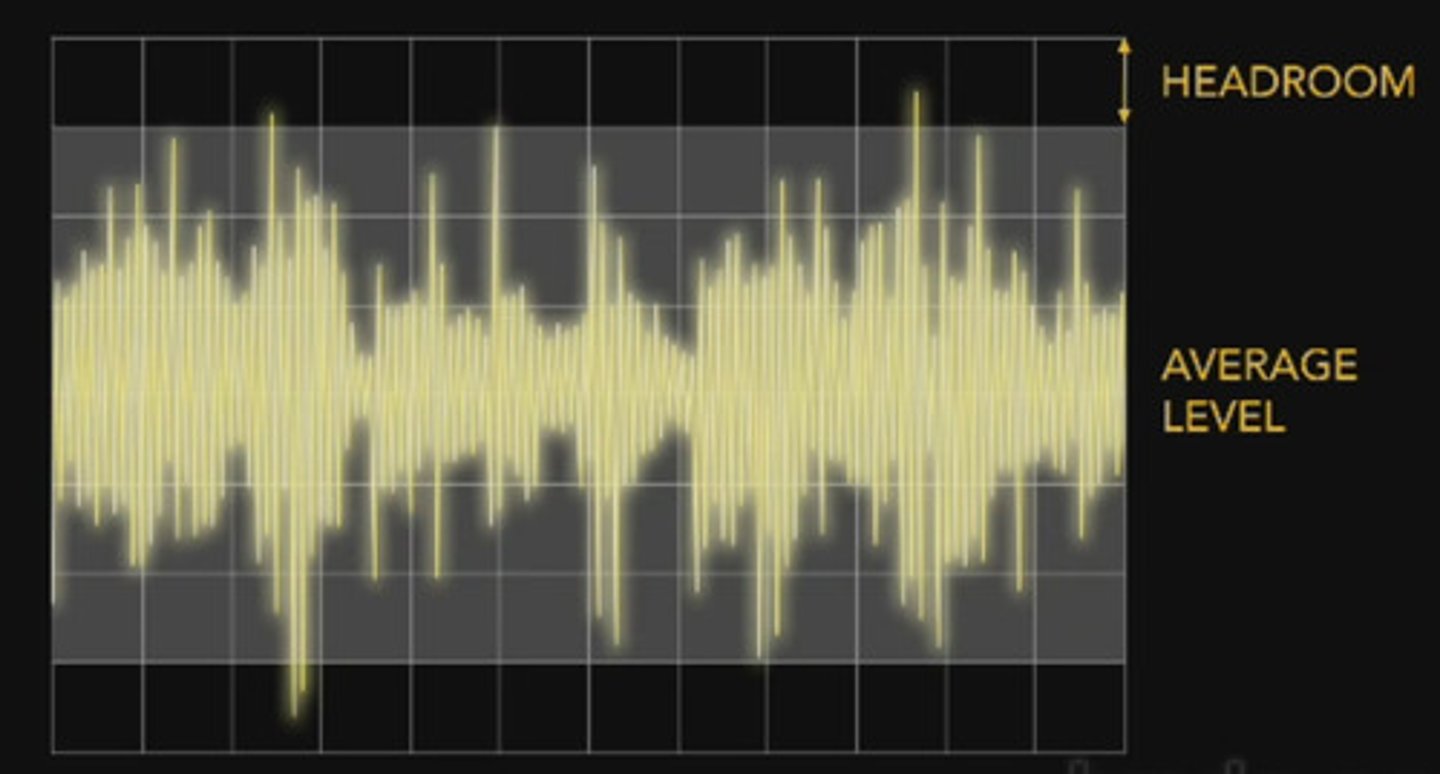
Headroom
The amount of available dynamic range before distortion occurs.
Impedance
The resistance of an audio circuit, important for matching microphones and speakers.
Interpolation
A digital process for smoothing out audio data when changing sample rates or pitch.
Interface (Audio Interface)
A device that connects microphones, instruments, and speakers to a computer.
Jitter
Timing irregularities in digital audio caused by clocking errors.
Key Tracking
A synthesis feature where a parameter changes depending on the pitch of a note played.
Knee (Compressor Knee)
The transition between uncompressed and compressed signal levels, can be soft or hard.
Latency
The delay between an input signal and the output, often an issue in digital systems.
Limiter
A type of compressor that prevents audio from exceeding a set level.
Loop
A repeated section of audio or MIDI, often used in electronic music production.
MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface)
A protocol for communicating performance data between electronic instruments and computers.
Mixing
The process of blending multiple audio tracks into a balanced final mix.
Modulation
The variation of a sound parameter over time, such as vibrato or tremolo.
Mono
Audio with a single channel, as opposed to stereo.
Normalisation
The process of increasing or decreasing an audio file's level to a maximum peak.
Nyquist Theorem
A principle stating that the sample rate must be at least twice the highest frequency of a signal to avoid aliasing.
Oscillator
The sound-generating component of a synthesizer.
Overdrive
A mild form of distortion, often used in guitar effects.
Pan (Panning)
The distribution of a sound within the stereo field.
Phaser
An effect that creates a sweeping sound by shifting phase relationships.
Pitch Bend
A function that alters the pitch of a note smoothly.
Plugin
A software component that adds functionality to a DAW (e.g., VST, AU, AAX).
Preamp (Preamplifier)
A device that amplifies weak signals, such as from a microphone.
Quantisation
The process of aligning notes or rhythms to a grid in a DAW.
Q Factor (Bandwidth)
Controls the width of a frequency band in an EQ.
Reverb
An effect that simulates reflections of sound in a space, creating ambience.
RMS (Root Mean Square)
A measurement of average audio signal level.
Routing
The assignment of audio signals through different paths in a DAW or mixing console.
Sample Rate
The number of times per second an audio signal is digitally captured (e.g., 44.1kHz, 48kHz).
Sampler
A device or plugin that plays back recorded audio snippets.
Sidechain Compression
A technique where one sound dynamically controls another, often used for ducking effects.
Sine Wave
A pure waveform with no harmonics, used as a basic building block in synthesis.
Stereo
Audio with two channels, creating a sense of width.
Sustain Pedal
A pedal that holds notes longer, commonly used with pianos.
Threshold
The level at which a compressor, limiter, or gate begins to affect a signal.
Time Stretching
A digital process that changes the speed of audio without affecting pitch.
Tremolo
A modulation effect that varies volume over time.
Tuning
The process of adjusting pitch accuracy, often using auto-tune or pitch correction.
Unison
When multiple voices or oscillators play the same note, often thickening a sound.
USB Audio Interface
A device that connects instruments and microphones to a computer via USB.
VCA (Voltage-Controlled Amplifier)
Used in synthesizers to control amplitude with voltage.
VCO (Voltage-Controlled Oscillator)
Generates waveforms in analogue synthesizers.
Velocity
The speed at which a MIDI note is played, affecting dynamics.
VST (Virtual Studio Technology)
A plugin format for effects and instruments in DAWs.
Waveform
A graphical representation of a sound's amplitude over time.
Wavetable Synthesis
A synthesis method that uses short digital waveforms as oscillators.
Wet/Dry Mix
The balance between processed (wet) and unprocessed (dry) signals in effect.
XLR
A type of balanced audio connector used for microphones.
Zero Crossing
A point where a waveform passes through zero amplitude, used in editing to prevent clicks.
Control Change