Basins
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:34 AM on 3/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
basins on continental crust
last longer
2
New cards
Three ways to make a sedimentary basin
RIFTING
THERMAL SUBSIDENCE
FLEXURE
THERMAL SUBSIDENCE
FLEXURE
3
New cards
RIFTING
1. extensional thinning of the lithosphere
2. followed by isostatic adjustment
3. timescale of adjustment ≈ 105 years
4
New cards
THERMAL SUBSIDENCE
1. following rifting, cooling of the lithosphere and the
asthenosphere, and subsequent isostatic adjustment
2. timescale of subsidence ≈ 50 x 106 yrs
5
New cards
FLEXURE
1. elastic bending of lithosphere under load
2. not permanent - if load is removed, some recovery on
timescales of 1-100 x 106 years
3. encountered in convergent margins
6
New cards
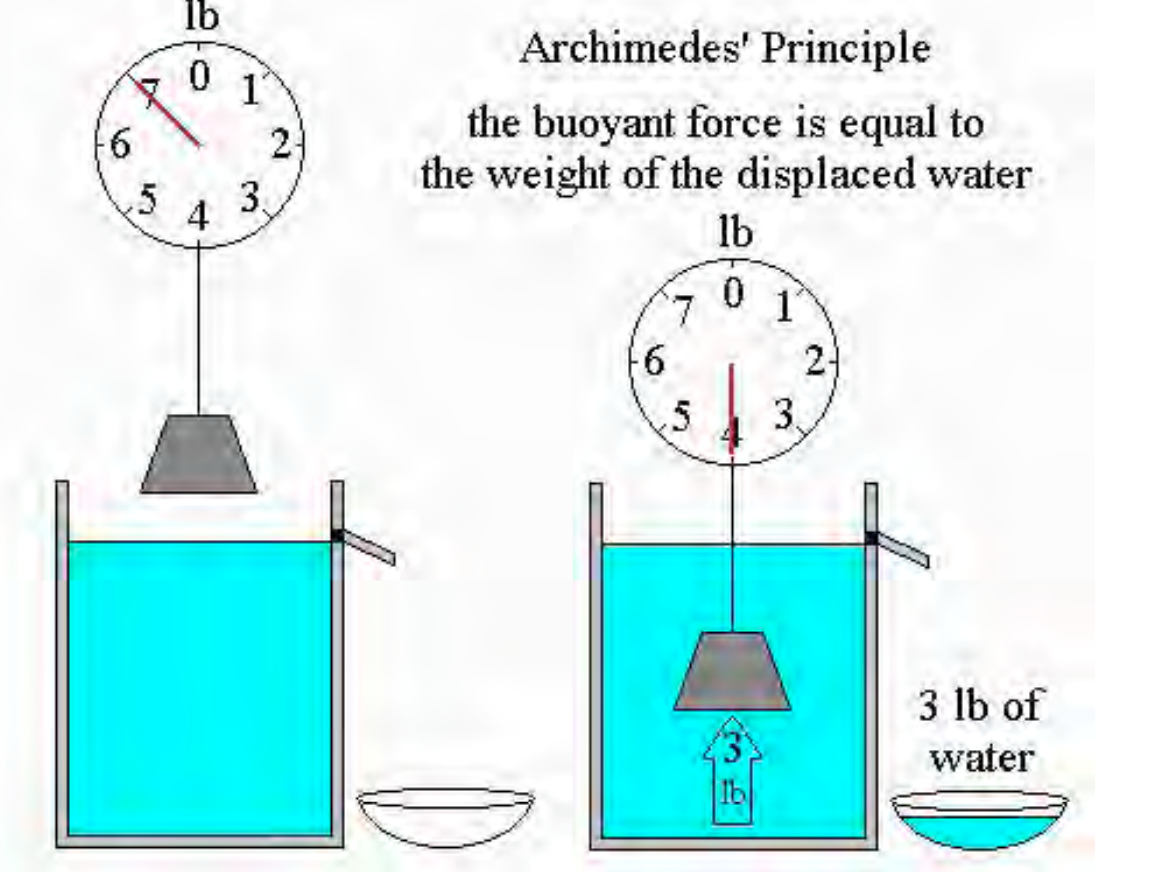
Archimede’s Principle
the boyant force in = to the displaced water
7
New cards
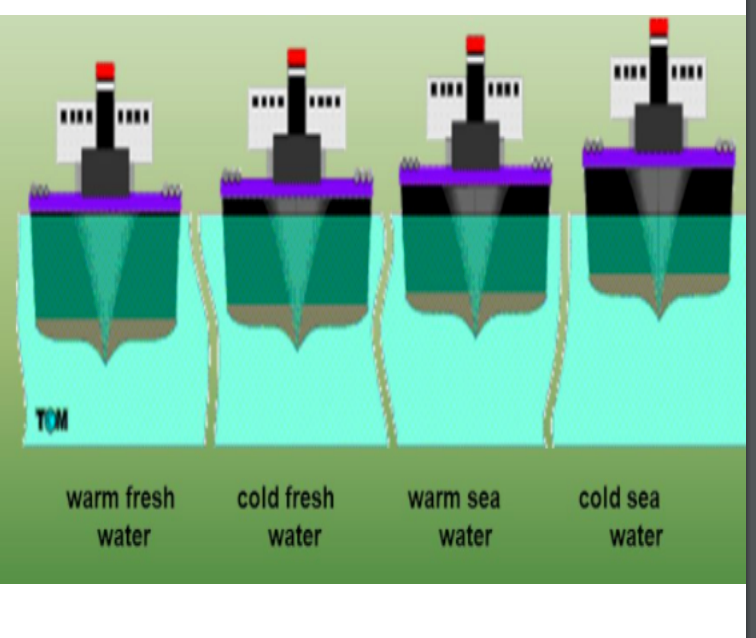
Isostasy
isostasy: state of gravitational equilibrium provided by buoyant force from a fluid that supports a floating solid
8
New cards
compensation depth
line of equal pressure form above and below
9
New cards
non-Newtonian fluid
viscosity changes with strain rate
deforms like solid under high strain rates (earthquakes!) deforms like a fluid under low strain rates (plate tectonics)
deforms like solid under high strain rates (earthquakes!) deforms like a fluid under low strain rates (plate tectonics)
10
New cards
Rifting and isostatic adjustment
lithosphere block will sink bc it has been thinned
created rift basin and a depression to collect water air and sediment
created rift basin and a depression to collect water air and sediment
11
New cards
most important factors of sediments thickness
B=how much thinning=orig thick/new thickness (cursta nd lisophere)
\
B^=ys^
\
ps= density of filling
ps^=ys^
\
\
\
B^=ys^
\
ps= density of filling
ps^=ys^
\
\
12
New cards
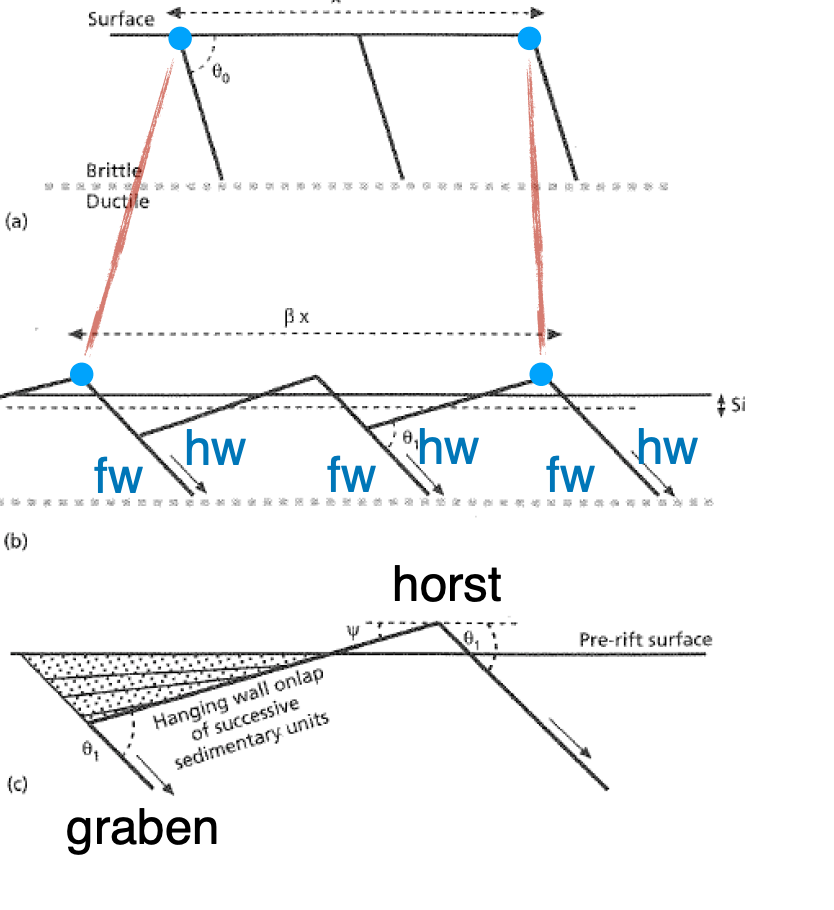
Rift basins
13
New cards
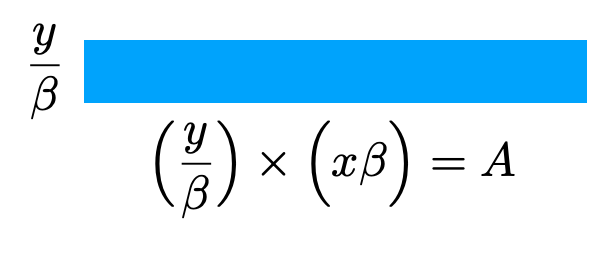
beta can show up as stretching
beta is always greater than 1
14
New cards
syn-rift sediments thicken
towards faults and are rotated more with increasing age
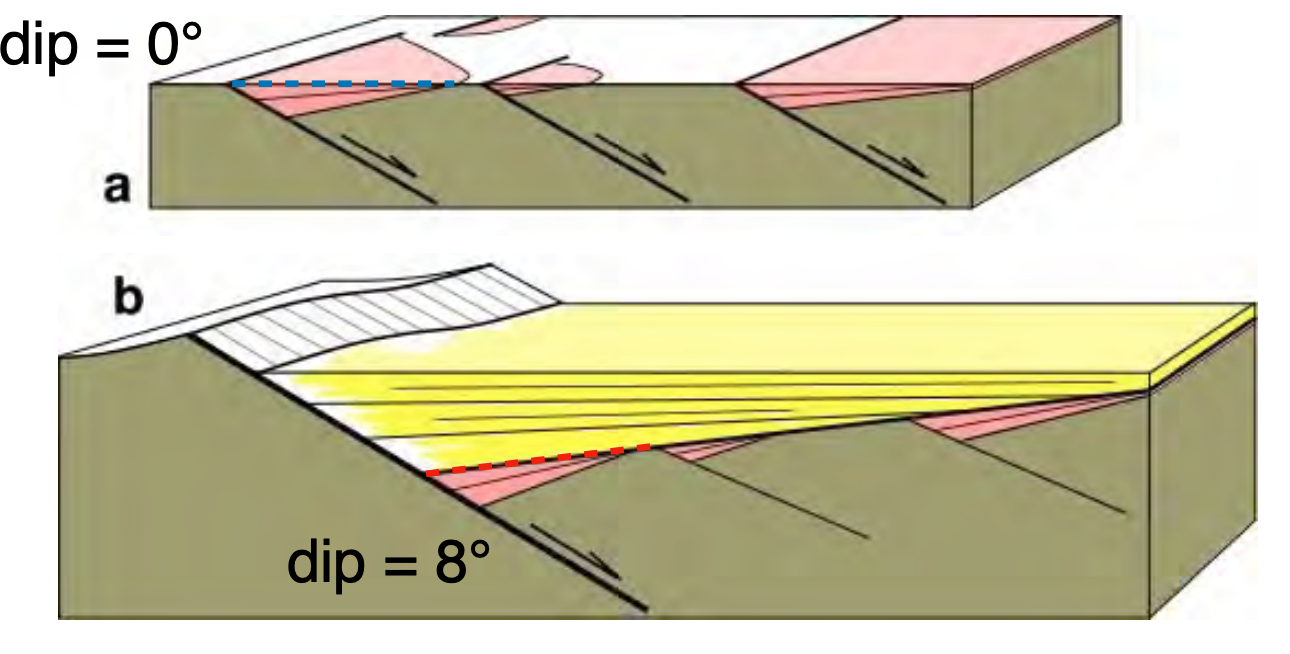
15
New cards
where will you find courses sediments in rift lake
footwalls form aluvial fans and steep systems
16
New cards
Rift basins - marine
rift sediments are fault bounded and more rotated with increasing age
17
New cards
marine vs lake
reefs form at foot wall bc of the nutrients and shallowness
18
New cards
after rifting
asthenosphere rises adds heat
cools to reach EQ and then sinks bc of density
thermal substance
cools to reach EQ and then sinks bc of density
thermal substance
19
New cards
cooling crust
as sea floor ages the dense lithospheric mantle thickens an the sea-flour gets deeper
\
older thicker lithosphere sinks deeper
\
older thicker lithosphere sinks deeper
20
New cards
Rift and Drift
**rift**: confined to the grabens the layers thicken towards fault plane
**drift:** gentle draping
**drift:** gentle draping
21
New cards
Garben and horst
gar
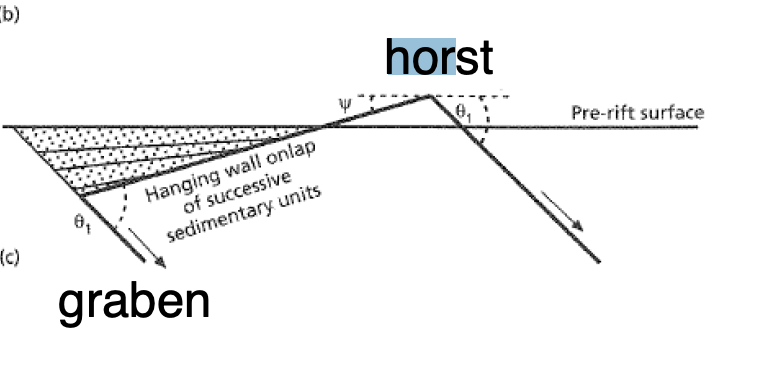
22
New cards
reFlex
1. elastic bending of lithosphere under load
2. not permanent - if load is removed, some recovery on
timescales of 1-100 x 106 years
3. encountered in convergent margins
23
New cards
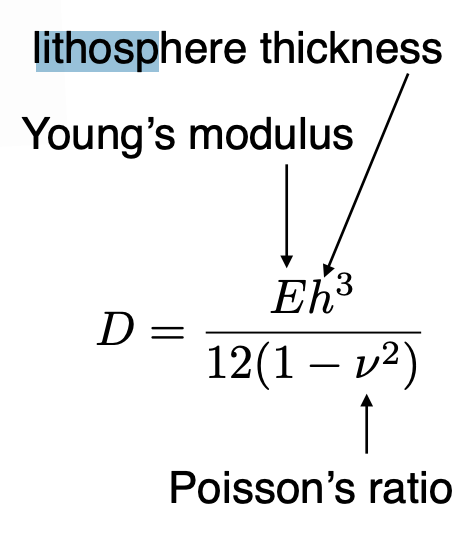
flexural rigidity
larger D = more rigid = less flexure
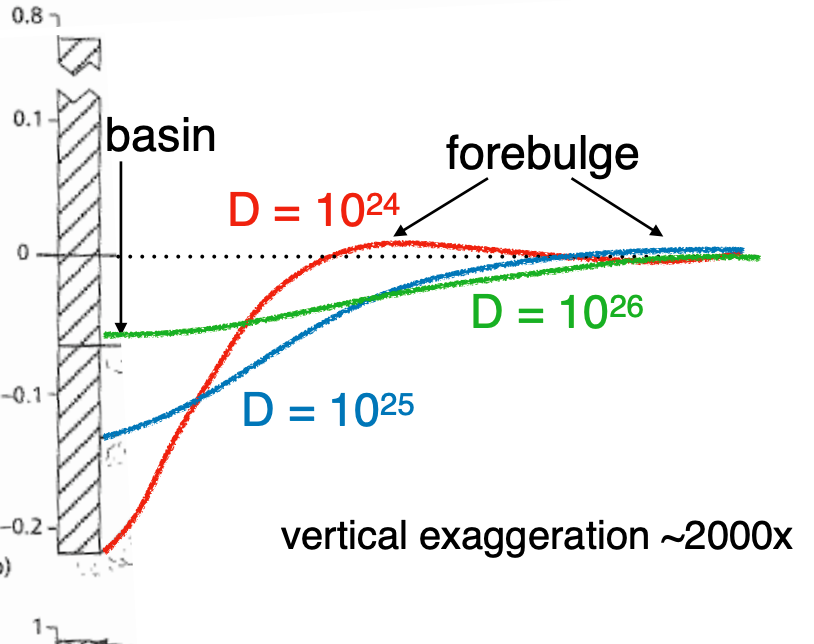
24
New cards
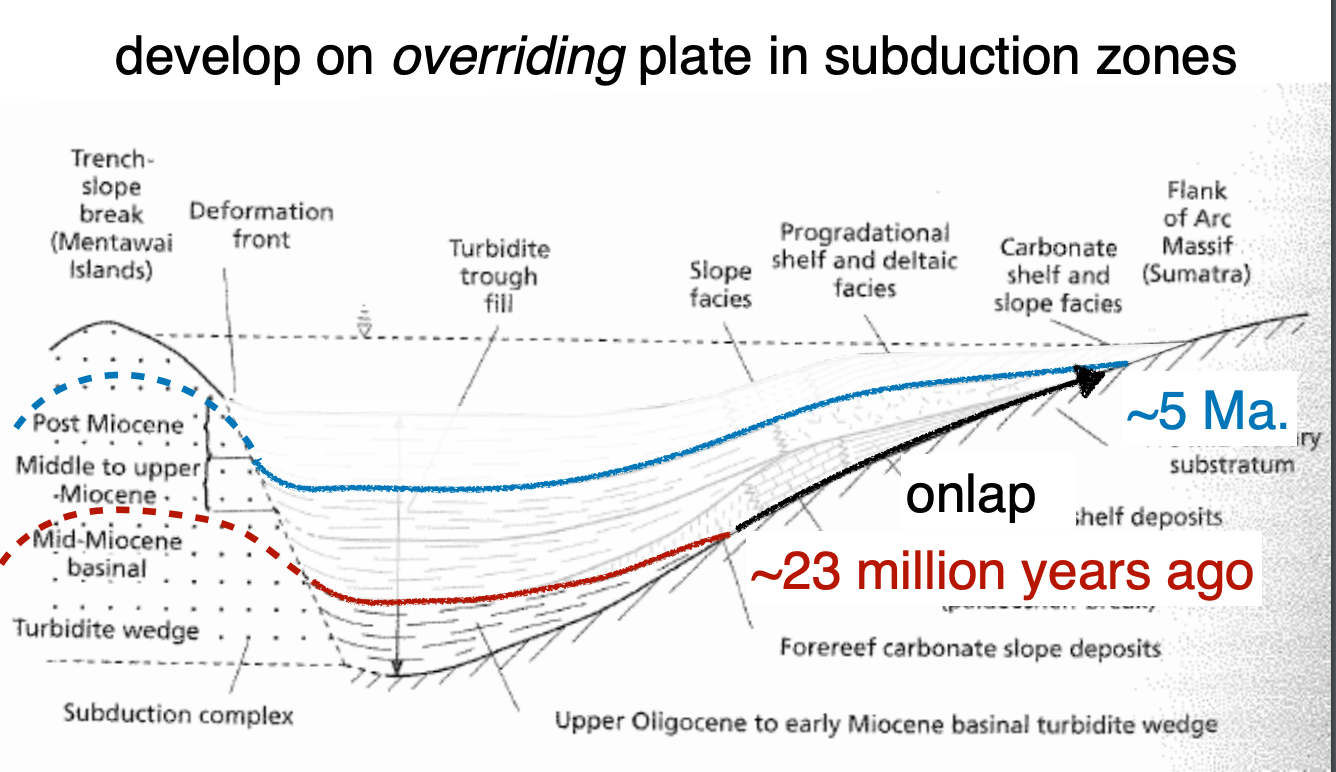
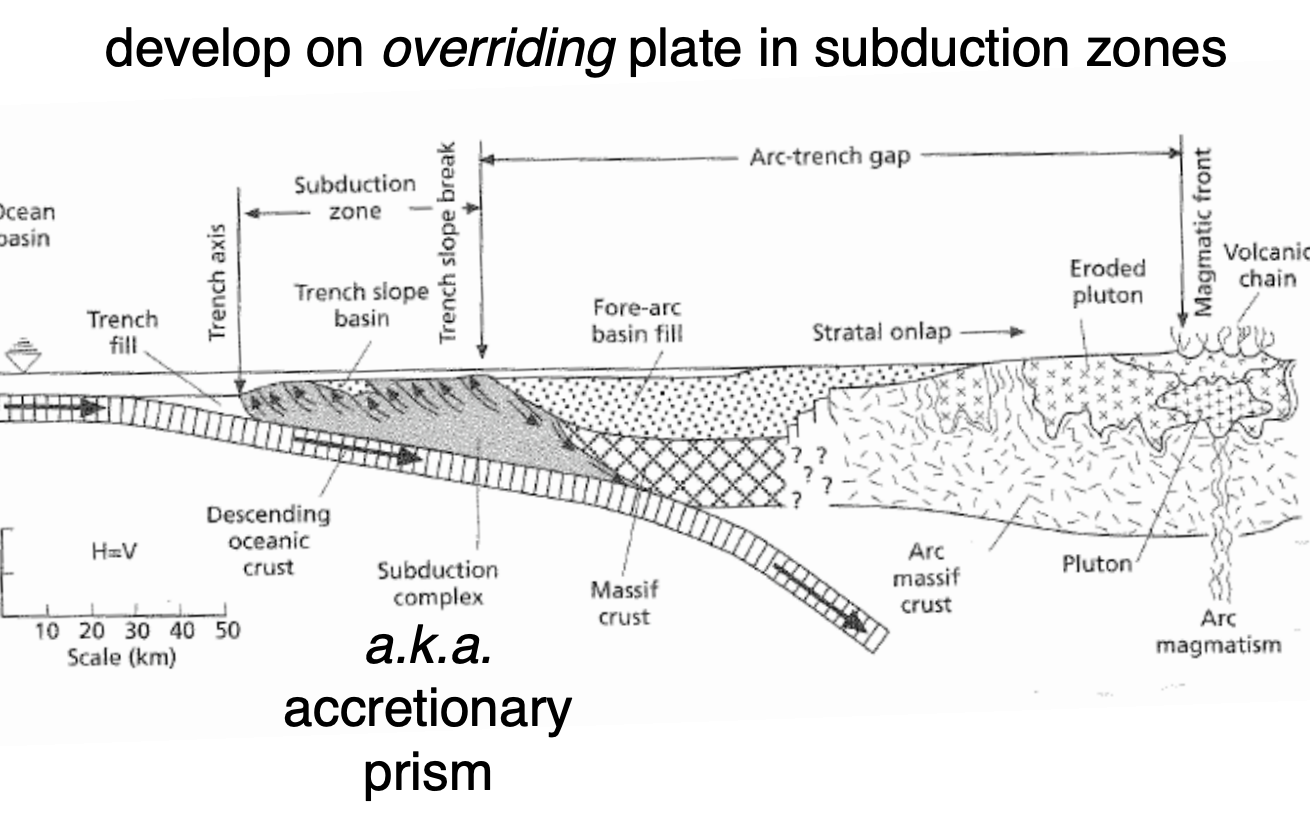
Fore arc basins
25
New cards
back arc
develop on overriding plate undergoing extension
mantle flow pulls
mantle flow pulls
26
New cards
Foreland basins
develop on continental crust of underridina/subducting plate
\
basin move landwards as oreogenic wedge grows with time
==sed rate increases with time as the wedge gets larger and mroe heavy==
\
\
basin move landwards as oreogenic wedge grows with time
==sed rate increases with time as the wedge gets larger and mroe heavy==
\
27
New cards
thermal subtinence sedimentation
Decreases with time