TOPIC 8: Metabolism, Cell Respiration, Photosynthesis
1.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:35 PM on 5/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
1
New cards
Cell Respiration
is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds (principally glucose) to produce ATP within cells
\
\
2
New cards
Organic molecules
**store** energy within their chemical bonds
* The energy is **not** easily accessible for use within the cell
\
* The energy is **not** easily accessible for use within the cell
\
3
New cards
ATP functions as
an immediate source of energy within cells
* The energy is readily accessible for use within the cell
* ATP is considered to be the *energy* currency of all cells
\
* The energy is readily accessible for use within the cell
* ATP is considered to be the *energy* currency of all cells
\
4
New cards
ATP consists of
nucleoside linked to 3 phosphates via high energy bonds
* When ATP is hydrolysed to ADP (+P), the energy contained is released for use
\
* When ATP is hydrolysed to ADP (+P), the energy contained is released for use
\
5
New cards
the two types off cell respiration
* **Anaerobic** respiration
* **Aerobic** respiration
\
* **Aerobic** respiration
\
6
New cards
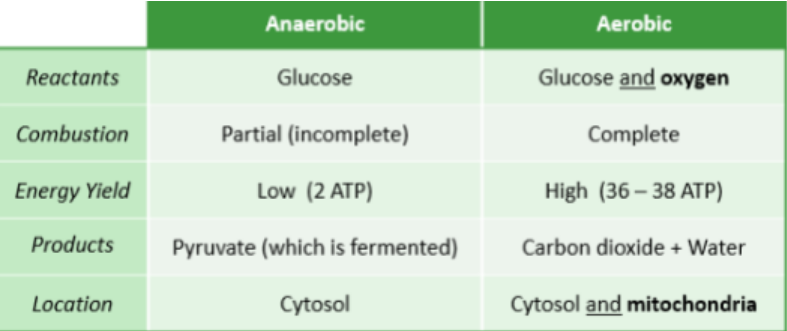
Anaerobic respiration
\
The **partial** breakdown of organic compounds for a small ATP yield. (net gain = 2 x AATP)
\
***Also takes place in the presence of oxygen***
Via glycolysis:
* Glucose is converted into pyruvate ( x2)
* There is a net gain of **two ATP**
* Oxidized carrier molecules (NAD+) are reduced to form two hydrogen carrier molecules (NADH)
The **partial** breakdown of organic compounds for a small ATP yield. (net gain = 2 x AATP)
\
***Also takes place in the presence of oxygen***
Via glycolysis:
* Glucose is converted into pyruvate ( x2)
* There is a net gain of **two ATP**
* Oxidized carrier molecules (NAD+) are reduced to form two hydrogen carrier molecules (NADH)
7
New cards
Aerobic respiration
The **complete** breakdown of organic compounds for a large ATP yield. (net gain = 36 x ATP)
* ***Takes place in the absence of oxygen***
\
Via aerobic respiration:
* Hydrogen carriers are made in large quantities
* These hydrogen carriers (NADH) are used to produce significant amounts of ATP (net = 36) via the process of oxidative phosphorylation
\
* ***Takes place in the absence of oxygen***
\
Via aerobic respiration:
* Hydrogen carriers are made in large quantities
* These hydrogen carriers (NADH) are used to produce significant amounts of ATP (net = 36) via the process of oxidative phosphorylation
\
8
New cards
Compare and contrast anaerobic and aerobic cell respiration
9
New cards
Oxidation
* Addition of oxygen atoms
* Removal of hydrogen atoms
* Loss of electrons from a substance
\
* Removal of hydrogen atoms
* Loss of electrons from a substance
\
10
New cards
Reduction
* Removal of oxygen atoms
* Addition of hydrogen atoms
* Addition of electrons to a substance
\
* Addition of hydrogen atoms
* Addition of electrons to a substance
\
11
New cards
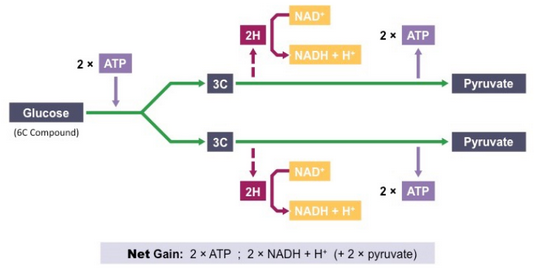
Glycolysis
occurs in the cytosol and does not require oxygen (it is an anaerobic process)
1. Phosphorylation
2. Lysis
3. Oxidation
4. ATP Formation
\
1. Phosphorylation
2. Lysis
3. Oxidation
4. ATP Formation
\
12
New cards
1. Phosphorylation
1. A hexose sugar (typically glucose) is phosphorylated by two molecules of ATP (to form a hexose bisphosphate)
2. This phosphorylation makes the molecule less stable and more reactive, and also prevents diffusion out of the cell
\
13
New cards
2. Lysis
1. The hexose bisphosphate (6C sugar) is split, with water, into two triose phosphates (3C sugars)
\
14
New cards
3. Oxidation
1. Hydrogen atoms are removed from each of the 3C sugars (via oxidation) to reduce NAD+ to NADH (+ H+)
2. Two molecules of NADH are produced in total (one from each 3C sugar)
\
15
New cards
4. ATP Formation
\
1. Some of the energy released from the sugar intermediates is used to directly synthesise ATP
2. This direct synthesis of ATP is called *substrate level phosphorylation*
3. In total, 4 molecules of ATP are generated during glycolysis by substrate level phosphorylation (2 ATP per 3C sugar)
\
16
New cards
At the end of glycolysis, the following reactions have occurred:
\
\
* Glucose (6C) has been broken down into two molecules of pyruvate (3C)
* Two hydrogen carriers have been reduced via oxidation (2 × NADH + H+)
* A **net** total of two ATP molecules have been produced (4 molecules were generated, but 2 were used)
\
* Two hydrogen carriers have been reduced via oxidation (2 × NADH + H+)
* A **net** total of two ATP molecules have been produced (4 molecules were generated, but 2 were used)
\
17
New cards
Fermentation
__**(occurs in cytoplasm)**__
releases energy from food molecules by producing ATP
* Follows glycolysis when **oxygen is not available** (anaerobic)
* By passing high-energy electrons back to pyruvic acid, NADH turns into NAD+ →allowing glycolysis to produce a steady supply of ATP
\
releases energy from food molecules by producing ATP
* Follows glycolysis when **oxygen is not available** (anaerobic)
* By passing high-energy electrons back to pyruvic acid, NADH turns into NAD+ →allowing glycolysis to produce a steady supply of ATP
\
18
New cards
Alcoholic Fermentation
\
\
* Used by yeasts and other microorganisms
* Produces ethyl alcohol and CO2
* Pyruvic Acid + NADH → Alcohol + CO2 + NAD+
\
* Produces ethyl alcohol and CO2
* Pyruvic Acid + NADH → Alcohol + CO2 + NAD+
\
19
New cards
Lactic Acid Fermentation
* Most organisms carry out fermentation by converting **pyruvic acid** to **lactic acid**
* Doesn’t give out CO2
* Regenerates NAD+ so glycolysis can continue
* NADH + Pyruvic Acid → Lactic Acid + NAD+
\
* Doesn’t give out CO2
* Regenerates NAD+ so glycolysis can continue
* NADH + Pyruvic Acid → Lactic Acid + NAD+
\
20
New cards
Explain the relationship between the structure and function of the mitchondria
* having two membranes(the inner and outer) → creates separate compartments within the mitochondrion
* Having these separate compartments also allows for a concentration gradient to occur(where the higher H+ concentration shifts to the area with the lower H+ concentration)
* this allows for diffusion to occur to power phosphorylation of ADP→ ATP
* Cristae increases the surface area of the inner membrane → this allows for more proteins that make up ETC→ this increases ATP molecule production
* Having these separate compartments also allows for a concentration gradient to occur(where the higher H+ concentration shifts to the area with the lower H+ concentration)
* this allows for diffusion to occur to power phosphorylation of ADP→ ATP
* Cristae increases the surface area of the inner membrane → this allows for more proteins that make up ETC→ this increases ATP molecule production
21
New cards
Where does the krebs cycle occur
in the matrix of the mitochondria
22
New cards
What is the general goal of the krebs cycle
over a series of reactions, the 6C compound is broken down to reform the original 4C compound(hence, a cycle)
\
Per glucose molecule, the Krebs cycle produces: 4 × CO2 ; 2 × ATP ; 6 × NADH + H+ ; 2 × FADH2
\
\
Per glucose molecule, the Krebs cycle produces: 4 × CO2 ; 2 × ATP ; 6 × NADH + H+ ; 2 × FADH2
\
23
New cards
Steps of the krebs cycle
* Two carbon atoms are released via decarboxylation to form two molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2)
* Multiple oxidation reactions result in the reduction of hydrogen carriers (3 × NADH + H+; 1 × FADH2)
* One molecule of ATP is produced directly via substrate-level phosphorylation
* As the link reaction produces **two** molecules of acetyl CoA (one per each pyruvate), the Krebs cycle occurs *twice*
\
\
* Multiple oxidation reactions result in the reduction of hydrogen carriers (3 × NADH + H+; 1 × FADH2)
* One molecule of ATP is produced directly via substrate-level phosphorylation
* As the link reaction produces **two** molecules of acetyl CoA (one per each pyruvate), the Krebs cycle occurs *twice*
\
\
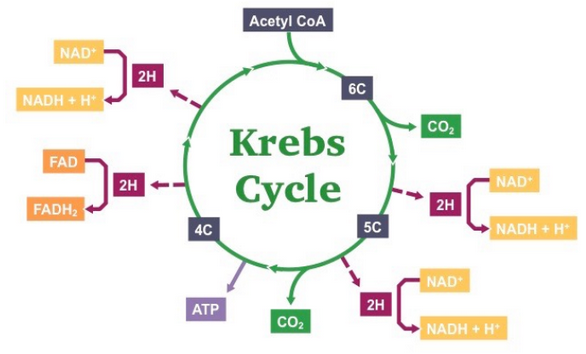
24
New cards
Where does the electron transport chain occur
the inner mitochondrial membrane
25
New cards
What is the general goal of the electron transport chain(ETC)
it releases the energy stored within the reduced hydrogen carriers in order to synthesize ATP → oxidative phosphorylation
26
New cards
Steps of the electron transport chain
1. NAD →NAD+ + e- + H+
1. Gets oxidized→ loses electron and H+
2. Electrons are used to pump H+ from matrix to intermembrane space
2. FADH2 → FAD + e+ + H+
1. Gets oxidized → loses electrons and H+
2. Electrons are used to pump H+ from matrix to intermembrane space
3. High concentration of H+ in intermembrane space; Low H+ concentration in matric →**concentration gradient (proton gradient)**
4. Oxygen is final electron acceptor; H2O is formed as waste product
* ADP + P → ATP
1. H+ flows down concentration gradient, diffusing through ATP synthase
\
27
New cards
Metabolism definition
describes the sum total of all reactions that occur within an organism in order to maintain life.
\
\
28
New cards
Pathways
are a series of reactions that result in most chemical changes in a cell.
* each step is controlled by a specific enzyme
* each step is controlled by a specific enzyme
29
New cards
Metabolic Pathways
allow for a greater level of regulation, as the chemical change is controlled by numerous intermediates
\
they are typically organized into chains or cycles of enzyme catalyzed reactions.
* examples of chains: glycolysis (in cell respiration), coagulation cascade (in blood clotting)
\
they are typically organized into chains or cycles of enzyme catalyzed reactions.
* examples of chains: glycolysis (in cell respiration), coagulation cascade (in blood clotting)
30
New cards
Examples off cycles
the krebs cycle (in cell respiration) and the calvin cycle (in photosynthesis)
31
New cards
Anabolism
the *building up* - desscribes the set of metabolic reactions that build up complex molecules from simpler ones
\
* **Synthesizes complex molecules from simpler ones**
* **Uses energy to construct new bonds (endergonic)**
* **Typically involves reduction reactions**
\
\
* **Synthesizes complex molecules from simpler ones**
* **Uses energy to construct new bonds (endergonic)**
* **Typically involves reduction reactions**
\
32
New cards
Condensation reactions occur when
monomers are covalently joined and water is produced as a by-product
33
New cards
monosaccharides are joined via
glycosidic linkage to form disaccharides and polysaccharides(via condensation)
34
New cards
amino acids are joined via
\
\
peptide bonds to make polypeptide chains
\
\
35
New cards
glycerol an fatty acids are joined via
\
\
ester linkage to create triglycerides
\
\
36
New cards
nucleotides are joined by
\
\
phosphodiester bonds to form polynucleotide chains
\
\
37
New cards
Condensation
smaller molecules are assembled into larger ones AND water is produced
38
New cards
Catabolism
*breaking down;* describes the set of metabolic reactions that break complex molecules down into simpler molecules
\
* **Breaking down complex molecules into simpler knees**
* **Releases energy when bonds are broken (exergonic)**
* **Typically involves oxidation reactions**
\
\
* **Breaking down complex molecules into simpler knees**
* **Releases energy when bonds are broken (exergonic)**
* **Typically involves oxidation reactions**
\
39
New cards
Hydrolysis reactions require
the consumption of water molecules to break the bonds within the polymer
40
New cards
Chlorophyll
* Main pigment in green plants
* Needed for photosynthesis
* Capture light
* Intakes red + blue/violet light
* Reflects green light
* 2 Forms: chlorophyll A & B
\
* Needed for photosynthesis
* Capture light
* Intakes red + blue/violet light
* Reflects green light
* 2 Forms: chlorophyll A & B
\
41
New cards
Xanthophyll
can be seen on leaves in the autumn; reflects yellow light
42
New cards
Carotene
can be seen on leaves in the autumn; reflects orange light
43
New cards
Light Dependent Reactions
\
* occurs in thylakoids
* uses light energy to make ATP and NADPH
* splits H2O in photolysis to replace electrons and H+ release O2 into the atmosphere
* 2 e- transport chains, Photosystems 2 and 1
use light energy to produce ATP and to split water (photolysis), making H+ ions
Photolysis: 6H2O → O2 + H+
* occurs in thylakoids
* uses light energy to make ATP and NADPH
* splits H2O in photolysis to replace electrons and H+ release O2 into the atmosphere
* 2 e- transport chains, Photosystems 2 and 1
use light energy to produce ATP and to split water (photolysis), making H+ ions
Photolysis: 6H2O → O2 + H+
44
New cards
Light independent reactions
* occurs in stroma
* uses ATP and NADH to form triose phosphate
* returns ADP, inorganic phosphate and NADP to light-dependent reactions
* involves calvin cycle
Some O2 is a waste product
use ATP and H+ ions to “fix” CO2, making glucose
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
→ ADP → ATP
\
* uses ATP and NADH to form triose phosphate
* returns ADP, inorganic phosphate and NADP to light-dependent reactions
* involves calvin cycle
Some O2 is a waste product
use ATP and H+ ions to “fix” CO2, making glucose
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
→ ADP → ATP
\
45
New cards
electromagnetic energy
* energy for photosynthesis, comes from light
* travels in wavelengths
* visible light spectrum is important for photosynthesis
* shorter wavelengths = higher energry
* specific pignments absorb light more efficiently within certain wavelengths
\
* travels in wavelengths
* visible light spectrum is important for photosynthesis
* shorter wavelengths = higher energry
* specific pignments absorb light more efficiently within certain wavelengths
\
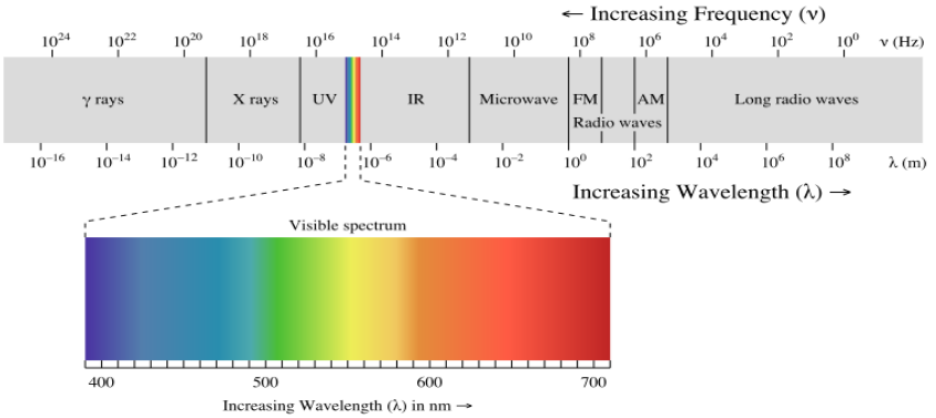
46
New cards
Spectrophometer
device to measure absorption at various light wavelengths
* produces absorption spectrum
* produces absorption spectrum
47
New cards
Absorption spectrum
combination of all absorption spectra of all pigments in chloroplasts
\
\
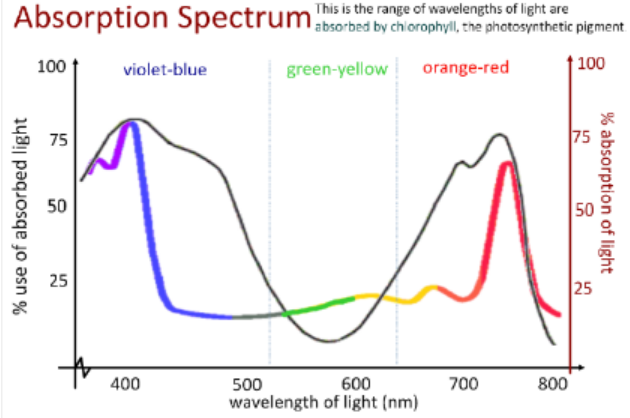
48
New cards
Action spectrum
* the rate of photosynthesis at particular wavelengths of visible light
* Produce action spectrum by measuring oxygen production → high oxygen = high rate of photosynthesis
* Light energy drives photosynthesis, the wavelength of the light absorbed by chloroplasts partly determines photosynthetic rate
\
* Produce action spectrum by measuring oxygen production → high oxygen = high rate of photosynthesis
* Light energy drives photosynthesis, the wavelength of the light absorbed by chloroplasts partly determines photosynthetic rate
\
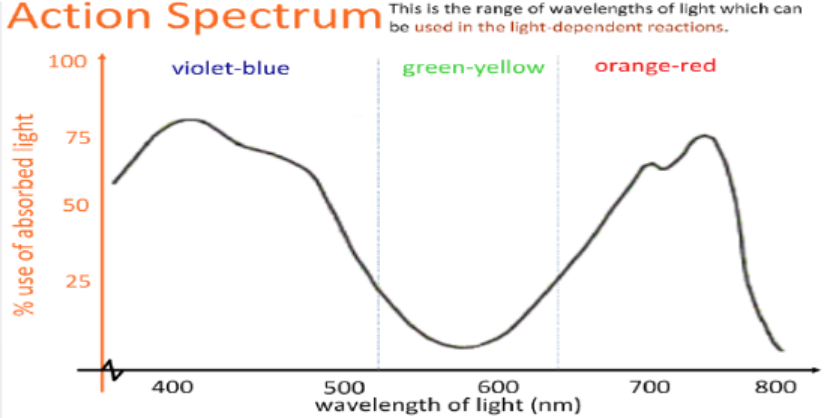
49
New cards
The __**action spectrum**__ of photosynthesis and __**absorption spectrum**__ of chlorophyll…
overlap each other - this tells us that chlorophyll is the most important of the photosynthetic pigments (there are others).
\
* __Blue light__ and __red light__ → __greatest absorption__ & peak in rate of photosynthesis
* __Green light__ → __Low absorption__ corresponds to lower rate of photosynthesis
\
\
* __Blue light__ and __red light__ → __greatest absorption__ & peak in rate of photosynthesis
* __Green light__ → __Low absorption__ corresponds to lower rate of photosynthesis
\
50
New cards
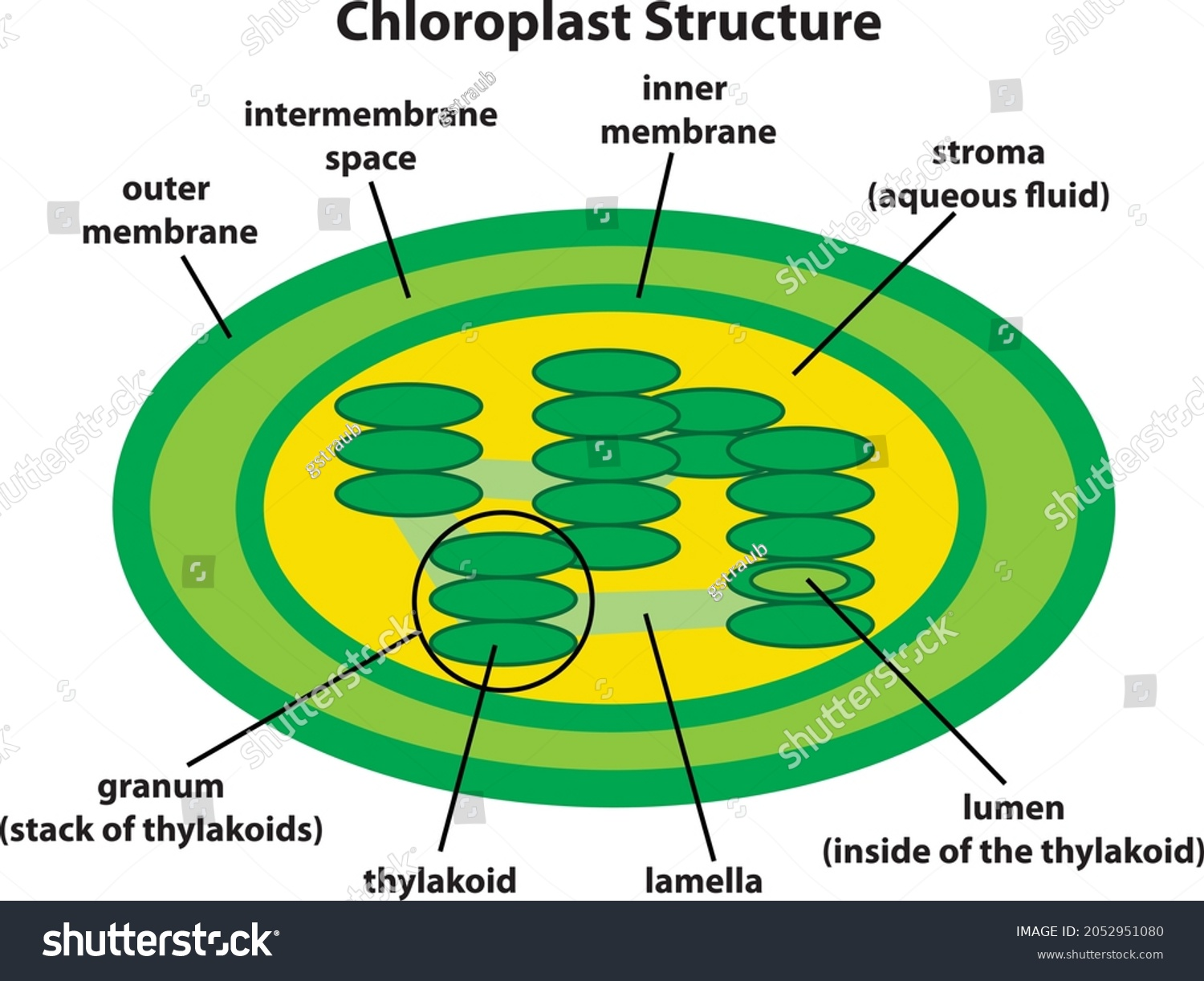
The chloroplast
where photosynthesis takes place
has:
* extensive membrane surface area of thylakoids
* small space(lumen) within thylakoids
* grana
* chlorophyll
* Stroma
* double membrane(inner and outer)
* isolates working parts and enzymes from surrounding cytoplasm
\
has:
* extensive membrane surface area of thylakoids
* small space(lumen) within thylakoids
* grana
* chlorophyll
* Stroma
* double membrane(inner and outer)
* isolates working parts and enzymes from surrounding cytoplasm
\
51
New cards
Thylakoids
internal structure of chloroplasts
* allows greater absorption of light by photosystems
* their lumen allows for faster accumulation of protons to create a concentration gradient
* allows greater absorption of light by photosystems
* their lumen allows for faster accumulation of protons to create a concentration gradient
52
New cards
grana
flattened disk shaped structure formed from thylakoids
53
New cards
chlorophyll
photosynthetic pigment embedded in thylakoids
54
New cards
stroma
colorless substance containing enzymes, RNA, DNA, and ribosomes that surrounds the thylakoids
* allows area for enzymes necessary for the calvin cycle
* allows area for enzymes necessary for the calvin cycle
55
New cards
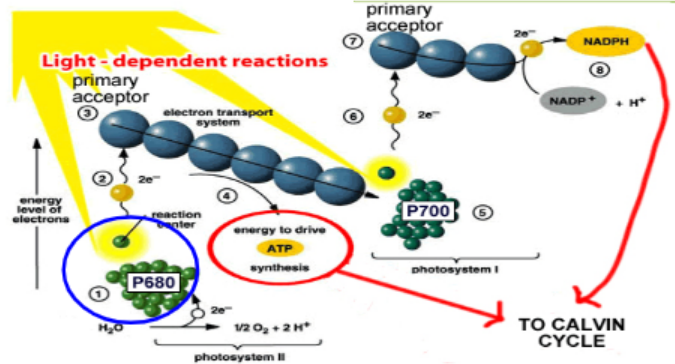
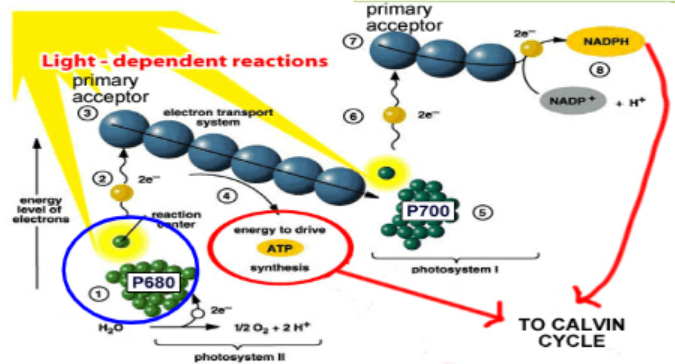
Light dependent reactions
light energy is absorbed and converted into chemical energy
* occur in the thylakoids of grana
* one stack of thylakoids=1 granum
* plants during this phase absorb sunglight (photons) using pigments such as chlorophyll and cartenoids
\
* occur in the thylakoids of grana
* one stack of thylakoids=1 granum
* plants during this phase absorb sunglight (photons) using pigments such as chlorophyll and cartenoids
\
56
New cards
The photosystems
* photosystem 1: most efficient at wavelength 700 nm
* photosystem 2: most efficient at wavelength 680 nm
* work together during non-cyclic electron transfer → non-cyclic phosphorylation
\
* photosystem 2: most efficient at wavelength 680 nm
* work together during non-cyclic electron transfer → non-cyclic phosphorylation
\
57
New cards
Steps for Light dependent reactionS
1. photoactivation of PS2
2. electron capture by primary electron acceptor of reaction center in PS2
3. replacing lost electrons
4. Electron transport chain
5. phosporylation of ADP to produce ATP
6. photon absorbed by pigments in PS1
7. high energy e- travel down second ETC
1. NADP enzyme catalyzes transfer of e- → NADPH and ATP are the final products
58
New cards
Step 1 of light dependent reactions
Photoactivation of PSII
* Photon absorbed by pigment in photosystem II and transferred to other pigment molecules until it reaches chlorophyll a (P680) in the reaction center
* Photon excites electrons to higher energy state → high energy electron
* Photon absorbed by pigment in photosystem II and transferred to other pigment molecules until it reaches chlorophyll a (P680) in the reaction center
* Photon excites electrons to higher energy state → high energy electron
59
New cards
Step 2 of light dependent reactions
* Electron captured by primary electron acceptor of reaction center in photosystem II
\
\
60
New cards
Step 3 of light dependent reactions
Replacing Lost Electrons
* Water split by enzyme →generates more **electron, hydrogens ions** (H+) and **oxygen**
* Process powered by energy in light → **photolysis**
* Electrons supplied to chlorophyll a molecules in the reaction center
\
* Water split by enzyme →generates more **electron, hydrogens ions** (H+) and **oxygen**
* Process powered by energy in light → **photolysis**
* Electrons supplied to chlorophyll a molecules in the reaction center
\
61
New cards
Step 4 of light dependent reactions
* High energy electrons go down electron transport chain →lose energy
* 1st carrier = **plastoquinone (PQ)**
* 2nd (middle) carrier = **cytochrome complex (cytochrome C)**
\
* 1st carrier = **plastoquinone (PQ)**
* 2nd (middle) carrier = **cytochrome complex (cytochrome C)**
\
62
New cards
Step 5 of light dependent reactions
* Energy lost as electrons move down ETC drives **chemiosmosis** → **phosphorylation** of **ADP to produce ATP**
* H ions are pumped into **thylakoid space** to create gradient
* H ions diffuse through ATP synthase→ providing energy to produce ATP
* H ions are pumped into **thylakoid space** to create gradient
* H ions diffuse through ATP synthase→ providing energy to produce ATP
63
New cards
Step 6 of light dependent reactions
* Photon absorbed by pigments in photosystems I
* Energy transferred until reaches chlorophyll (P700)
* High energy electrons produced
* De-energized electrons from photosystem II resupply the electrons needed in photosystem I
* Energy transferred until reaches chlorophyll (P700)
* High energy electrons produced
* De-energized electrons from photosystem II resupply the electrons needed in photosystem I
64
New cards
Step 7 of light dependent reactions
* High energy electrons travel down second ETC
* Carrier = ferredoxin
\
* Carrier = ferredoxin
\
65
New cards
Step 8 of light dependent reactions
* NADP enzyme catalyzes transfer of the electron from ferredoxin to the energy carrier NADP+ → NADPH
* 2 electrons required to fully reduce NADP+ → NADPH
* **NADPH & ATP are final products of light reactions**
* **Supply energy needed to power the light-independent reactions**
\
* 2 electrons required to fully reduce NADP+ → NADPH
* **NADPH & ATP are final products of light reactions**
* **Supply energy needed to power the light-independent reactions**
\
66
New cards
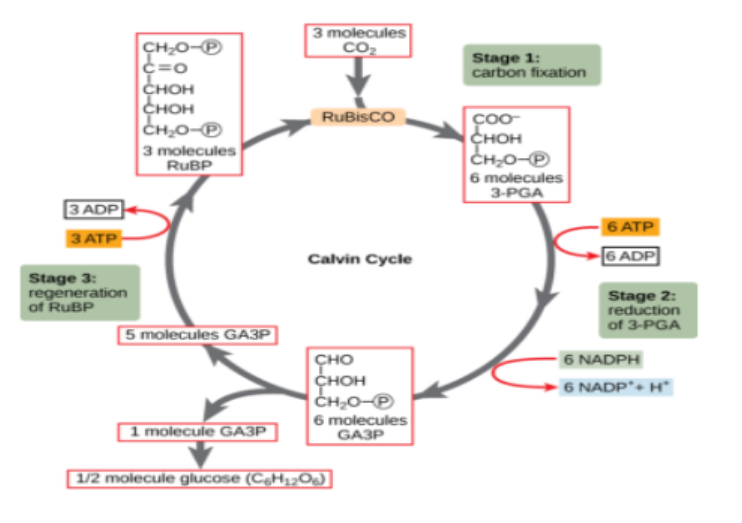
Light- Independent Reactions
* Occurs within stroma or cytosol-like region of chloroplast
* ATP and NADPH provide energy to power these reactions
* Glucose produced
* Involves **Calvin cycle** (begins and ends with same substance - hence cycle)
\
* ATP and NADPH provide energy to power these reactions
* Glucose produced
* Involves **Calvin cycle** (begins and ends with same substance - hence cycle)
\
67
New cards
The Calvin Cycle
outlines the events that result in the formation of organic molecules from inorganic sources (CO2)
* Ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) is carboxylated by carbon dioxide (CO2) to form a hexose biphosphate compound
* The hexose biphosphate compound immediately breaks down into molecules of glycerate-3-phosphate (GP)
* The GP is converted by ATP and NADPH into molecules of triose phosphate (TP)
* TP can be used to form organic molecules or can be recombined by ATP to reform stocks of RuBP
* Ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) is carboxylated by carbon dioxide (CO2) to form a hexose biphosphate compound
* The hexose biphosphate compound immediately breaks down into molecules of glycerate-3-phosphate (GP)
* The GP is converted by ATP and NADPH into molecules of triose phosphate (TP)
* TP can be used to form organic molecules or can be recombined by ATP to reform stocks of RuBP
68
New cards
Calvin cycle compounds
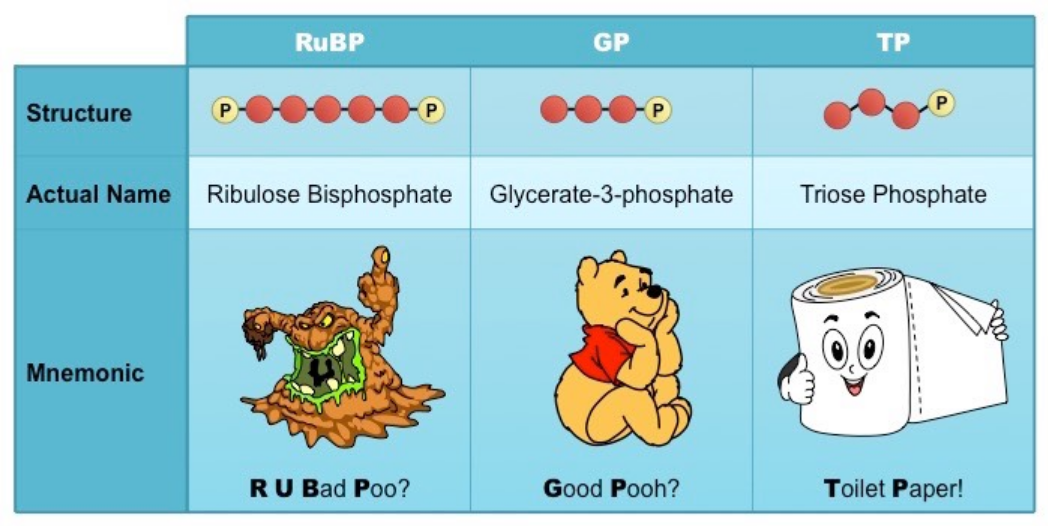
69
New cards
Step 1 of the calvin cycle
* **Ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) - 5 carbon compound binds to CO2 from the air → carbon fixation**
* This step is catalyzed by **RuBP carboxylase** (**Rubisco**)
* Results in **6 carbon compound**
\
* This step is catalyzed by **RuBP carboxylase** (**Rubisco**)
* Results in **6 carbon compound**
\
70
New cards
Step 2 of the calvin cycle
* Unstable 6 carbon compound breaks down into 3-carbon compounds → **glycerate-3-phosphate**
\
\
71
New cards
Step 3 of the calvin cycle
* Glycerate-3-phosphate acted on by ATP and NADPH to form triose phosphate (TP)
* Reduction Reaction
* Reduction Reaction
72
New cards
Step four of the calvin cycle
* Molecules of **TP** (triose phosphate) have two options
* 1. Some leave cycle to become sugar phosphates, may become more complex carbohydrates
* 2. Continue in the cycle to reproduce origination compound of the cycle, RuBP
* 1. Some leave cycle to become sugar phosphates, may become more complex carbohydrates
* 2. Continue in the cycle to reproduce origination compound of the cycle, RuBP
73
New cards
Step 5 of the calvin cycle
* To regain RuBP from TP, ATP is used
74
New cards
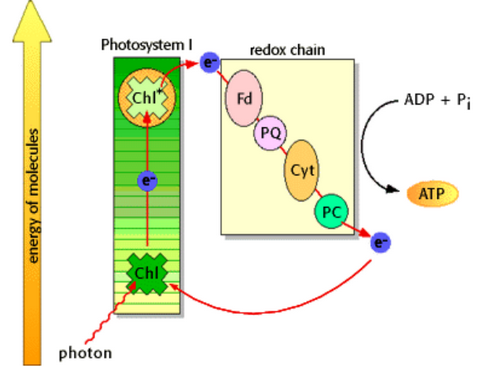
Cyclic Phosphorylation
* is another way to produce ATP during the light-dependent reactions
* proceeds only when light is not a limiting factors
* and when there is an accumulation of NADPH
\
Occurs in three steps
* proceeds only when light is not a limiting factors
* and when there is an accumulation of NADPH
\
Occurs in three steps
75
New cards
Step 1 of cyclic phosphorylation
light energized electrons from photosystem 1 flow back to cytochrome c
76
New cards
Step 2 of cyclic phosphorylation
electrons flow down the remaining ETC. allowing ATP synthesis via chemiosis
* electrons do NOT go down a secondd ETC - that would produce NADPH
* electrons do NOT go down a secondd ETC - that would produce NADPH
77
New cards
Step 3 of cyclic phosphorylation
additional ATPs sent to calvin cycle so it can go faster
78
New cards
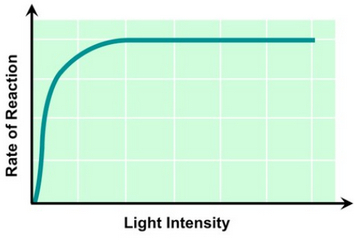
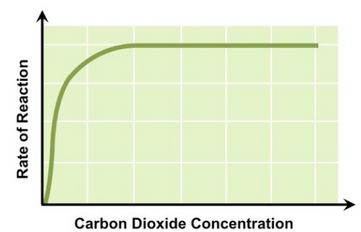
Factors limiting photosynthesis
* light intensity
* CO2 levels
* temeprature
* CO2 levels
* temeprature
79
New cards
Light intensity on photosynthesis
80
New cards
CO2 concentration on photosynthesis
81
New cards
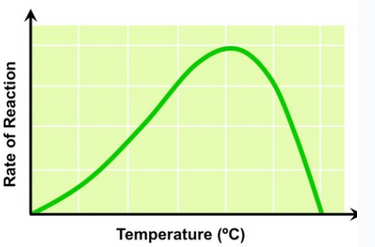
Temperature on photosynthesis