Chapter 4 Biology Honors
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Last updated 4:50 AM on 11/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
Types of Microscopes
- Light microscope (LM)
- Transmission electron microscope (TEM)
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Transmission electron microscope (TEM)
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)

2
New cards
Cells surface area
is important for carrying out the cell's functions, such as acquiring adequate nutrients and oxygen. A small cell has more surface area relative to its cell volume and is more efficient.
3
New cards
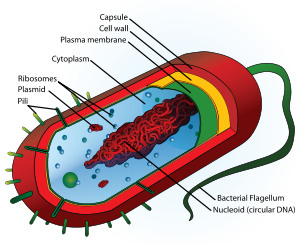
Prokaryotic Cells
Bacteria and Archaea. Have no distinct nucleus and no true organelles.
4
New cards
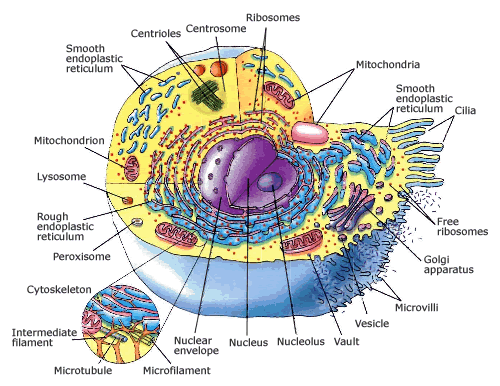
Eukaryotic cells
Animals, plants, fungi, protozoa, and algae. Have a membrane-bound nucleolus and a number of other organelles.
5
New cards
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Similarities
Both cells have a plasma membrane, one or more chromosomes and ribosomes.
6
New cards
4 Life processes in Eukaryotic cells that depend upon structures and organelles
1. Manufacturing
2. Breakdown of molecules
3. Energy processing
4. Structural support, movement, and communication
2. Breakdown of molecules
3. Energy processing
4. Structural support, movement, and communication
7
New cards
Plant cells DON'T have:
- lysosomes
- centrioles
- centrioles
8
New cards
Plants DO Have:
- a rigid cell wall
- chloroplasts
- central vacuole (not found in animal cells)
- chloroplasts
- central vacuole (not found in animal cells)
9
New cards
Plasma Membrane
controls movement of molecules into and out of the cell, a trait called selective permeability. The structure of the membrane with its component molecules is responsible for this characters.
Membranes are made of lipids, proteins, and some carbohydrate, but the most abundant lipids are phospholipids.
** Phospholipids bilayer is selective permeability, only some molecules can cross it**
Membranes are made of lipids, proteins, and some carbohydrate, but the most abundant lipids are phospholipids.
** Phospholipids bilayer is selective permeability, only some molecules can cross it**
10
New cards
cell membrane
semipermeable membrane surround the cytoplasm of a cell
11
New cards
semipermeable
allowing certain substances to pass through it but not others, especially allowing the passage of a solvent but not of certain solutes.
12
New cards
membrane proteins
phospholipids form basic structure of cell membrane, called lipid bilayer. Are important for transporting substances across the cell membrane.
13
New cards
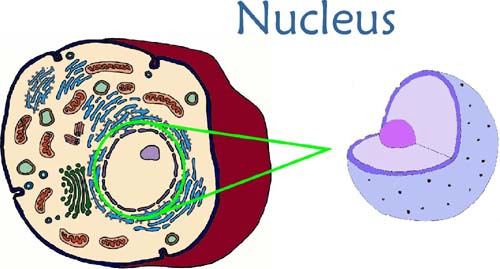
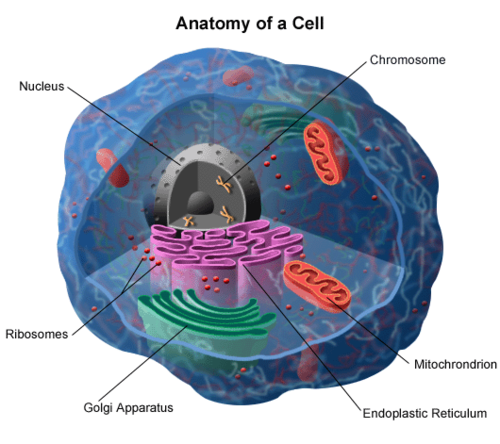
Nucleus
controls cell's activities and is responsible for inheritance.
14
New cards
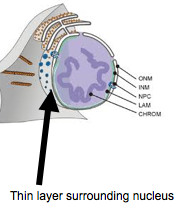
nuclear membrane
also known as nuclear envelope, is the double lipid bilayer membrane which surrounds the genetic material and nucleolus in eukaryotic cells. Consists of two lipid bilayers - inner and outer nuclear membrane.
15
New cards
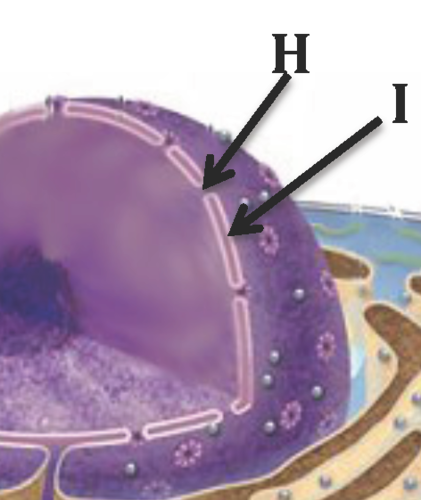
nuclear pore
hole in the nuclear membrane, how stuff gets out of the nucleus (like a transport protein)
16
New cards
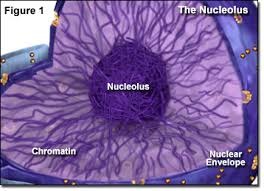
nucleolus
visible dark spot in the middle of nucleus where the ribosomes are made.
17
New cards
Chromatin
inside nucleus is a complex of proteins and DNA - makes up the cells chromosomes. DNA is copied within the nucleus prior to cell division. The nuclear membrane attached to a network of cellular membranes called the endoplasmic reticulum.
18
New cards
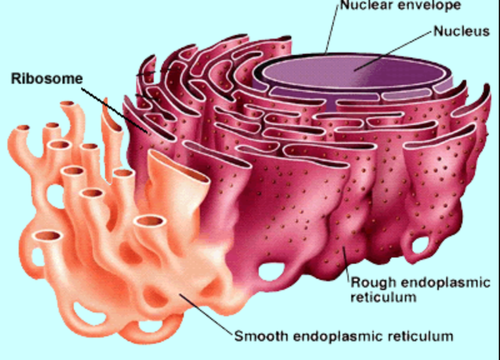
Ribosomes
Make proteins for use in the cell and export
Make proteins for use in the cell and export
produce the cell's proteins. Ribosomes are synthesized in the nucleolus, a structure inside the nucleus. Cells that must synthesize large amounts of protein have a large number of ribosomes.
Some ribosomes are free ribosomes; others are bound. Free ribosomes are suspending in the cytoplasm. Bound ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) associated wit the nuclear envelope.
Some ribosomes are free ribosomes; others are bound. Free ribosomes are suspending in the cytoplasm. Bound ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) associated wit the nuclear envelope.
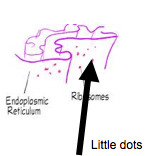
19
New cards
Free ribosomes vs. Bound Ribosomes
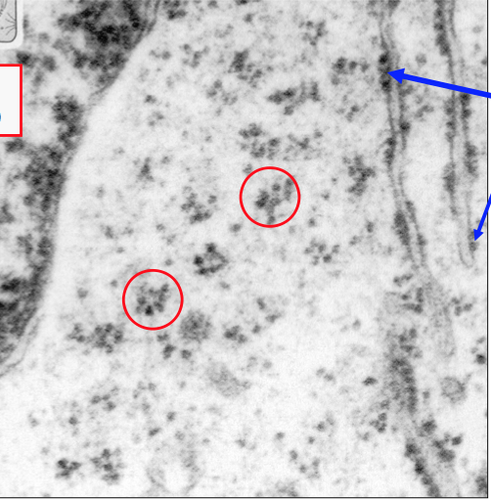
20
New cards
cytoplasm
thick solution that fills each cell and is enclosed by cell membrane. Mainly composed of water, salts, and proteins. In Eukaryotic cells, it includes all of the material inside the cell and outside the nucleus.
21
New cards
pilli
are organelles of adhesion allowing bacteria to colonize environmental surfaces or cells and resist flushing.
22
New cards
capsule
very large structure of some prokaryotic cells, such as bacterial cells. It is a polysaccharide layer that lies outside the cell envelope of bacteria, and is thus deemed part of the outer envelope of a bacterial cell.
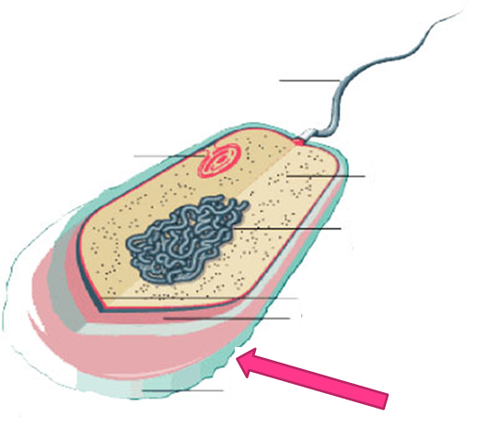
23
New cards
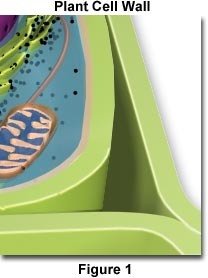
cell wall
rigid layer of polysaccharides lying outside the plasma membrane of the cells of plants, fungi, and bacteria. IN algae and higher plants consists mainly of cellulose.
24
New cards
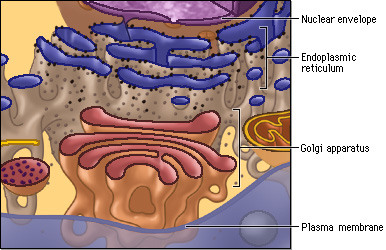
Endomembrane system
membranes within a eukaryotic cell are physically connected. Includes the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and the plasma membrane.
25
New cards
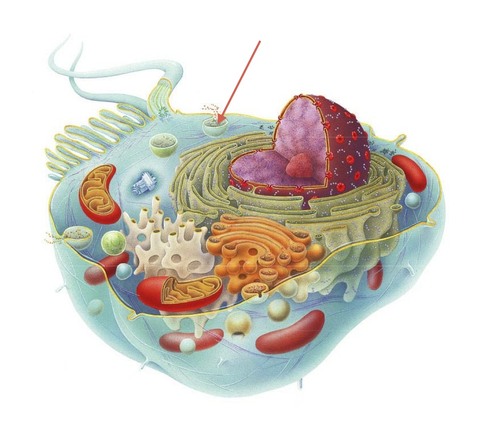
Vesicles
Some components of the endomembrane system are able to pass material to other components by formation and transfer of small membrane segments or sacs. Used to synthesize, store, and export molecules.
26
New cards
2 Kinds of Endoplasmic Reticulum
smooth and rough, differ in structure and function, but are connected. Smooth ER lacks attached ribosomes. Rough ER has ribosomes on outer surface of its membranes.
27
New cards
Smooth ER
detoxifies poisons, processes carbohydrates. Produces membrane making components
Enzymes produced by smooth ER make lipids, oils, phospholipids and steroids
Enzymes produced by smooth ER make lipids, oils, phospholipids and steroids
28
New cards
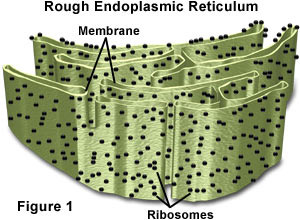
Rough ER
makes additional membrane for itself and proteins to be transported in vesicles to other parts of the endomembrane system. Proteins are synthesized right into the lumen of the rough ER. Proteins are transported in vesicles to other parts of the endomembrane system. Some proteins are exported from the cell like hormones, antibodies, and enzymes.
29
New cards
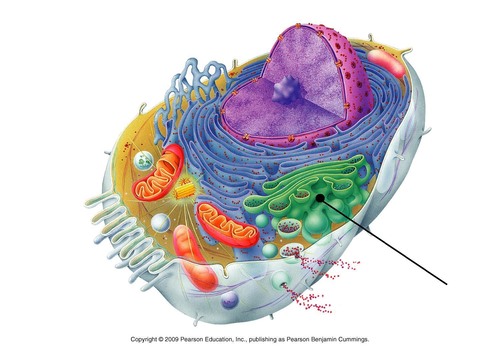
Golgi apparatus
finishes, sorts and ships cell products. Functions in conjunct with the ER by modifying products of the ER. Products travel in transport vesicles from the ER to the Golgi Apparatus. One side of the Golgi functions as a receiving dock for the product and the other as a shipping dock. Products are modified as they go from one side of the Golgia apparatus to the other and travel in vesicles to other sides.
30
New cards
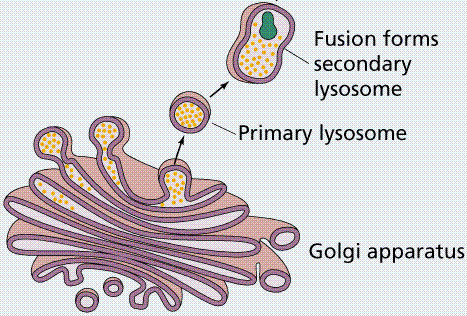
Lysosomes
is a membranous sac toning digestive enzymes. The enzymes and membrane are produced by the ER and transferred to Golgi for processing. The membrane seres to safely isolate these potent enzyme from the rest of the cell. One of the several functions of lysosomes is to remove or recycle damaged parts of a cell.
31
New cards
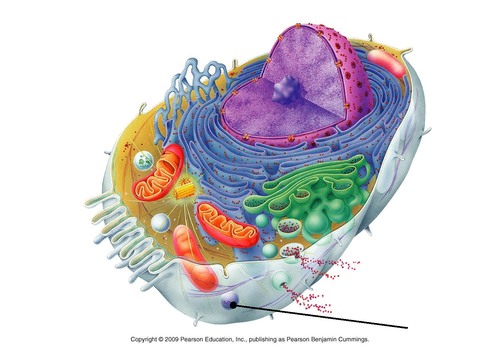
Peroxisome
small, membrane-enclosed organelles that contain enzymes involved in a variety of metabolic reactions, including several aspects of energy metabolism.
32
New cards
Vacuole
is a general word for a large membrane enclosed sac. The central vacuole in plants; with hydrolytic functions. Pigment vacuoles in plants provide color to flowers. Contractile vacuole sin some protozoa to exe water from the cell.
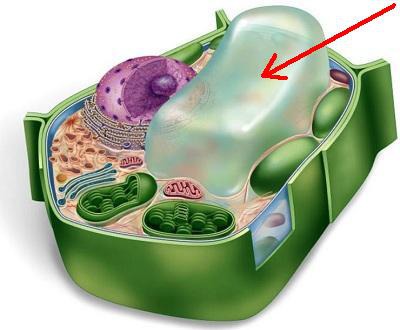
33
New cards
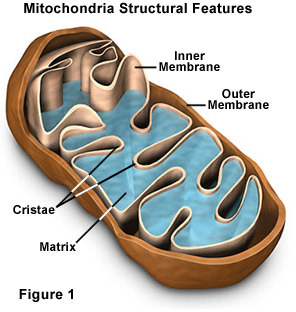
Mitochondria
cellular respiration is accomplished in mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. Respiration occurs at cell membrane and is cytoplasm of prokaryotes. Cell respiration: conversion of chemical energy in foods to chemical energy in ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Has 2 internal compartments inter membrane space, which encloses the mitochondrial matrix where materials necessary for ATP generation are found.
34
New cards
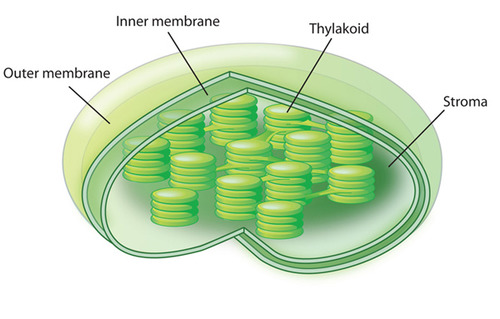
Chloroplasts
are photosynthesizing organelles of plants. Chloroplasts are partitioned into compartments. The important part of chloroplasts are stoma, thylakoids and grana
35
New cards
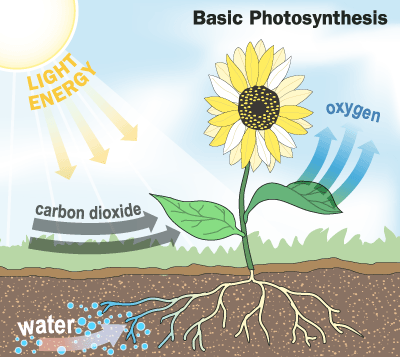
Photosynthesis
is conversion of light energy to chemical energy of sugar molecules.
36
New cards
Endosymbiosis
hypothesis proposes that mitochondria and chloroplasts were formerly small prokaryotes that began living within larger cells. Symbiosis benefited both cell types.
When compared, you find that mitochondria and chloroplasts have (1) DNA and (2) Ribosomes inside
When compared, you find that mitochondria and chloroplasts have (1) DNA and (2) Ribosomes inside
37
New cards
Plasmodesma
Hole in the cell wall of plants and lets one plant cell sends stuff (sugar, water, etc.) to its neighbors
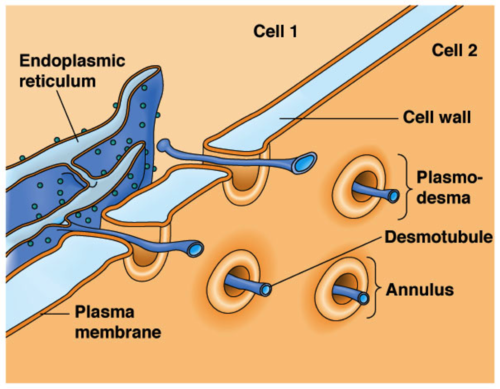
38
New cards
Cytoskeleton
cells contain a network of protein fibers, function in cell structural support and mobility. Composed of 3 kinds of fibers.
39
New cards
motor proteins
Helps the cell move.
40
New cards
3 Kinds of Protein Fibers found in the Cytocskcleon:
microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Help support the cells shape, keep the organelles where they are suppose to be and help the cell move.
41
New cards
centriole
is a small set of microtubules arranged in a specific way. When two centrioles are found next to each other, they are usually at high angles. Is found in paris and move towards the poles (opposite ends) of the nucleus when it its time for cell division.
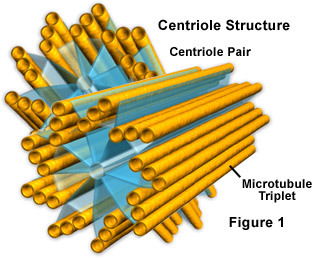
42
New cards
Flagellum
Propells a cell by an undulating, whiplike motion. Ways for them to move or to move other things.
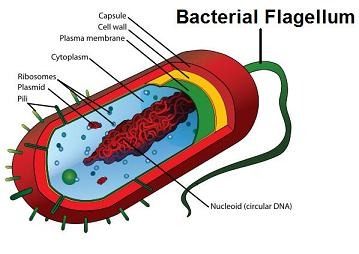
43
New cards
Cilia
Work together more like oars. Ways for them to move or to move other things. Cells that sweep mucus out of our lungs have cilia. Animal sperm are flagellated.
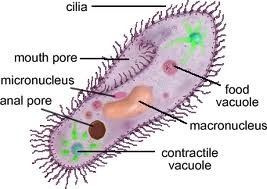
44
New cards
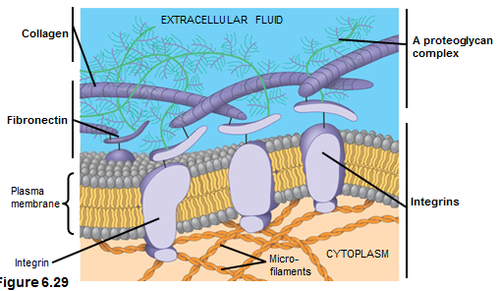
extracellular matrix (ECM)
cell synthesize and secrete the ECM that is essential to cell function. ECM is composed of strong fibers of collagen.
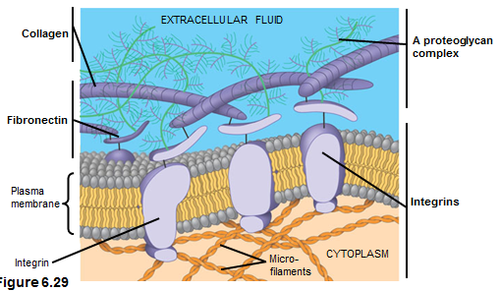
45
New cards
integrins
proteins that sits in the membrane and stretches from the cytoskeleton inside the cell to the extracellular matrix outside the cell.