Hematology Exam 2: Anemia and Microcytic Hypochromic anemia
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Anemia
inability of circulating blood to supply tissues with adequate O2, usually a decrease in Hgb
Anemia signs and symptoms
-Difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
-vertigo
-light headedness
-muscle weakness
-lethargy
-rapid developing anemia can be associated with hypotension and tachycardia
Heme Synthesis
Ferrous iron combines with protoporphyrin’s in the mitochondria of the RBC to form Heme
Ferritin
storage form of iron
directly proportional to amount of iron stored
Sideroblast
a ferritin-containing Rubriblast in the bone marrow makes up from 20%-90% of Rubriblast in the marrow
Serum iron
measurement of transferrin bound iron
early morning spec preferred
TIBC total iron binding capacity
capacity the body has to bind to transferrin
inversely proportional to iron
Anemia of iron disorders
Non-hemolytic
Iron Deficiency Anemia (IDA)
-Most common
-Decreased Hgb, Hct, and MCV. High RDW
-Decreased Serum Iron
-Decreased serum Ferritin
-Decreased serum Transferrin saturation
-Increased total iron binding capacity (TIBC)
-Increased retics so anisocytosis, high RDW
-Increased Free erythrocyte protoporphyrin (FEP)
-increased serum soluble transferrin receptor level
Ugly blood so lots of aniso and poik, binds zinc instead
Anemia of chronic Diseases
-Most common in hospitals
—Chronic infections, chronic renal failure, chronic inflammation, cancer/malignant neoplasms. blocks transfer of storage iron to precursors in the BM.
—Low MCV
-Decreased serum iron
-Increased/normal serum ferritin
-Decreased transferrin saturation
-Decreased Total Iron binding capacity TIBC
-increased FEP
-normal serum soluble transferrin receptor levels
Hepcidin- iron trapped within macrophage
Normally normocytic, can me hypo or normochromic
Decreased sideroblast
Not much aniso or poik
Lead Intoxication
-Increased blood lead levels
-increased FEP or ZPP
-Characteristic basophilic stippling
Hereditary and Acquired Hemoatochromatosis / Iron Overload
-Increased serum ferritin
-Accumulation of excess iron in cells of varying tissue
-iron metabolism error
-Gene on chromosome 6, most with mutation in C282Y tyrosine for cystine, also C282Y/H63D.
-Takes a while to show up, less severe in women because monthly bleeding.
-Can be reversible but not when damage is already done.
-Increased serum iron
-Increased serum ferritin
-Increased serum transferrin saturation >45%
-normal Hgb and Hct
Symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, abdominal pain, skin color change, diabetes, heart problems.
Treatment is avoid iron rich foods, iron chelation’s doesn’t work. Also frequent phlebotomy blood removal over a long period.
Sideroblastic Anemia
-Mitochondrial disorder
-Low MCV
-iron accumulates in mitochondria, unable to incorporate it, heme syn thus defective
-Sideroblasts on Prussian blue stain
-Ringed Sideroblasts seen under microscopic exam of BM around the nucleus
-Hereditary is usually microcytic hypochromic, acquired is dimorphic
-Increased serum iron
-increased serum ferritin
-increased transferrin saturation
-decreased TIBC
-decreased transferrin
-normal/high serum transferrin receptor
Porphyria’s (Heme synthesis abnormality)
-Block in Porphyrin synthesis due to defect in enzyme
-causes porphyrin heme precursors to accumulate in tissues
Symptoms include photosensitivity that can cause severe damage, alopecia, glowing red incisors, taught skin that makes teeth stick out. Nervous system involvement
Congenital porphyria CEP
- enzyme defect in uroporphyrinogen III
-Hemolytic anemia
-gunther’s disease
-excess uro and co
-EXCRETED IN URINE and fluoresce
-aniso and poik,
-BM- hyperplasia and fluoresce
-normal iron studies
-ZPP increased as well
Erythropoietic protoporphyria EEP
-enzyme defect in ferrochelatase
-anemia is rare
-overproduction of protoporphyrin
-builds up in cells and leaks into skin
-found in blood, liver, skin, and feces
-DOES BOT COME OUT IN URINE
-blood and BM normal
protoporphyrin in RBC (FEP) not bound to zinc, plasma, feces
Thalassemia
-Globin chain synthesis disorder
-produce unstable hemoglobin
-Alpha thalassemia- reduced or absent alpha chains
-Beta thalassemia- reduced or absent beta chains
-Normal serum iron
-Normal/Increased serum ferritin
-Normal/increased serum transferrin
-Normal TIBC
-Normal serum transfer receptor
-Must do hemoglobin electrophoresis to diagnose beta-thalassemia by identifying abnormal hemoglobin types like elevated HbA2. Genetic testing for Alpha thalassemia.
-Really ugly microcytic hypochromic cells on smear, values very low compared to other microcytic anemias.
Megaloblastic anemia
-Anemia of abnormal nuclear development
-defect in DNA metabolism
-Cell maturation in BM is abnormal, defective DNA synthesis, asynchronous development.
-MCV >110fl
-Macrocytic normochromic
-Hype segmented
-acquired b12/folate disorder
—CDA subgroup no B12 or folate deficiency, abnormal RBC precursors in BM
What is the main function of the hexose-monophosphate shunt in the RBC?
Produce NADPH
A CLS finds evidence of Heinz bodies in the RBCs of a 30-year-old male. This is evidence of which of the following?
increased oxidant concentration in the cell
Which situations are G6PD deficiency episodes related to?
oxidative stress, free radicals and peroxide damage
Heinz bodies may be seen in what hematologic disease?
G6PD deficiency, thalassemia’s, severe liver diseases.
all of the above
What can a deficiency in the hexose monophosphate shunt result in?
hemolytic anemia, oxidative denaturation of the RBC, H2O2, G6PD deficiency
G-6-P-D is found in which of the following pathway?
pentose phosphate pathway or hexose monophosphate shunt
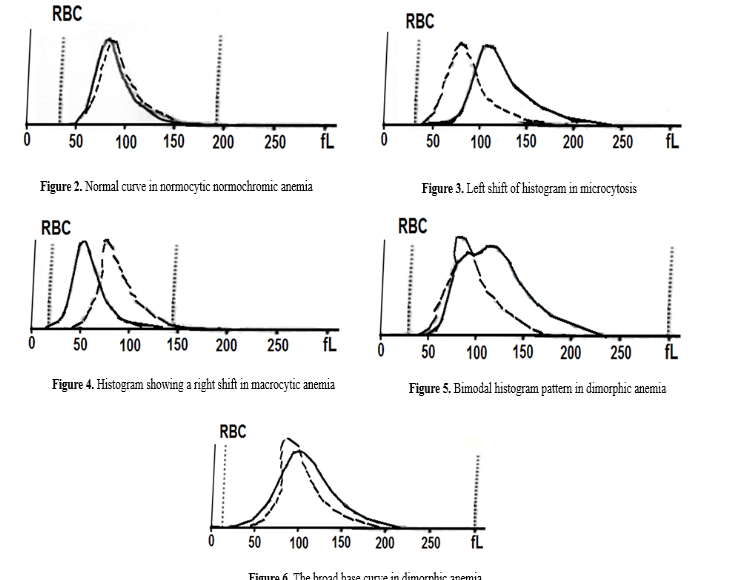
Relate RBC histograms to different types of anemia
shift left is microcytosis
shift right is macocytosis
double bump thing is dimorphic
wide base is RDW increased variation in RBC size
What is the number one cause of a Megaloblastic asynchronous development in the bone marrow?
impaired DNA synthesis
From the standpoint of hematologic studies, what are the usual diagnostic criteria for anemia?
decreased Hgb and Hct, also decreased RBC count
What might cause a microcytosis?
- thalassemia
- sideroblastic anemia
- iron deficiency
- lead poisoning
- anemia of chronic disease
- porphyrias
Who can IDA be distinguished from anemia of chronic infection?
TIBC is high in IDA and low in ACI
Which anemia has red cell morphology similar to that seen in IDA?
Thalassemia
What are the iron study results and how can you characterize Iron deficiency anemia using the iron studies?
-Decreased Serum Iron
-Decreased serum Ferritin
-Decreased serum Transferrin saturation
-Increased total iron binding capacity (TIBC)
-Increased retics so anisocytosis, high RDW
-Increased Free erythrocyte protoporphyrin (FEP)
-increased serum soluble transferrin receptor level
What are the characteristics associated with sideroblastic anemia?
increased in all serum iron levels except TIBC, RBC protoporphyrin is NOT increased, the iron buildup in mitochondria.
Can a patient with polycythemia vera (very high RBC count) who is treated by phlebotomy is develop a anemia? If so, what type of deficiency would this patient develop?
iron
Which of the following parameters may be similar for the anemia of inflammation and IDA?
decreased serum iron concentrations
Where and in what form is the majority of iron in an adult found?
hemoglobin
What is the anemia of chronic infection characterized by?
decreased serum iron and increased serum ferritin
What are the characteristic of lead poisoning?
basophilic stippling, increased ZPP and FEP
Which of the following represent(s) an acquired sideroblastic anemia producing a microcytic hypochromic anemia, skin lesions, and neurological dysfunction?
lead poisoning
Hemosiderosis is the accumulation of excess __________ in the macrophages of various tissues
hemosiderin, iron storage complex
Which of the following is MOST closely associated with idiopathic hemochromatosis?
iron overload in tissues, genetic mutation
Which of the following blood findings does NOT correlate with the presence of ringed sideroblasts in the bone marrow?
increased TIBC
what is the major mechanism responsible for the anemia of chronic disease?
hepsidin, iron trapped in macrophages
what is an excessive accumulation of iron in body tissues called?
hemochromatosis, iron overload