BIOL 203 Past Exam MCQ and Collaborative Quizzes
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
What type of bonds occur between functional groups to maintain the structure of a ꞵ-pleated sheet?
a. Van der Waals
b. Ionic
c. Disulfide
d. Covalent
e. Hydrogen.
e. Hydrogen.
If a double-stranded DNA sample was composed of 30 percent adenine, what would be the percentage of cytosine?
A. 15
B. 20
C. 25
D. 50
E. None of the above
B. 20
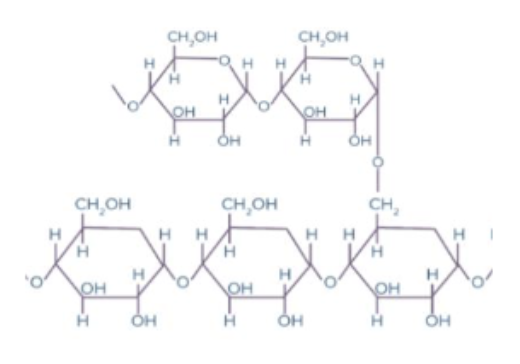
Phosphorylase and amylase are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of glycogen (pictured) and starch, respectively. What types of bonds do they break?
A. ⍺-1,4-glycosidic bonds
B. Hydrogen bonds
C. Ionic bonds
D. β-1,4-glycosidic bonds
E. Peptide bonds
A. ⍺-1,4-glycosidic bonds
Why is RNA less stable compared to DNA?
A. DNA contains a more reactive hydrogen group on the 2’ carbon of the sugar
B. RNA contains a more reactive hydroxyl group on the 2’ carbon of the sugar
C. RNA and DNA have no difference in stability
D. DNA has stronger phosphodiester bonds than RNA
E. RNA lacks complementary base pairing, so it degrades faster
B. RNA contains a more reactive hydroxyl group on the 2’ carbon of the sugar
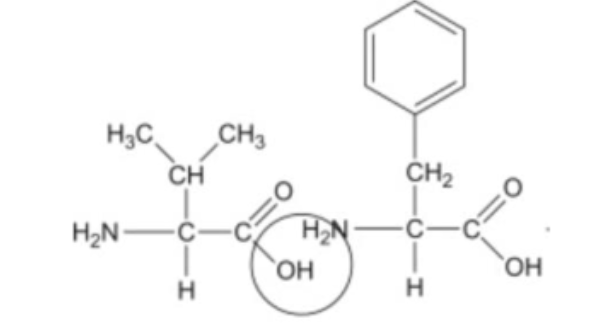
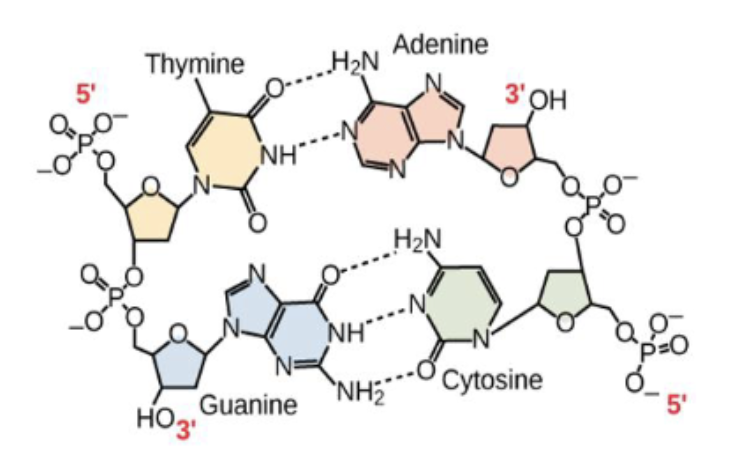
The chemical reaction illustrated in the accompanying figure _______.
A. results in a β-1,4-glycosidic bond
B. is a hydrolysis reaction
C. results in a peptide bond
D. results in an α-1,4-glycosidic bond
E. joins two nucleotides together
C. results in a peptide bond
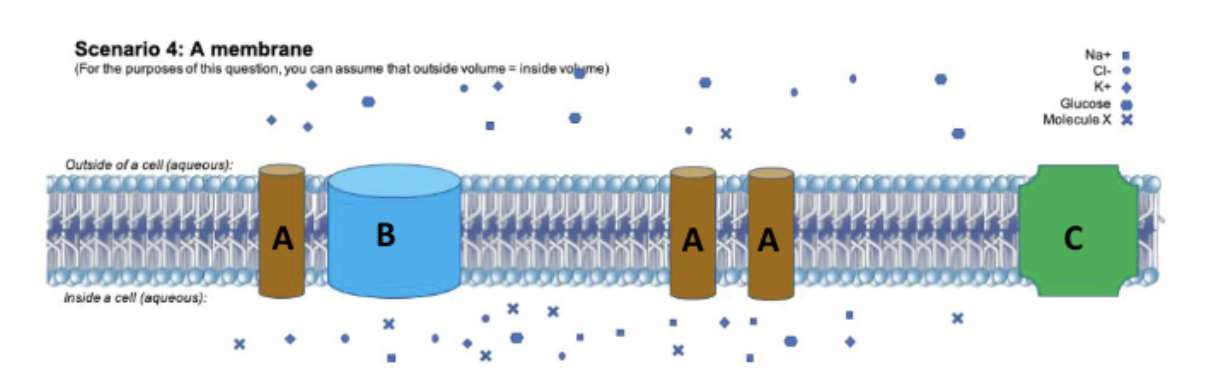
If molecule C is the glucose transporter, GLUT-1, what does the above diagram indicate is happening?
A. Simple diffusion out of the cell.
B. Facilitated diffusion out of the cell.
C. Active transport out of the cell.
D. Active transport into the cell.
E. Facilitated diffusion into the cell
E. Facilitated diffusion into the cell
Both proteins and DNA can be (i) denatured and (ii) undergo hydrolysis. Denaturation involves using heat to disrupt specific interactions whereas hydrolysis involves breaking bonds, which requires enzymes. What would happen to protein molecules treated with proteinase K?
A. The phosphodiester linkages of the sugar-phosphate backbone would be broken.
B. The two strands of the double helix would separate.
C. The interactions between the R-groups would be disrupted.
D. The peptide bonds would be broken.
E. The phosphate groups would be separated from the sugars.
D. The peptide bonds would be broken.
Suppose a cell is placed in a solution with high concentration of potassium and no sodium. How would the cellular sodium-potassium pump function in this environment?
A. It would stop moving ions across the membrane.
B. It would continue using ATP to pump sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell.
C. It would move sodium and potassium ions across the membrane, but no ATP would be used.
D. It would reverse the direction of pumping sodium and potassium ions to move them against
their gradients.
E. It would allow sodium and potassium to diffuse freely across the membrane down their
gradients
B. It would continue using ATP to pump sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell.
What determines the primary structure of an RNA molecule?
A. Complementary base pairing
B. Deoxyribonucleotide sequence
C. Stem-and-loop configuration
D. Hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonding
E. Ribonucleotide sequence
E. Ribonucleotide sequence
Which of the following is not dependent upon hydrogen bonding interactions?
A. An α-helix in an integral membrane protein
B. Complementary base pairing in DNA
C. Peptidoglycan forming fibers in the bacterial cell wall
D. Cellulose forming fibers in the plant cell wall
E. Adhesion experienced by plants
C. Peptidoglycan forming fibers in the bacterial cell wall
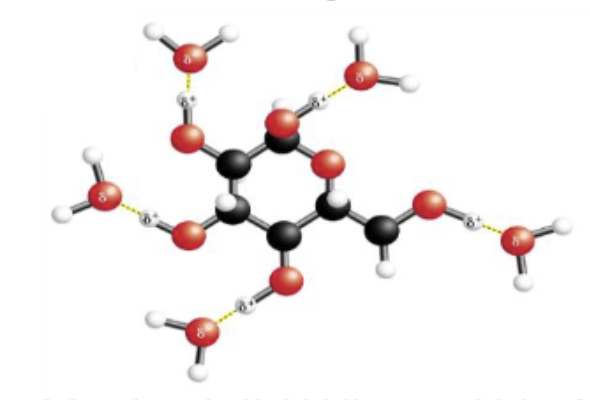
The water molecule has many unique properties attributing to its importance in life. The polarity of the water molecule makes it an effective solvent for charged and polar solutes like the glucose molecule below. What is the attraction between the water molecules and glucose called, as indicated by the dashed lines?
A. A hydrogen bond
B. A polar covalent bond
C. An ionic bond
D. A van der Waals interaction
E. A hydrophobic interaction
A. A hydrogen bond
Given what you know about the chemical properties of the phospholipid bilayer, which of the following proteins is UNLIKELY to be found associated with the membrane?
A. A protein with a 20-30 amino acid stretch of alternating polar and nonpolar amino acids
B. A protein consisting of ONLY hydrophobic amino acids
C. A protein consisting of ONLY hydrophilic amino acids
D. A globular protein with nonpolar amino acid side chains folded into the interior of the protein
and hydrophilic side chains exposed on the surface.
E. None of the above
B. A protein consisting of ONLY hydrophobic amino acids
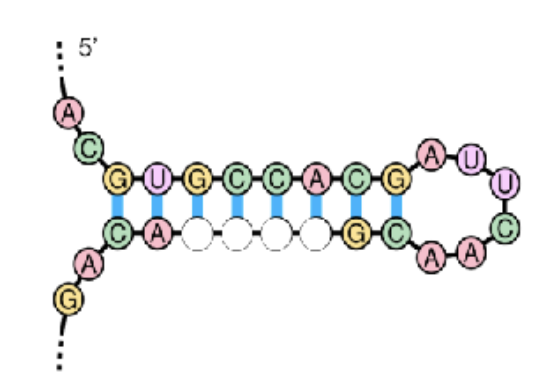
The molecule below shows the stem-loop structure for an RNA
molecule. Fill in the complementary bases to complete the stem.
A. 5’- UGGC-3’
B. 3’- CGGU-5’
C. 5’- UGCC-3’
D. 3’- GUCU-5’
E. None of the above
A. 5’- UGGC-3’
B. 3’- CGGU-5’
A mutation occurs in this portion of a chromosome where cytosine replaces thymine. What impact do you think this will have on the DNA structure below?
A. This will have very little effect on the DNA secondary (2º) structure.
B. This will cause the phosphodiester bonds to break, and the DNA will hydrolyze.
C. This will cause the DNA secondary (2º) structure to denature or unzip.
D. This will cause a bulge in the DNA secondary (2º) structure.
E. This will cause a major distortion in the DNA secondary (2º) structure
A. This will have very little effect on the DNA secondary (2º) structure.
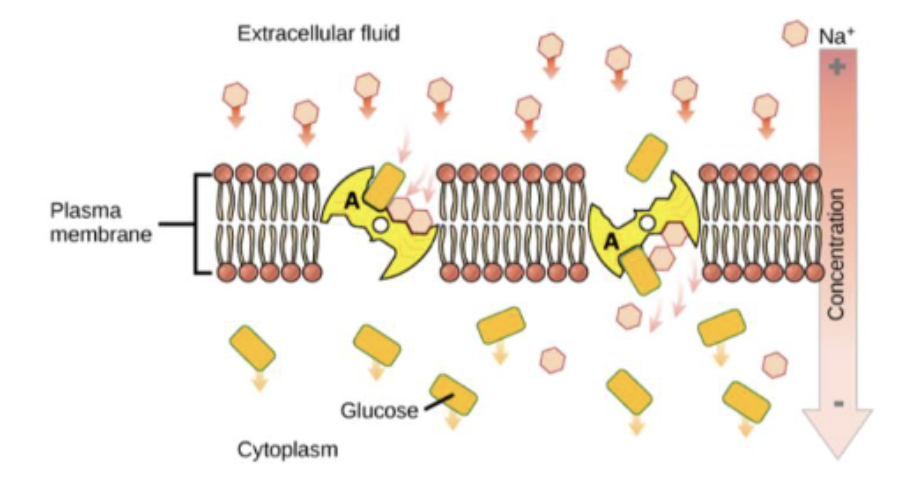
According to the diagram to the right, Na+ is experiencing ______________ and Glucose is experiencing _____________?
A. Facilitated diffusion; passive
transport
B. Active transport; secondary active
transport
C. Secondary active transport;
facilitated diffusion
D. Passive transport; secondary active
transport
E. None of the above
D. Passive transport; secondary active transport
How do the α and ꞵ forms of glucose differ?
A. The oxygen atom inside the ring is located in a different position.
B. Their ring structures differ in the location of a hydroxyl group.
C. Their linear structures differ in the location of a hydroxyl group.
D. The α form can be involved in 1,4- and 1,6-glycosidic linkages; the ꞵ form can participate only in 1,4 linkages
B. Their ring structures differ in the location of a hydroxyl group.
Mad cow disease is an infection disease where one misfolded protein causes all other copies of the protein to begin misfolding. This is an example of a disease impacting ____ structure.
A. Primary
B. Secondary
C. Tertiary
D. Quaternary
E. A and B
C. Tertiary
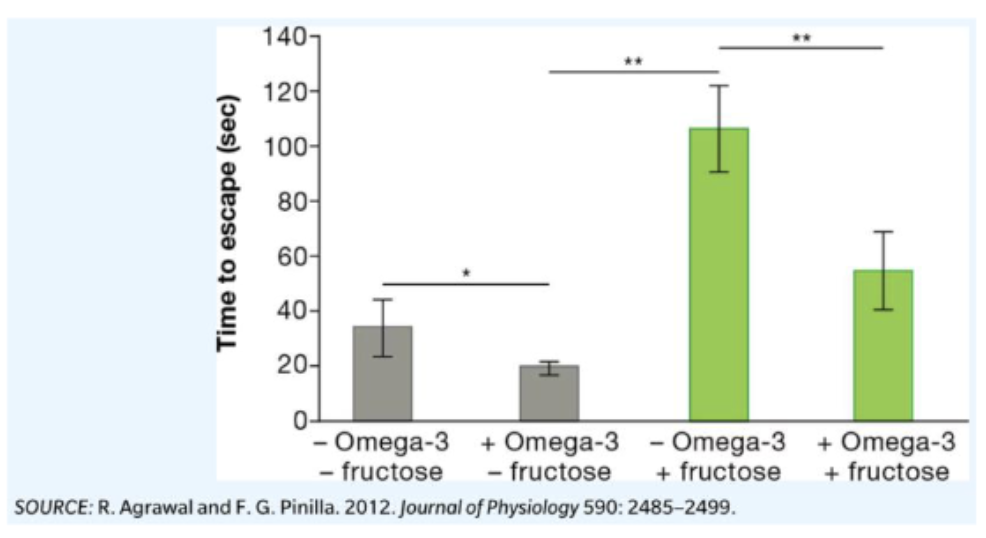
The effect of diet on human health is often evaluated using animal models. Researchers tested the impact of drinking fructose solutions on memory by using rats trained to find an escape chamber in a maze. The effect of eating omega-3 fatty acids was also tested. The rats were fed various diets consisting of chow and drinking
water. After six weeks on the diets, the rats were tested again on the same maze, and their escape times were recorded and graphed below. The researchers hypothesize that excessive fructose impairs the ability to recall since fructose metabolism is less
controlled, which can lead to neuroinflammation in the brain. What can you conclude from these results about learning retention in rats?
A. These results suggest that fructose impaired the rats’ ability to recall what they had
learned about finding the escape chamber with statistical significance.
B. These results suggest that omega-3 fatty acids impaired the rats’ ability to recall what they had
learned about finding the escape chamber with statistical significance.
C. These results suggest that fructose and omega-3 fatty acids impaired the rats’ ability to recall
what they had learned about finding the escape chamber with statistical significance.
D. These results suggest that omega-3 fatty acids enhanced the rats’ ability to recall what they had
learned about finding the escape chamber but without statistical significance.
E. These results suggest that fructose and omega-3 fatty acids did not have a statistically
significant effect on the rats’ ability to recall what they had learned about finding the escape
chamber
A. These results suggest that fructose impaired the rats’ ability to recall what they had
learned about finding the escape chamber with statistical significance.
A number of systems for pumping ions across membranes are powered by ATP. Such ATP-powered pumps are often called ATPases, although they do not often hydrolyze ATP unless they are simultaneously transporting ions. Because small increases in calcium ions in the cytosol can trigger several different intracellular reactions, cells keep the cytosolic calcium concentration quite low under normal conditions, using ATP-powered calcium pumps. For example, muscle cells transport calcium from the cytosol into the membranous system called the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR). If a resting muscle cell's cytosol has a free calcium ion concentration of 10-7 while the
concentration in the SR is 10-2, then how is the ATPase acting?
A. ATPase activity must be powering an inflow of calcium from the outside of the cell into the SR.
B. ATPase activity must be pumping calcium from the cytosol to the SR against the
concentration gradient.
C. ATPase activity must be opening a channel for the calcium ions to diffuse back into the SR along the concentration gradient.
D. ATPase activity must be routing calcium ions from the SR to the cell's environment
B. ATPase activity must be pumping calcium from the cytosol to the SR against the
concentration gradient.
Proteins and nucleic acids have definite directionality. Stated another way, one end of the molecule is different from the other end. How are the ends of a protein described?
A. One end has an unlinked 3' hydroxyl group; the other end has an unlinked 5' phosphate group.
B. One end has an unlinked carboxyl group; the other end has an unlinked amino group.
C. One end has an unlinked amino group; the other end has an unlinked hydroxyl group.
D. One end has an unlinked phosphate group; the other end has an unlinked carboxyl group.
E. One end has an unlinked 3' phosphate group; the other end has an unlinked 5' hydroxyl group
B. One end has an unlinked carboxyl group; the other end has an unlinked amino group.
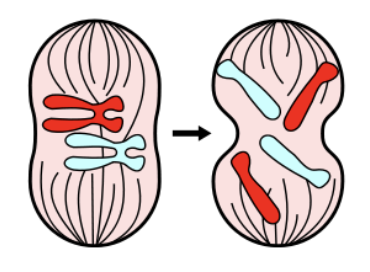
Compare the two cells shown in this image. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. The right cell has twice as many chromosomes as the left cell, but both cells contain the same amount of DNA.
B. The right cell contains twice the number of chromosomes and amount of DNA as the left cell.
C. Both cells contain the same number of chromosomes and the same amount of DNA.
D. The number of chromosomes in both cells is the same, but the right cell contains twice the amount
of DNA as the left cell
A. The right cell has twice as many chromosomes as the left cell, but both cells contain the same amount of DNA.
Which of the following statements correctly identify a role of the ATP produced in the light-capturing reactions?
I. ATP from the light-capturing reactions is used by rubisco to fix CO2 to ATP
II. ATP from the light capturing reactions is used to regenerate RuBP from G3P molecules
III. ATP from the light capturing reactions serves the same role as ATP produced by mitochondria
IV. ATP from the light capturing reactions is used to produce G3P molecules during reduction
A. I only
B. II and III only
C. IV only
D. II and IV only
E. All of the above
D. II and IV only
Imagine you expose chloroplast to red photons and observe low O2 production, but high ATP production. Which of the following best explains this observation?
A. The electrons from water are directly transferred to NADP+, which is used to generate ATP
B. PS II is not splitting water, and the ATP is being produced by cycling electrons via PSI
C. O2 is being converted to water as a terminal electron acceptor in the production of ATP
D. Electron transport has stopped, and ATP is being produced by the Calvin Cycle
E. None of the above
B. PS II is not splitting water, and the ATP is being produced by cycling electrons via PSI
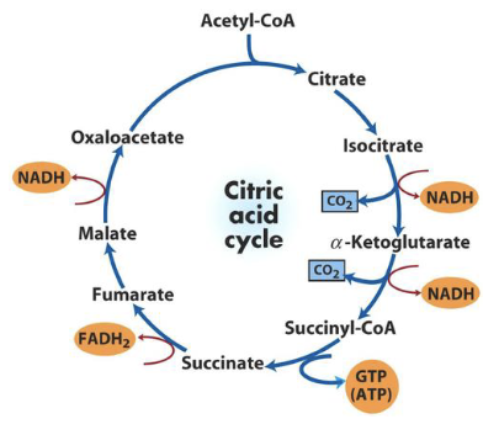
What if pyruvate oxidation is suddenly inhibited, what will happen to the levels of oxaloacetate and citric acid (citrate) in the citric acid cycle shown in the accompanying figure to the right?
A. Oxaloacetate will decrease, and citric acid will accumulate.
B. Oxaloacetate will accumulate, and citric acid will decrease.
C. Both oxaloacetate and citric acid will decrease.
D. Both oxaloacetate and citric acid will accumulate
B. Oxaloacetate will accumulate, and citric acid will decrease.
Reactions that require ATP take place in ________.
A. the light reactions only
B. the Calvin cycle only
C. Glycolysis only
D. Both A and C
E. Both B and C
E. Both B and C
Cells get past cell-cycle checkpoints by ________________.
A. Cdks working on their own to phosphorylate other proteins
B. Cyclins working on their own to phosphorylate other proteins
C. Cdks bound to cyclins phosphorylating other proteins
D. Cyclins being present at the same level during the entire cell cycle
C. Cdks bound to cyclins phosphorylating other proteins
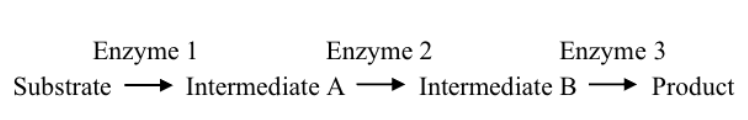
Please examine the metabolic pathway below: Imagine that you observe a buildup of Intermediate A and a gradual decrease in the amount of
Intermediate B in a cell over time. Which of the following scenarios most likely accounts for this?
A. allosteric inhibition of Enzyme 1 by Product
B. competitive inhibition of Enzyme 2 by Intermediate B
C. allosteric inhibition of Enzyme 2 by Product
D. competitive inhibition of Enzyme 1 by Intermediate B
C. allosteric inhibition of Enzyme 2 by Product
What would happen if all of the cells in a developing frog embryo expressed the same type of cadherin on their surfaces?
A. Cells would easily dissociate from each other as the wrong cadherins would bind to each other.
B. All the channels between cells would be blocked, so there would be no cell-to-cell communication.
C. Antibodies would not be able to bind to cadherin as all the receptors would be blocked.
D. All of the cells in the embryo would be capable of attaching to one another regardless of the cell type
D. All of the cells in the embryo would be capable of attaching to one another regardless of the cell type
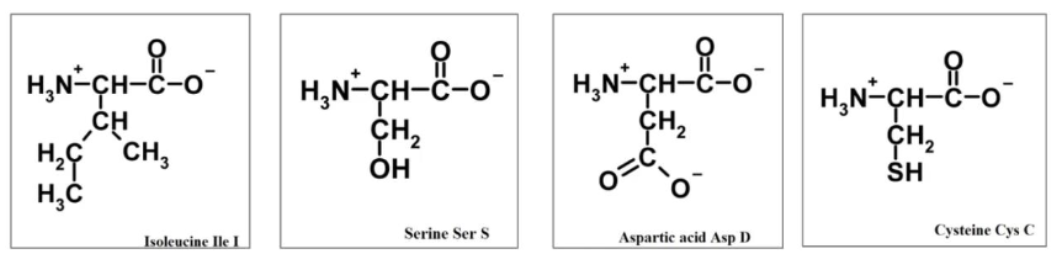
Which of the following amino acids has the highest potential energy?
A. isoleucine
B. serine
C. aspartic acid
D. cysteine
A. isoleucine
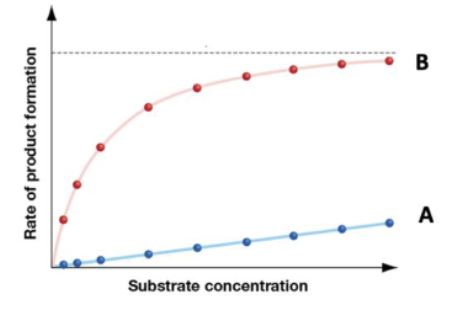
The graph below shows the rate of product formation in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying substrate concentration, with the concentration of
enzyme constant. What if this enzyme was regulated by competitive inhibition and the regulatory molecule is left out of the reactions. Which graph would best represent
the rate of product formation.
A. Graph A
B. Graph B
C. Neither graph A nor B
B. Graph B
In cell signaling, signals (ligands) are classified as lipid-soluble and lipid insoluble. Adrenaline is classified as a lipid insoluble signal, and its receptors are activated when ________.
A. the signal crosses the membranes of target cells containing the intracellular receptors
B. the signal binds to G-protein-coupled receptors, present only on target cells
C. target cells produce second messengers in response to the signal
D. target cells possess the cytosolic enzymes that transduce the signal
B. the signal binds to G-protein-coupled receptors, present only on target cells
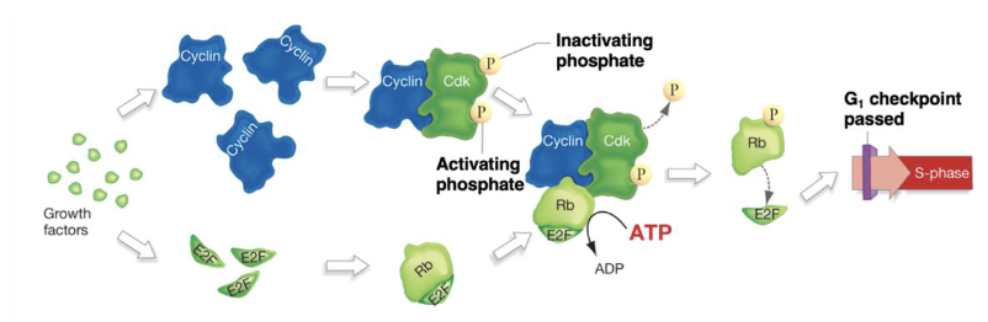
Using your knowledge of the cell cycle and the following diagram, indicate which of the following will lead to formation of a tumor (uncontrolled cell division).
1. Ras with a GTP that cannot be hydrolyzed
2. Overexpression of MPF, the M-phase cyclin-Cdk
3. Nonfunctional E2F protein
4. Under-expression of G1 cyclin
5. Nonfunctional Rb protein
A. 2, 3, 4 only
B. 2 and 5 only
C. 1, 2, 5 only
D. 1 and 5 only
E. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
D. 1 and 5 only
The normal heart rhythm depends on adjacent cardiac muscle cells sharing ions, second messengers, and electrical impulses. __________________ are the membrane channels that connect cardiac muscle cells, providing this chemical and electrical communication leading to the synchronous contraction of the heart.
A. Plasmodesmata
B. Gap junctions
C. Desmosomes
D. Tight junctions
E. Extra cellular matrix
B. Gap junctions
Not all signaling between cells require transduction. Which one of the following signals would be processed without transduction?
A. A lipid-soluble signal
B. A Notch signal
C. A signal that binds to a receptor in the cell membrane
D. A lipid-insoluble signal
A. A lipid-soluble signal
Consider this pathway: adrenaline → G-protein-coupled receptor → G-protein-GTP → adenylyl cyclase → cAMP → Protein Kinase A. The second messenger in this pathway is ________.
A. cAMP
B. G-protein-GTP
C. Protein Kinase A
D. adenylyl cyclase
E. G-protein-coupled receptor
A. cAMP
Scientists experimentally modified the gene encoding the HER2 receptor by removing all zip codes/tags/signals and added a nuclear export signal and a mannose-6-phosphate tag. What is the normal location of the HER2 receptor and its possible new location, respectively?
A. Cytosol; Nucleus
B. Plasma Membrane; Lysosome
C. Cytosol; Lysosome
D. Plasma Membrane; Cytosol
E. None of the above
D. Plasma Membrane; Cytosol
Steroid hormones bind to soluble receptors in the cytosol of the cell and alter their conformation. The hormone-receptor complex is then transported into the nucleus, where it can directly bind DNA and affect gene expression. To get from the location where the receptor binds the hormone to its site where it binds DNA, the hormone-receptor complex must ________.
A. contain a mannose-6-phosphate tag
B. contain an ER signal sequence
C. diffuse to its new location
D. contain an NLS (nuclear localization signal)
E. become phosphorylated
D. contain an NLS (nuclear localization signal)
Axonemal dynein is responsible for the movement of cilia and flagella, whereas cytoplasmic dynein facilitates movement of organelles and other cargo, just like kinesin. These motor proteins walk on microtubules carrying their cargo. If a cell receives a vesicle by endocytosis, which motor protein would deliver the vesicle to its destination in the cell and how?
A. Kinesin walking towards the plus end of the microtubule.
B. Kinesin walking towards the minus end of the microtubule.
C. Dynein walking towards the plus end of the microtubule.
D. Dynein walking towards the minus end of the microtubule
D. Dynein walking towards the minus end of the microtubule
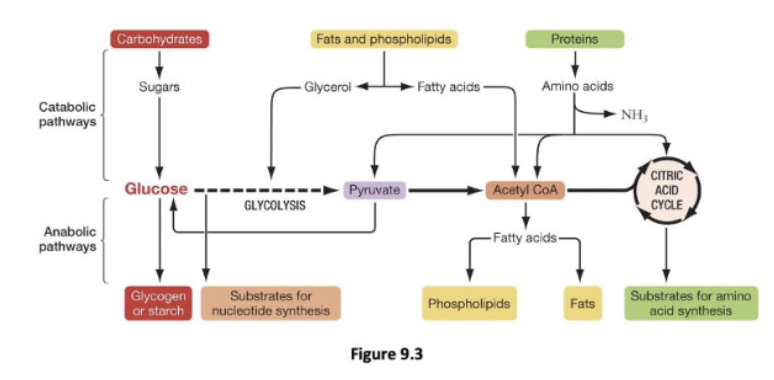
You eat a large plate of non-fat pasta for a late evening snack. Using your knowledge of the central role cellular respiration plays in metabolism and the figure below as a reference, indicate if it is possible for the carbon atoms contained in the pasta to end up in the indicated molecules.
1. Cellulose stored in your muscle cells
2. A sodium ion actively transported by the sodium/potassium-ATPase
3. A lysosomal hydrolase
4. Water made in cellular respiration
5. Oxygen used in cellular respiration
A. 3 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 3, 5 only
D. 2, 3, 4 only
E. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
A. 3 only
Canine phosphofructokinase (PFK) deficiency afflicts Springer spaniels, affecting an estimated 10 percent of the breed. Given its critical role in glycolysis, one implication of the genetic defect resulting
in PFK deficiency in dogs is ________.
A. Early embryonic mortality (death)
B. Elevated glucose levels in the dog’s blood
C. An intolerance for exercise
D. A reduced life span
C. An intolerance for exercise
What if the gene encoding primase is defective due to a frameshift mutation in a cell preparing to undergo replication of its DNA. What will the leading and lagging strand of DNA at a single replication fork look like?
A. leading strand will be complete, lagging strand will consist of Okazaki fragments without RNA primers
B. leading strand will be complete, lagging strand will consist of Okazaki fragments with RNA primers
C. leading and lagging strands will both be complete
D. leading and lagging strands will both be non-existent
D. leading and lagging strands will both be non-existent
What would happen if you used a human DNA polymerase III in PCR rather than Taq polymerase?
A. Since all DNA polymerases are able to build new strands of DNA, PCR would continue as normal.
B. The human DNA polymerase would denature at the high temperatures required to break the hydrogen bonds holding complementary DNA strands together – PCR would fail
C. The human DNA polymerase would be unable to synthesize new strands of DNA without the addition of primase – PCR would fail
D. The human DNA polymerase would be unable to synthesize the lagging strand without the addition of helicase – PCR would fai
B. The human DNA polymerase would denature at the high temperatures required to break the hydrogen bonds holding complementary DNA strands together – PCR would fail
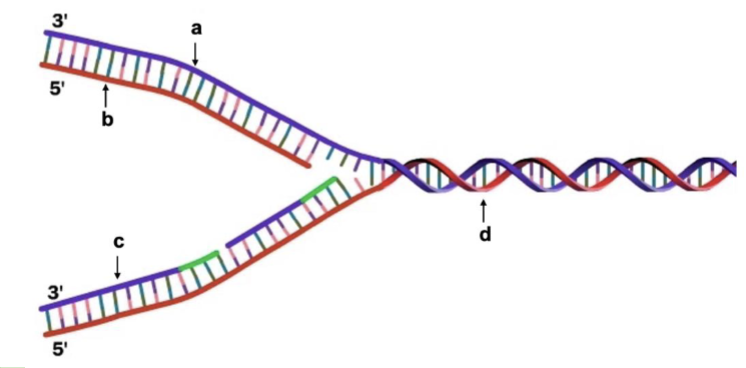
Identify the lagging strand during DNA replication in the figure below.
A. a
B. b
C. c
D. d
C. c
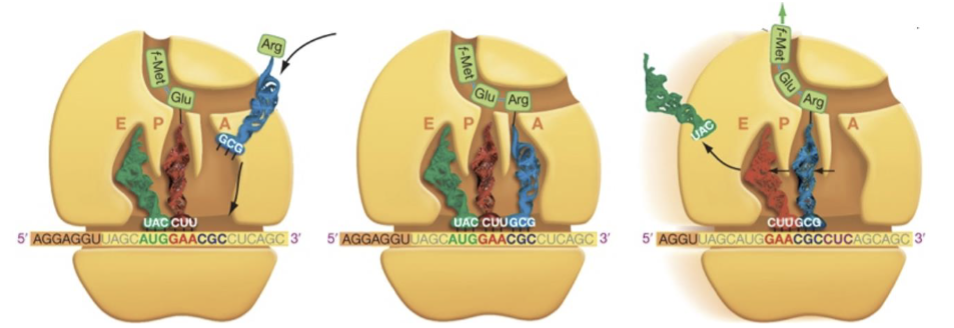
Use the following diagram to answer questions 4, 5 and 6.
Which of the following are required for the specific process occurring above?
1. DNA
2. rRNA
3. mRNA
4. tRNA
5. Charged tRNA
6. snRNPs (snurps)
7. DNA Polymerase
8. RNA Polymerase
A. 1 & 7
B. 2, 3, & 5
C. 1, 3, 6, & 8
D. 1, 2, 3, 5, & 8
E. 2, 3, 4, & 8
B. 2, 3, & 5
Using the 5th codon in the diagram above, find the sequences for the DNA template strand corresponding to the codon and the anticodon.
A. DNA template: 5’-ACC-3’; Anticodon: 5’-ACC-3’
B. DNA template: 5’-GCT-3’; Anticodon: 5’-GCU-3’
C. DNA template: 5’-CCA-3’; Anticodon: 5’-CCA-3’
D. DNA template: 5’-TCG-3’; Anticodon: 5’-UCG-3’
B. DNA template: 5’-GCT-3’; Anticodon: 5’-GCU-3’
In a ribosome, a mutation has changed a nucleotide in the active site of the large subunit rRNA. The ribozyme cannot cause the formation of a covalent bond. Which of the following might be a reasonable explanation of how this might affect translation?
A. Transcription would continue, producing a pre-mRNA because ribozyme function is not needed for forming phosphodiester bonds.
B. Translation would continue, producing a series of free amino acids, all unattached because the ribozyme is unable to form peptide bonds.
C. Transcription would continue, but no mature mRNA would be produced because ribozymes are needed for splicing out introns in the RNA.
D. Translation would stop because ribozymes are needed to attach the codons with the anticodons.
B. Translation would continue, producing a series of free amino acids, all unattached because the ribozyme is unable to form peptide bonds.
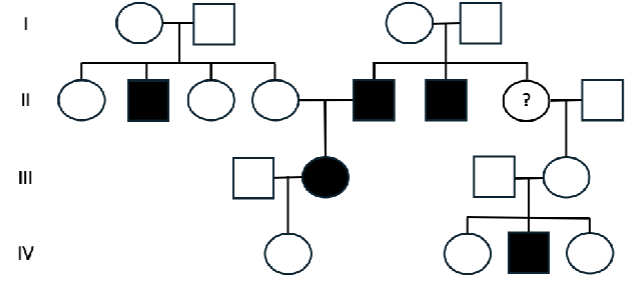
Please examine the pedigree below, which illustrates the pattern of inheritance for a particular condition. Individuals who exhibit the condition of interest are shaded, while individuals who do not exhibit the condition of interest are unshaded. Given this information, what is the most likely genotype of the individual indicated with a question mark?
A. aa
B. Aa
C. XAXa
D. XAXA
C. XAXa
Suppose that you want to introduce the human insulin gene into bacteria to synthesize the insulin protein. Which of the following are pre-requisites for gene expression to occur?
A. The exons need to be removed from the mRNA.
B. A eukaryotic promoter must be present in the mRNA.
C. Eukaryotic ribosomes and tRNAs must be provided.
D. The introns need to be removed and a bacterial promoter must be present in the mRNA.
E. The introns need to be removed, a bacterial promoter must be present in the mRNA, and eukaryotic ribosomes and tRNAs must be provided
D. The introns need to be removed and a bacterial promoter must be present in the mRNA.
Which of the following types of mutation, resulting in an error in the mRNA just after the AUG start of translation, is likely to have the most harmful effect on the polypeptide product?
A. A deletion of a codon
B. A deletion of two nucleotides
C. A substitution of the third nucleotide in an ACC codon
D. A substitution of the first nucleotide of a GGG codon
E. An insertion of a codon
B. A deletion of two nucleotides
Which of the following is an exception to the central dogma?
A. The discovery of RNA viruses that synthesize DNA from RNA using reverse transcriptase
B. The discovery that DNA contains the instructions for making proteins
C. The discovery of ribozymes
D. The discovery of the Wobble Hypothesis
A. The discovery of RNA viruses that synthesize DNA from RNA using reverse transcriptase
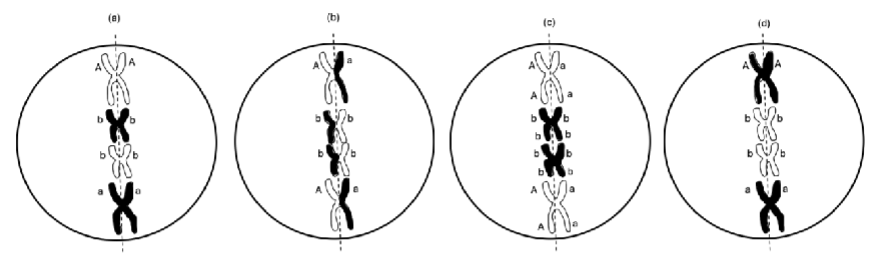
Please examine the following four cells, each of which represents four chromosomes in a cell undergoing mitosis. Imagine that shared color reflects chromosomes that are derived from the same parent and that genes are represented as letters (A/a or B/b) next to the locus at which each is found.
Which cell illustrates a possible arrangement of genes on chromosomes for this individual?
A. (a)
B. (b)
C. (c)
D. (d)
A. (a)
In a Eukaryotic Gene “X”, a mutation changes the first AUG (for Methionine) in the mRNA to AUA.
Of the following, which would be more likely to happen in this cell?
A. The mRNA would remain inside the nucleus and no translation would occur.
B. Translation would begin normally, and at the same location.
C. Translation would NOT occur, because the first start codon AUG has been altered.
D. If there is a second AUG, translation would begin here, and the protein would be shorter.
D. If there is a second AUG, translation would begin here, and the protein would be shorter.

In an experimental situation, a student researcher inserts an mRNA molecule into the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell after she has removed its 5’ cap and poly-A tail. Which of the following would you expect her to find?
A. The mRNA is quickly converted into a ribosomal subunit.
B. The cell adds a new poly-A tail to the mRNA.
C. The mRNA attaches to a ribosome and is translated, but more slowly.
D. The molecule is digested by enzymes because it is not protected at the 5’ end.
D. The molecule is digested by enzymes because it is not protected at the 5’ end.
Which of the following molecules makes a “charged” tRNA molecule?
A. DNA polymerase
B. RNA polymerase
C. Primase
D. Ribozyme
E. Aminoacyl t-RNA synthetase
E. Aminoacyl t-RNA synthetase
Suppose that you have a mutation that modifies the nucleotides at the exon-intron borders. This results in a mature mRNA that includes an intron. What would be the result of this at the organismal level?
A. The organism would have no effect, since the ribosomes cannot bind to messages containing introns.
B. The organism would have no effect, since there are no anticodons in the tRNAs that correspond to the codons in the intron mRNA.
C. The introns sequences would get removed during posttranslational modifications.
D. The information in the intron would be translated and this would result in additional amino acids being incorporated into the protein and possibly frameshift mutations.
D. The information in the intron would be translated and this would result in additional amino acids being incorporated into the protein and possibly frameshift mutations.
In humans, Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP) is a disorder where individuals develop thymine dimer lesions caused by exposure to ultraviolet light. Given the damage caused by UV radiation, the kind of gene affected in those with XP is one whose gene product is involved with ________.
A. mending of double-strand breaks in the DNA backbone
B. breakage of cross-strand covalent bonds
C. the ability to excise single-strand damage and replace it
D. the removal of double-strand damaged areas
E. causing affected skin cells to undergo apoptosis
C. the ability to excise single-strand damage and replace it
Telomere shortening puts a limit on the number of times a cell can divide. Research has shown that telomerase can extend the life span of cultured human cells. How might adding telomerase affect cellular aging?
A. Telomerase will speed up the rate of cell proliferation.
B. Telomerase eliminates telomere shortening and slows down aging.
C. Telomerase shortens telomeres, which delays cellular aging.
D. Telomerase would have no effect on cellular aging
B. Telomerase eliminates telomere shortening and slows down aging.
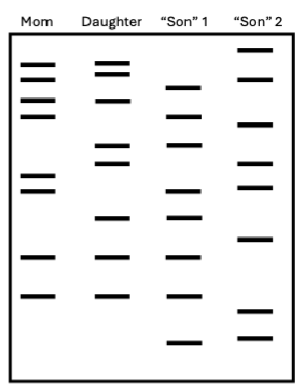
Imagine that a wealthy man dies and leaves a large inheritance to his wife and daughter. Following his death, two men come forward, both claiming to be the
long-lost son placed up for adoption by the rich man and his wife before they were married. To evaluate the truthfulness of each claim, a judge orders that DNA markers for each man be compared against the mother and daughter of the rich man. Based on the results of this analysis (shown in the gel on the right), what can you conclude about the likelihood that each man is this long-lost son?
A. “Son” 1 could be the long-lost son, while “Son” 2 can be definitively excluded
B. “Son” 2 could be the long-lost son, while “Son” 1 can be definitively excluded
C. Neither man is the long-lost son
D. Both men could be the long-lost son; neither can be ruled out and further analysis is needed
A. “Son” 1 could be the long-lost son, while “Son” 2 can be definitively excluded
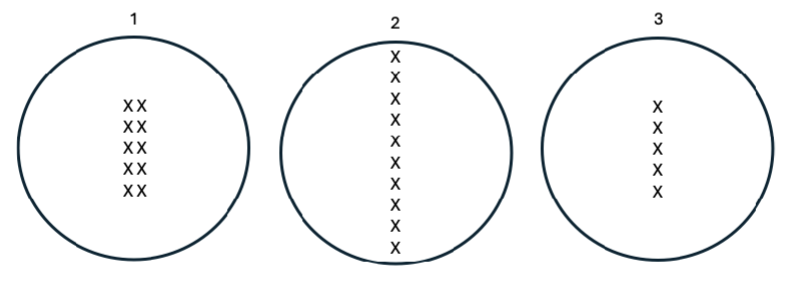
Please examine cells 1-3 below and statements (I - V) that follow. If all three cells can be found in the same organism, which of the following statements about these three cells is correct?
I. Cell 1 is undergoing meiosis, while Cells 2 and 3 are undergoing mitosis.
II. Cells 1 and 3 will give rise to gametes, while Cell 2 will give rise to a somatic cell.
III. Cells 1 and 2 are diploid, while Cell 3 is haploid.
IV. Chromosomes are replicated in Cell 1 and unreplicated in Cells 2 and 3.
V. Cells 1, 2, and 3 are all eukaryotic.
A. Statements (I), (II), and (III) are correct.
B. Statements (I) and (IV) are correct.
C. Statements (II) and (III) are correct.
D. Statements (II), (III), and (V) are correct.
D. Statements (II), (III), and (V) are correct.
In Labrador retrievers, primary coat color (black, chocolate, or yellow) is determined by the specific combination of alleles that an individual possesses at two genes. Variation at one gene, TYRP1, determines the amount of eumelanin that an individual produces, with one allele (B) coding for high enzymatic activity resulting in high eumelanin production (leading to black pigmentation) and the other (b) coding for low enzymatic activity resulting in low eumelanin production (leading to chocolate pigmentation). Variation at a second gene, MC1R, determines whether this pigment is deposited into
the fur. At this locus, allele E codes for a functional receptor that allows eumelanin deposition to occur, while allele e codes for a non-functional receptor that prevents eumelanin deposition from occurring. Imagine that two dogs, one with genotype Bbee, and the other with genotype BBEe, are crossed. What coat color ratio is expected in the puppies?
A. 100% black
B. 50% black, 50% chocolate
C. 50% black, 50% yellow
D. 50% black, 25% chocolate, 25% yellow
C. 50% black, 50% yellow
Read the following sentences, and then choose one option below:
“In this study, we tested the hypothesis that the cause of muscle mass loss after nerve damage is an increase in the protein TRB3.”
“In this study, we tested the hypothesis that treatment with an antibody that blocks the enzymatic activity of protein PAPP-A will reduce atherosclerotic plaque progression.”
"In this study, we tested the hypothesis that Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is caused by misfolded prion proteins (PrPSc) and leads to rapid neurodegeneration.”
Option A: Both 1 and 2 are hypotheses.
Option B: 1 is a hypothesis, but 2 is a prediction.
Option C 1 is a prediction, but 2 is a hypothesis.
Option D Both 1 and 3 are hypotheses
Option E Both 2 and 3 are hypotheses
Option B: 1 is a hypothesis, but 2 is a prediction.
Both starch and cellulose are found in plants. However, enzymes that readily break starch apart cannot hydrolyze the bonds found in cellulose. Why is this logical?
Option A: Starch is held together by hydrogen bonding, not covalent bonding.
Option B: Cellulose molecules are highly branched, and enzymes are too bulky to fit.
Option C: The geometry of the bonds is different, and the shapes of enzyme active sites are highly specific.
Option D: Starch is held together by peptide bonds, not glycosidic linkages.
Option C: The geometry of the bonds is different, and the shapes of enzyme active sites are highly specific.
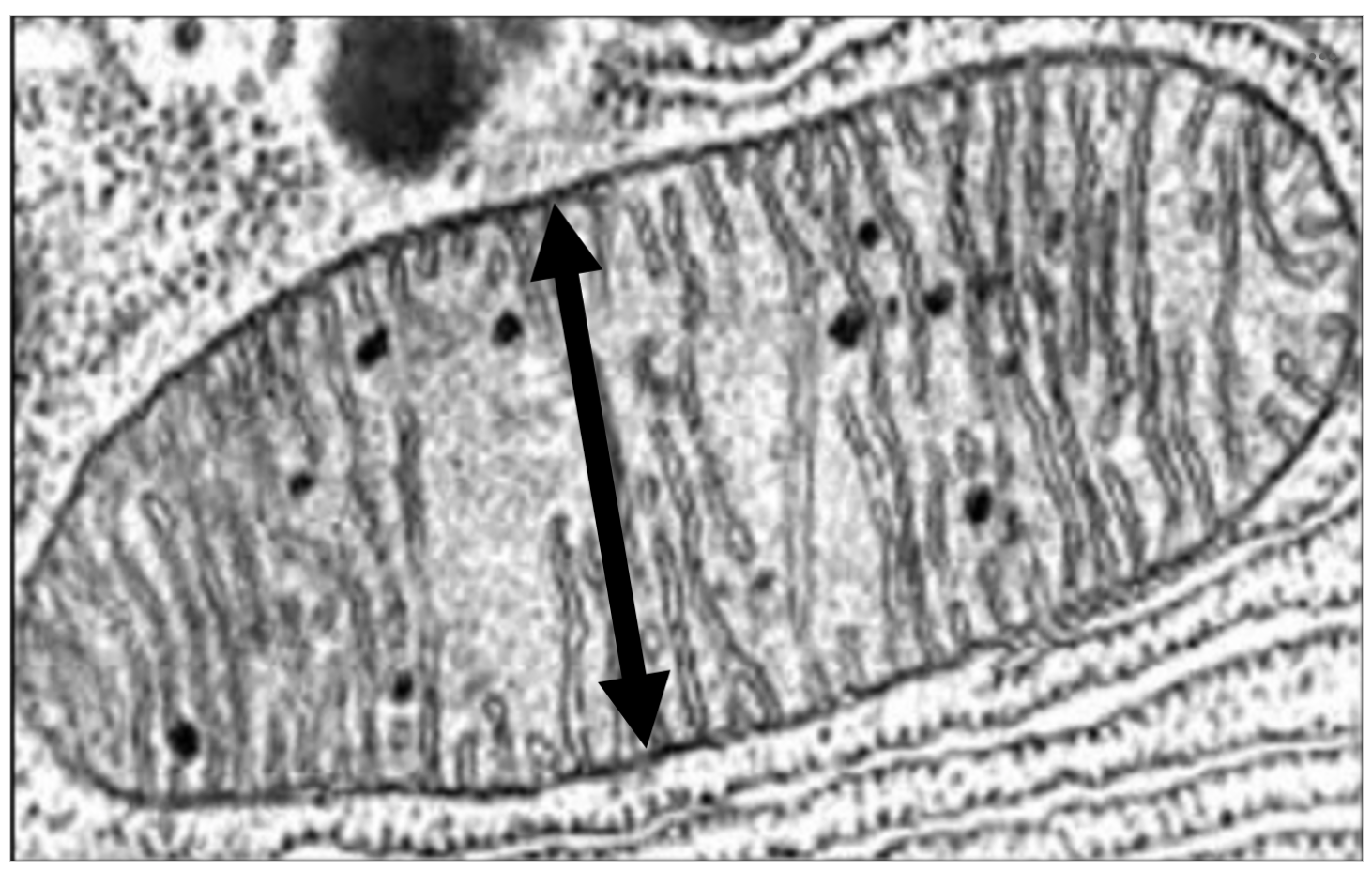
Use the bacterial ruler to estimate the length of the double-sided arrow in this image. You may take a screen grab if you would like to annotate the image on another app to estimate the length of the arrow.
Option A: 240 µm
Option B: 120 µm
Option C: 0.24 µm
Option D: 0.12 µm
Option C: 0.24 µm
If one strand of a DNA molecule has the sequence of bases 5'-TATTCGA-3', the complementary strand sequence would read _____.
Option A: 5'-ATAAGCT-3'
Option B: 3'-UAUUGCU-5'
Option C: 5'-UAUUGCU-3'
Option D: 5'-TCGAATA-3’
Option D: 5'-TCGAATA-3’
Suppose a cell contains the enzymes sucrase and fructase, and sucrose is introduced into the cell. Predict what would happen to the concentration of monosaccharides in the cell over time.
Option A: Fructose and sucrose would both decrease.
Option B: Fructose would decrease and glucose would accumulate.
Option C: Fructose and glucose would both decrease over time.
Option D: Sucrose and glucose would both decrease over time.
Option B: Fructose would decrease and glucose would accumulate.
Water molecules can adhere to biological surfaces such as cell membranes and extracellular matrices. Which of the following best explains the significance of this adhesion?
Option A: Adhesion allows water to form hydrogen bonds with the hydrocarbon backbone of cellulose
Option B: Adhesion via hydrogen bonding to polar groups maintains hydration and proper membrane function
Option C: Adhesion allows water to form covalent bonds with membrane proteins
Option D: Adhesion ensures that water molecules move independently of the extracellular matrix and membranes
Option B: Adhesion via hydrogen bonding to polar groups maintains hydration and proper membrane function
Bacteria, insects, and plants use carbohydrates to build structures. Which of the following is TRUE of structural carbohydrates?
Option A: Different types of pentose monomers form the basis of all carbohydrate-based structures.
Option B: Structural carbohydrates show a high degree of branching.
Option C: All structural carbohydrates are made from the same monomer, α-glucose.
Option D: Structural carbohydrates are long strands, which are chemically linked into a network
Option D: Structural carbohydrates are long strands, which are chemically linked into a network
Proteins that interact with DNA often interact with the phosphates that are part of this molecule. Which of the following types of amino acids would you predict to be present in the part of the protein that interacts with the phosphates in DNA?
Option A: Basic amino acids
Option B: Acidic amino acids
Option C: Polar amino acids
Option D: Nonpolar amino acids
Option A: Basic amino acids
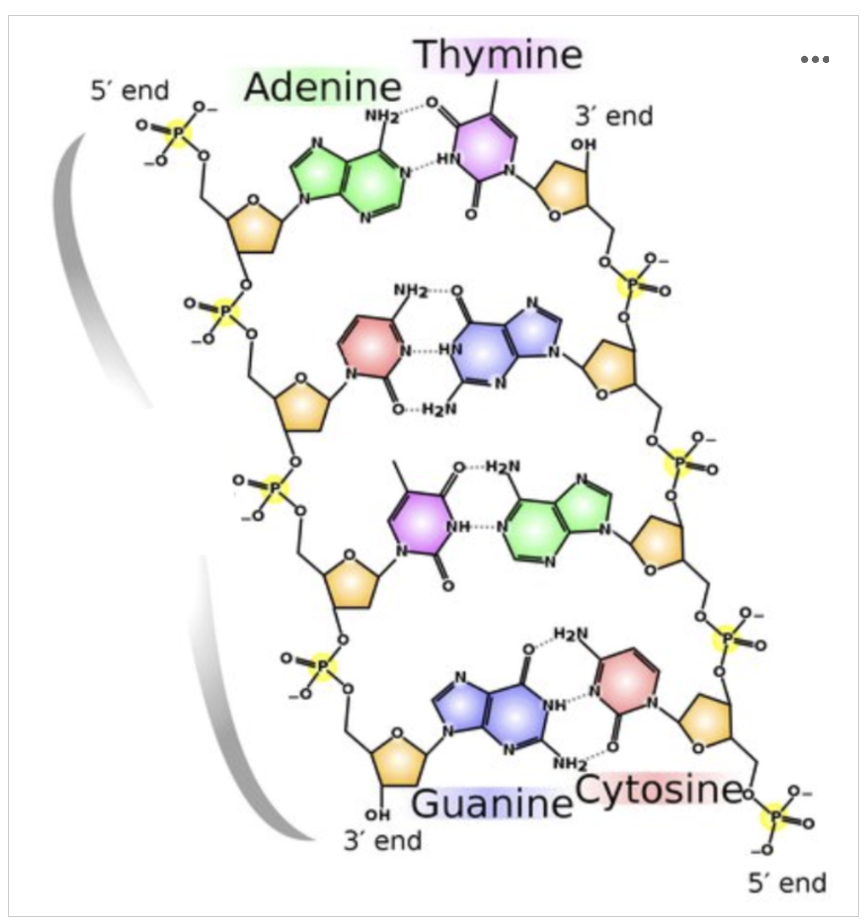
A mutation occurs in this middle portion of a DNA molecule, where an adenine replaces a cytosine. What impact do you think this will have on the DNA structure?
Option A: Adenine is larger than cytosine and will not be able to base pair properly with the guanine on the opposing strand. This will cause the phosphodiester bonds to break, and the DNA will hydrolyze.
Option B: Adenine is larger than cytosine and will not be able to base pair properly with the guanine on the opposing strand. This will cause the DNA to denature or unzip.
Option C: Adenine is larger than cytosine and will not be able to base pair properly with the guanine on the opposing strand. This will cause the DNA to bulge.
Option D: Since adenine is still a nitrogenous base, this mutation will have no impact on the DNA structure
Option C: Adenine is larger than cytosine and will not be able to base pair properly with the guanine on the opposing strand. This will cause the DNA to bulge.
Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) play a key role in RNA splicing by catalyzing the cutting of RNA molecules. Which bonds are being broken during this process?
Option A: Peptide bonds between nucleotides
Option B: Phosphodiester linkages between amino acids
Option C: Disulfide bonds between amino acids
Option D: Phosphodiester linkages between nucleotides
Option D: Phosphodiester linkages between nucleotides
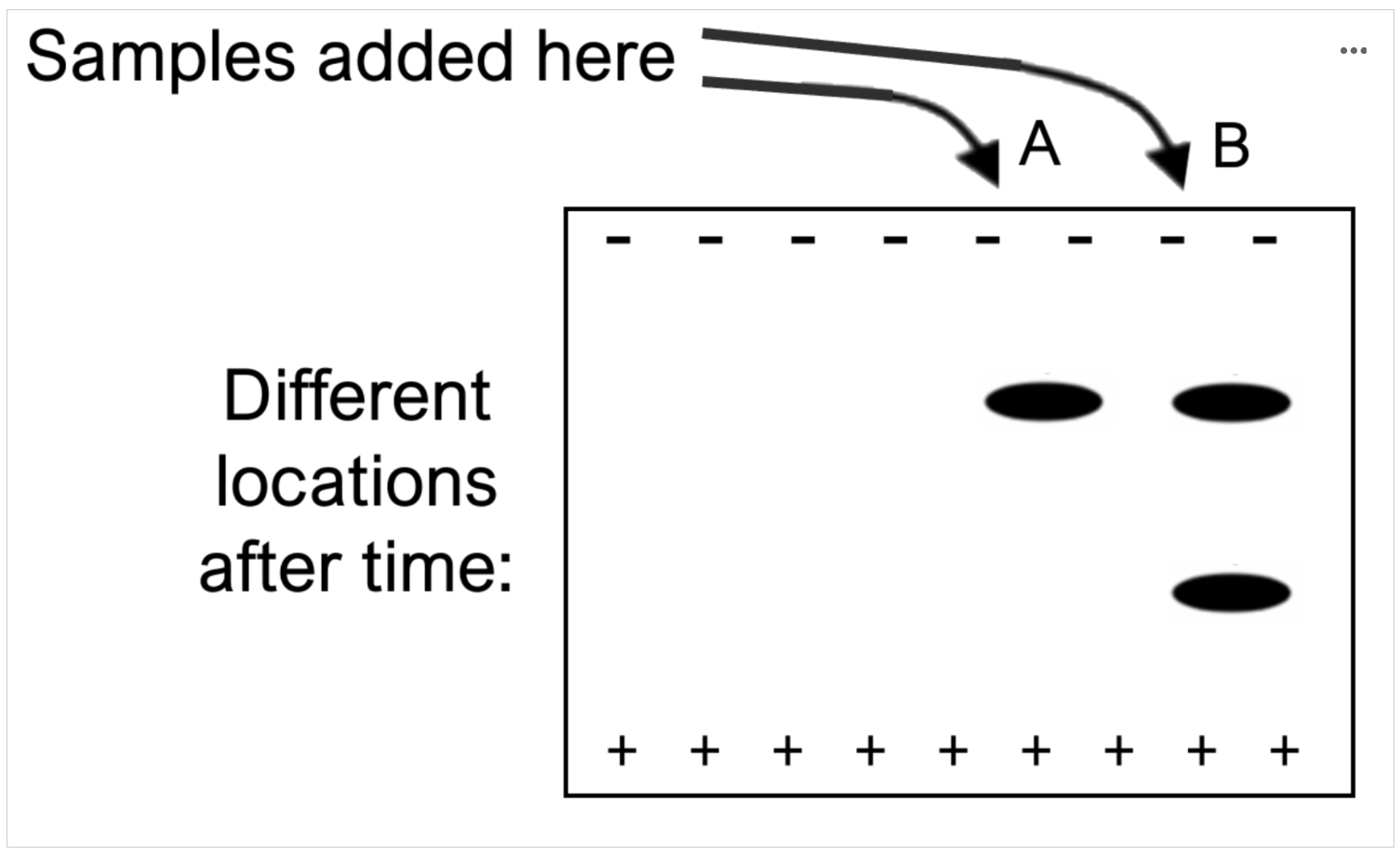
Gel electrophoresis is a technique that can be used to separate Your Favorite Protein from other proteins. The gel contains pores of different sizes allowing different molecules to pass through at different rates. Electrodes are attached so that the top end of the gel shown has a negative charge, and the bottom edge has a positive charge. After a period of time, the electrodes are removed, the gel is stained, and the location of the sample is visualized. In the gel below, a purified sample of Your Favorite Protein is in lane B. What can you conclude about Your Favorite Protein from this result?
Option A: Your Favorite Protein has quaternary structure.
Option B: Your Favorite Protein is a heterodimer.
Option C: Your Favorite Protein has an α-helix and a β-pleated sheet.
Option D: All of the above
Option A: Your Favorite Protein has quaternary structure.
The molecular chaperone Hsp70 normally contains a valine in its binding pocket, allowing it to interact with regions of newly synthesized proteins. Suppose a mutation changes this valine to aspartic acid. Predict what might happen to the folding of a protein’s alpha and beta subunits.
Option A: The protein’s alpha and beta subunits would fold properly
Option B: The protein’s alpha and beta subunits would fold properly but the tertiary structure would aggregate and misfold
Option C: The protein would remain in a linear, unfolded state
Option D: The protein would be unable to fold properly and aggregate
Option D: The protein would be unable to fold properly and aggregate
In the following reaction, the fatty acid palmitic acid (CH3(CH2)14COOH) is broken down. In this _____________ reaction, _____________ is oxidized and _____________ is reduced.
CH3(CH2)14COOH + NAD+ → CH3(CH2)12 COOH + NADH + H+
Option A: Exergonic; Palmitic Acid; NAD+
Option B: Exergonic; NADH; Palmitic Acid
Option C: Endergonic; NAD+; Palmitic Acid
Option D: Endergonic; Palmitic acid; NADH
Option A: Exergonic; Palmitic Acid; NAD+
Patients with Gaucher’s Disease have a mutation in the beta-glucosidase (GBA) gene, which leads to a deficiency in the lysosomal enzyme glucocerebrosidase. Which of the following does glucocerebrosidase require to be correctly delivered to the lysosome? Select all that apply.
Option A: Nuclear localization signal (NLS)
Option B: Nuclear export signal (NES)
Option C: Mannose-6-phosphate tag (M6P)
Option D: Endoplasmic reticulum signal sequence (ERSS)
Option E: Glycosylation in the rough ER
Option C: Mannose-6-phosphate tag (M6P)
Option D: Endoplasmic reticulum signal sequence (ERSS)
Option E: Glycosylation in the rough ER
Enzyme activity refers to the rate at which a reaction is catalyzed, whereas enzyme regulation is when, where, and how a reaction occurs. Which of the following best distinguishes between enzymatic activity and regulation?
Option A: Enzymatic activity is influenced by factors such as temperature and pH, while enzyme regulation depends on the binding of an allosteric activator
Option B: Enzymatic activity is controlled only by substrates, while enzyme regulation is controlled only by cofactors
Option C: Enzymatic activity depends only on the presence of inhibitors, while enzyme regulation depends on environmental factors such as temperature and pH
Option D: Enzymatic activity is constant, while enzyme regulation is temporary
Option A: Enzymatic activity is influenced by factors such as temperature and pH, while enzyme regulation depends on the binding of an allosteric activator
How might a change of one amino acid at a site, distant from the active site of an enzyme, alter an enzyme's substrate specificity?
Option A: By changing the enzyme's location in the cell
Option B: By changing the enzyme's stability
Option C: By changing the overall shape of an enzyme
Option D: By changing the enzyme's optimum pH
Option C: By changing the overall shape of an enzyme
Which of the following correctly matches a component of the cytoskeleton to one of its functions?
Option A: Microtubules carry vesicles across the cell
Option B: Microfilaments aid animal cells in cell division
Optin C: Intermediate filaments cause bending of cilia
Option D: Actin filaments anchor the nucleus
Option A: Microtubules carry vesicles across the cell
Axonemal dyneins are responsible for the movement of cilia and flagella, whereas cytoplasmic dynein facilitates movement of organelles and other cargo, just like kinesin. These motor proteins, dynein and kinesin, walk on microtubules carrying their cargo. If a cell receives a molecule by endocytosis, which motor protein would deliver the vesicle to its destination in the cell and how?
Option A: Kinesin walking towards the plus end of the microtubule
Option B: Kinesin walking towards the minus end of the microtubule
Option C: Dynein walking towards the plus end of the microtubule
Option D: Dynein walking towards the minus end of the microtubule
Option D: Dynein walking towards the minus end of the microtubule
Hexokinase binds to glucose and catalyzes a chemical reaction that changes the glucose to glucose 6-phosphate. Once this reaction occurs, hexokinase _____.
Option A: has been converted to glucose 6-phosphate
Option B: is the product of the reaction
Option C: cannot be used again
Option D: is unchanged
Option D: is unchanged
In a series of enzyme catalyzed reactions of A + B → C → D → E, we find that increasing the concentration of A & B to 10 M steadily increases the rate of production of E. When A & B are raised to 11 M or more, the rate of production of C continues to rise, but the rate of production of D & E does not change. What might be occurring?
Option A: Saturation of the enzyme that catalyzes C → D.
Option B: Competitive inhibition of the enzyme that catalyzes A + B → C.
Option C: Feedback inhibition of E on the enzyme that catalyzes A + B → C.
Option D: Competitive inhibition of the enzyme that catalyzes D → E.
Option A: Saturation of the enzyme that catalyzes C → D.
In the series of enzyme catalyzed reactions of A + B → C → D → E, you learn that the enzyme that catalyzes the A + B → C reaction has three known inhibitors: Inhibitor 1, Inhibitor 2, and Inhibitor 3. You observe the following:
Inhibitor 1 binds reversibly to the enzyme. Its inhibitory effect can be overcome by increasing the concentration of its substrate.
Inhibitor 2 binds at a site other than the active site to decrease enzyme activity. However, its inhibition cannot be overcome by increasing the concentration of its substrate.
Inhibitor 3, which is structurally distinct from the enzyme’s substrate, only accumulates when high levels of product E are produced. Inhibitor C binds to the same site as Inhibitor 2 to reduce enzyme activity.
How would you classify Inhibitor 1 and Inhibitor 3, and how would you describe the regulation of this metabolic pathway?
Option A: 1: Allosteric inhibitor; 3: Allosteric inhibitor; Regulation: Feedback inhibition
Option B: 1: Competitive inhibitor 3: Feedback inhibitor; Regulation: Allosteric inhibition
Option C: 1: Competitive inhibitor 3: Allosteric inhibitor; Regulation: Feedback inhibition
Option D: 1: Allosteric inhibitor; 3: Competitive inhibitor; Regulation: Competitive inhibition
Option E: 1: Competitive inhibitor; 3: Feedback inhibitor; Regulation: Feedback inhibition
Option C: 1: Competitive inhibitor 3: Allosteric inhibitor; Regulation: Feedback inhibition
A solution of starch at room temperature does NOT readily decompose to form a solution of simple sugars because __________ .
Option A: the starch solution has less free energy than the sugar solution
Option B: the activation energy barrier for this reaction cannot easily be surmounted at room temperature
Option C: the hydrolysis of starch to sugar is endergonic
Option D: starch cannot be hydrolyzed in the presence of so much water
Option B: the activation energy barrier for this reaction cannot easily be surmounted at room temperature
In a synthesis reaction, glucose and fructose are combined to make sucrose. Under standard conditions, the ΔG of this uncoupled reaction is +27 kJ/mol. Predict how introducing ATP will affect this synthesis reaction.
Option A: The uncoupled reaction is endergonic. Coupling the reaction with ATP hydrolysis lowers the enzyme’s activation energy, but the reaction is still endergonic.
Option B: The uncoupled reaction is endergonic. Coupling the reaction with ATP hydrolysis divides the reaction into two steps, both of which are exergonic.
Option C: The uncoupled reaction is exergonic. Coupling the reaction with ATP hydrolysis lowers the enzyme’s activation energy, and the reaction becomes endergonic.
Option D: The uncoupled reaction is exergonic. Coupling the reaction with ATP hydrolysis divides the reaction into two steps, both of which are endergonic.
Option E: Adding ATP does not affect the reaction.
Option B: The uncoupled reaction is endergonic. Coupling the reaction with ATP hydrolysis divides the reaction into two steps, both of which are exergonic.
Recall the "Ticket to Nowhere" case study where you were a student intern under the mentorship of Dr. Crumpler. Maria and Francisco Silva were so happy with the arrival of their new baby girl, Ana Sophia. By the time she was six months old, however, her parents had some concerns about her growth and development. Dr. Crumpler feared that Ana Sophia may have a rare disorder. She invited you to investigate the most common Lysosomal Storage Disorders and their underlying causes. While conducting your research and working on Ana Sophia's case, which of the following statements did you find to be true (select all that apply):
Option A: Ana Sophia's lysosomal hydrolases were found in the lysosomes of her cells, but they were nonfunctional because the pH in the lysosome was too acidic.
Option B: Ana Sophia's lysosomal hydrolases were found outside her cells in the blood, and they were functional when tested at an acidic pH.
Option C: It is possible that Ana Sophia's lysosomal hydrolases were synthesized without an ER signal sequence and left the cell by facilitated diffusion.
Option D: It is possible that Ana Sophia's lysosomal hydrolases were properly tagged with mannose-6-phosphate in the Golgi and were delivered to the lysosome.
Option E: It is possible that Ana Sophia's lysosomal hydrolases were not properly tagged with mannose-6-phosphate in the Golgi and were delivered to the plasma membrane for exocytosis.
Option F: Ana Sophia was ultimately diagnosed with a lysosomal storage disorder called Gaucher's Disease.
Option B: Ana Sophia's lysosomal hydrolases were found outside her cells in the blood, and they were functional when tested at an acidic pH.
Option E: It is possible that Ana Sophia's lysosomal hydrolases were not properly tagged with mannose-6-phosphate in the Golgi and were delivered to the plasma membrane for exocytosis.
You have introduced a mutation in the electron carrier plastocyanin (PC) so it can no longer accept electrons from plastoquinone (PQ) in the cytochrome complex. Predict how this mutation would immediately affect production of ATP and NADPH.
Option A: a. Both ATP and NADPH production stop completely
Option B: b. ATP production continues at normal levels, but NADPH production stops
Option C: c. ATP production decreases, but NADPH production stops completely.
Option D: d. Both ATP and NADPH production decrease, but neither stops completely
Option E: e. ATP production stops completely, but NADPH production continues at normal levels.
Option C: c. ATP production decreases, but NADPH production stops completely.
A signaling pathway is observed in a tissue where:
Signal transmission occurs between adjacent cells
The receptor is embedded in the plasma membrane
Signal transduction occurs without the activation of a phosphorylation cascade
The signal results in a change in cellular gene expression
Which of the following signaling pathways does this description most accurately describe?
Option A: a. Lipid soluble signaling
Option B: b. Notch signaling
Option C: c. G-protein coupled receptor signaling
Option D:d. Enzyme-linked receptor signaling
Option B: b. Notch signaling
Assume the outer mitochondrial membrane is punctured so that the mitochondrial intermembrane space is no longer separated from the cytosol. This damage will most directly affect the ________.
Option A: a. ATP synthesis through substrate-level phosphorylation
Option B: b. The process of glycolysis
Option C: c. The process of fermentation
Option D: d. ATP synthesis through oxidative phosphorylation
Option D: d. ATP synthesis through oxidative phosphorylation
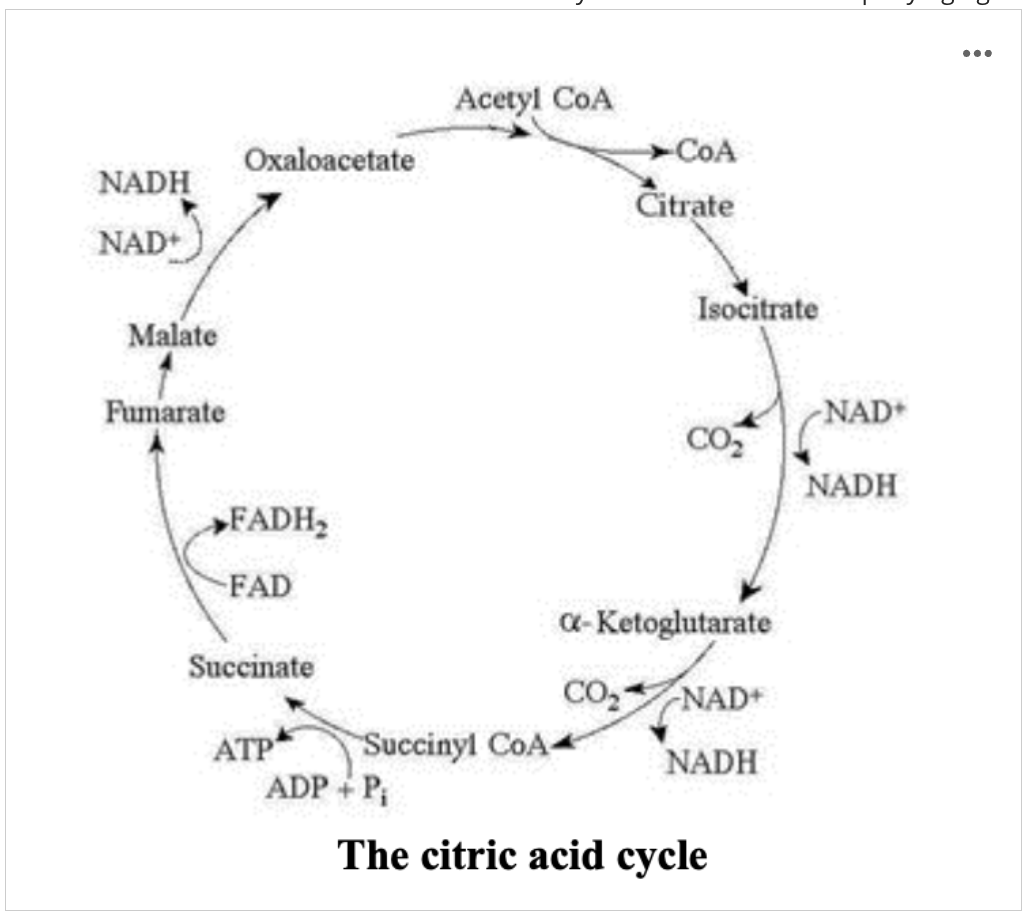
What if NADH competitive inhibition occurs, what will happen to the levels of malate and isocitrate in the citric acid cycle shown in the accompanying figure?
Option A: a. Malate will decrease, and isocitrate will accumulate
Option B: b. Both malate and isocitrate will decrease
Option C: c. Malate will accumulate, and isocitrate will decrease
Option D: d. Both malate and isocitrate will accumulate
Option E: e. Malate will remain constant, and isocitrate will increase
Option A: a. Malate will decrease, and isocitrate will accumulate
Reactions that require CO2 take place in ________.
Option A: a. Both the light reactions and the Calvin cycle
Option B: b. The Calvin cycle only
Option C: c. The C4 cycle only
Option D: d. Both the Calvin cycle and the C4 cycle.
Option D: d. Both the Calvin cycle and the C4 cycle.
What would happen if all of the cells in a developing frog embryo expressed the same type of cadherin on their surfaces?
Option A: Cells would easily dissociate from each other as the wrong cadherins would bind to each other.
Option B: All the channels between cells would be blocked, so there would be no cell-to-cell communication.
Option C: Antibodies would not be able to bind to cadherin as all the receptors would be blocked.
Option D: All of the cells in the embryo would be capable of attaching to one another regardless of the cell type.
Option D: All of the cells in the embryo would be capable of attaching to one another regardless of the cell type.
Normal breast cells have HER2 receptors in their plasma membrane. The epidermal growth factor is the signal molecule that binds to this receptor. What if a normal breast cell develops a mutation in protein kinase 2 (aka MEK) that prevents the active form of MEK from being recognized by phosphatases. What effect would this have on the cell?
Option A: Since MEK contains a phosphate, it is unable to transduce the signal and the cell would not grow and divide.
Option B: Since MEK contains a phosphate, it is able to transduce the signal continuously and the cell would continue to grow and divide, possibly leading to cancer.
Option C: Since the phosphatase removes the phosphate from MEK, this will stop the signaling and the cell would stop growing.
Option D: Since the phosphatase cannot remove the phosphate from MEK, this will stop the signaling and the cell would stop growing.
Option B: Since MEK contains a phosphate, it is able to transduce the signal continuously and the cell would continue to grow and divide, possibly leading to cancer.
When electrons flow along the electron transport chains of mitochondria, which of the following changes occurs?
Option A: The pH of the matrix decreases
Option B: ATP synthase pumps protons by active transport
Option C: NADH is reduced.
Option D: The pH of the intermembrane space decreases
Option D: The pH of the intermembrane space decreases
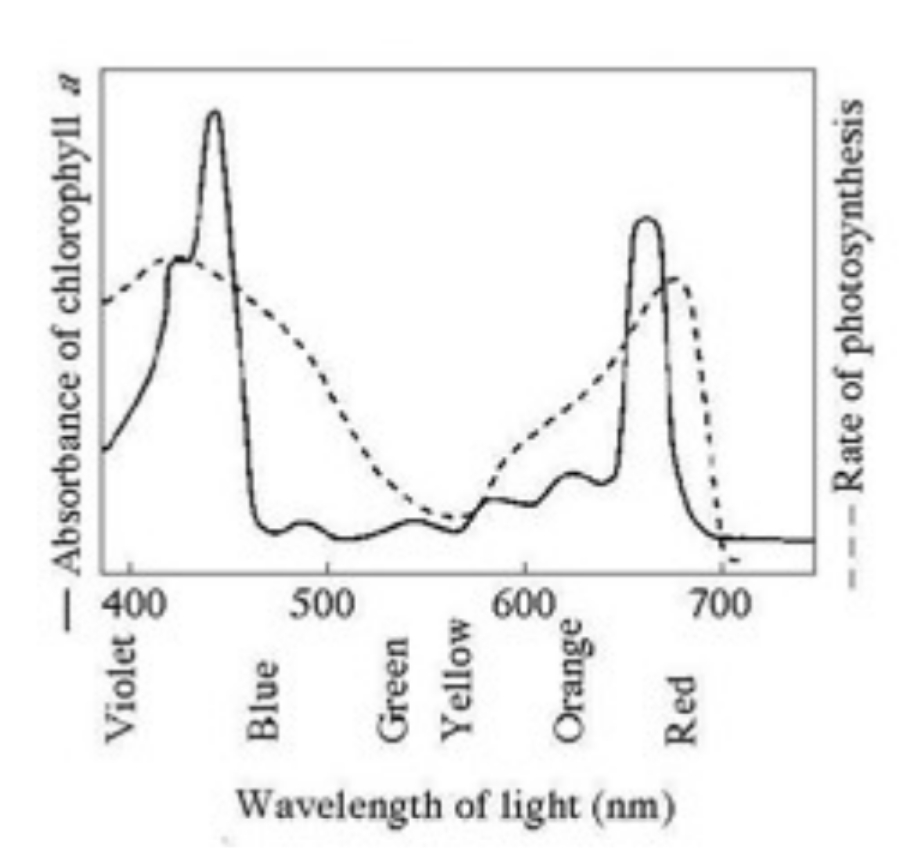
What wavelength of light in the accompanying figure is most effective in driving photosynthesis?
Option A: 625 mm
Option B: 575 mm
Option C: 420 mm
Option D: 475 mm
Option C: 420 mm
Lipid-soluble signaling molecules, such as cortisol, cross the membranes of all cells but affect only target cells because ________.
Option A: G-protein-coupled receptors are present only in target cells
Option B: intracellular receptors are present only in target cells
Option C: only target cells produce second messengers in response to cortisol
Option D: only target cells posses the cytosolic enzymes that transduce the cortisol
Option B: intracellular receptors are present only in target cells
CAM plants keep stomata closed in the daytime, thus reducing loss of water. They can do this because they ________.
Option A: Fix CO2 into organic acids during the night
Option B: Fix CO2 into sugars in the bundle-sheath cells
Option C: Fix CO2 into pyruvate in the mesophyll cells
Option D: Use the enzyme PEP carboxylase, which outcompetes Rubisco for CO2 in the bundle sheath cells.
Option A: Fix CO2 into organic acids during the night
Which of the following would halt (stop) glycolysis:
Option A: Lack of O2
Option B: Lack of CO2
Option C: Lack of NAD+
Option D: Both A and C
Option C: Lack of NAD+
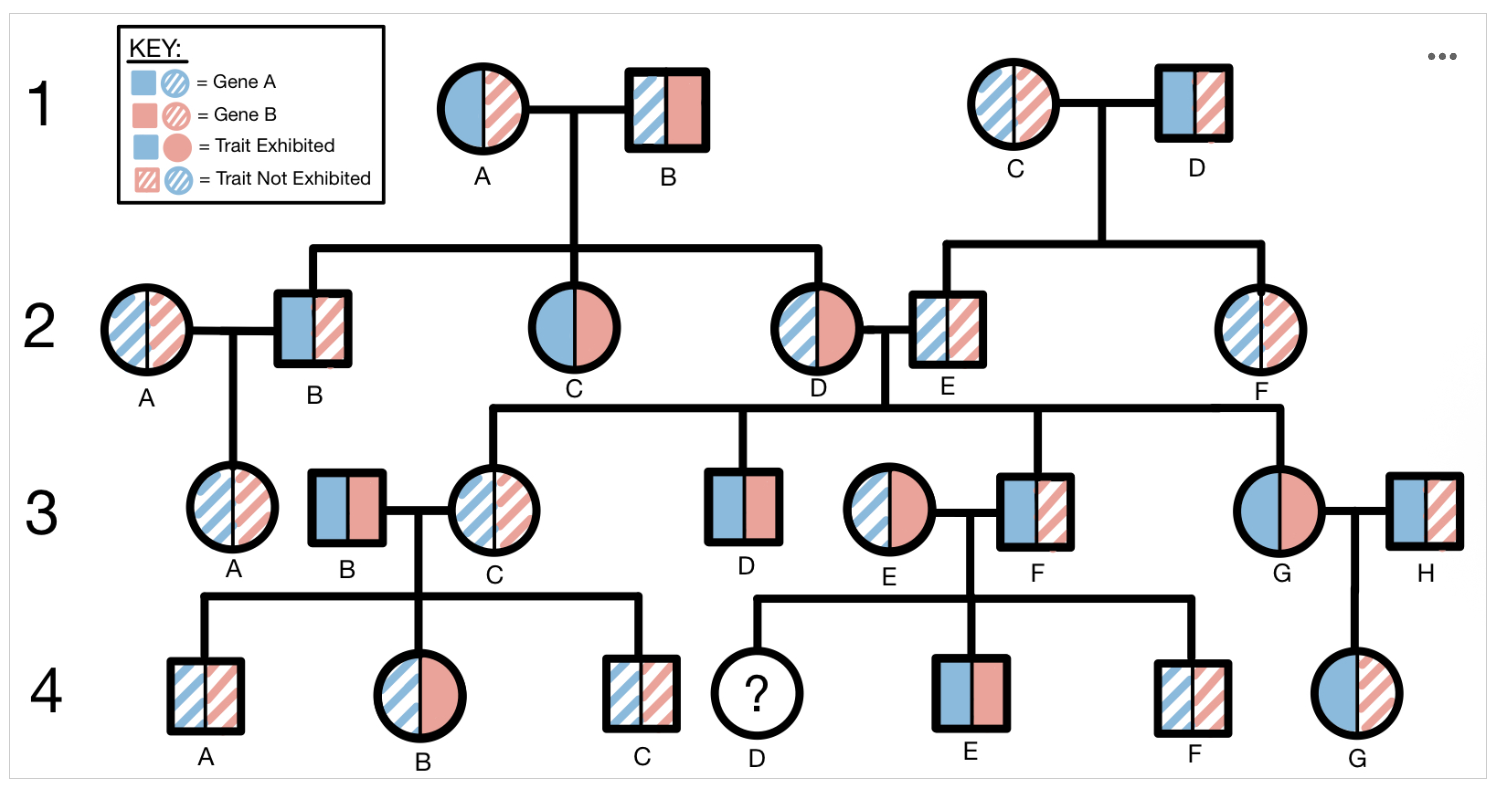
Questions #1-3 refer to the following pedigree. This pedigree illustrates the inheritance pattern of two unrelated traits, Trait Blue and Trait Red, across four generations of one family. Trait Blue is one phenotype of the protein encoded by Gene A, while Trait Red is one phenotype of the protein encoded by Gene B. In this pedigree, squares represent males and circles represent females. Solid-colored shapes represent an individual who exhibits a trait and dashed lines represent an individual who does not exhibit the trait. Trait Blue is depicted on the left side of each shape while Trait Red is depicted on the right side of each shape.
What type of inheritance pattern does Trait Blue most likely follow?
Option A: Autosomal dominant
Option B: Autosomal recessive
Option C: Sex-linked dominant
Option D: Sex-linked recessive
Option B: Autosomal recessive
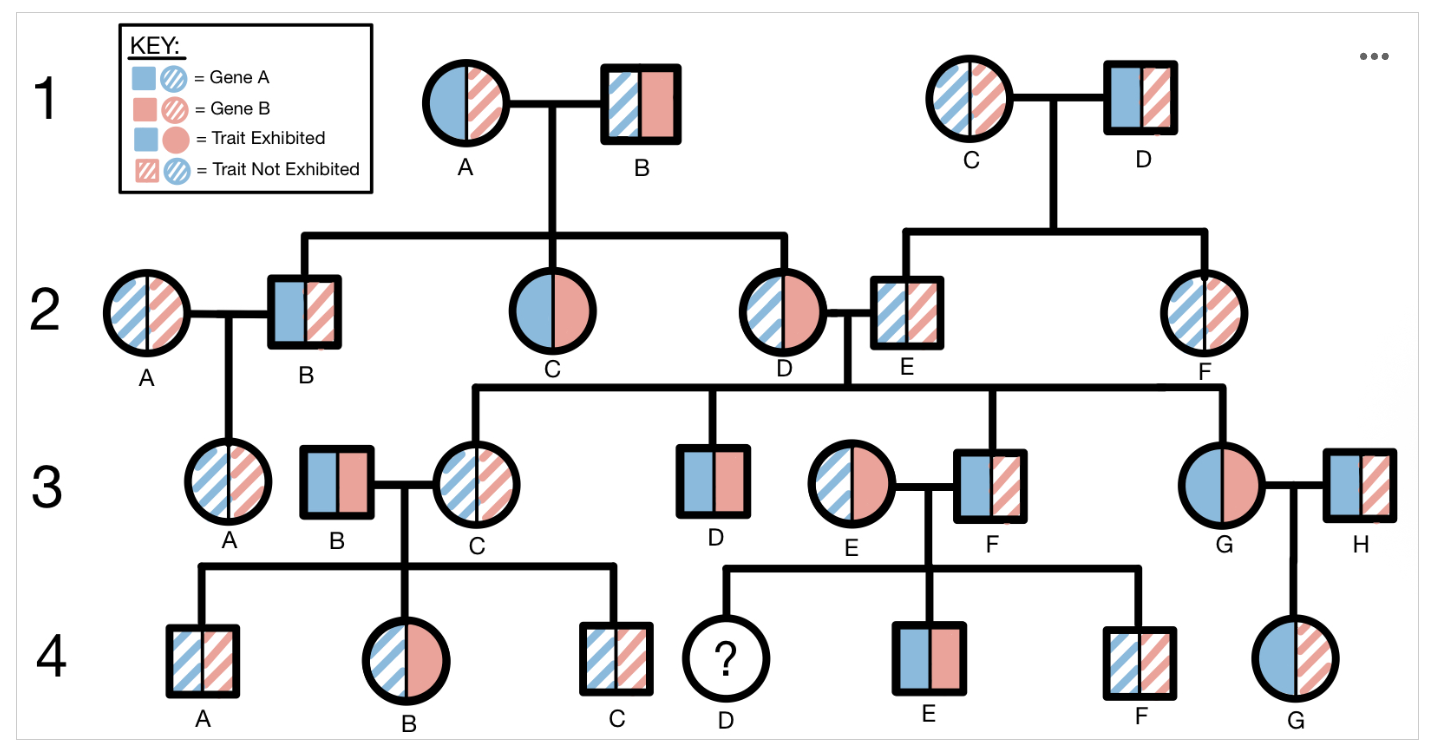
Questions #1-3 refer to the following pedigree. This pedigree illustrates the inheritance pattern of two unrelated traits, Trait Blue and Trait Red, across four generations of one family. Trait Blue is one phenotype of the protein encoded by Gene A, while Trait Red is one phenotype of the protein encoded by Gene B. In this pedigree, squares represent males and circles represent females. Solid-colored shapes represent an individual who exhibits a trait and dashed lines represent an individual who does not exhibit the trait. Trait Blue is depicted on the left side of each shape while Trait Red is depicted on the right side of each shape.
What type of inheritance pattern does Trait Red most likely follow?
Option A: Autosomal dominant
Option B: Autosomal recessive
Option C: Sex-linked dominant
Option D: Sex-linked recessive
Option C: Sex-linked dominant
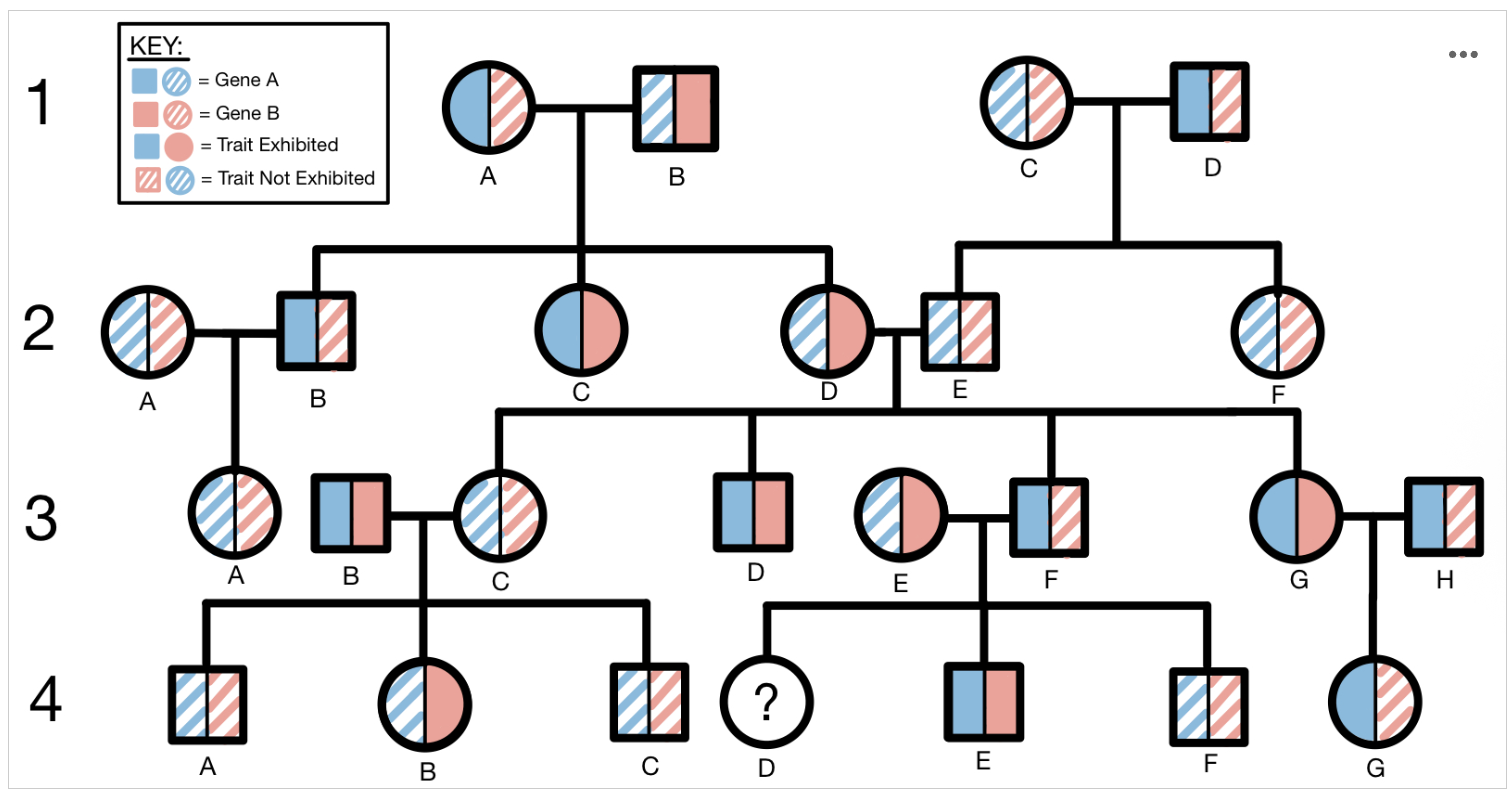
Questions #1-3 refer to the following pedigree. This pedigree illustrates the inheritance pattern of two unrelated traits, Trait Blue and Trait Red, across four generations of one family. Trait Blue is one phenotype of the protein encoded by Gene A, while Trait Red is one phenotype of the protein encoded by Gene B. In this pedigree, squares represent males and circles represent females. Solid-colored shapes represent an individual who exhibits a trait and dashed lines represent an individual who does not exhibit the trait. Trait Blue is depicted on the left side of each shape while Trait Red is depicted on the right side of each shape.
Assuming that individual 3E has a heterozygous genotype for both genes 1 and 2, what is the likelihood that individual 4D will exhibit both Trait Blue and Trait Red?
Option A: 0%
Option B:12.5%
Option C: 25%
Option D: 37.5%
Option E: 50%
Option F: 62.5%
Option G: 75%
Option H: 87.5%
Option I:100%
Option C: 25%
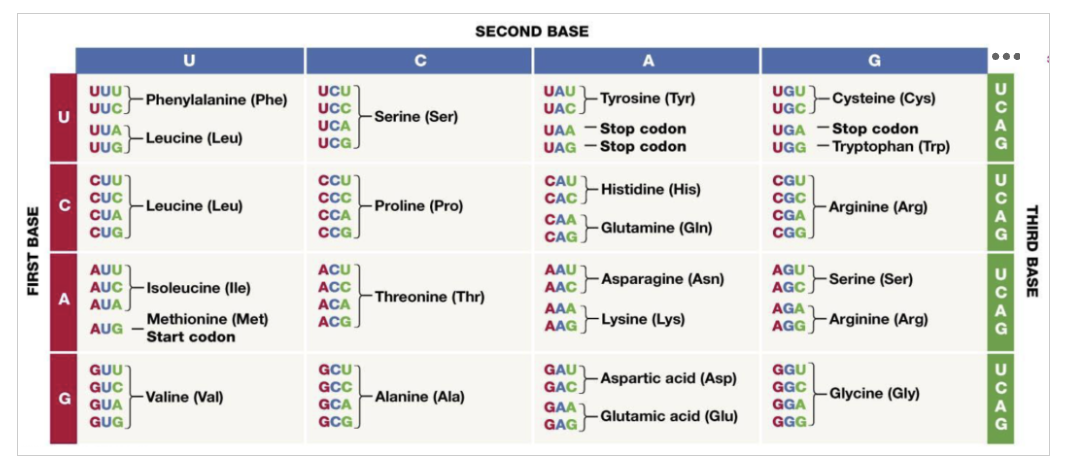
Based on the following mRNA codon sequence, what amino acid sequence will be generated?
5’-ACUGAUGACCCAUGGCGUGUGAGCU-3’
Option A: Thr-Asp-Asp-Pro-Trp-Arg-Val-Ser
Option B: Ser-Ser-Val-Arg-His-Pro-Val-Val
Option C: Met-Ala-Cys-Glu-Pro
Option D: Met-Thr-His-Gly-Val
Option D: Met-Thr-His-Gly-Val