100 anatomy
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
Last updated 12:34 AM on 11/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
Where is the needle inserted for an LP
L3/L4, L4/L5 upper point of the iliac crests
2
New cards
Where does the spinal cord end
L2 in adults, L3 in kids, dural sac goes up to S2
3
New cards
Where do herniated discs usually happen in under 50
L4/L5, L5/S1 or C5/C6 C6/C7
4
New cards
What causes herniations
they follow degenerative changes in the anulus fibrosus, with compression to the nucleus pulposus
5
New cards
Causes of kyphosis
exaggeration of thoracic curvature,
can happen in elderly w/ osteoporosis (multiple compression fracture) or disk degeneration
can happen in elderly w/ osteoporosis (multiple compression fracture) or disk degeneration
6
New cards
Causes of lordosis
lumbar curve; pregnancy spondylolisthesis, potbelly
7
New cards
Scoliosis
lateral deviation, poliomyelitis, leg length discrepancy, hip disease
8
New cards
What is injured in a fracture of the surgical neck of the humerus
axillary nerve, posterior humeral circumflex artery
9
New cards
Midshaft fracture
Radial nerve, profunda brachii artery
10
New cards
Supracondylar fracture
brachial artery median nerve
11
New cards
Medial epicondyle fracture
ulnar nerve
12
New cards
Transverse fracture?
distal 2 cm of radius, most common fracture of the forearm post 50
13
New cards
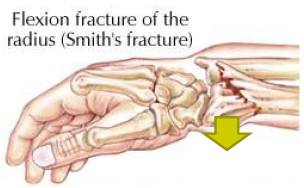
Smiths fracture
fall or blow to dorsal side of flexed wrist; distal fragment of wrist anteriorly displaced
14
New cards
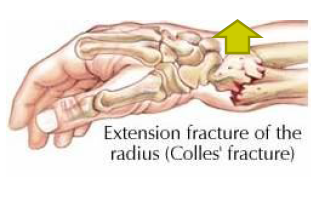
Colles' fracture
forced extension, trying to ease a fall; distal fragment displaced dorsally; ulnar styloid often avulced
15
New cards
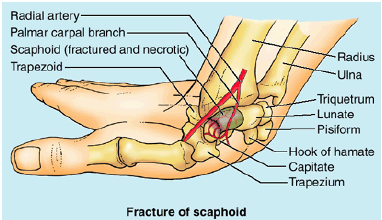
Scaphoid fracture
fall onto palm w/ abducted; pain on lateral side exten abduct; deep tenderness in anatomical snuffbox; proximal avn
16
New cards
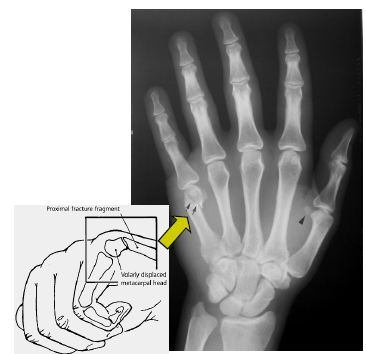
boxers fracture
metacarpal necks, 4/5 in amateur 2/3 in pros
17
New cards
Rotator cuff
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus,
Teres minor, Subscapularis; reinforces joint except inferiorly
Teres minor, Subscapularis; reinforces joint except inferiorly
18
New cards
abduction of upper limb
0-15 (supraspinatus muscle, subscap nerve); 15-110 (deltoid muscle, axillary nerve); 110-180 (trapezius/ accessory), (serratus anterior, LTN)
19
New cards
Subacromial bursitis
calcific supraspinatus tendonitis, painful arc of abduction
20
New cards
Medial epicondylitis
common flexor tendon of the wrist at the medial epicondyle (golf)
21
New cards
Lateral epicondylitis
repeated flexion and extension; common extensor tendon periosteum over the lateral epicondyle; pain over lateral down posterior part of arm; opening door/lifting glass
22
New cards
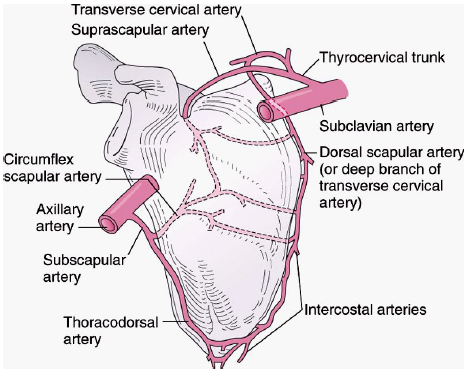
blockage of subclavian/axillary
thyrocervial/ subscap
23
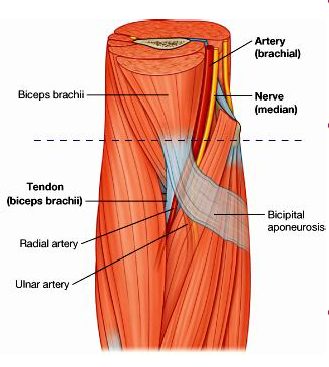
New cards
Cubital fossa
contents: biceps tendon, brachial artery, median nerve
subcut structures: cephalic vein, median cubital vein, basilic vein
subcut structures: cephalic vein, median cubital vein, basilic vein
24
New cards
Carpal tunnel
dislocation of lunate bone, median nerve most affected, altered sensation on lateral 3.5 fingers; apehand deformity absent of opposition
25
New cards
Upper brachial palsy
Excessive increase of angle between neck and shoulder (C5, C6 superior trunk) affecting axillary, suprascapular, musculocutaneous nerves; waiter's tip hand, loss of sensation in lateral aspect
26
New cards
Lower brachial palsy
(C8/T1 inferior trunk) intrinsic muscles of the hand affected, ulnar nerve (claw) and median nerve (ape). Loss of sensation in the medial aspect of limb and medial 1.5 fingers
27
New cards
musculocutaneous nerve
weakens flexion of elbow and supination of forearm (biceps); may have lateral anesthesia
28
New cards
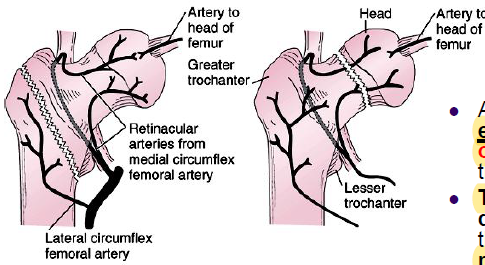
AVN of femoral head
elderly women with osteoporosis
transcervical fracture disrupts blood supply via retinacular arteries from medial circumflex femoral artery and may cause avn
transcervical fracture disrupts blood supply via retinacular arteries from medial circumflex femoral artery and may cause avn
29
New cards
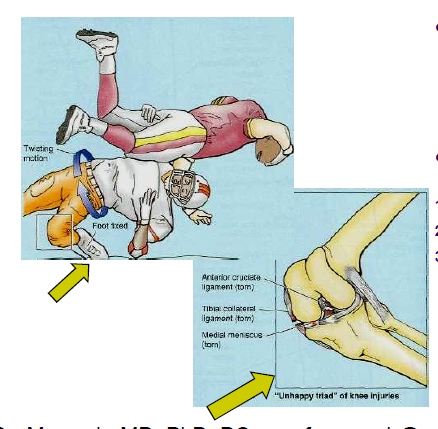
Unhappy triad
lateral blow to knee, MCL, medial meniscus, ACL
30
New cards
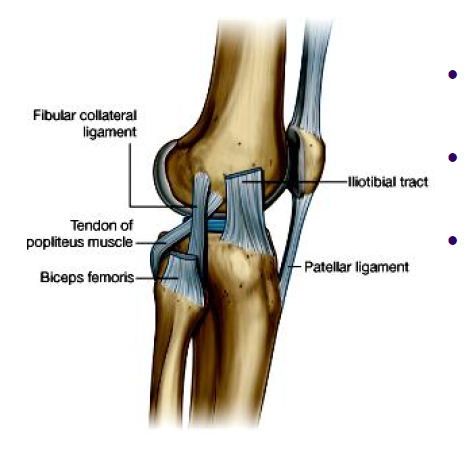
LCL
does not blend with joint capsule, does not attach to meniscus, limits extension and adduction of leg at knee
31
New cards
prepatellar bursa
between superficial patella and skin
32
New cards
suprapatellar bursa
distal end of femur and quadriceps muscle, usual place for intraarticular injections
33
New cards
patellar reflex
femoral nerve (L2-L4) knee jerk -> spinal L2-L4
34
New cards
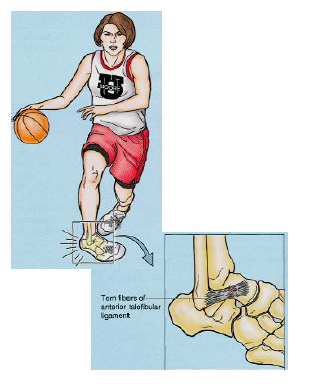
Sprained ankle
almost always inversion injury, plantarflexed; lateral ligament (anterior talofibular ligament) weaker and more injured, in sever cases lateral malleolus may be fractured
35
New cards
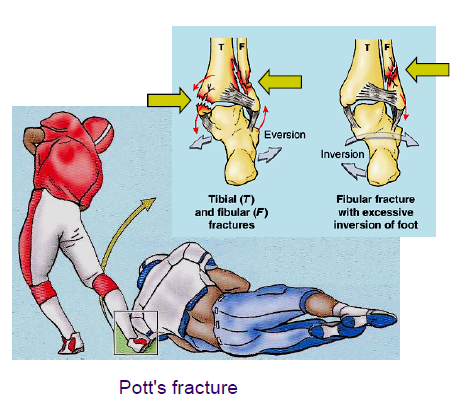
Pott's fracture
forced eversion/ abduction of the foot; medial ligament detaches medial malleolus or the medial ligament tears, and the fibula fractures at a higher level.
36
New cards
ankle jerk
spinal nerves s1-s2 reflex arc limbs are s1,s2
37
New cards
pirifomis
inflammation or spasm -> pain like sciatica, supination of the hip
38
New cards
injury to sciatic nerve
weakened hip extension and knee flexion; footdrop and flail foot; improperly placed gluteal injections or posterior hip dislocation
39
New cards
superior gluteal nerve injury
posterior dislocation, surgery of the hip or poliomyelitis; paralysis of the gluteus medius and minimus, losing ability to lift pelvis and abduct thigh on contralateral side
40
New cards
inferior gluteal nerve injury
weakened hip extension (gluteus maximus)
41
New cards
avulsion of hip bone and hamstrings
biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus; extension of the hip and flexion of the knee; supplied by tibial nerve
42
New cards
Femoral sheath
extension of transversalis fascia and iliacus fascia that enters thigh deep to inguinal ligament
contains: femoral artery, vein, canal
contains: femoral artery, vein, canal
43
New cards
Femoral hernia
passes through the femoral ring, swelling inferior lateral to pubic tubercle; may protrude through the saphenous hiatus into superficial fascia; more in females, sac may get strangulated; aberrant obturator artery vulnerable during surgical repair
44
New cards
rupture of achilles tendon and triceps surae
disables gastroc and soleus, cannot plantarflex
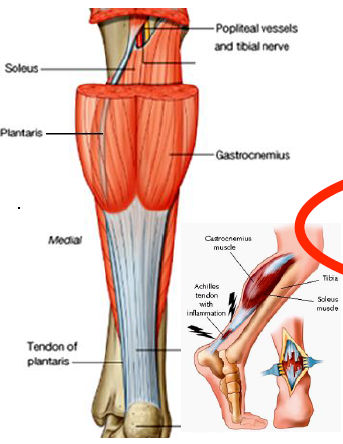
45
New cards
injury to tibial nerve in popliteal fossa
can't plantarflex, can't stand on toes
46
New cards
fracture of fibular neck
injures common peroneal nerve, wraps around neck of fibula, cant dorsiflex or evert -> foot drop
47
New cards
breast carcinoma
malignant, usually adenocarcinoma from epithelia cells from lactiferous ducts; attaches to suspensory ligaments, causing dimpling of the skin
48
New cards
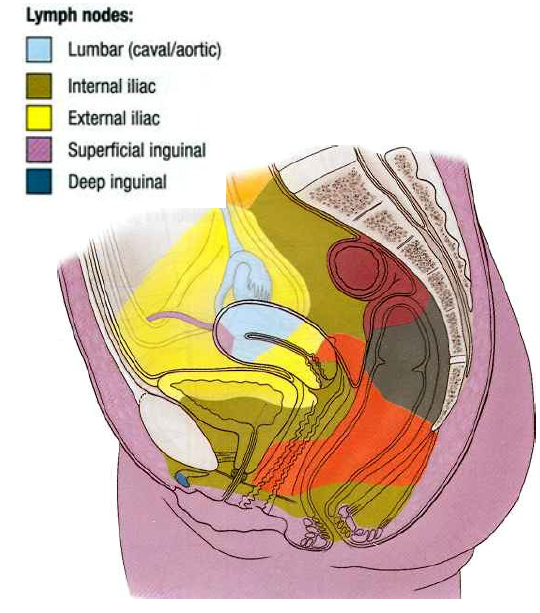
Lymph drainage of the breast
pectoral to axillary for most, rest to parasternal or opposite breast
49
New cards
mastectomy
ltn may be lesioned, winged scapula, cant abduct above 90, serratus anterior paralyzed; intercostobrachial nerve can be damaged, numbness in the medial arm
50
New cards
mastitis
most during breastfeeding; swelling redness, increased temp, bacteria from babies mouth enter milk duct
51
New cards
diaphragm paralysis
paralysis due to lesion on phrenic nerve; injured side pushed up during inspiration
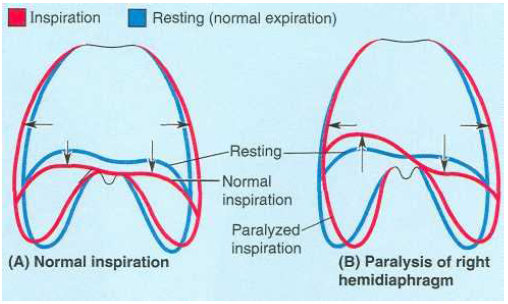
52
New cards
diaphragm rupture
blunt, mvc left side, large radial tears on poserolateral aspect
53
New cards
cardiac hypertrophy
Left atrial enlargement secondary to mitral valve failure may compress the esophagus; seen with barium swallow
54
New cards
cardiac shadow
RA, SVC; Aa, PT, LA, LV
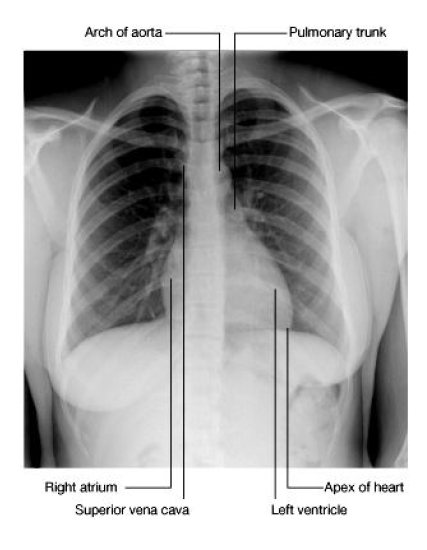
55
New cards
RCA
right atrium and right ventricle, anastamoses with the marginal branch of the left coronary artery;
anterior cardiac branches supplies right atrium, nodal branch supplies SA and AV node, marginal artery supplies right ventricle, posterior IV artery supplies diaphragmatic of both ventricles and posterior of IV septum
anterior cardiac branches supplies right atrium, nodal branch supplies SA and AV node, marginal artery supplies right ventricle, posterior IV artery supplies diaphragmatic of both ventricles and posterior of IV septum
56
New cards
LCA
Anterior IV artery, anterior heart wall, anterior septum, bundle of his, apex of heart;
circumflex, left atrium and left ventricle
circumflex, left atrium and left ventricle
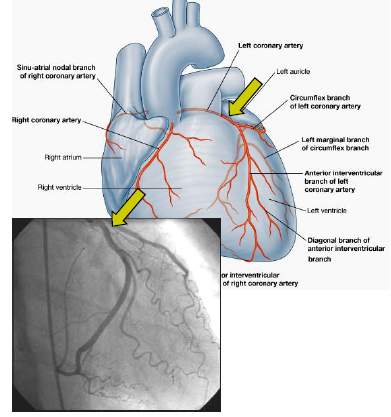
57
New cards
foreign bodies
more likely to enter right primary bronchus and pass into middle or lower lobe bronchi; usually falls to the posterior basal segment of the right inferior lobe
58
New cards
pneumonia CXR
opacity of lung parenchyma, and enlargement of bronchomediastinal lymph nodes
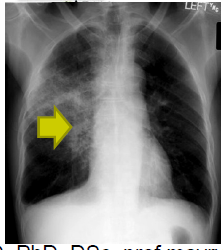
59
New cards
bronchogenic carcinoma
from the mucosa of large bronchi, early mets to thoracic lymph nodes,
pancoast tumor, apex of the lung causes TOS
pancoast tumor, apex of the lung causes TOS
60
New cards
open pneumothorax
during inspiration, air will compress, pushing healthy side
61
New cards
nerve supply of pleura
parietal- somatic sensory
costal -intercostal nerves
mediastinal - phrenic nerve
diaphragm- phrenic over the domes/ lower 6 intercostal on the periphery
visceral - auto from pulmonary plexus
costal -intercostal nerves
mediastinal - phrenic nerve
diaphragm- phrenic over the domes/ lower 6 intercostal on the periphery
visceral - auto from pulmonary plexus
62
New cards
abdomen quadrants

63
New cards
referred pain
foregut referred to epigastric
midgut referred to umbilical region
hindgut referred to hypogastric
midgut referred to umbilical region
hindgut referred to hypogastric
64
New cards
indirect inguinal hernia
most common form, congenital; through the deep inguinal ring lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels, inguinal canal, superficial inguinal ring, and descend into scrotum; 20x more men; more common on right, processus vaginalis obliterated later, right testis descends later
65
New cards
Direct inguinal hernia
abdominal contents through weak area of posterior wall of inguinal canal medial to inferior epigastric vessels in inguinal triangle, though superficial ring
66
New cards
lesser omentum

67
New cards
epiploic foramen
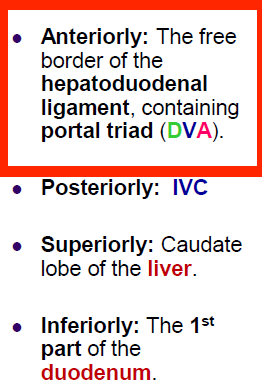
68
New cards
pouch of douglas
deeper in peritoneal space vertically, pelvic abscess location;
vesicouterine pouch, between uterus and bladder
vesicouterine pouch, between uterus and bladder
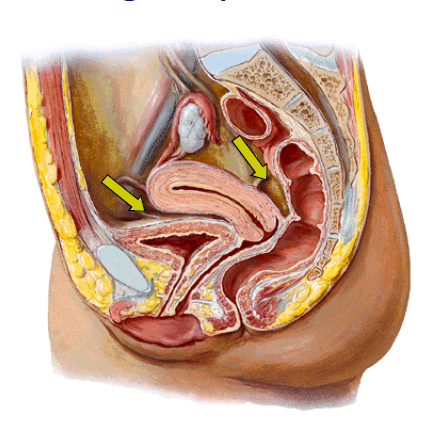
69
New cards
Foregut
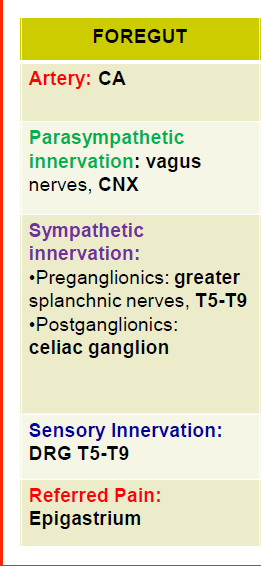
70
New cards
Midgut

71
New cards
Hindgut

72
New cards
Posterior gastric ulcer
may erode to pancreas, causing referred pain, may also erode splenic artery
73
New cards
congenital diaphragmatic hernia
through posterolateral defect in diaphragm. high mortality rate because of left lung hyperplasia
74
New cards
Sliding hiatal hernia
hernia of cardia of stomach into thorax; can damage vagal trunks, causing hyposecretion of gastric juice
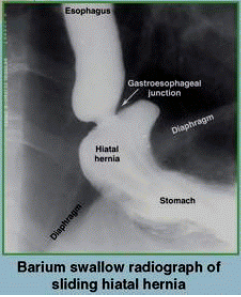
75
New cards
Meckel's diverticulum
persistent portion of vitellointestinal duct; asymptomatic but can ulcer; diverticulitis can mimic appendicitis
76
New cards
appendicitis pain
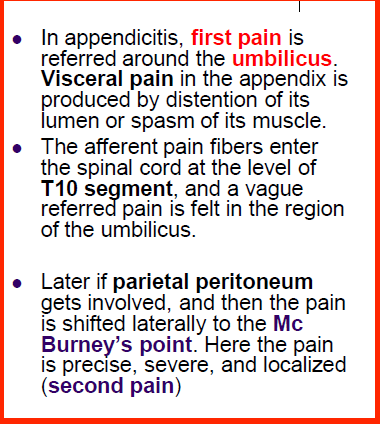
77
New cards
Hirschsprung's disease
common in downs; inadequate motility as a result of aganglionic section (absent of postganglionic parasympathetic neurons, causing megacolon); failure to pass meconium; remove portion to treat.
78
New cards
AA branches
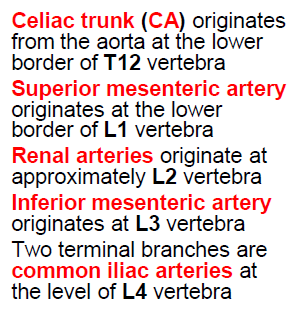
79
New cards
Celiac trunk
passes above superior border of pancreas, splits; left gastric, common hepatic, splenic
80
New cards
left gastric
lesser curvature of stomach; branches to esophageal, gastric, anastomosis with right
81
New cards
common hepatic
superior surface of duodenum, branches into proper hepatic and gastroduodenal
82
New cards
proper hepatic artery
gives off right gastric, reaches porta hepatis, splits into right and left hepatic; right hepatic gives rise to cystic artery;
83
New cards
gastroduodenal
posterior to first part of duodenum, erosion by penetrating ulcer; right gastro epiploic anastamoses with LGEP; superior pancreaticoduodenal arteries (head), anstamoses w/ ipd of SMA
84
New cards
Hepatic artery
collateral circulation through the left and right gastric , gastroepiploic, and gastroduodenal arteries
85
New cards
splenic artery
tortuous horizontal course to the left, is retroperitoneal until the tail of the pancreas, where it enters the splenorenal ligament to enter the hilum of the spleen; branches to the spleen, neck body and tail of pancreas, left GEP, short gastric which supplies the fundus
86
New cards
SMA branches
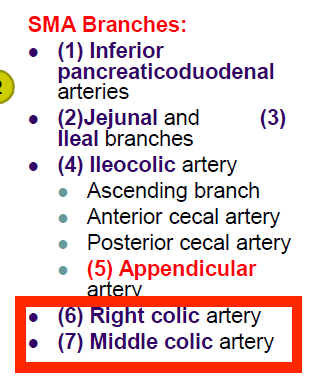
87
New cards
IMA branches

88
New cards
biliary system
gallbladder lies in a fossa on the visceal surface of the right of quadrate lobe; common bile duct descends in the heptaoduodenal duct, posterior to the first part of the duodenum; forms hepatopancreatic duct/sphincter of oddi at the major duodenal papilla
89
New cards
gallstones
cystic duct obstruction causes biliary colic, does not produce jaundice; stone in the body of the gallbladder may ulcerate into intestine and obstruct at ileocecal jxn
90
New cards
spleen ligaments
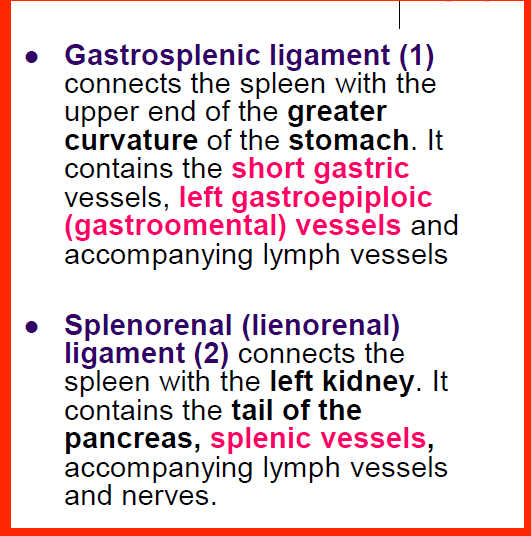
91
New cards
kidney location

92
New cards
Right kidney
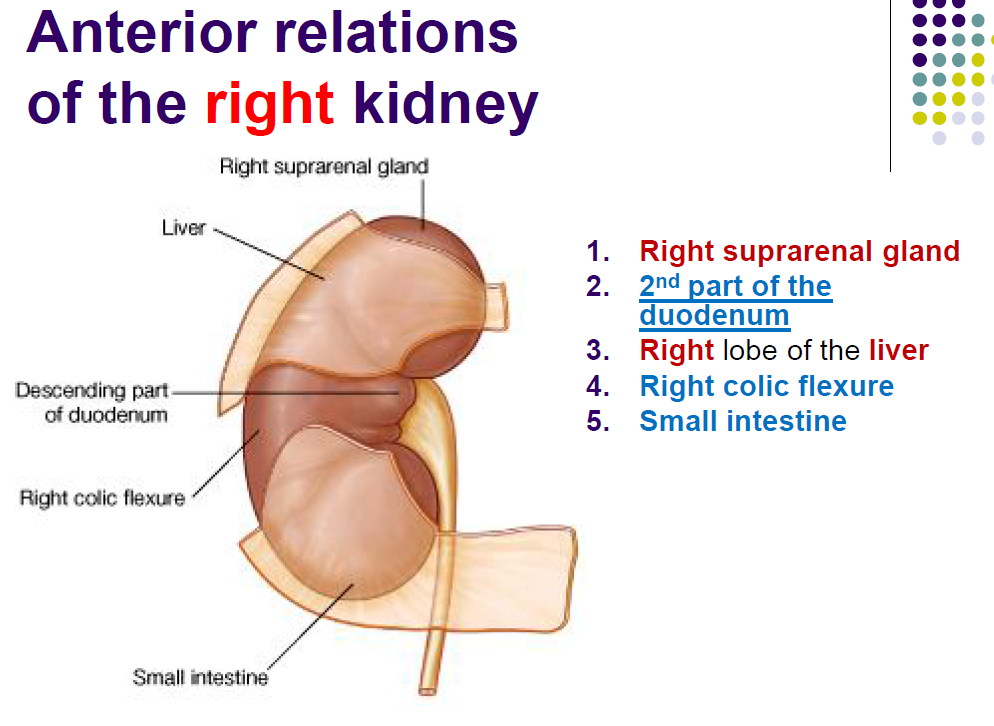
93
New cards
Left kidney
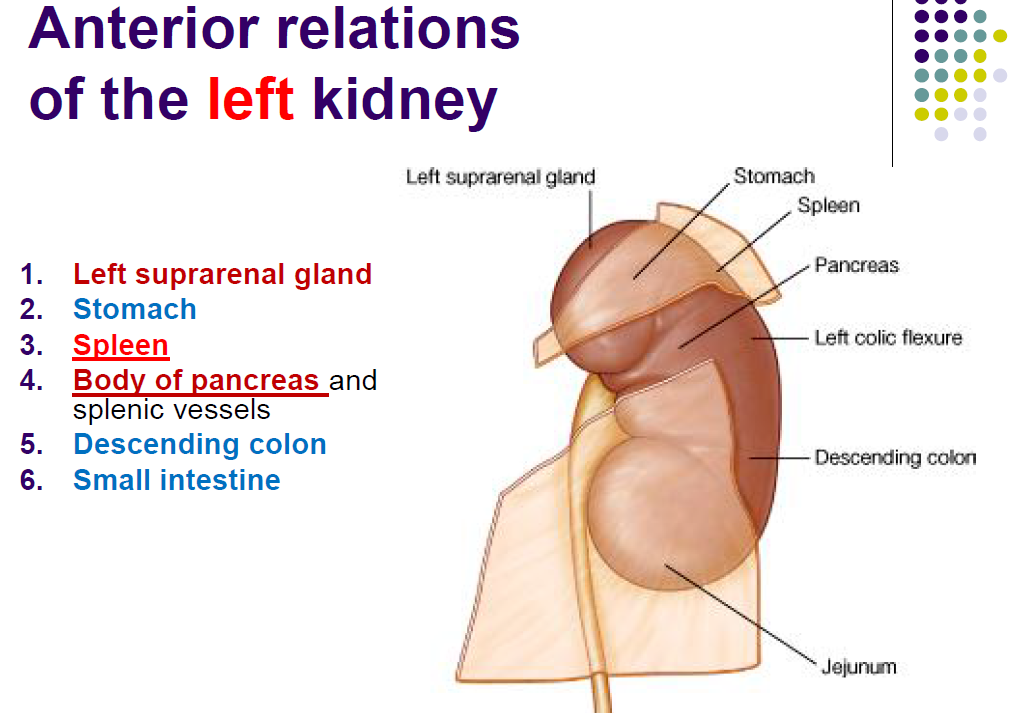
94
New cards
varicocele

95
New cards
ureter
in women, crossed anteriorly and superiorly by the uterine artery in the broad ligament
96
New cards
PC mets

97
New cards
BPH
median lobe vs posterior
98
New cards
hydrocele

99
New cards
lymph drainage of male viscera
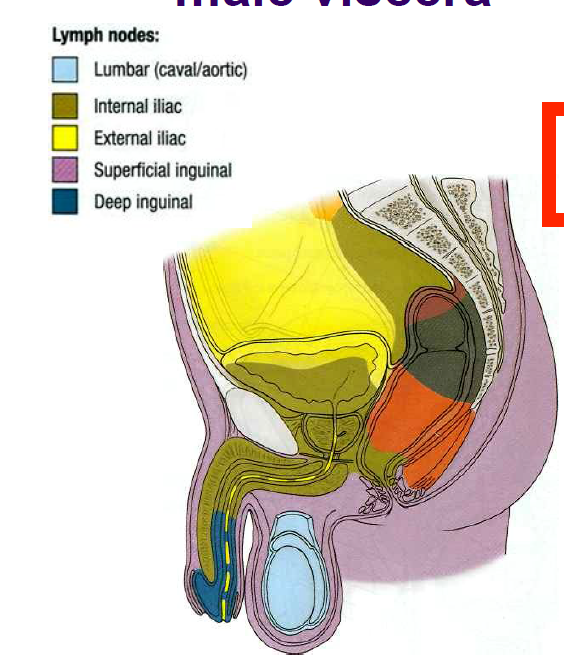
100
New cards
lymph drainage of male viscera