B5- homeostasis and response
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
homeostasis
The process by which living organisms regulate their internal environment to maintain stable, constant conditions despite external changes.
negative feedback
when the level of something gets too high or too low, the body initiates processes to counteract this change and bring the level back to its set point.
describe what happens when an internal condition is too high or low
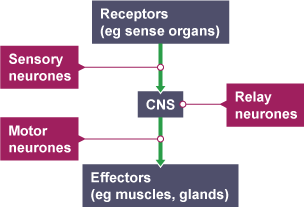
receptor detects a stimulus ( level is too high or low)
the coordination center receives the info and organises a response
effector produces a response which counteracts the change and restores the optimum level
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord, responsible for processing information and coordinating responses.
sensory neurones
the neurones that carry information as electrical impulses from the receptors to the central nervous system.
Motor neurones
the neurones that carry electrical impulses from the central nervous system to effectors.
effectors
The organs or cells that act in response to signals from the nervous system, such as muscles or glands.
receptors
the cells that detect stimuli from the environment and convert them into electrical impulses to send to sensory neurones.
what is the order the body takes to respond to a stimuli
The order is: stimulus, receptor, sensory neurone, central nervous system, motor neurone, effector, response.
synapse
the connection between two neurones. the nerve signal is transferred by chemicals which diffuse across the gap and set off a new electrical signal in the next neurone
reflexes
reflexes are rapid automatic responses to a certain stimuli that don’t involve the conscious part of the brain
relay neurones
connect sensory neurones to motor neurones
what is the practical for investigating reaction time
ruler drop
computer tests e.g click the mouse
why are computer tests better than the ruler drop
more precise - measure time to a millisecond
remove possibility of human error
unpredictable timing
hormones
chemical molecules released directly into the blood. they control things in organs and cells that need constant adjustment
Pituitary gland
produces many hormones which act on other glands directing them to release hormones. found at the base of the brain
thyroid
produces thyroxine which regulates rate of metabolism, HR and temperature
ovaries
(females) produce oestrogen which is involved in the menstrual cycle
adrenal gland
produces adrenaline which prepares the body for ‘flight or fight’ response. found above the kidneys
testes
(male) produce testosterone, which controls puberty and sperm production in males
pancreas
produces insulin, which is used to regulate the blood glucose levels
difference between nerves and hormones
nerves :
fast action
short time
precise area
hormones:
slower action
act for long time
general way
what happens when blood glucose levels are too high
insulin is secreated into the blood from the pancreas
the glucose moves from the blood into the liver
insulin makes the liver turn glucose into glycogen
blood glucose is reduced
what happens when blood glucose levels are too low
glucagon secreted by pancreas
enters the liver
glucagon makes liver turn glycogen into glucose
glucose released into blood
Type 1 diabetes
the pancreas produces little or no insulin meaning their blood glucose can rise to levels that can kill them
insulin therapy- injections throughout the day, making sure glucose is removed quickly
type 2 diabetes
a person becomes resistant to their own insulin
being overweight increases chances
carb controlled diet and regular exercise controls it
4 stages of the mensural cycle
stage 1: mensuration starts - lining of the uterus breaks down for about 4 days (period)
stage 2 : uterus lining builds up again ( day 4-14)
stage 3 : an egg develops and is released from the ovary
stage 4 : the wall is maintained until about day 28
the four hormones of the menstrual cycle
FSH
Oestrogen
LH
Progesterone
what does FSH do?
produced in the pituitary gland
causes an egg to mature in one of the ovaries in a follicle
stimulates ovaries to produce oestrogen
what does oestrogen do
produced in the ovaries
causes the lining of the uterus to grow
stimulates release of LH
what does LH do
produced in the pituitary gland
stimulates the release of an egg
what does progesterone do
produced in the ovaries
maintains lining of uterus during the second half of the cycle
inhibits the release of LH and FSH
methods of contraception using hormones
contraceptive patch - contains oestrogen and progesterone(1 week)
contraceptive implant - releases a continuous amount of progesterone, which stops the ovaries releasing an egg (3 years)
contraceptive injection- progesterone (2-3 months)
intrauterine devise (IUD)- inserted into the uterus to kill sperm
non hormonal forms of contraception
condom- also prevents STD
diaphragm- shallow plastic cup that fits over the cervix
spermicide
other ways to avoid pregnancy
sterilisation - involves cutting or tying the fallopian tube or the sperm duct
natural methods - avoiding sexual intercouse when a woman is fertile
abstinence- no intercourse
pros and cons of fertility drugs
pros :
it helps a lot of women to get pregnant
Cons :
it doesnt always work- some women have to do it multiple times and it becomes expensive
too many eggs could be stimulated resulting in twins, triplets …
what is IVF
involves collecting eggs and fertalising them in a lab using the mans sperm
the sperm is injected directly into the egg
the fertalised eggs are then grown into embryos in an incubator
they are then transferred into the womens uterus to improve the chance of pregnancy
pros and cons of IVF
Pros :
can give an infertile couple a child
Cons:
multiple births
success rate is low
emotional and physical stress on the woman
side effects- abdominal pain, vomiting, dehydration
why are some people against IVF
often reults in unused embryos - unethical because of wasted potential life
genetic testing of embryos before use - people think it could lead to the selection of desired characteristics
how does adrenaline prepare the body for ‘flight or fight’
it triggers mechanisms that increase the supply of oxygen and glucose to cells in the brain and muscles - increases heart rate
how is the level of thyroxine controlled
negative feedback