Y9S1 Unit 4 - Generating Electricity
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
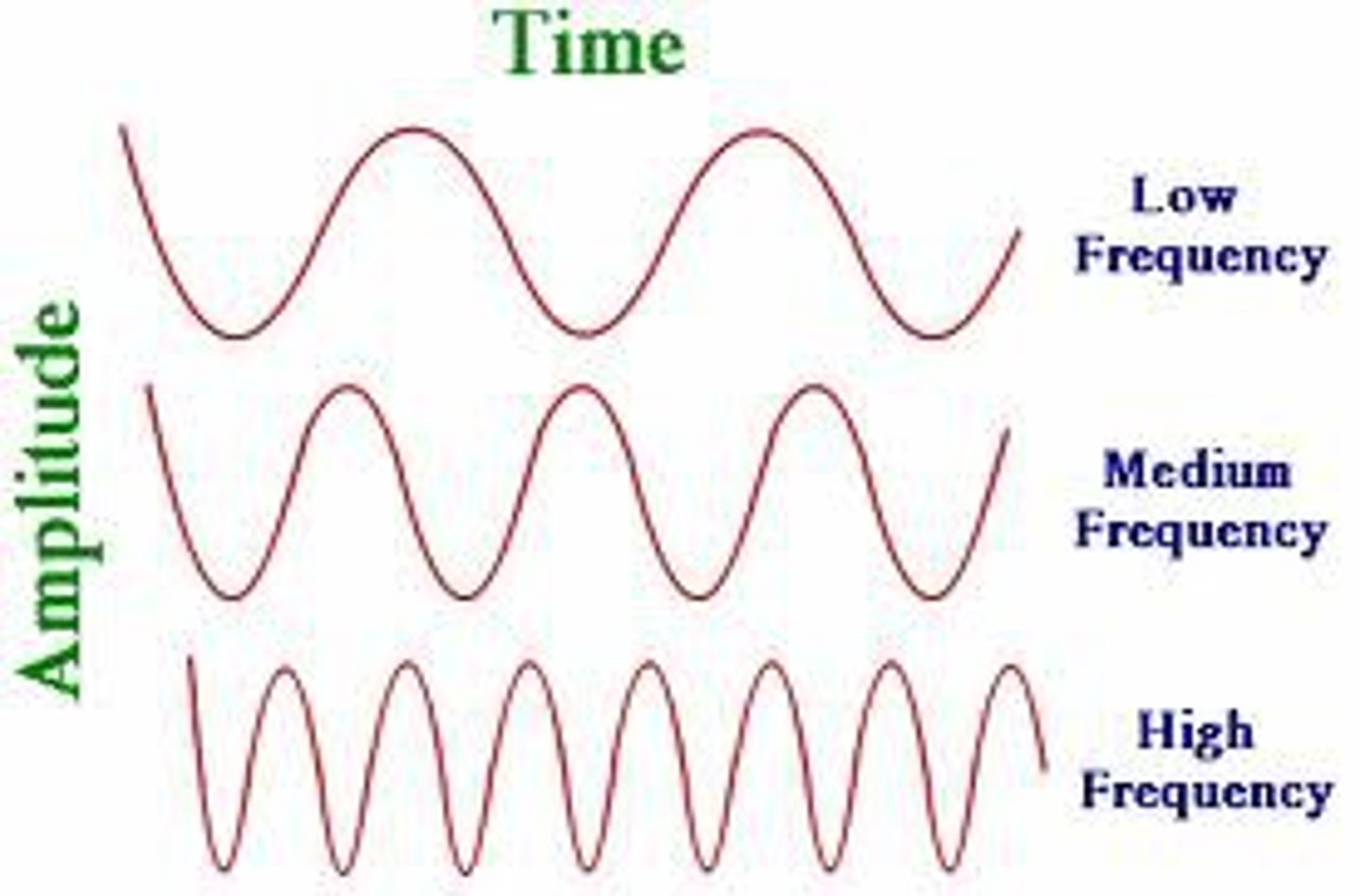
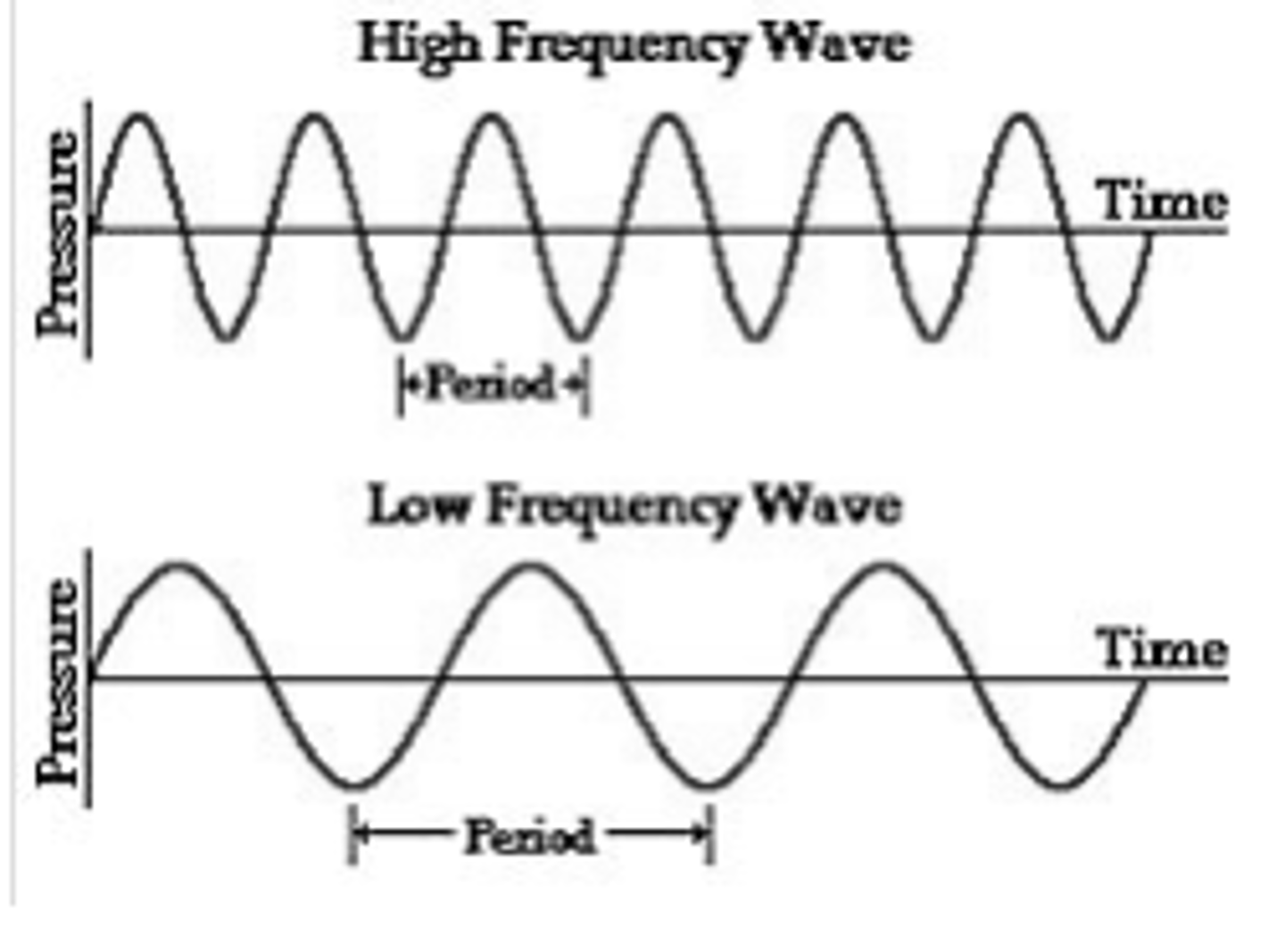
Frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
Photovoltaic cell
Solar energy cells, usually made from silicon, that collect photons to generate electricity.
Transverse Wave
A wave that causes the medium to vibrate at right angles to the direction in which the wave travels
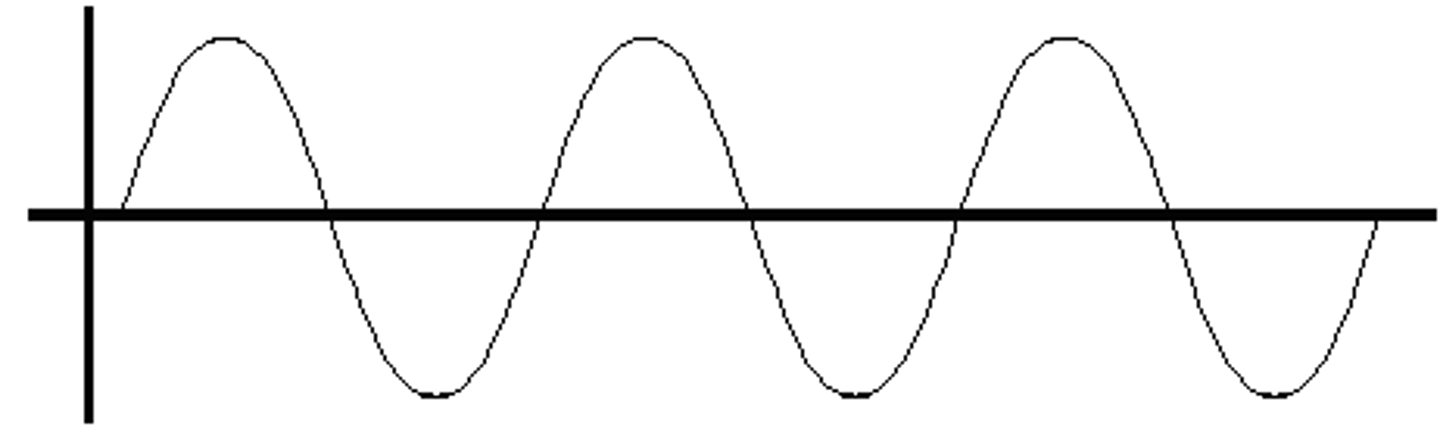
Longitudinal Wave
A wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate in the same direction as the wave travels
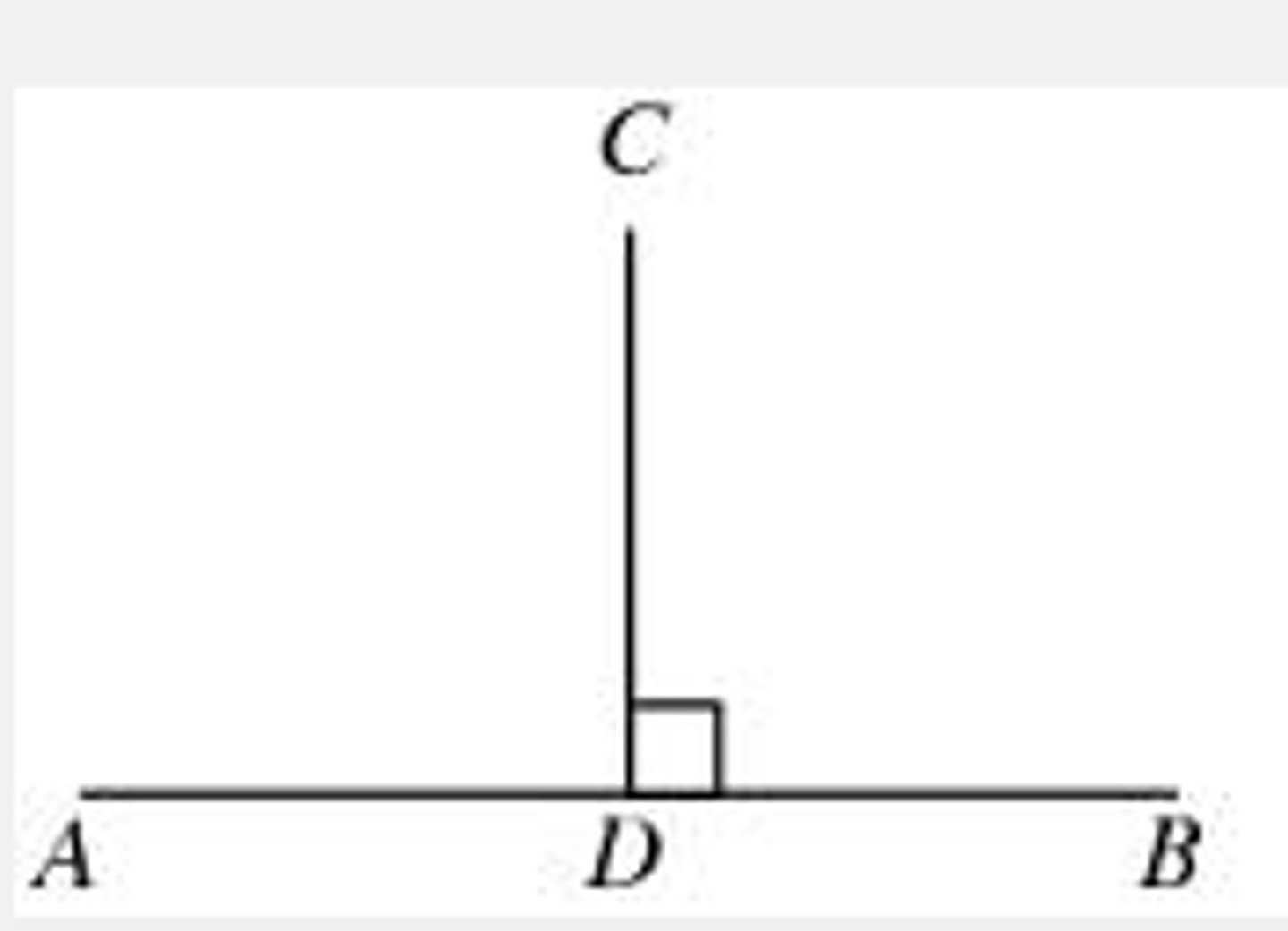
Perpendicular
Intersecting at or forming right angles
Parallel
In the same direction

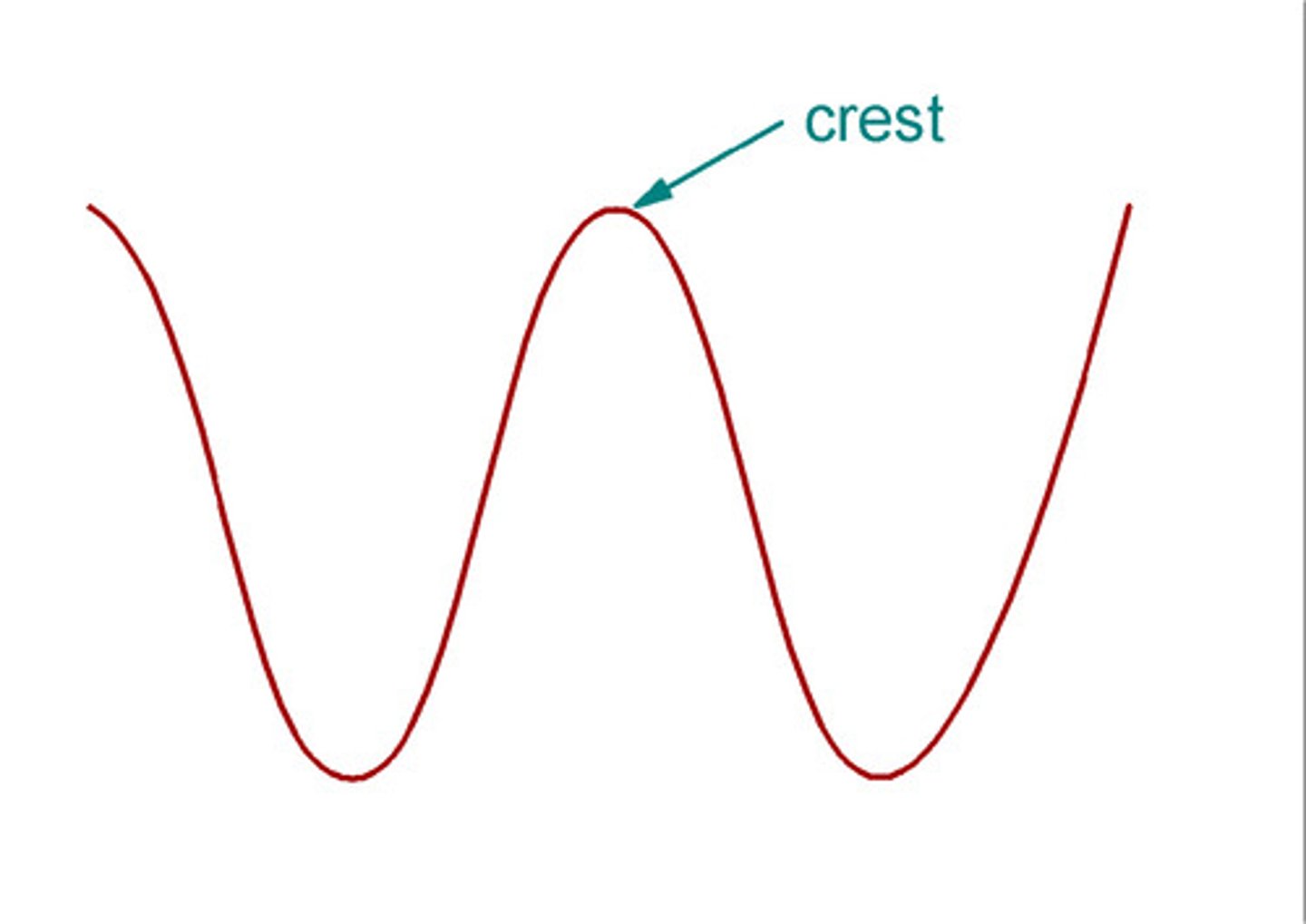
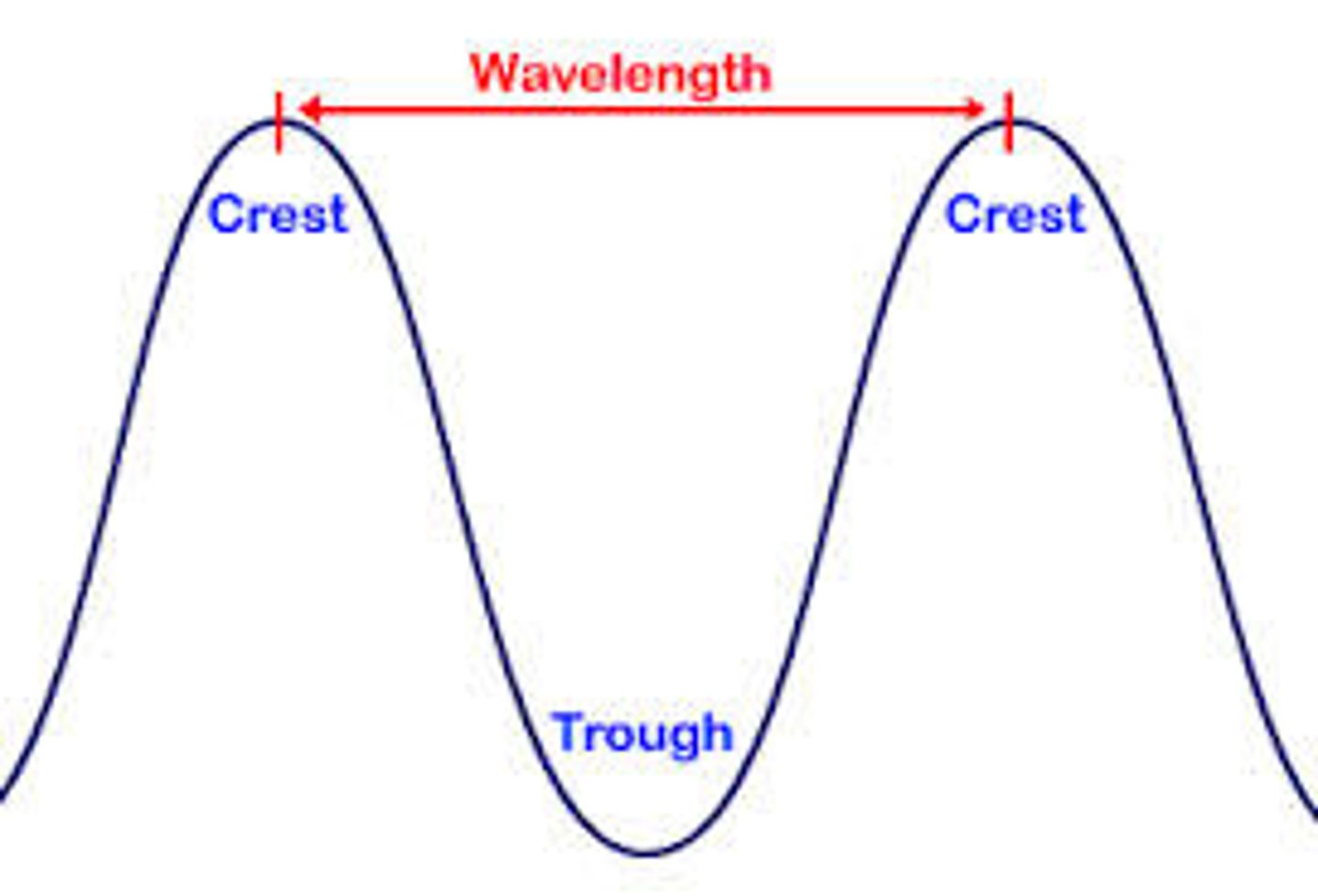
Crest
Highest point of a wave
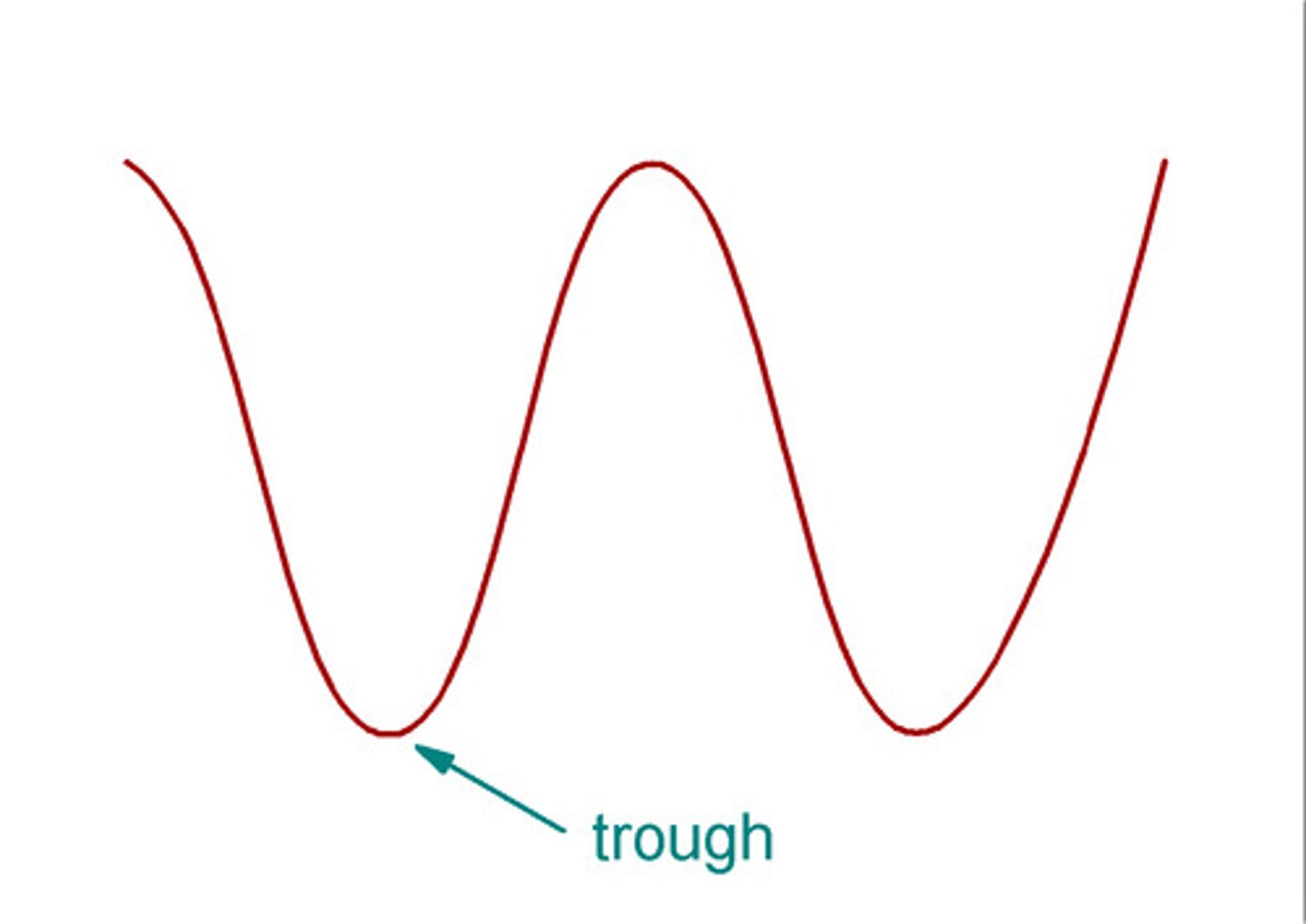
Trough
Lowest point of a wave
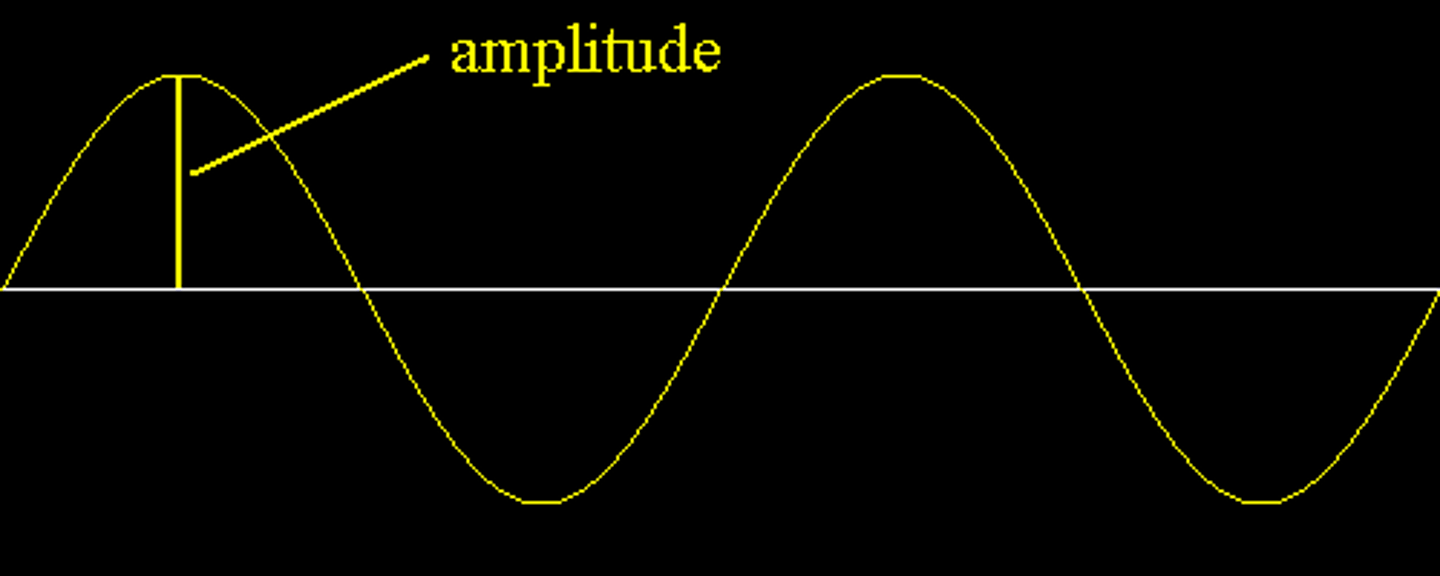
Amplitude
Height of a wave
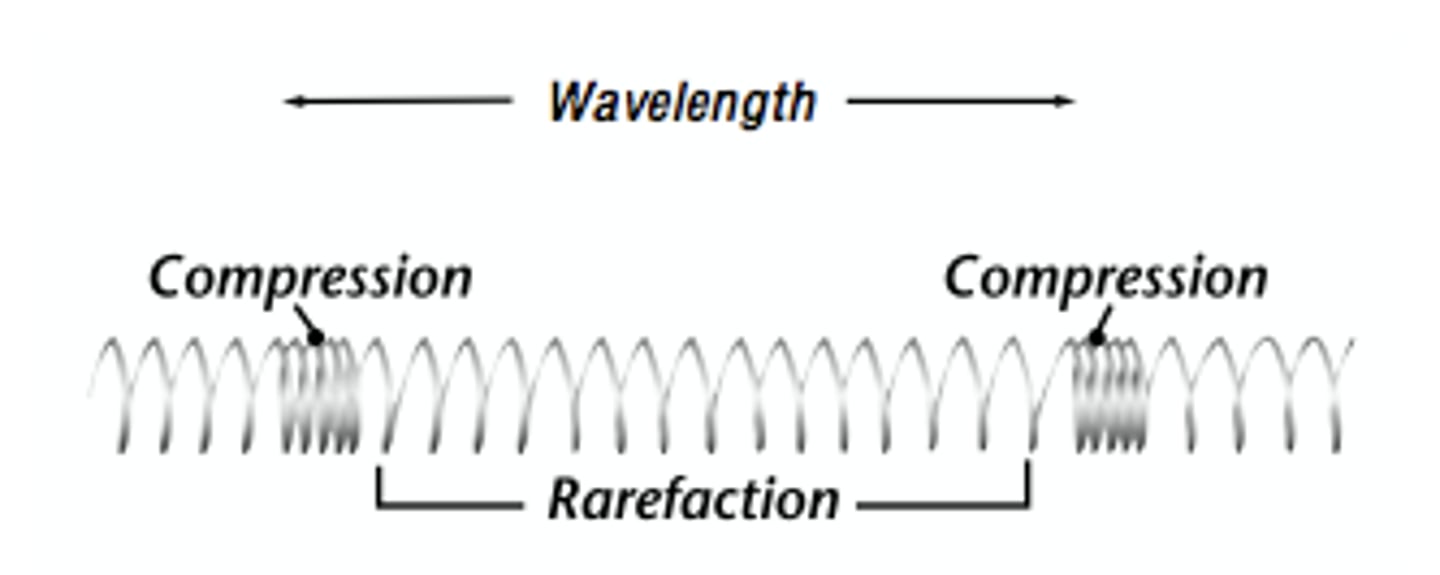
Compression
The part of a longitudinal wave where the particles of the medium are close together.
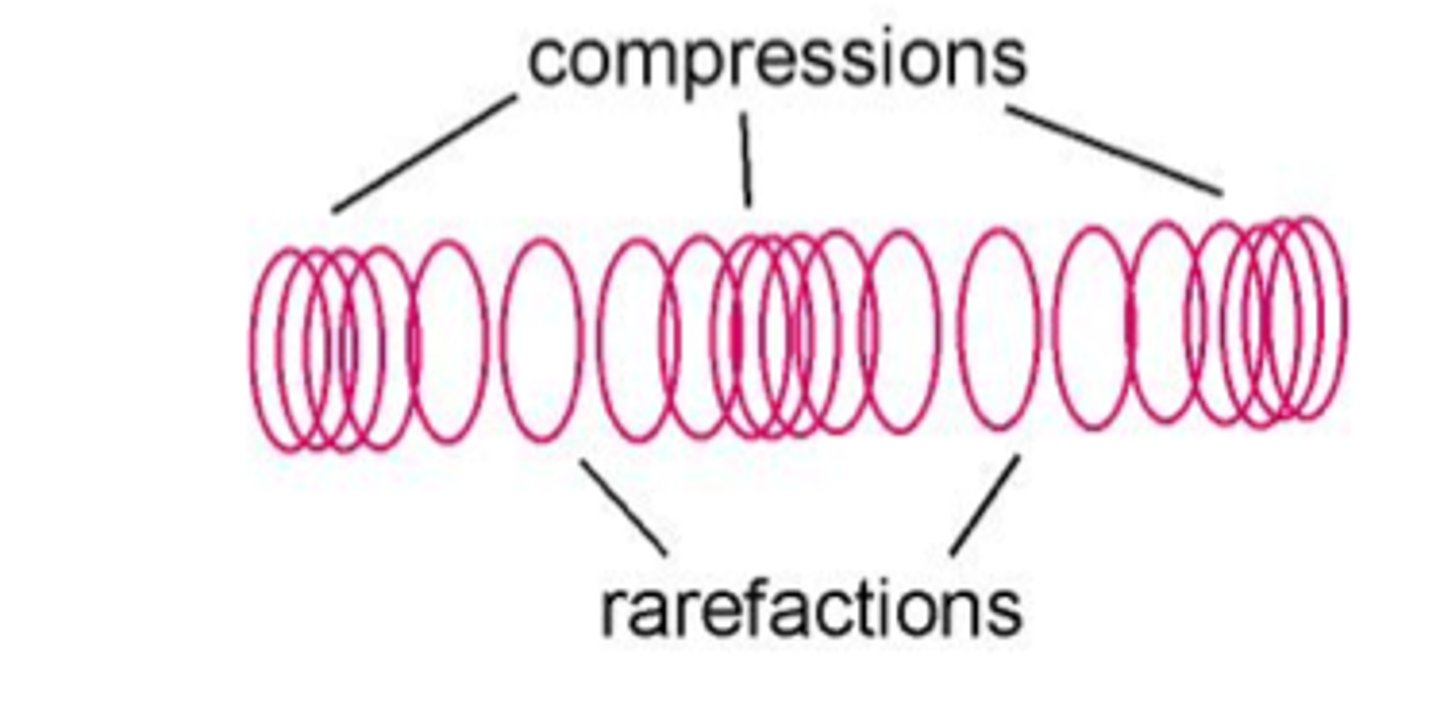
Rarefaction
a part in a longitudinal wave where the particles are spread apart
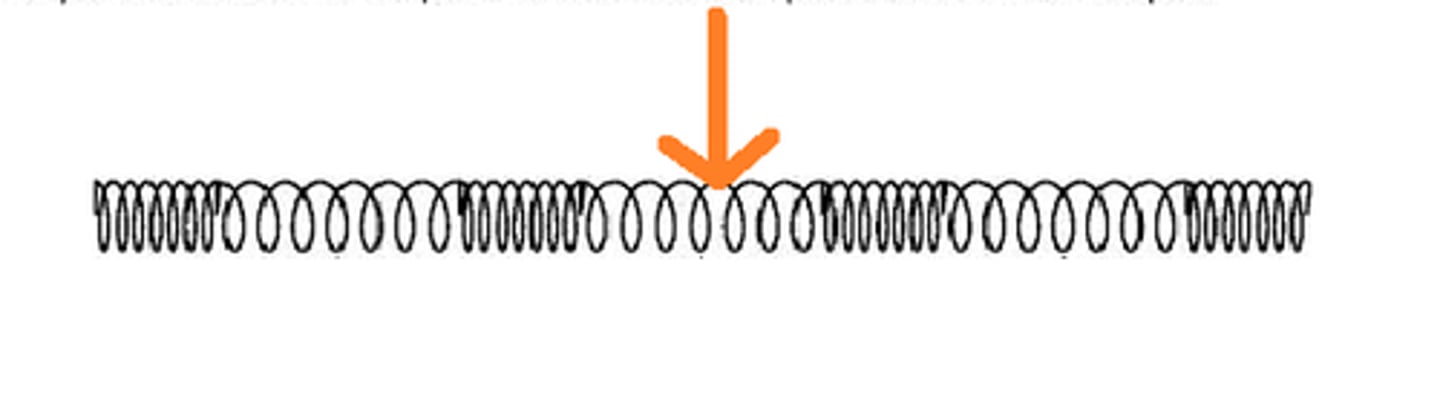
Wavelength
The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave
Period
The time taken for a particle to complete one complete vibration
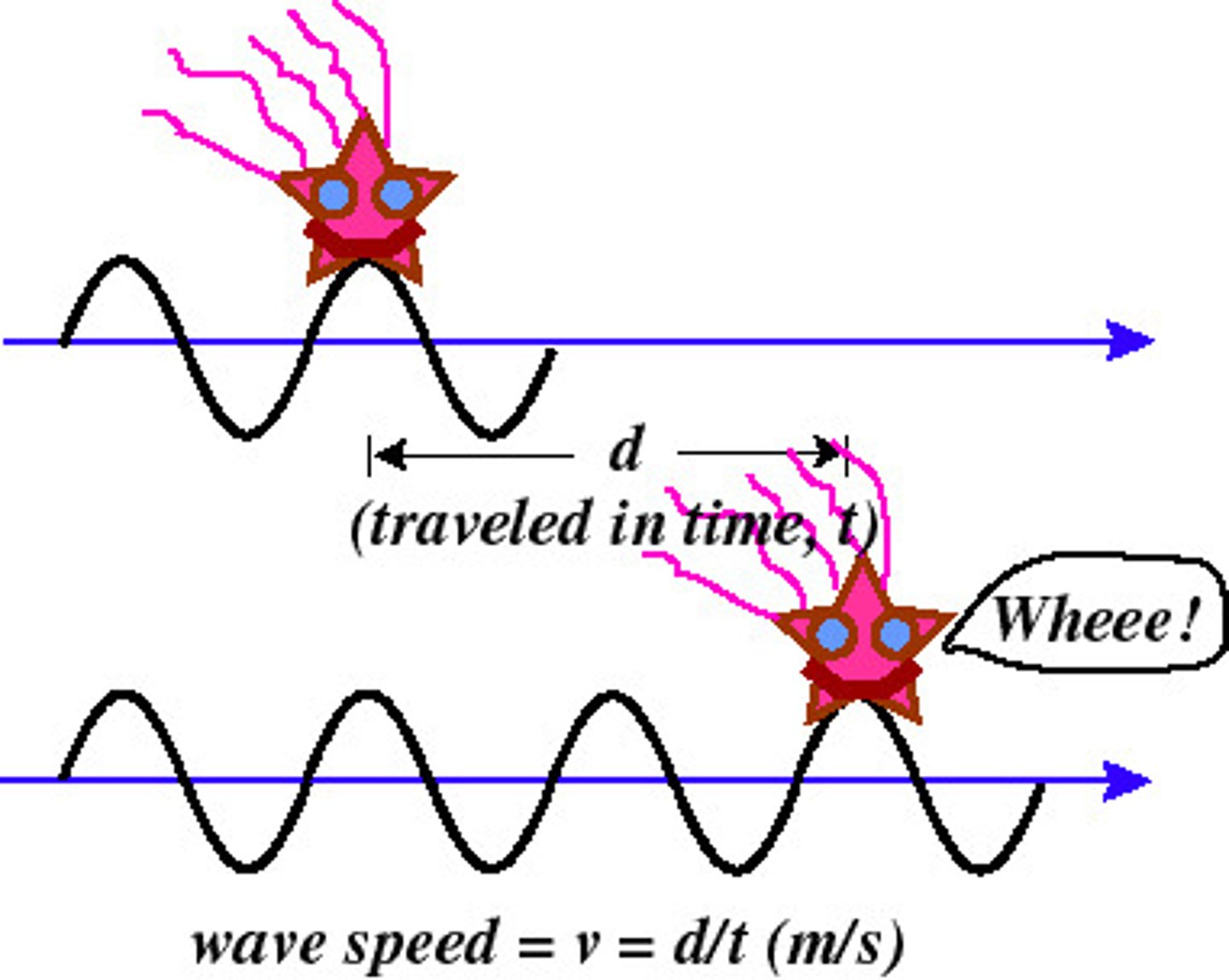
Wave Speed
the speed at which a wave travels through a medium
Medium
matter through which a wave travels
Visible Light
electromagnetic waves that are visible to the human eye
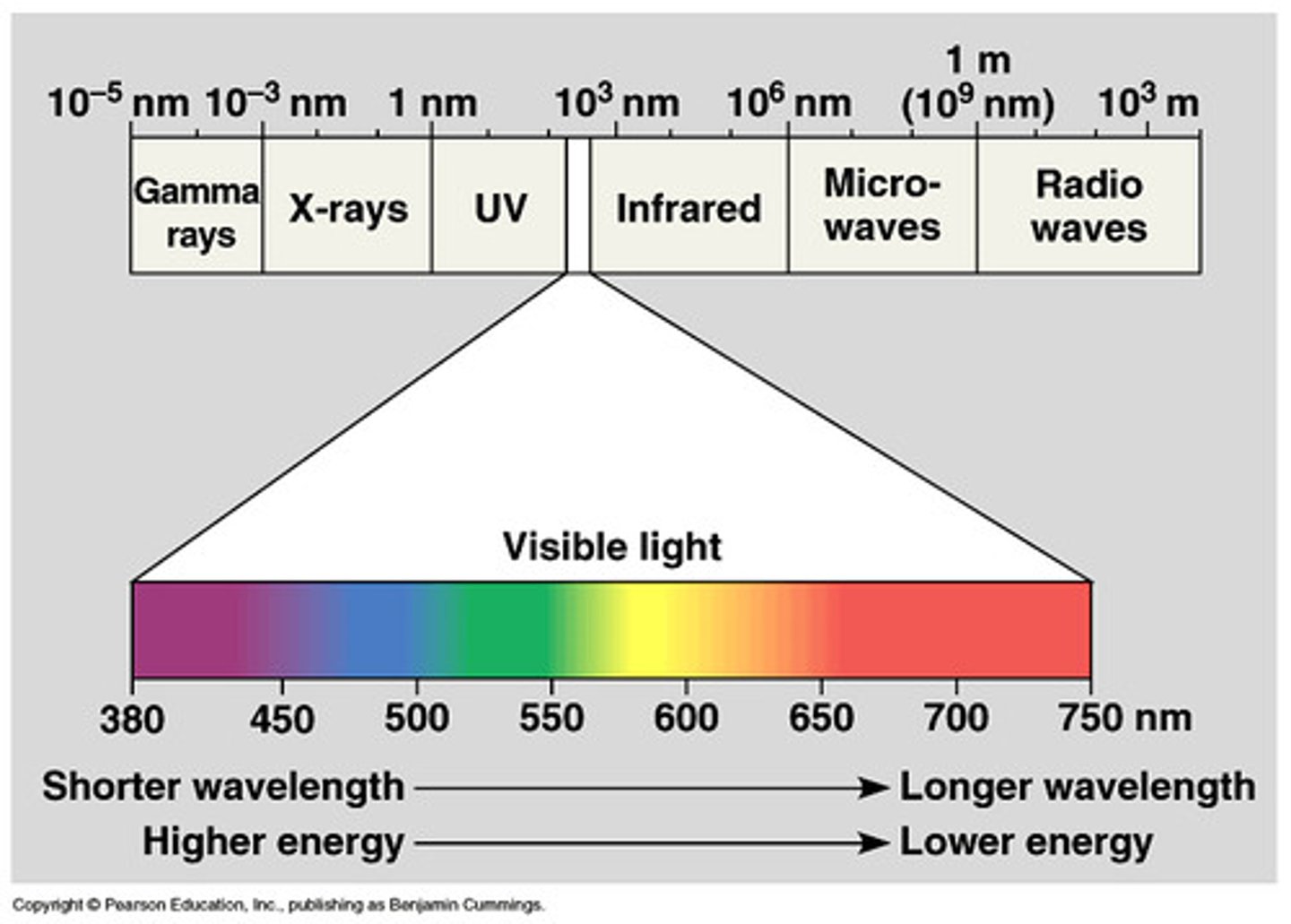
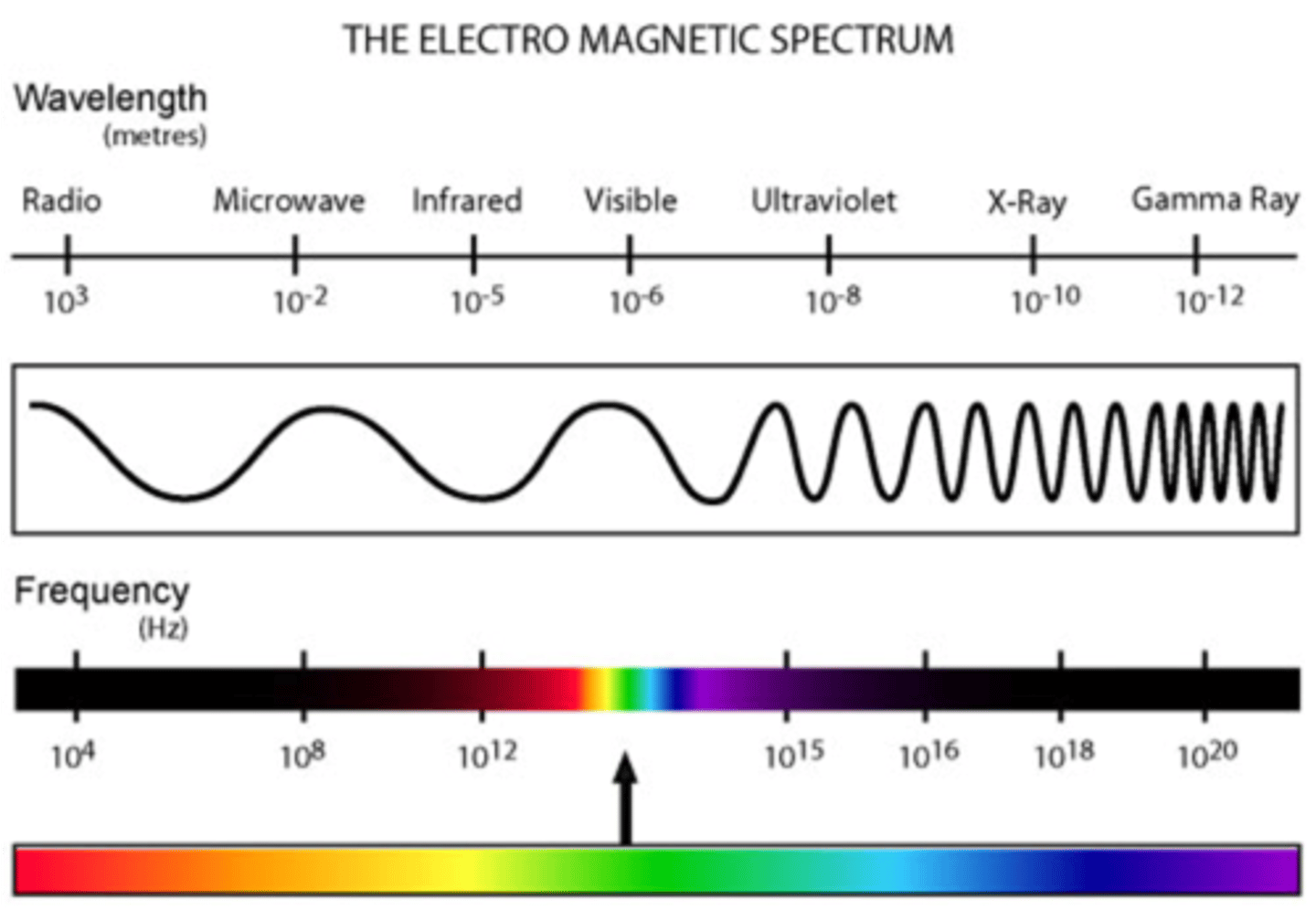
Electromagnetic Spectrum
All of the frequencies or wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation
Speed of light
300,000 km/s

Photon
A particle of electromagnetic radiation with no mass that carries a set amount of energy
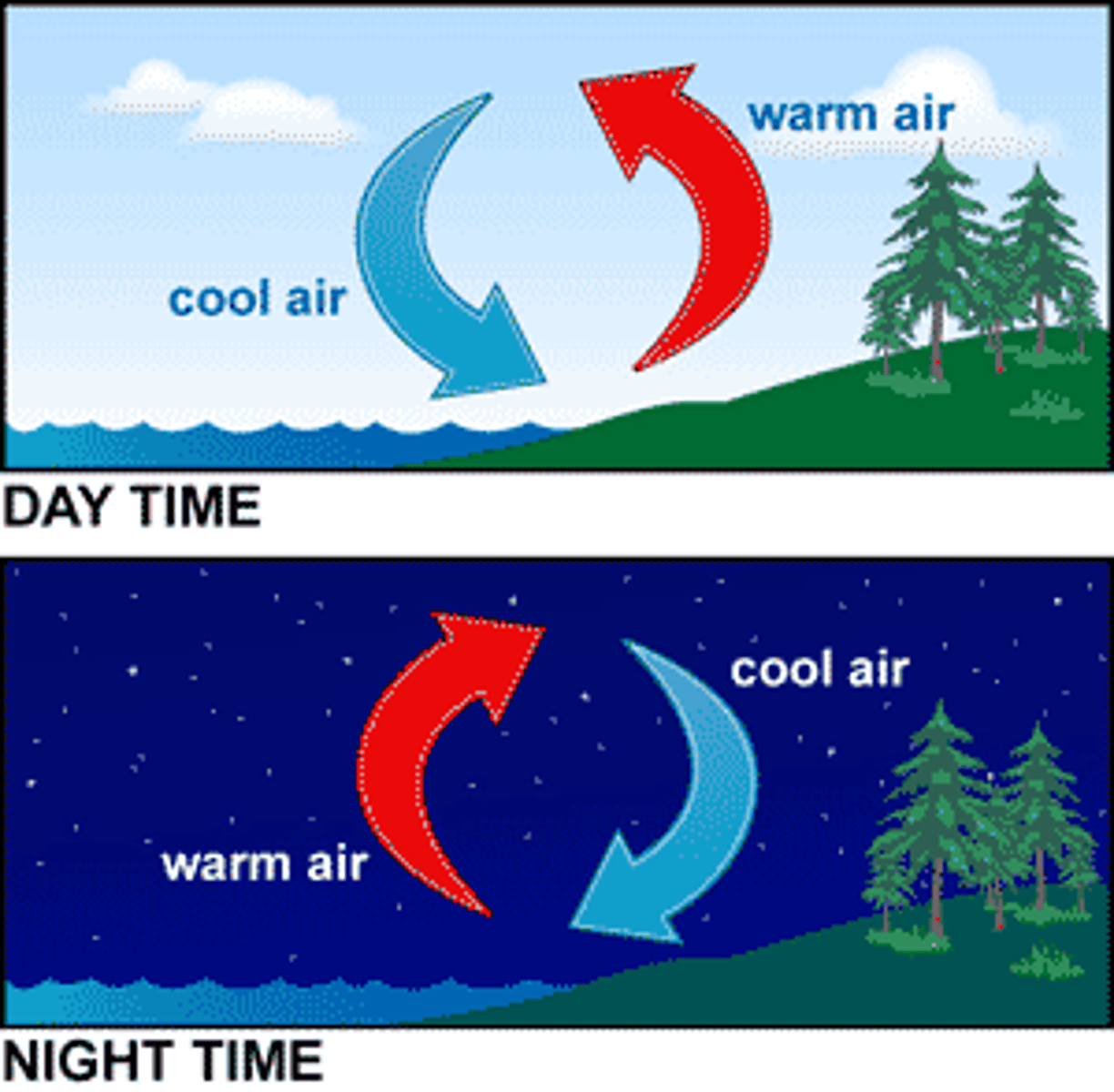
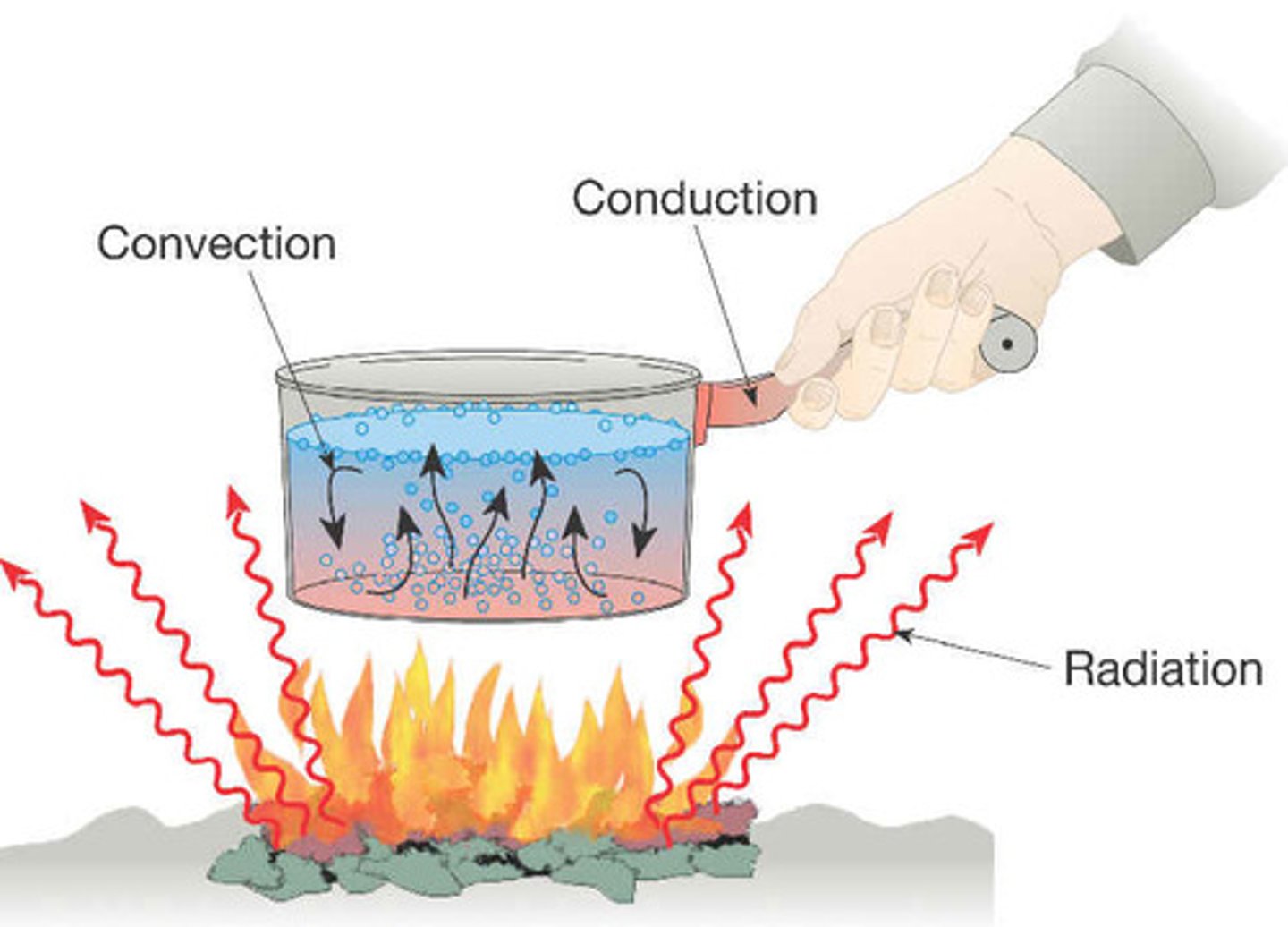
Convection
Process by which, in a fluid being heated, the warmer part of the mass will rise and the cooler portions will sink.
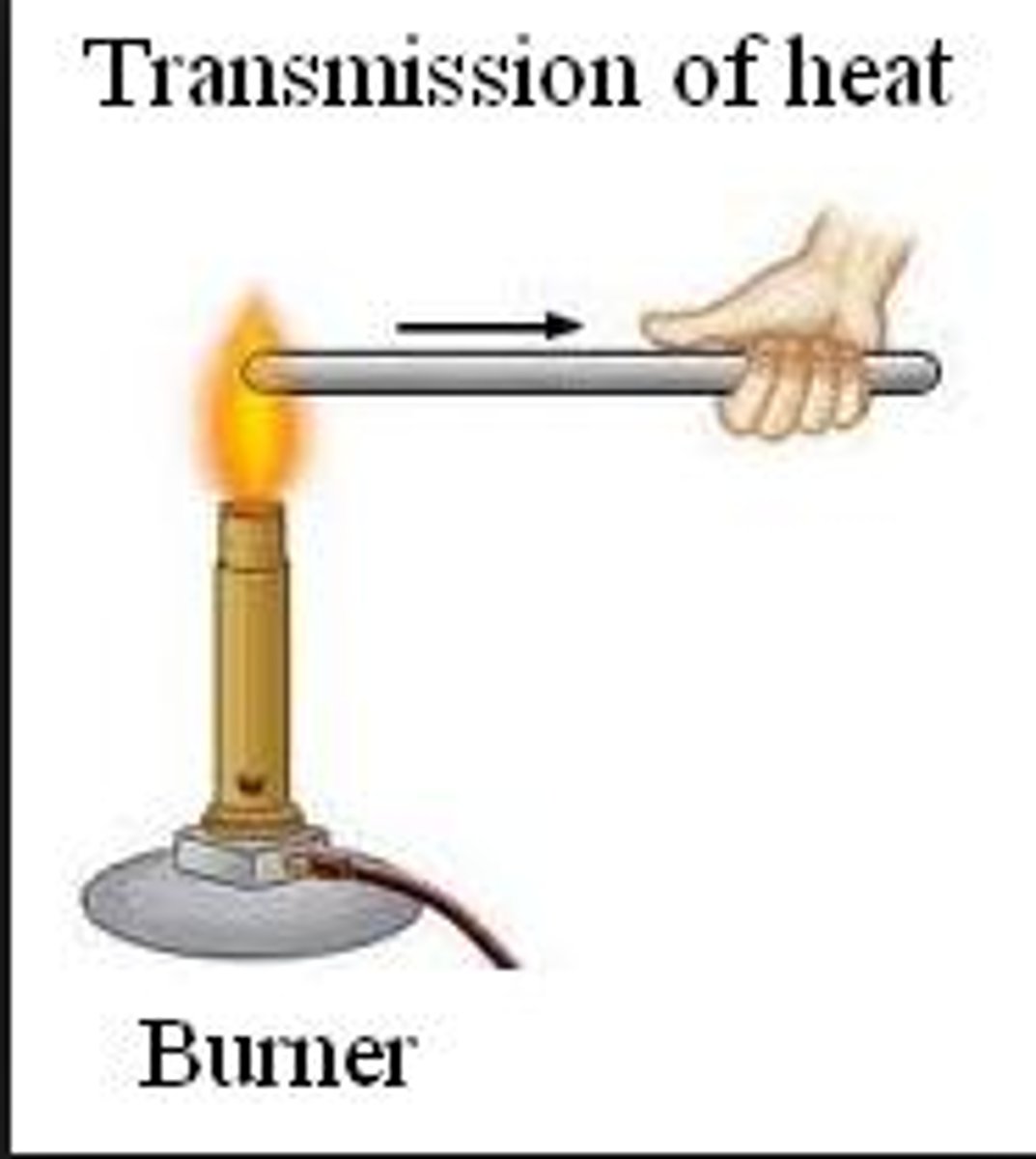
Conduction
Form of heat transfer where heat energy is directly transferred between molecules through molecular collisions or direct contact.
Radiation
The transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves
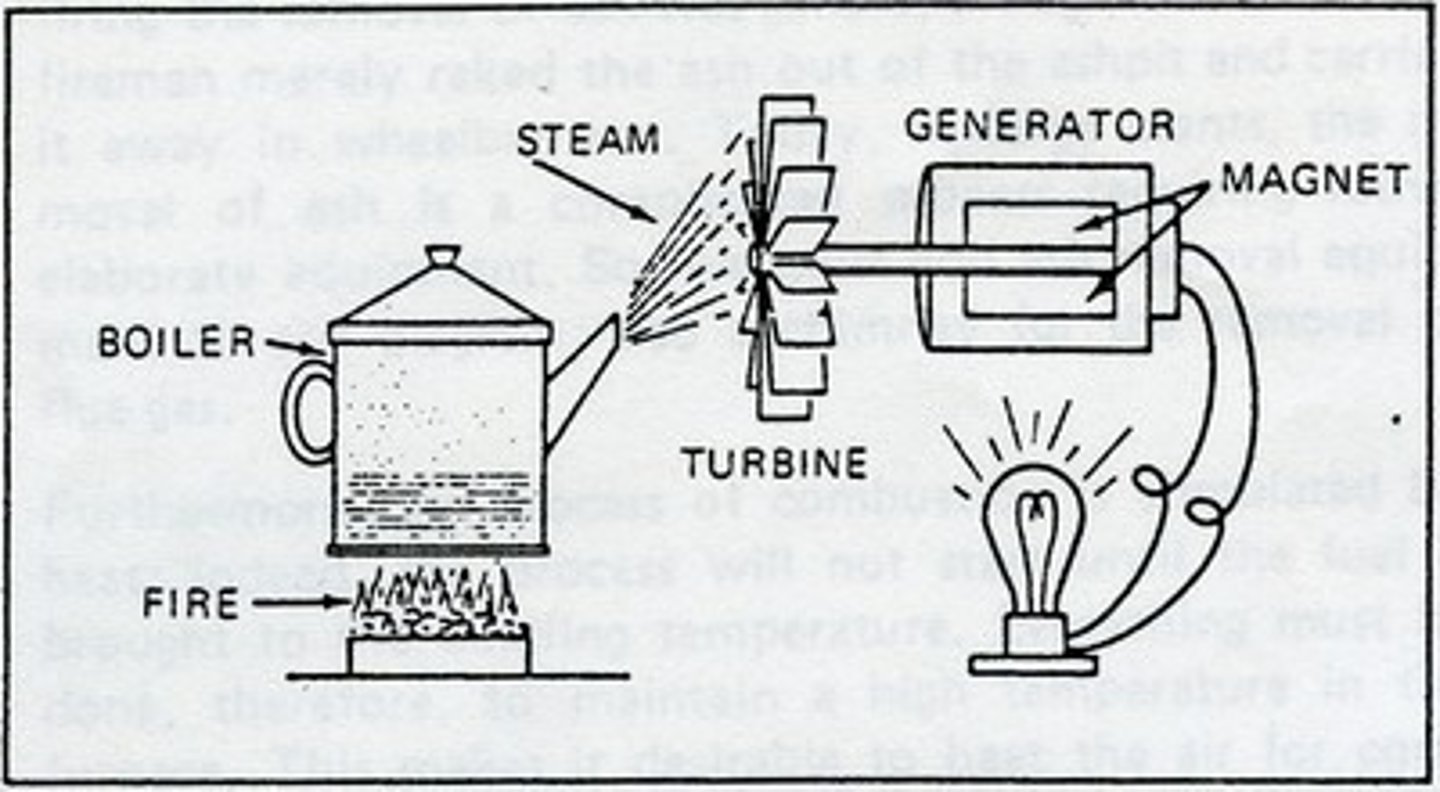
Turbine Generator
A generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
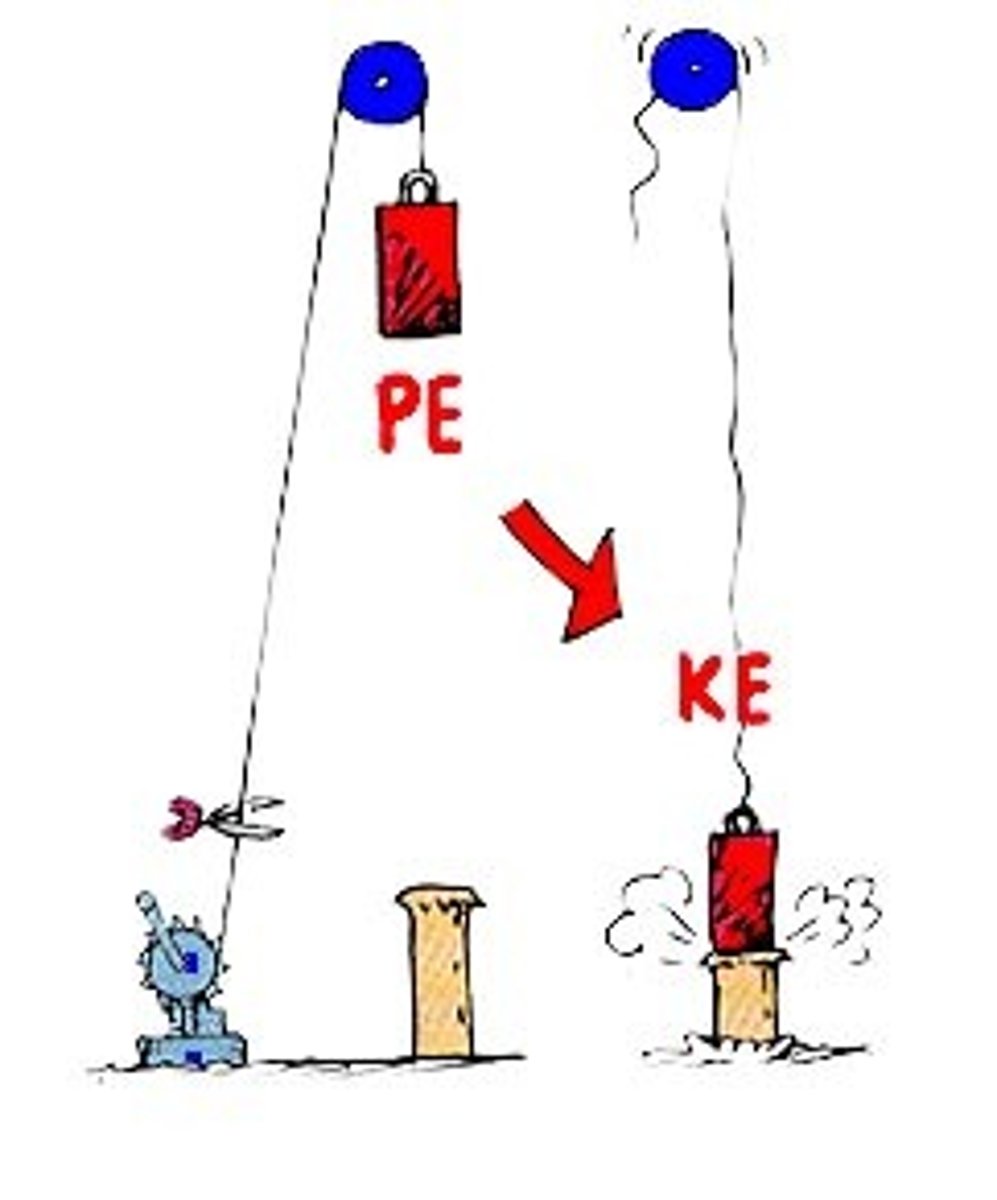
Mechanical Energy
Kinetic or potential energy associated with the motion or position of an object.
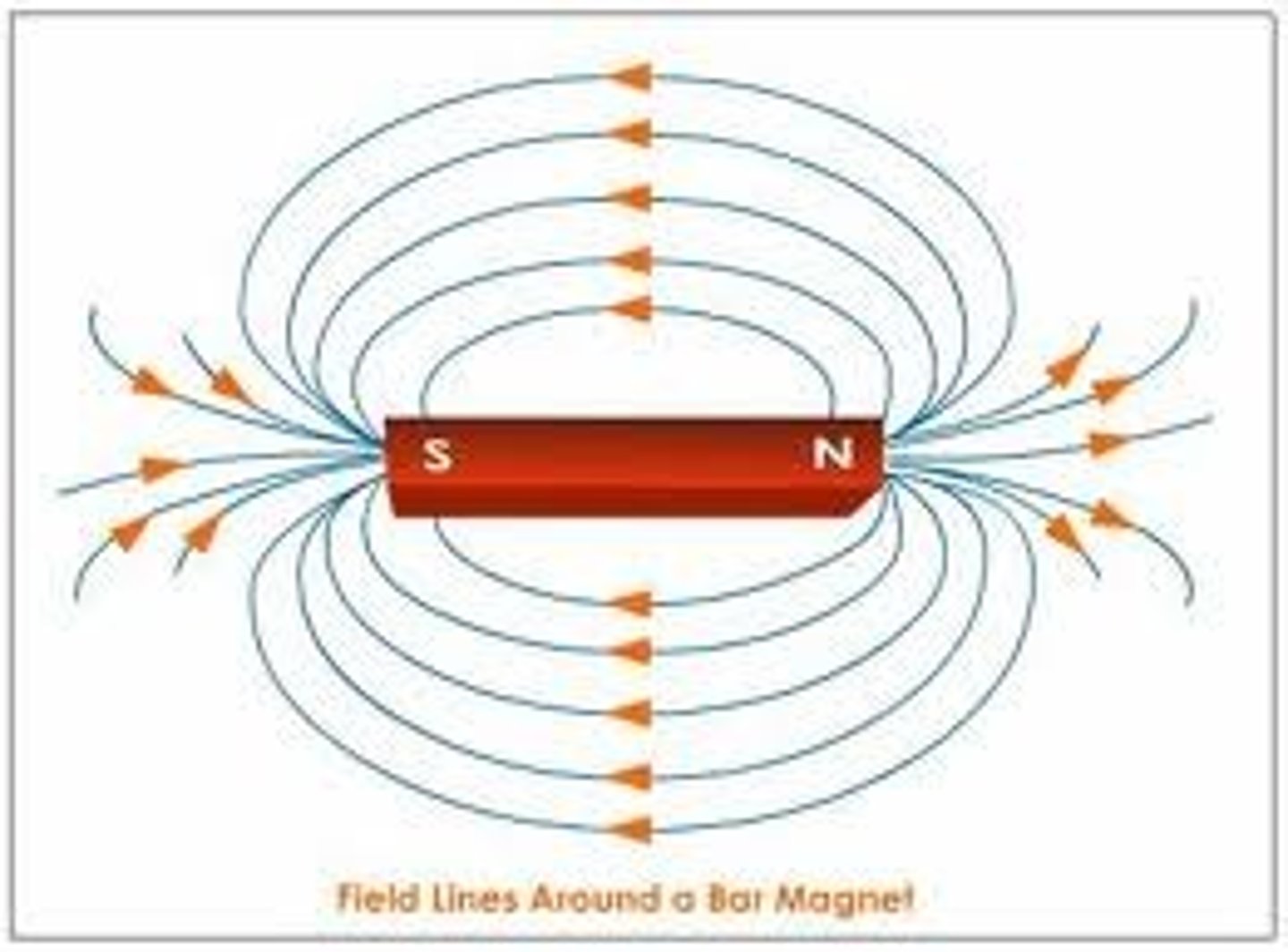
Magnetic Field
A region around a magnetic material within which the force of magnetism acts.
Wind Power
The use of a windmill to drive an electric generator

Hydroelectricity
electricity generated by the kinetic energy of moving water

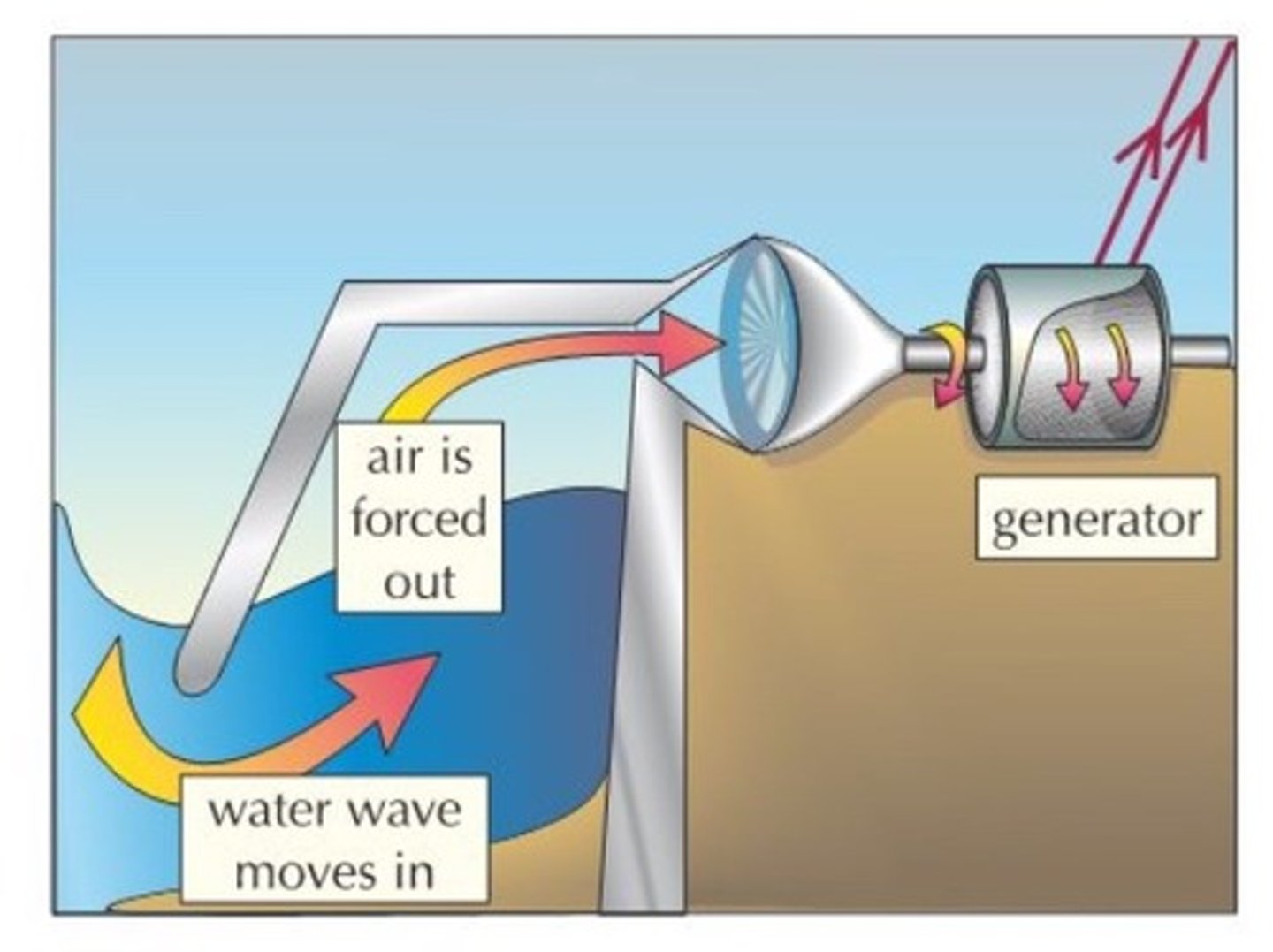
Wave Power
power obtained by harnessing the energy produced by waves at sea.
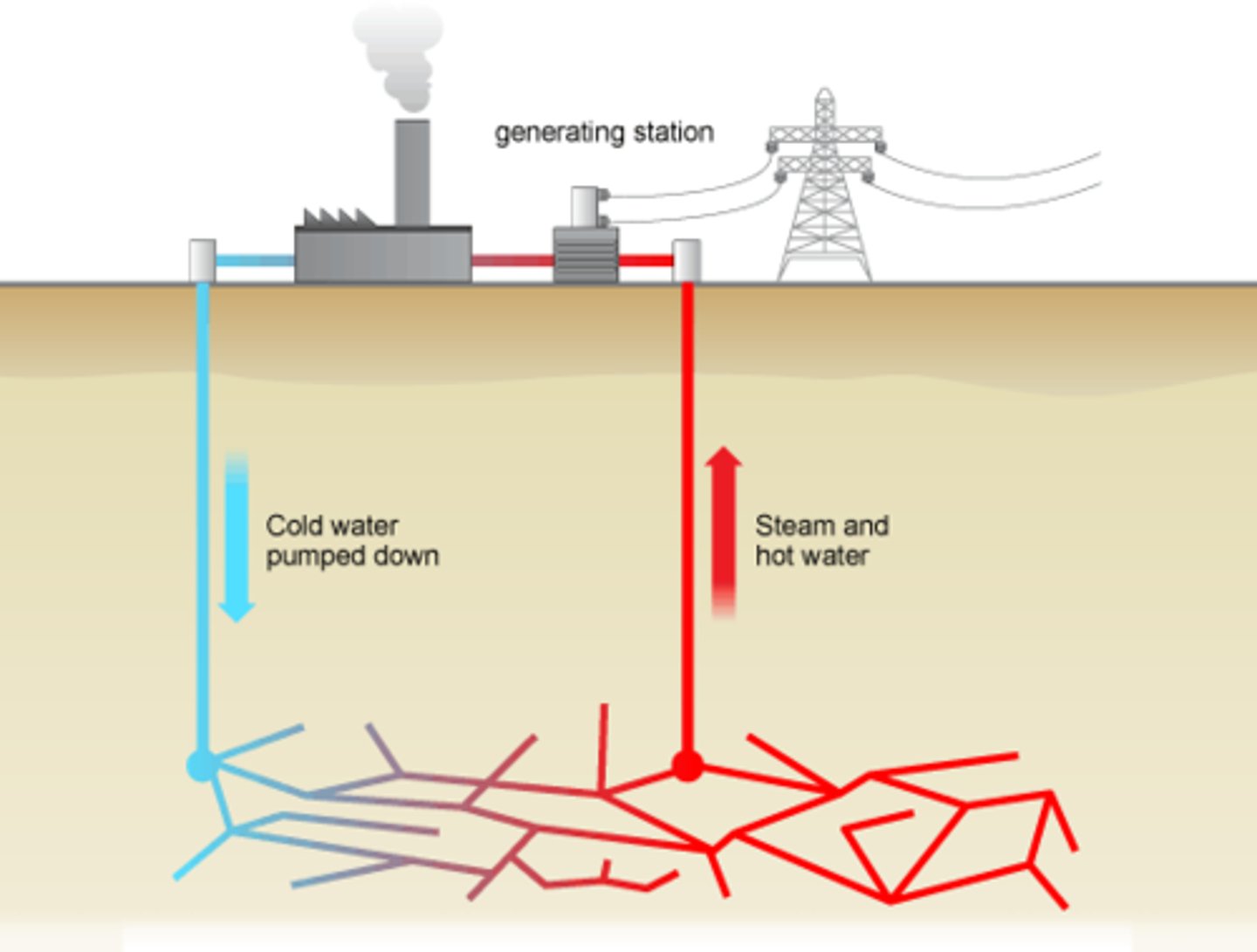
Geothermal Energy
Energy derived from the heat in the interior of the earth
Biomass Energy
The chemical energy stored in living things.
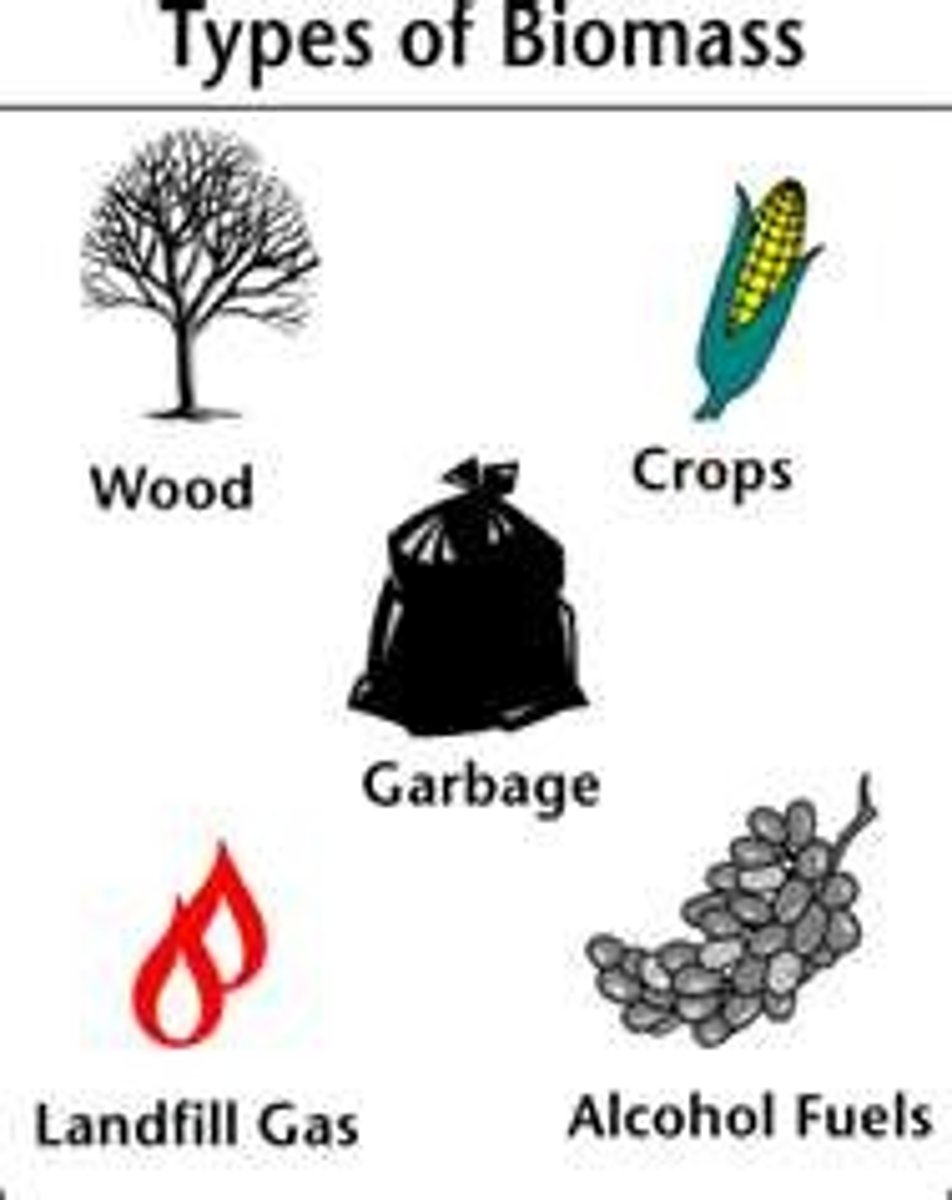

Biofuels
A fuel derived directly from living matter.
