Capacity & Duration of STM & LTM
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What was Miller’s estimate of the capacity of short-term memory?
5-9
Average of 7
Explain what evidence Miller based his claim on
Review of digit span experiments
Observations of everyday life
Explain how the capacity of short term memory can be extended
through chunking information
Into more meaningful groupings of information
What is the serial position effect?
People tend to recall items from the:
Beginning of the list (primacy effect)
End of the list (Recency effect)
Serial Position effect = primacy effect + recency effect
U shaped curve
Outline the case study of Clive Wearing
Virus destroyed large parts of hippocampus in his brain
Has virtually no memories of events since damage
STM is largely normal - hold information for at least 7 seconds
Memories pre damage are intact and frozen in time
STM functions but doesn’t transfer to LTM
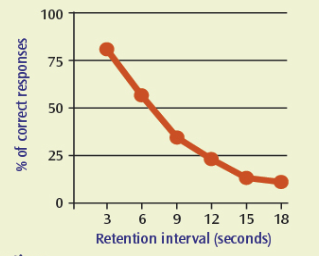
Explain the procedure of the Peterson’s experiment on the duration of short-term memory (3)
Trigrams shown to participant
Participant counts backwards in 3s from 100
Tested at 1 interval of 3 seconds during countdown
What did Peterson’s claim about the duration of STM from this experiment? (1)
It was around 18 seconds
Explain the procedure of Bahrick’s study of the duration of long term memory (4)
High School Graduates
Tested after 15 & 48 years on recall of class mates:
Tested by free recall/
/cued recall (using photos)
Outline the main results of Bahrick’s study of the duration of LTM (4)
Free Recall: 60% (15 years), 30% (48 years)
Recognition: 90% (15 years), 70% (48 years)
Explain what conclusions can be drawn from Bahrick’s study of the duration of LTM (2)
Long-term memories can remain stored for a very long time
Cues increase recall from LTM