Market Structures 3.4
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are the 4 efficiencies
Allocative
productive
dynamic
X- efficiency
Allocative efficiency
when resources are used to produce goods and services which consumers want and value the most are maximised. Value to society = marginal cost of production. P=MC
Productive efficiency
when products are produced at the lowest average cost so the fewest resources are used to produce each product. Minimum resourses, maximum output. MC=AC
Dynamic efficiency
When resources are allocated efficiently over time. AR>AC. Achieved in markets where competition encourages innovation but there are differences in products and copyright laws. SNP is required for incentive to invest
X-inefficiency
if a firm fails to minimise its average costs at a given level of output, it is x-inefficient and there is organisational slack. Occurs when their fail to minimise their cost for a specific output
Examples of monopolistic competiton
Hairdressers
estate agents
resturants
Characteristics of monopolistic competition
Large number of buyers and sellers
Low barriers to entry or exit
differentiated goods/products
price making power is limited
imperfect information
non-price competiton e.g loyalty cards, renovation
Conditions for monopolistic competition
AC=AR, MR=MC. They are not allocatively or productively eficient as MR doesnt equal AR so AC cant equal MC and AC cant equal MR
What efficiencyis monopolistic competition likely to be
Dymanic efficient since they are differentiated products and so innovative products will give advantage over competitors, allowing SNP in the short run
When does pure monopoly exist
when one firm is the sole seller of a product in a market.
Application - Pure Monopoly
Closest example of a pure monopoly is google, who have 88% of the market share
What is third degree price discrimination
when monopolists charge different prices to different people for the same goods. E.g different times of the day, varied by region, discounts for elderly people
Price discrimination diagram
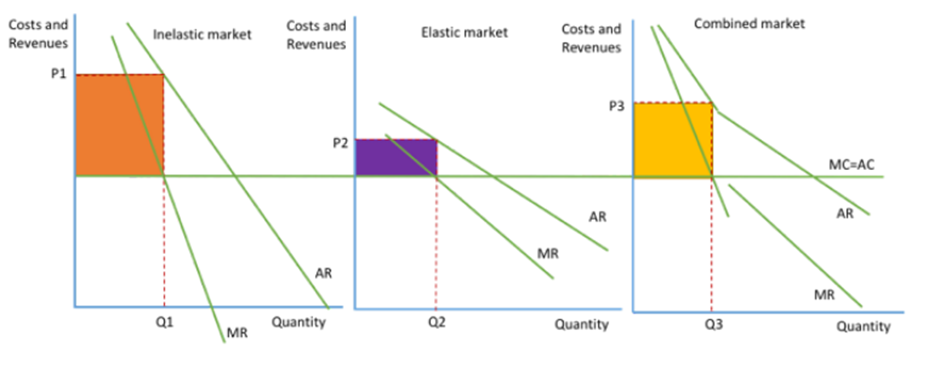
The diagram shows the separate markets for separate groups; those with elastic demand and those with inelastic demand
Second degree price discrimination
different prices for different quantities
Natural monopoly
The EOS are so large that even a single producer is not able to fully exploit them all. Natural monopolies tend to be found in industries with very high fixed costs such as railways.
Natural monopoly diagram
Pointless to encourage competition since it would raise average costs for the industry. If new firm enters the market, they will easily be priced out as their costs will be so much higher
cost and benefits of monopolies
potential to make huge profits through profit maximisation
SNP means firms will have finance for investments; able to build up reserves to overcome short term difficulties
Able to compete against large overseas organisations
maximise EOS, reducing corst and increasing profit further
However, x-inefficiencies, sales/revneue maximising, profit satisfying or contestability wont allow for profit maximisation.
Employees and suppliers - Monopoly
fewer workers due to lower output
employees may recieve higher wages, particularly directors and senior managers
reduce suppliers’ profits if monopolist buys all goods as monopsolist will reduce prices
Consumers - monopoly
tend to be better off than if there was competition
EOS= More efficiency so customers will enjoy higher consumer surplus
increased range of goods and services due to cross subsidisation
price discrimination allows for survival of a product or service, and benefits some customers while its negative for others.
may pay higher prices and see porrer quality due to lack of competition
less choice for consumers since only one firm is producing
What inefficiency is a monopoly likely to be
productively inefficient, since they dont produce at MC=AC. also Allocatively inefficient as P>MC
what efficiency is monopoly likely to be
dynamically efficient, as they are likely to make supernormal profits
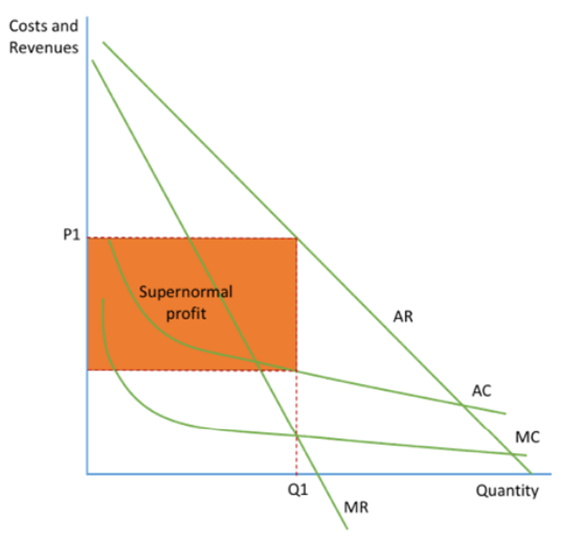
Difference between SNP and Normal Profit
TR=TC is Normal profit. TR>TC is Supernormal Profit