AP Biology Unit 1 - Chemistry of Life
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
What is a covalent bond?
The bond type in which atoms share electrons (eg. water)
How is water polar?
The covalent bond between hydrogen in oxygen results in an unequal sharing of electrons between the two molecules. This is because oxygen is more electronegative.
What type of bonding can result in polarity?
covalent bonding
What does it mean to be polar? (What is polarity?)
There is a difference in the electronegativity of the atoms that are bonded
Hydrogen Bond
weak
between the negative and positive regions of two separate molecules
only occurs between polar molecules
Cohesion
two of the same molecules form a hydrogen bond (eg. two water molecules)
Adhesion
two different molecules forming a hydrogen bond
What can hydrogen bonds result in?
surface tension
Surface tension (Why is it important?)
increased hydrogen bonds between water molecules
ONLY at the surface
eg. water droplet on a penny
plants need to float on leaves
Water Solvency (Why is it important?)
water has very high solvency as liquid
it allows living things to absorb nutrients through water
Ice Floating (Why is it important?)
water is less dense as a solid than as a liquid
this is not normal
fish can survive in frozen over lakes
Water’s Heat Capacity (Why is it important?)
can absorb a lot of thermal energy before becoming steam
aquatic animals require this to maintain body temperature
Capillary Actions (Why is it important?)
adhesive and cohesive properties allow water to climb upwards by attaching to itself
plants take water from the ground through its roots
Law of Conservation of Energy
energy can only be transformed
Where is the energy mainly used by living systems stored?
chemical bonds
What are atoms and molecules from the environment necessary for in living systems?
exchange of matter
building new molecules
(eg. carbs, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids)
Which element is used to make all macromolecules?
carbon
What is carbon’s unique bonding ability? What does it help do?
It can bond to other carbon to create “carbon skeletons”
Very large and complex molecules
Used to store energy
Form basic cell strucutes
Monomers
chemical sub-unit for polymers
makes up macro-molecules
Polymer
macromolecule of monomers
What type of bond connects monomers to each other?
covalent bond
Carbohydrate Monomer
Monosaccharide
Carbohydrates are the POLYMER
Protein Monomer
amino acid
proteins are the POLYMER
Nucleic Acid Monomer
nucleotide
nucleic acids are the POLYMER
Lipid Monomer
fatty acids (kind of)
no true monomer
1 glycerol + 3 fatty acid chains
Dehydration Synthesis Reaction (What bond is formed? Byproduct?)
a water molecule is removed from the atoms to combine them
H from one and OH from the other
covalent bond is formed
a water molecule is the byproduct
Hydrolysis Reaction (Opposite of Dehydration Synthesis)
breaks down polymers
covalent bonds are broken
a water molecule is added back into the monomers
H is added to one original monomer and OH is added to the other
eg. digestion
What are dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis used to form/transform?
macromolecules
What factor determines the structure and function of carbohydrates?
directionality of sub-components
eg. (OH on the bottom and H on the top vs. the other way)
the type of monomer
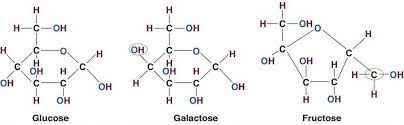
What are the different shapes that carbs can be?
branched and linear
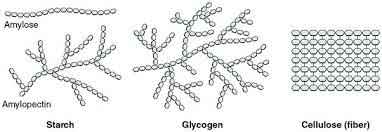
What is the structure and function of starch and glycogen?
branched
energy storage
(starch can sometimes be linear)
What is the structure and function of cellulose?
linear
plant cell wall structure
What are the 3 monosaccharides?
Glucose
Frucstose
Galactose
Disaccharides
Sucrose
Lactose
Maltose
Polysaccharides
Starch (Amlopectic and Amylose)
Glycogen
Cellulose
Chitin
What are carbohydrates comprised of? (in terms of structure and types of bonds)
linear chains of sugar molecules connected by covalent bonds
What types of bonds link carbohydrates?
covalent bonds
What are the characteristics of a lipid?
nonpolar
hydrophobic
Which lipids contain fatty acids?
triglycerides and phospholipids
What are the two types of fatty acids? What defines them?
saturated - only single bonds between their carbon acids
unsaturated - at least one double bond between their carbon atoms
How do double bonds affect a lipids structure an function?
unsaturated
kink in the carbon chain
more kinks = more unsaturated
more liquid at room temperature
What are the types of lipids?
Phospholipids
Steroids
Triglycerides (Fats)
What are the uses of fats?
provide energy storage
support cell function (heat insulation)
Steroids
hormones that support physiological functions
eg. growth, development, metabolism, homeostasis
Cholesterol
common steroid found in cell membranes
animal cell membranes
maintains structural stability (maintain fluidity)
Phospholipids
form cell and plasma membranes
Hydrophilic head (outside of membrane)
Hydrophobic tail (inside of membrane)
Similarities between DNA and RNA
5-carbon sugar
phosphate group
nitrogenous base
sugar-phosphate backbone
Connect on the 5 prime end and 3 prime end
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
Deoxyribose (sugar without oxygen)
Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine, Thymine
Double-stranded (strands are anti-parallel)
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Ribose (sugar)
Cytosine, Guanine, Adenine, Uracil
Single-stranded
What does it mean that DNA strands are anti-parallel?
one strand has 5 prime at top and 3 prime on bottom
the second strand has 3 prime on top and 5 prime on bottom
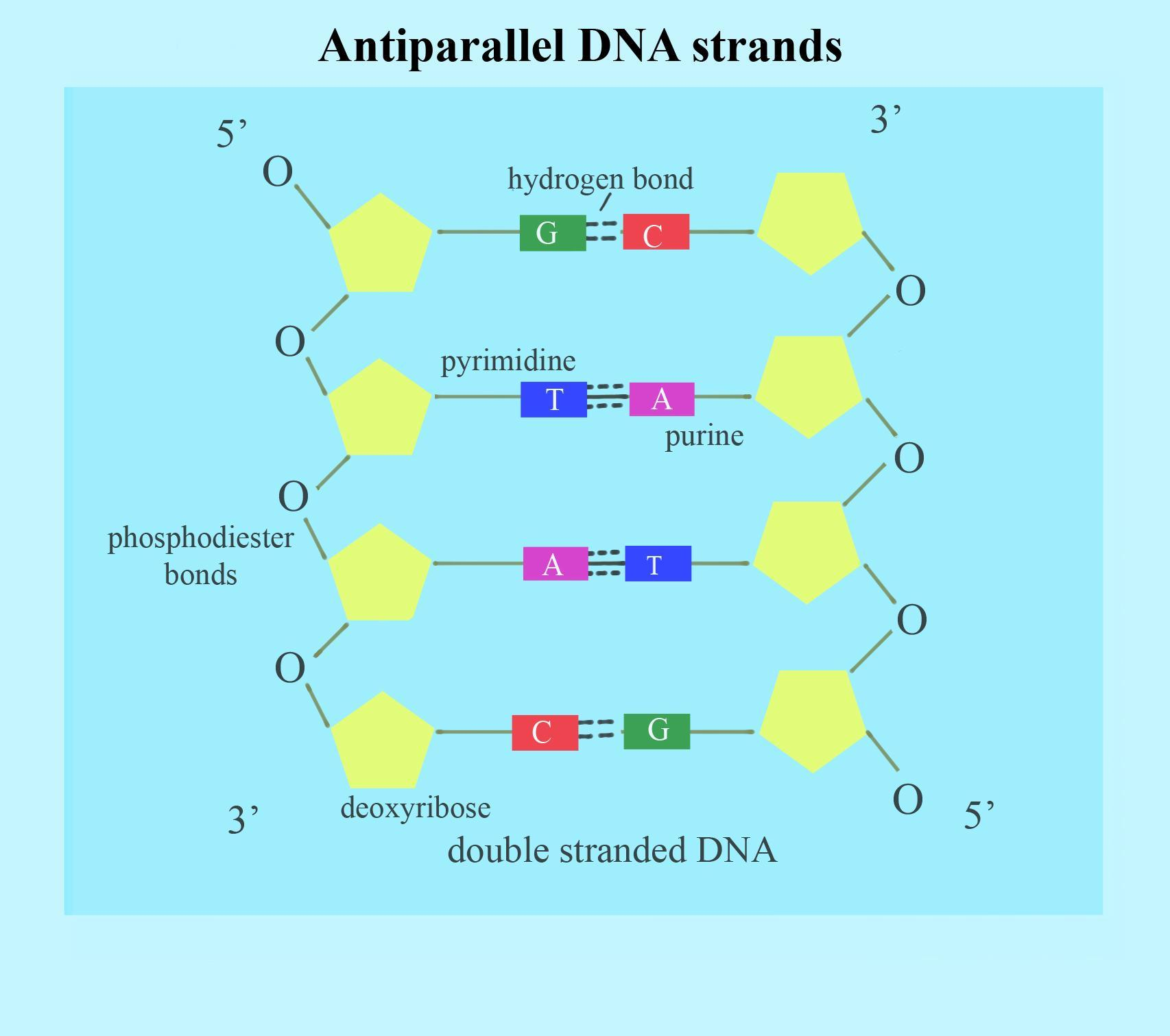
How is the linear sequence of all nucleic acids characterized?
3’ hydroxyl
5’ phosphate
of the sugar in the nucleotide
What type of bonds hold together the nitrogen base pairs?
hydrogen bonds
How many hydrogen bonds are in the A - T pair? the G - C pair?
A - T has two bonds
G - C has three bonds (stronger and better for stable structure)
Which is the only “prime” end that nucleotides can be added to each other on?
3’ end (covalent bond)
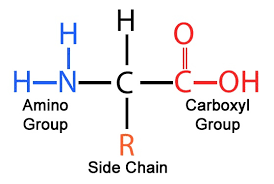
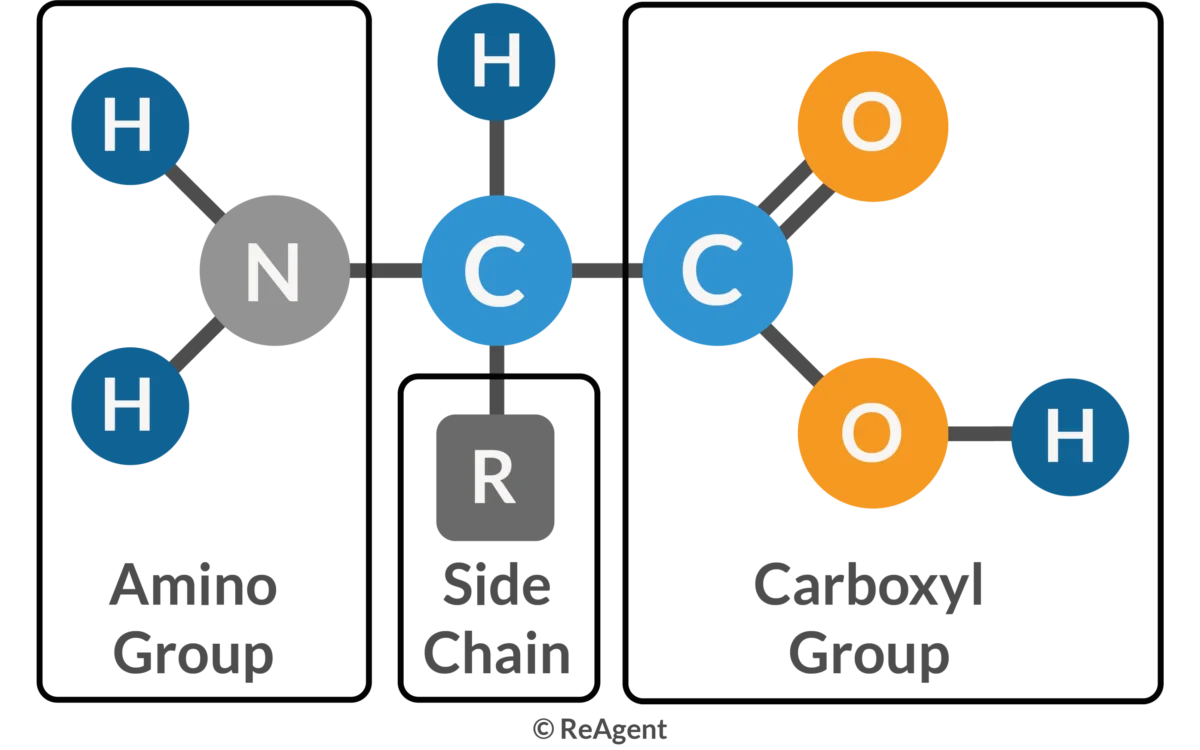
What is the are two terminus (ends) of an amino acid?
amino terminus (NH2) on left
carboxyl terminus (COOH) on right
Which terminus are new amino acids added to to form a peptide bond?
carboxyl group
amino group of new amino acid attaches to carboxyl group
Peptide Bonds
covalent bond
between carboxyl and amino group in amino acids
Primary Protein Structure
determined by sequence of amino acids
peptide bonds (covalent bonds)
not yet functional
Secondary Protein Structure
folding of the amino acid chain in primary structure
alpha-helix
beta-sheets
not yet functional
Tertiary Protein Structure
3D shape of protein
one chain wrapped around to make a 3D shape
many are functional at this level
Quaternary Protein Structure
many tertiary chains wrapped together to make 3D shape
needed for some proteins
eg. hemoglobin in red blood cells
Receptor Protein
receives chemical signals
signal molecule must have a similar structure
How does change in an amino subunit (such as change in polarity) affect the structure and function of a protein?
change at the primary level
changes structure and function of protein
What are amino acids composed of?
central carbon with hydrogen attached
amino group
carboxyl group
varying R group (hydrophobic/non-polar, ions, disulfide bridges, polar/hydrophillic)
Through what method are peptide bonds formed?
dehydration synthesis (covalent bond)
What type of bonds are in secondary protein structure?
hydrogen bonds (oxygen and hydrogen)
twisting around backbone = alpha helix
folding back and forth = beta sheet
What type of bonds are in tertiary and quaternary protein structure?
interactions between the different R-groups
hydrogen bonds
hydrophobic interactions
ionic interactions
disulfide bridges
What levels of a protein structure determine the function?
all of them!
Chemical Makeup of Carbohydrates
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
1:2:1 CHO ratio
Chemical Makeup of Lipids
always
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
sometimes
phosphorous (phospholipids)
nitrogen
sulfur
(CHOP “ns”)
Chemical Makeup of Proteins
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
nitrogen
sometimes
sulfur
phosphorous (less common)
(CHON “ps”)
Chemical Makeup of Nucleic Acids
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
nitrogen
phosphorous
(CHONP)
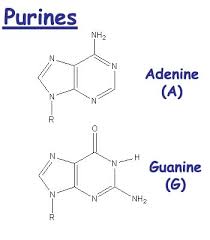
What are purines?
adenine
guanine
double-ring structure
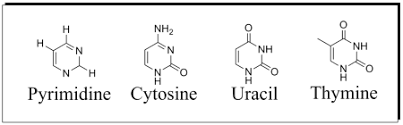
What are pyrimidines?
cytosine
thymine
uracil
singe-ring structure
What is the function of carbohydrates?
main fuel source for cells and organisms
quick energy (glucose)
energy storage (starch and glycogen)
structural support (cellulose and chitin)
What are the functions of lipids?
energy storage (triglycerides)
cell membrane structure (phospholipids)
hormones and signaling (steroids)
What are the functions of nucleic acids?
storing genetic material
building protein
What are the different types of RNA and what are their functions?
mRNA - carry genetic info from nucleus → ribosomes
rRNA - in ribosomes
tRNA - brings amino acids to ribosome for protein construction
What are the functions of protein?
catalysis
structure
transport
signalling
defense
movement