Small Animal Anatomy Thoracic Limb
1/168
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
List bones of thoracic limb in order proximal to distal
scapula, humerus, radius and ulna, carpal bones, metacarpal bones, phalanges
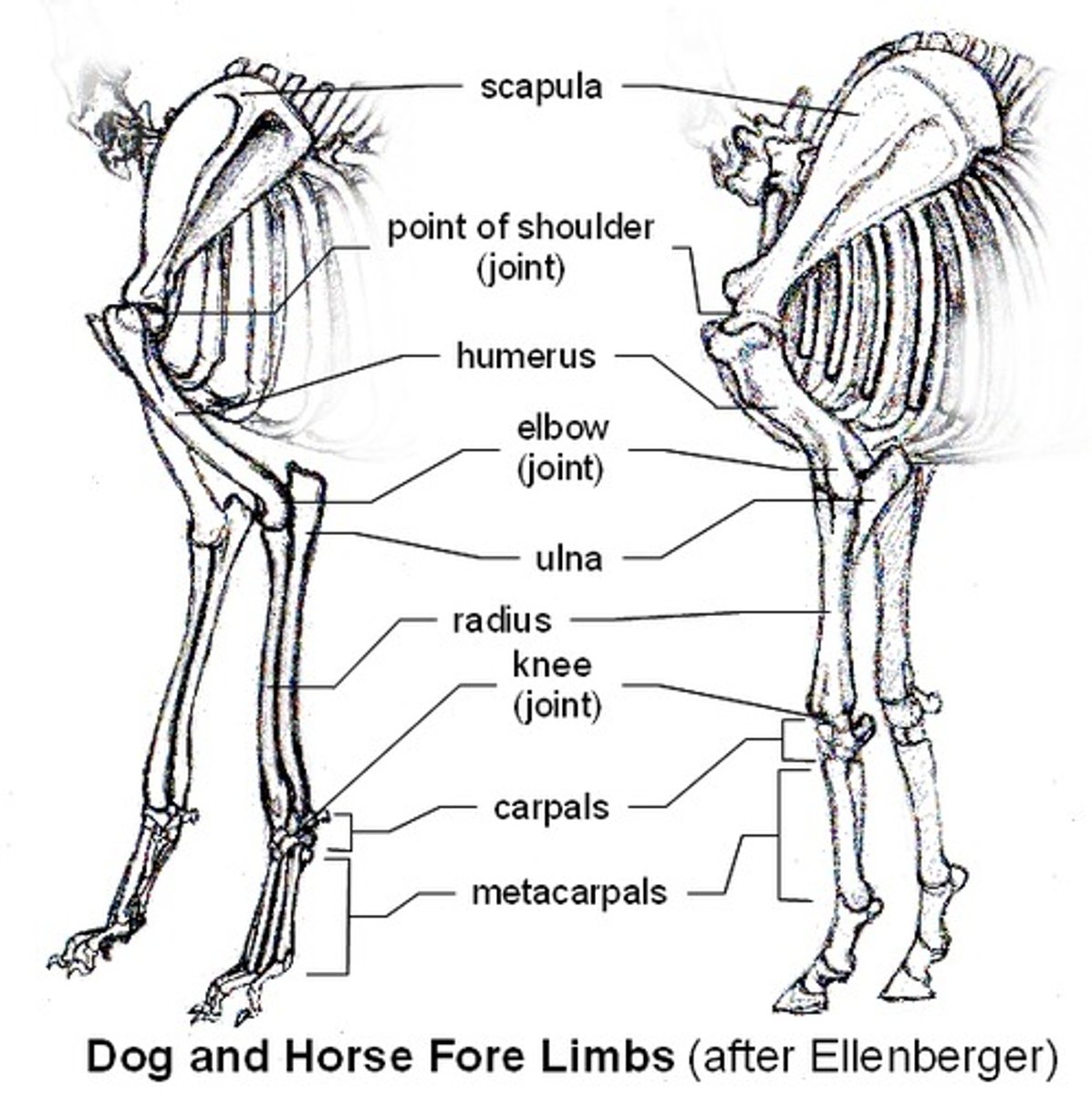
spine and acromion of scapula
spine- bony prominence of scapula.
Acromio- distal end of the spine, a truncated process
Name the part of the scapula that is lateral and cranial to the spine of the scapula
supraspinous fossa
Name the part of the scapula that is caudal to the spine
infraspinous fossa
Name the medial proximal part of the scapula
serrated face
medial part of the scapula that is nearly flat with a slight indentation?
subscapular fossa
scapular notch
depression in the cranial ventral border of scapula
what muscle attaches to the dorsal border of the scapula
rhomboideus
what structure of the scapula is located on the distal caudal border
infraglenoid tubercle
what structure on the scapula articulates with head of humerus?
glenoid cavity
what is the structure of the scapula at the cranial part of the glenoid cavity?
supraglenoid tubercle
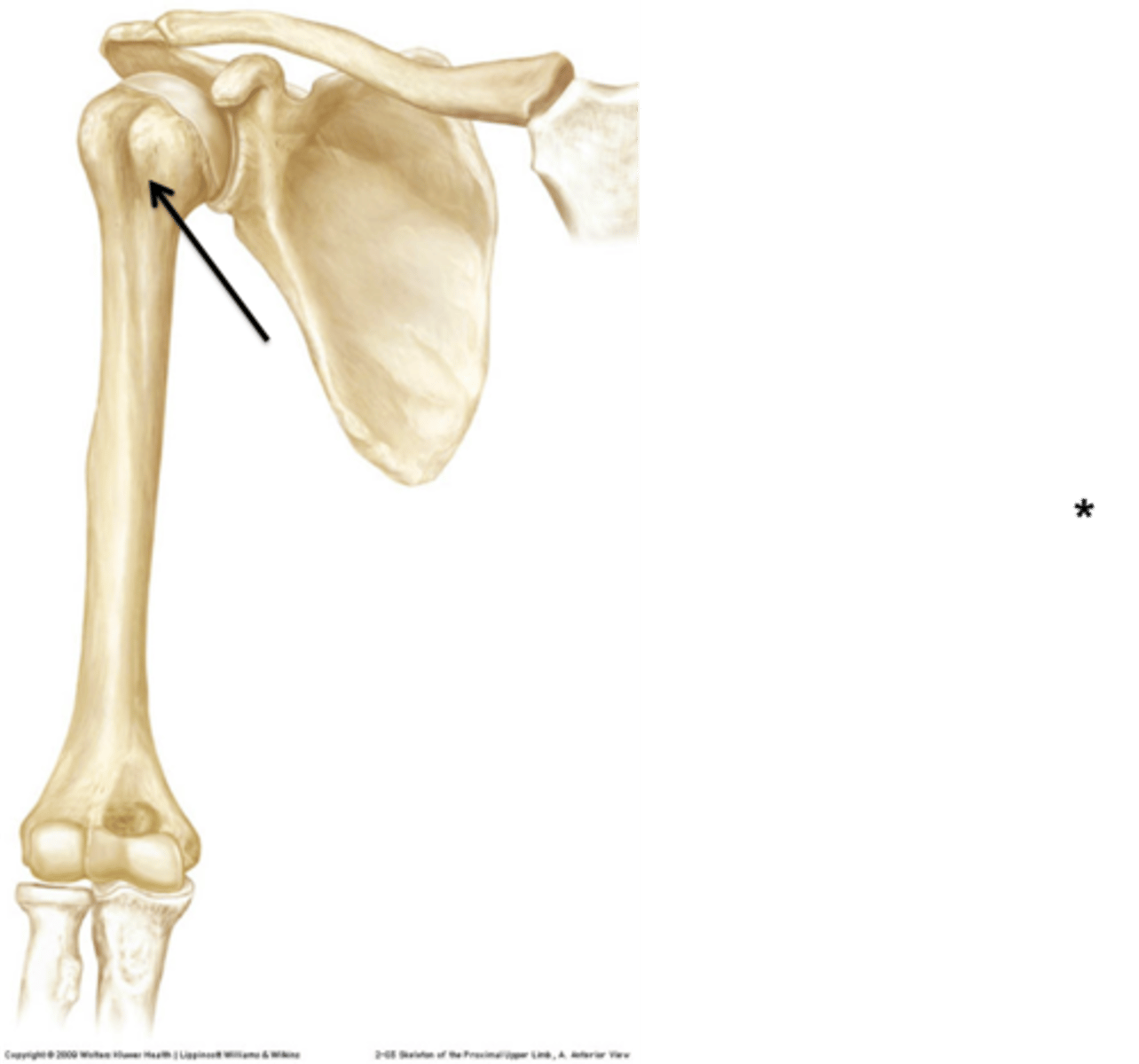
which part of the humerus articulates with scapula?
head
what is the part of the proximal humerus that separates the two tubercles and houses the tendon of origin of the biceps brachii
intertubercular groove
craniolateral part of the proximal humerus
greater tubercle
proximal and medial extremity of the humerus
lesser tubercle
which part of the humerus serves as attachment point for the brachicephalicus and part of pectorals?
cranial surface of humerus
What part of the humerus extends proximally in a craniomedial direction and is a ridge
crest of greater tubercle
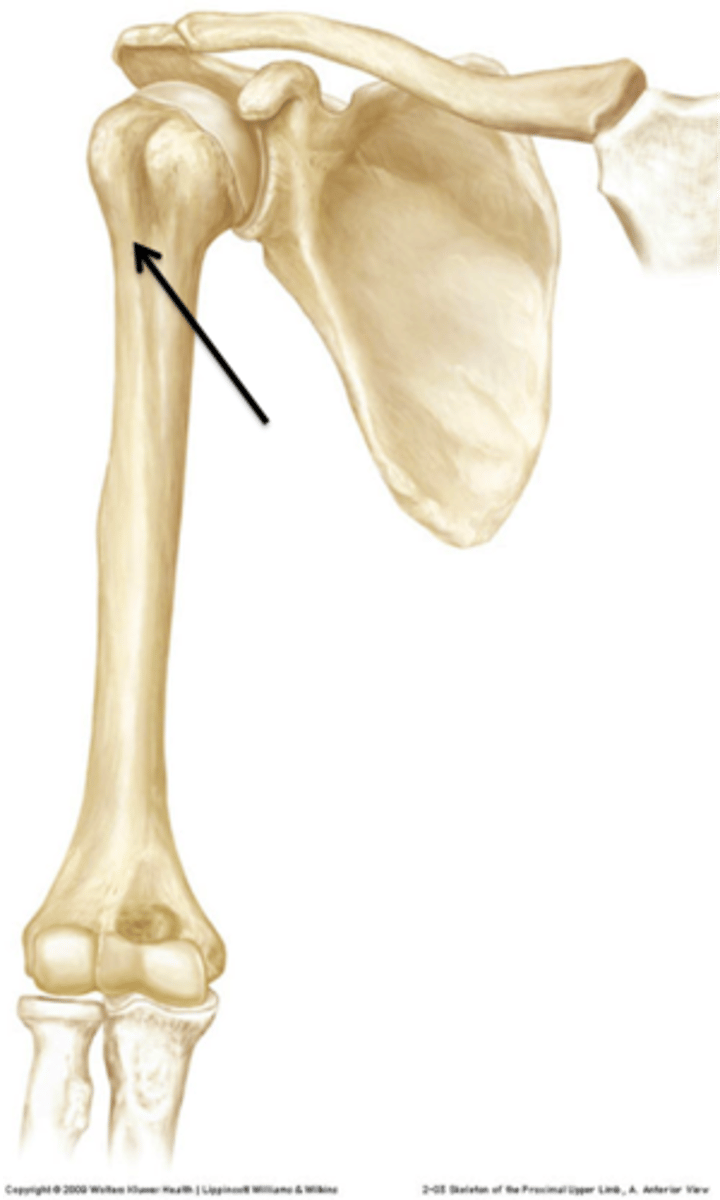
which ridge extends the caudal part of the greater tubercle
the lateral surface of the humerus
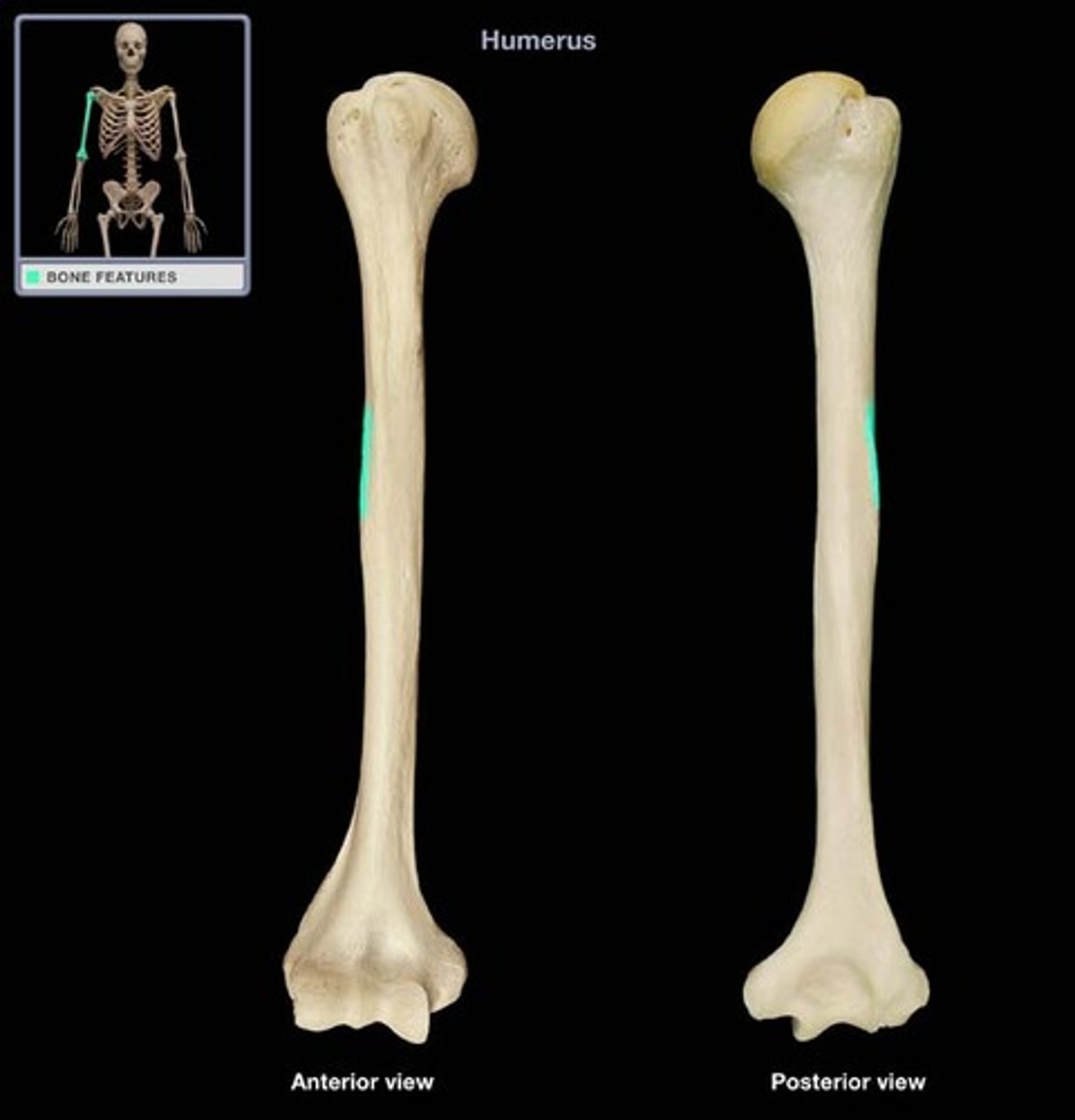
the thickened, distal portion of the lateral surface of the humerus
deltoid tuberosity
a prominence of the humerus that spans from the deltoid tuberosity to the to the caudal greater tubercle
tricipital line
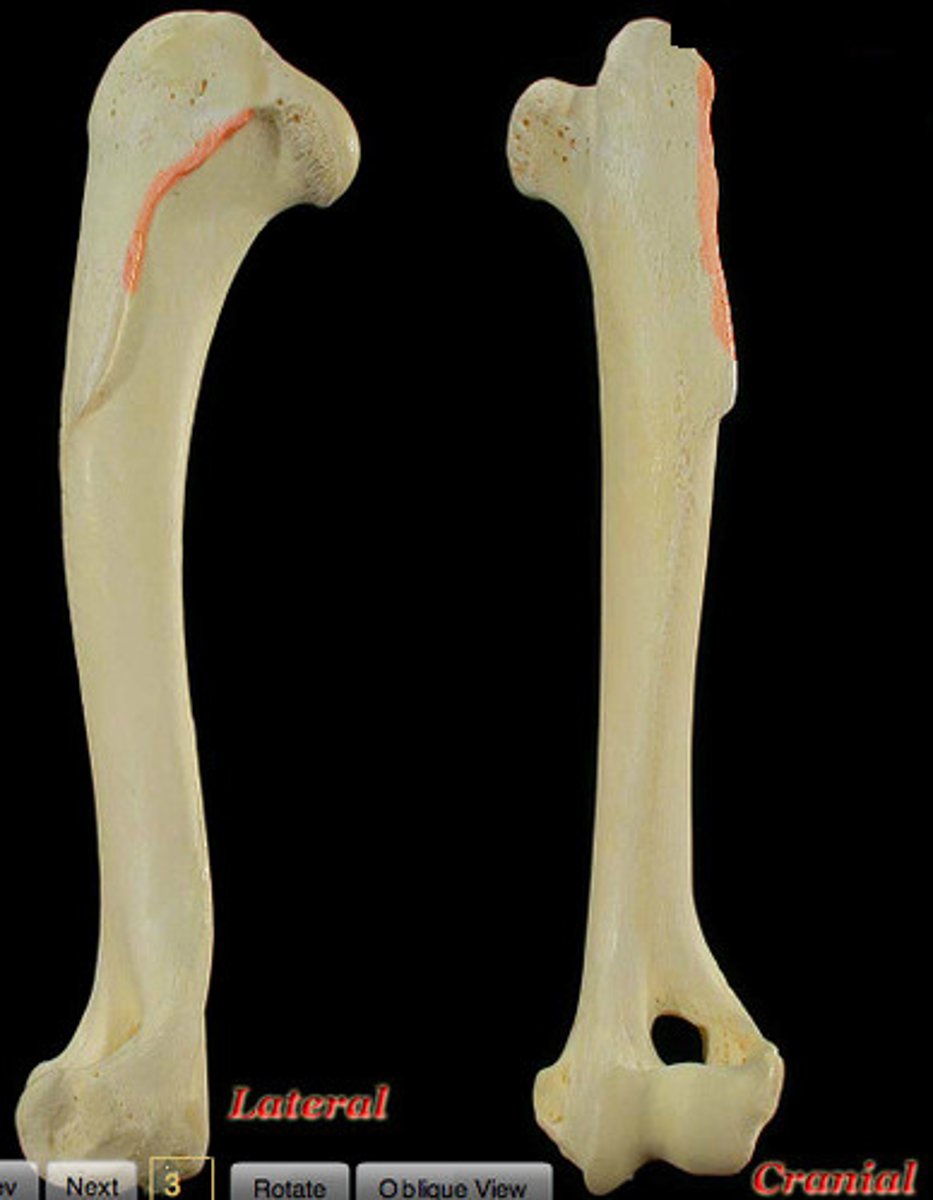
where does the teres minor insert on the humerus; location?
tuberosity of teres minor; proximal to the tricipital line, distal to the greater tubercle
what part of the humerus is on the lateral surface of the body
brachialis groove
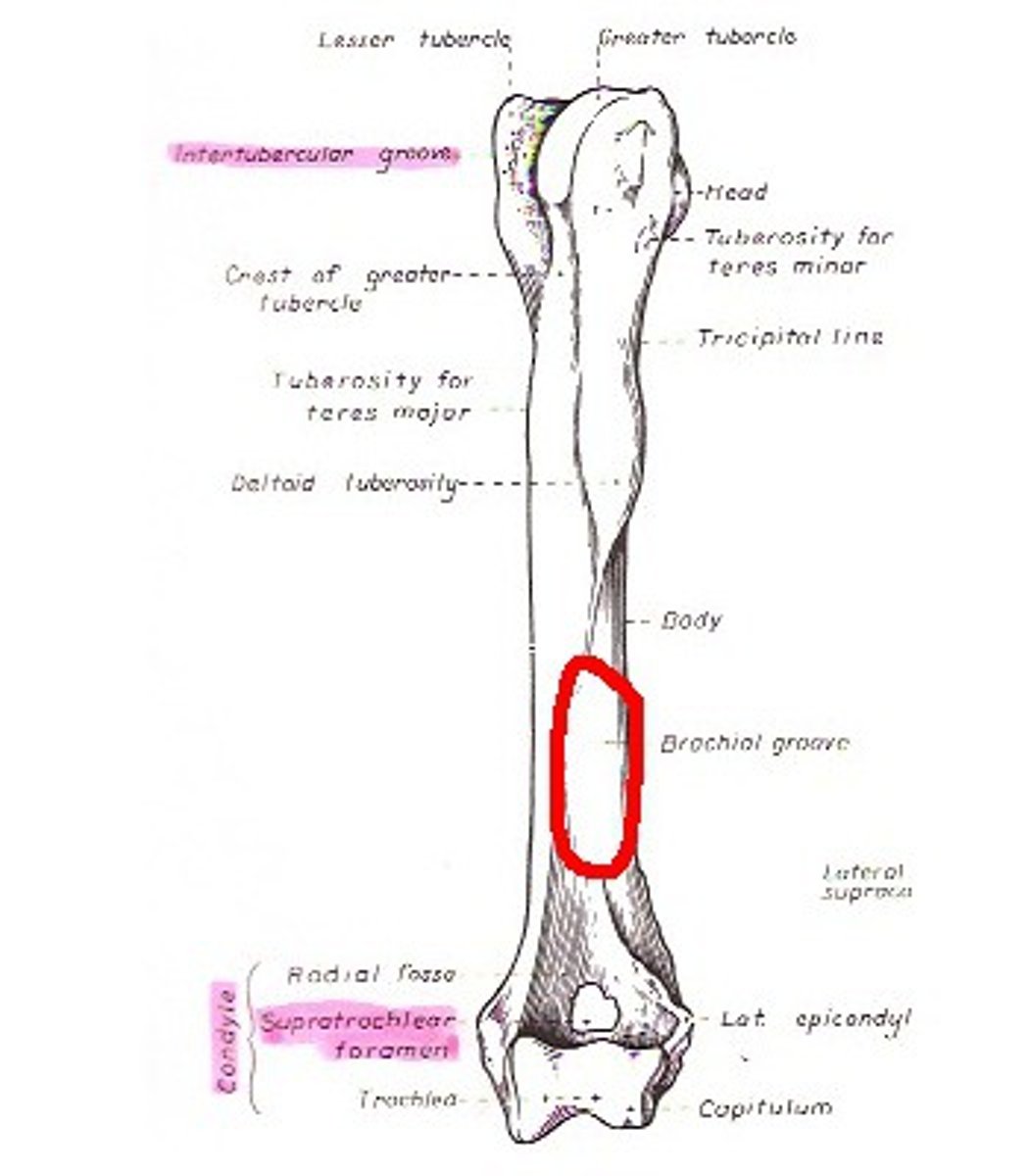
what thick part of the humerus is just distal to the brachialis groove
lateral supracondylar crest
what crest crosses the proximal end of the medial surface of the humerus
crest of lesser tubercle
what bony prominence is just distal to the crest of the lesser tubercle of the humerus
teres major tuberosity
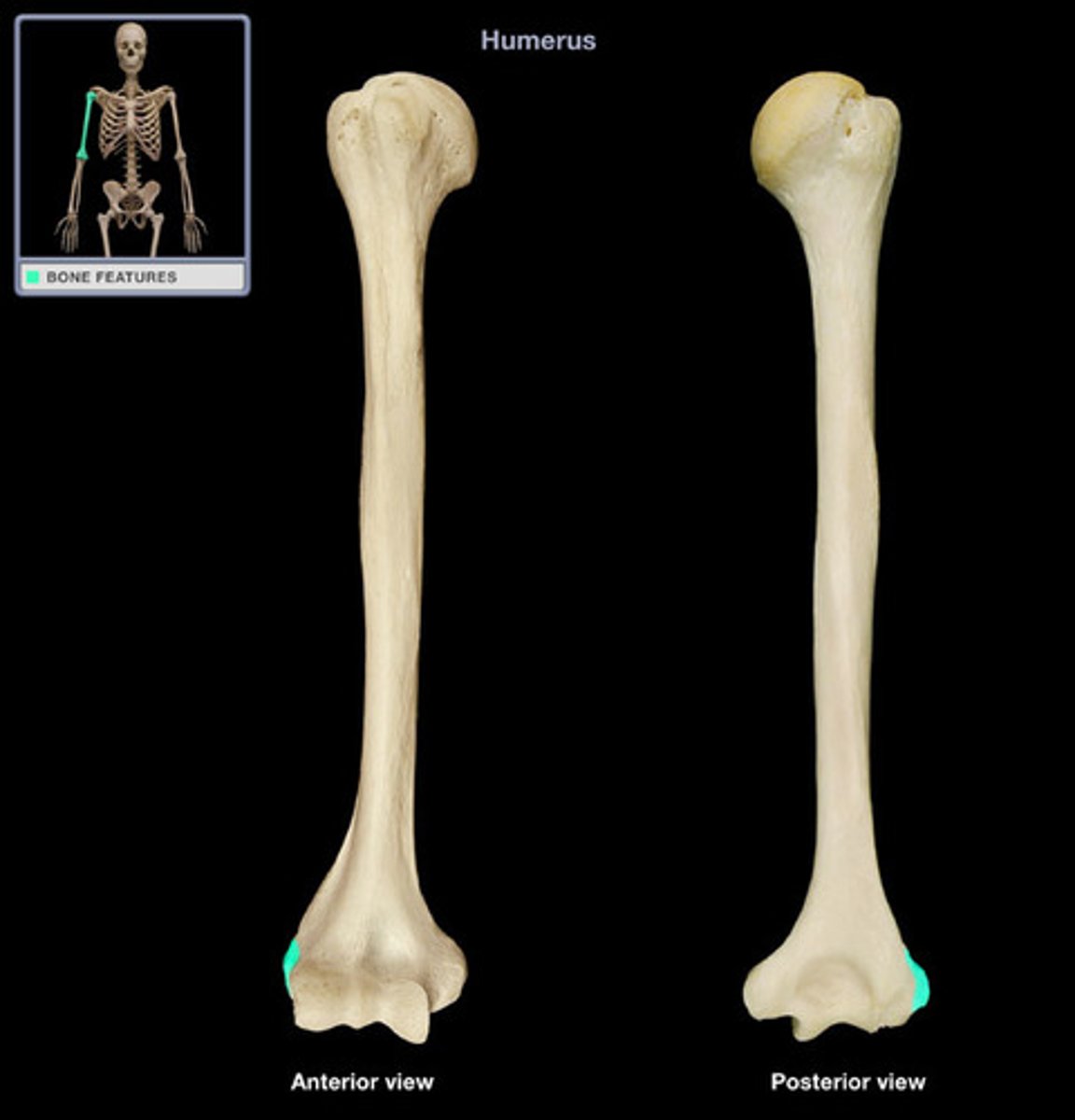
Humoral condyle
distal end of the humerus
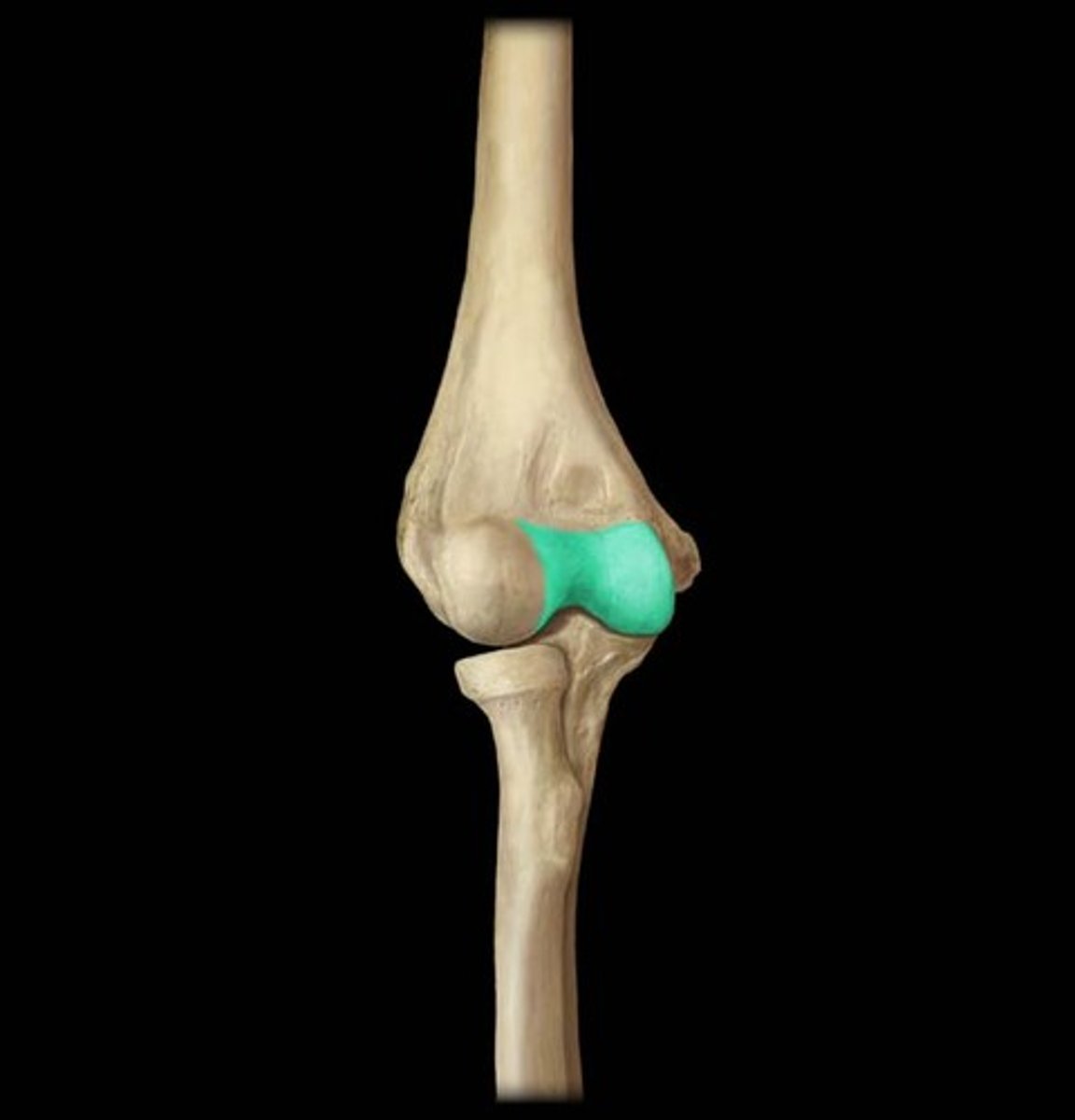
Trochlea of the humerus
large area medial to the ridge of the humeral condyle
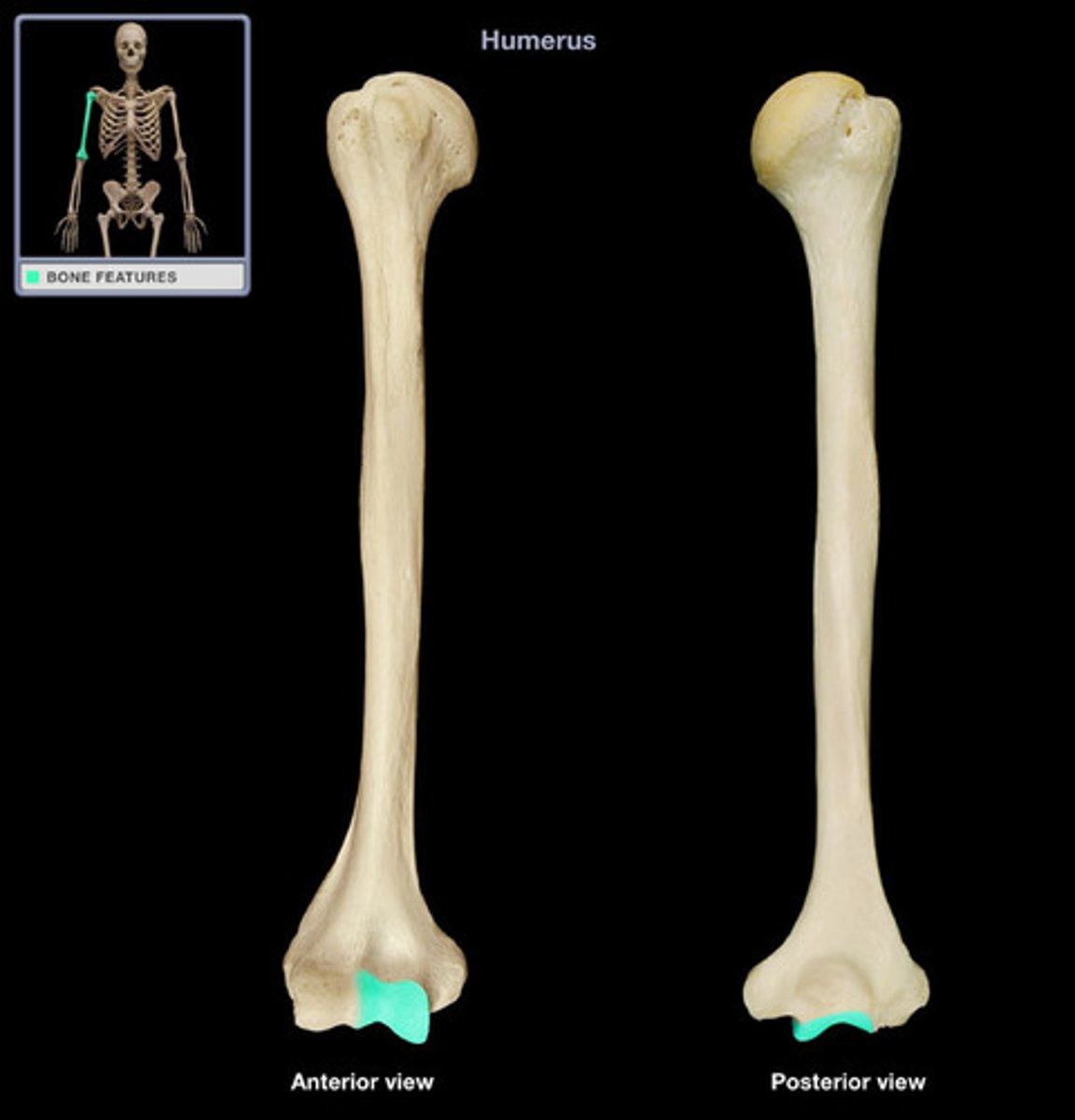
capitulum
small articular area lateral to the ridge of the humeral condyle
lateral epicondyle
part of humerus proximal to capitulum
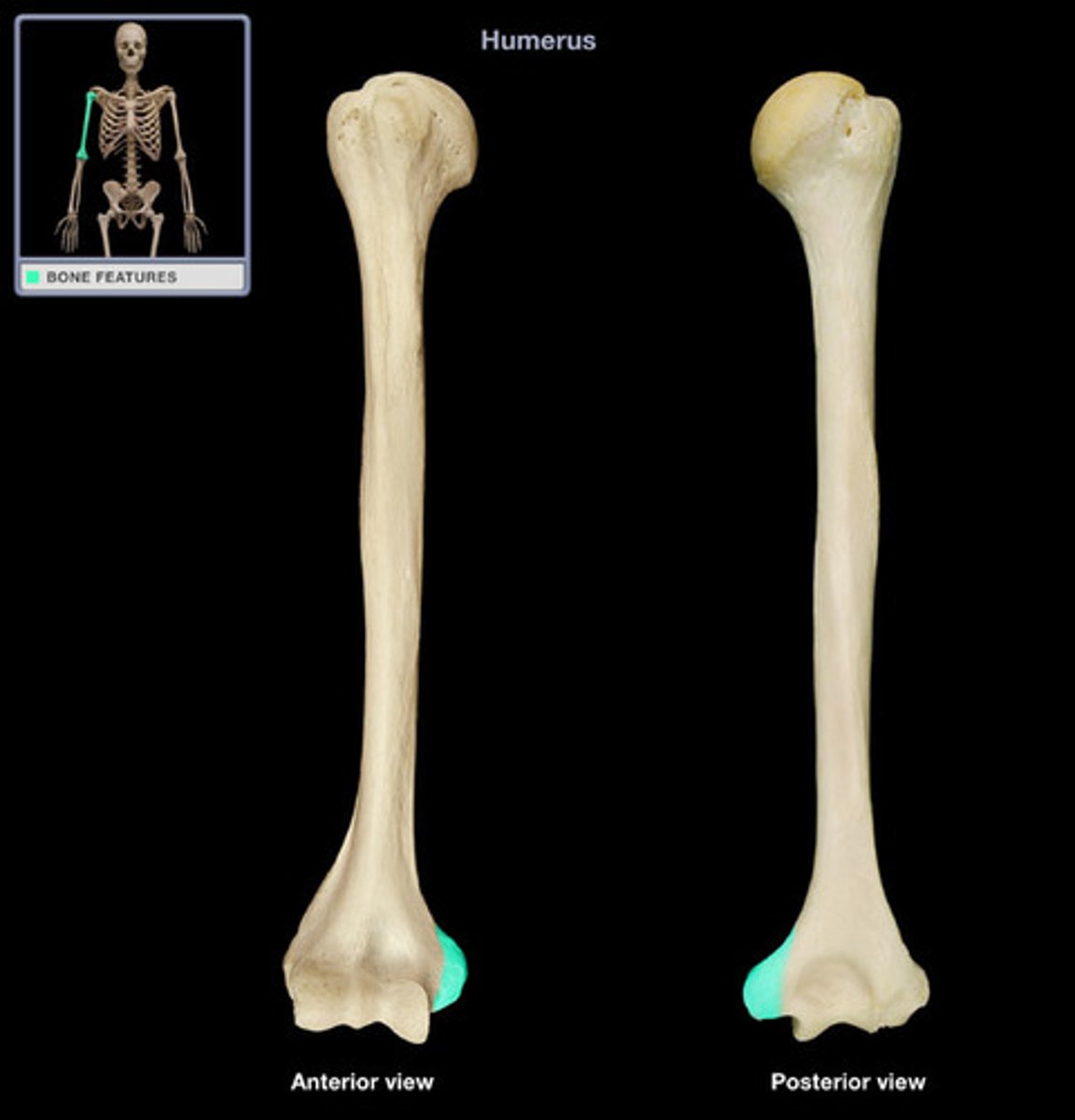
medial epicondyle
the enlarged, distomedial end of the humerus proximal to the trochlea
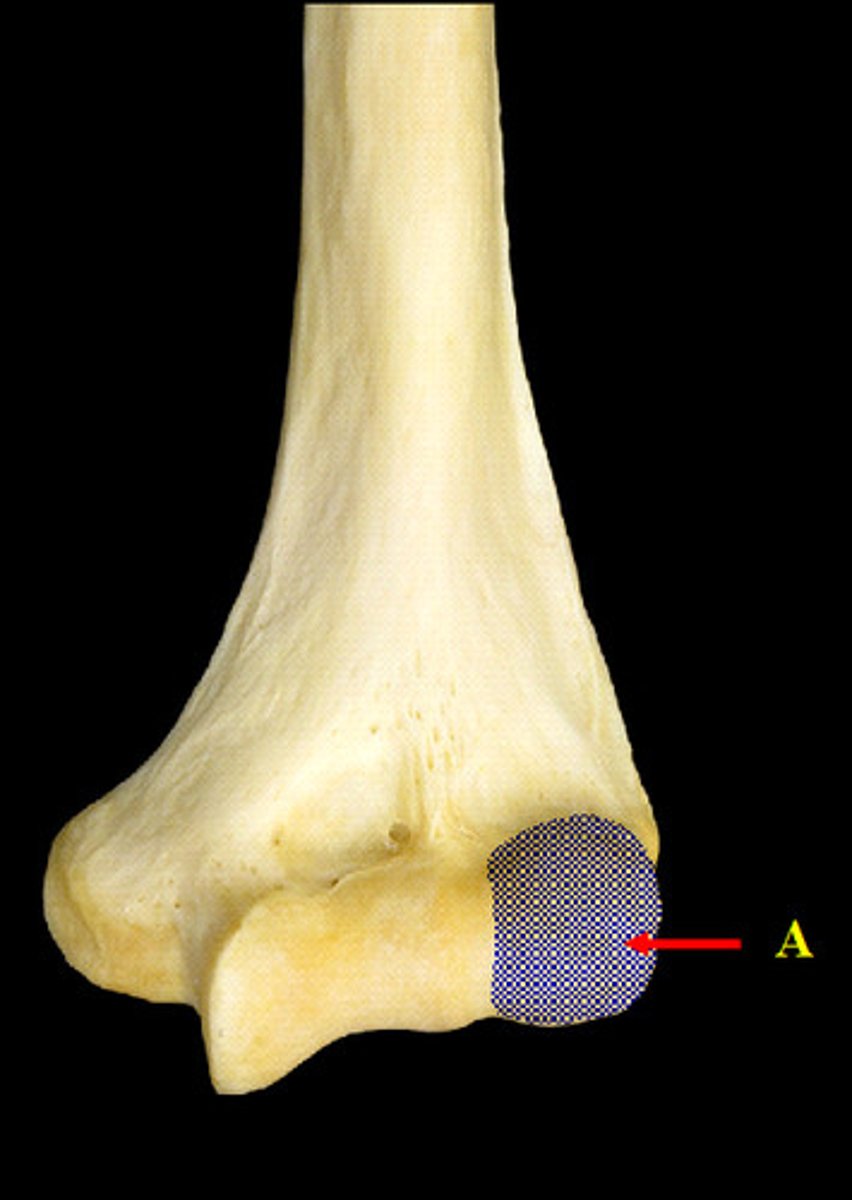
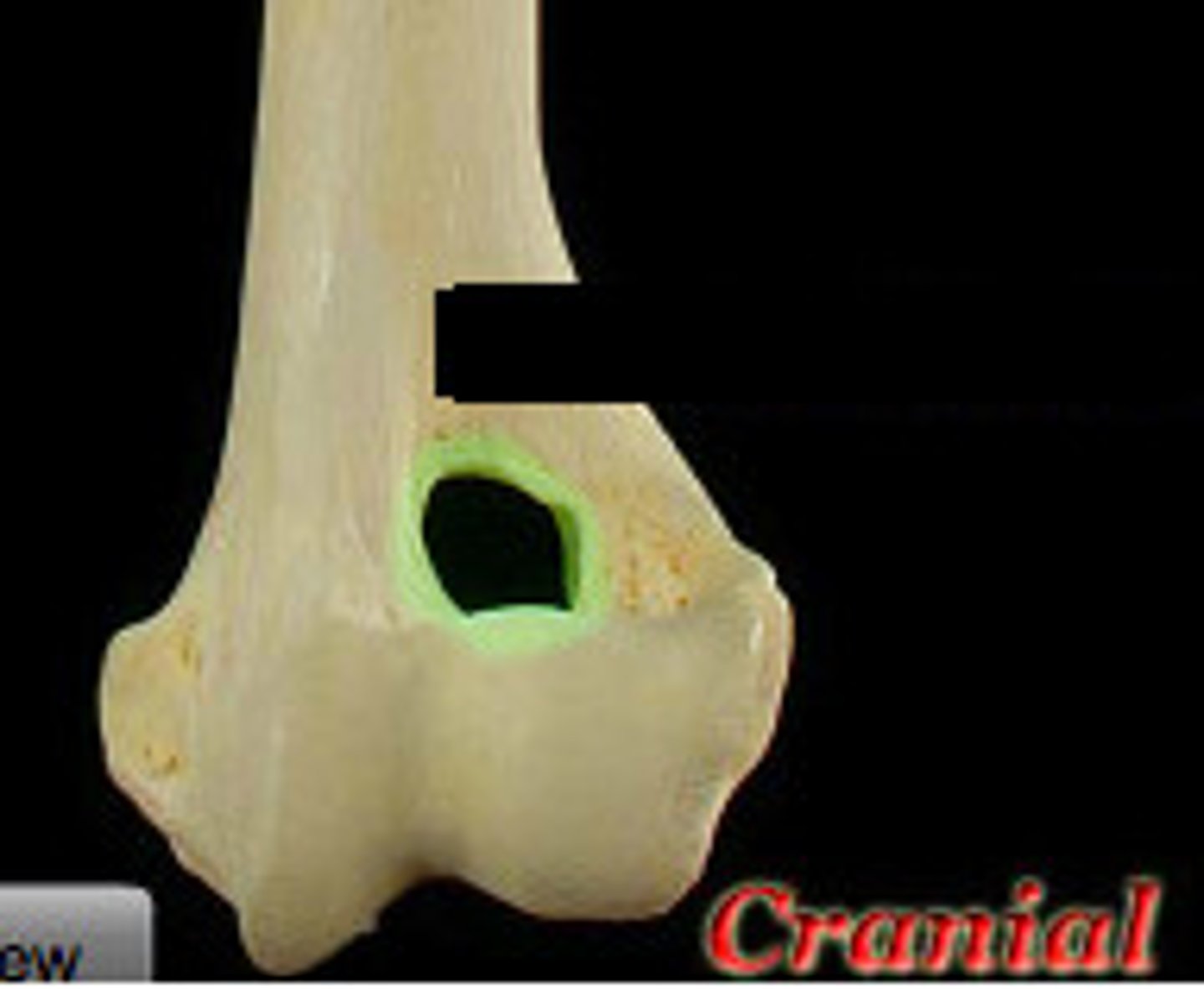
olecranon fossa
deep excavation of the caudal part of the humeral condyle. during extension of the elbow, the anconeal process of the ulna fits into this
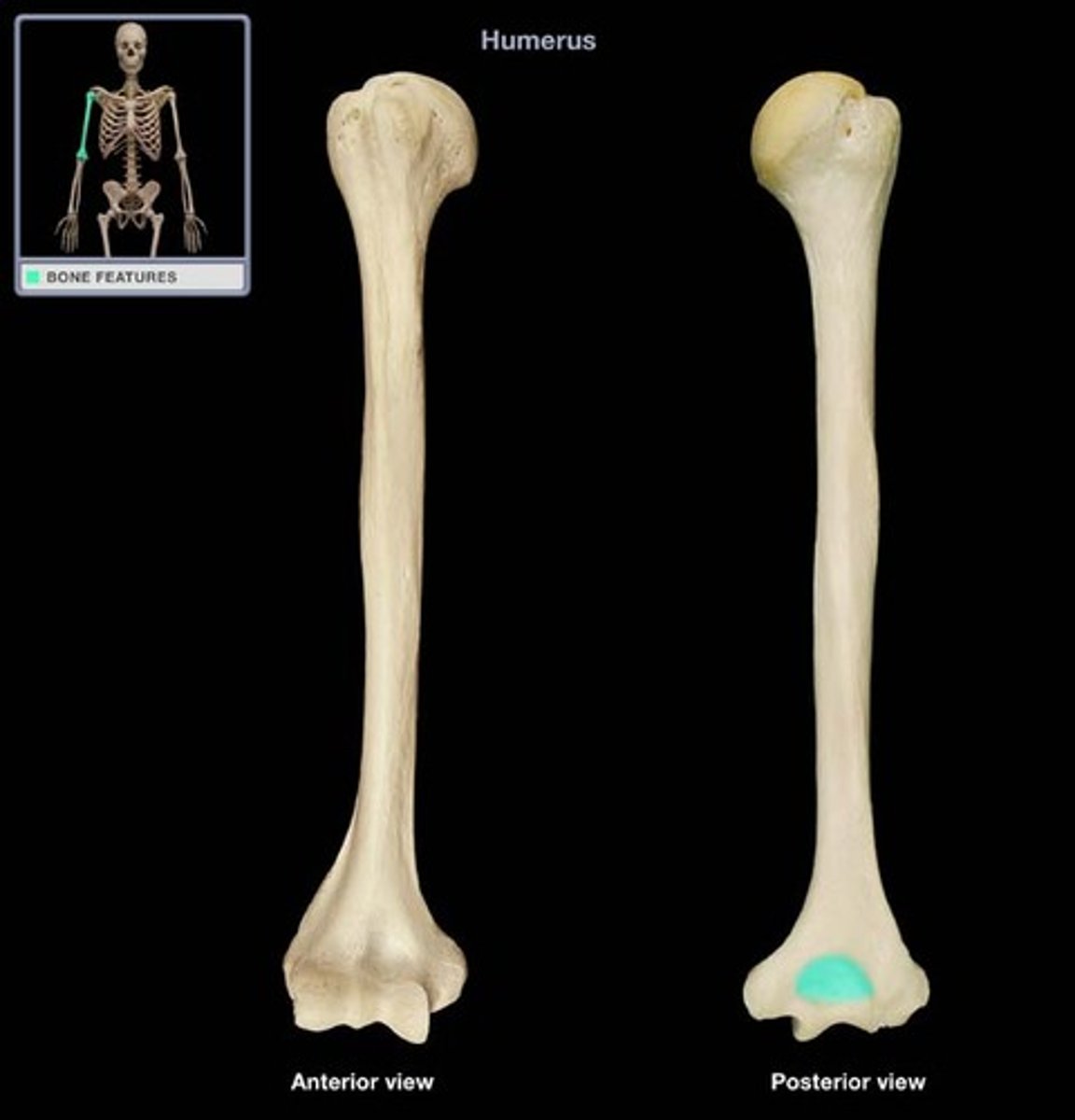
radial fossa of humerus
depression on the cranial surface of the humeral condyle
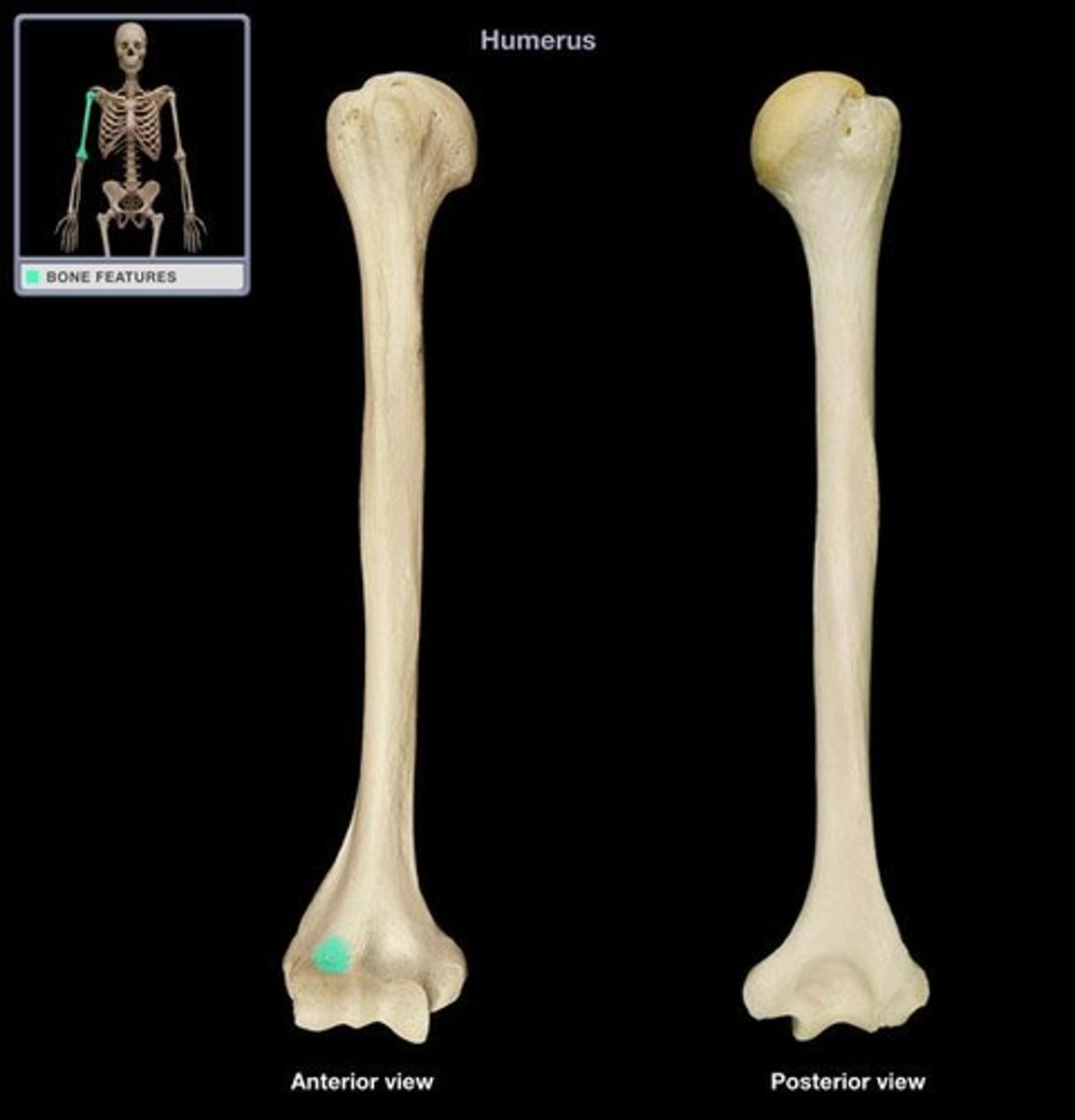
supratrochlear foramen
hole in humerus in which the radial fossa and the olecranon fossa communicate
pronation
turning downward
supination
movement that turns the paw up
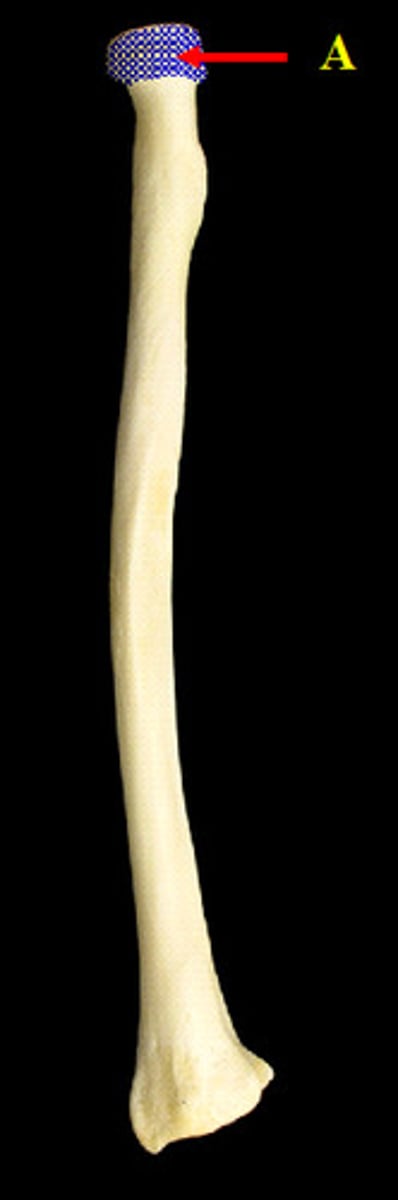
radius
shorter bone of the antebrachium
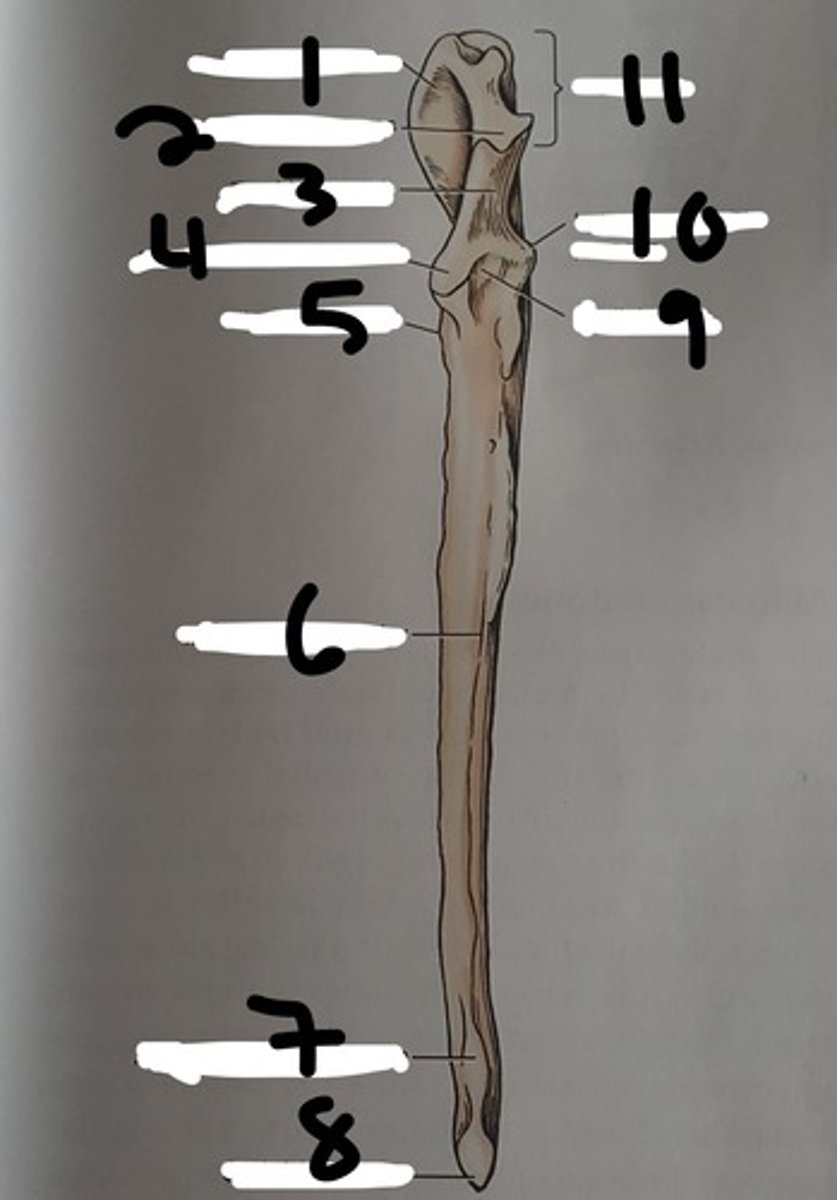
head of radius
most proximal portion of the radius that forms the fovea capitis
fovea capitis
part of the head of the radius that articulates with the capitulum of the humerus
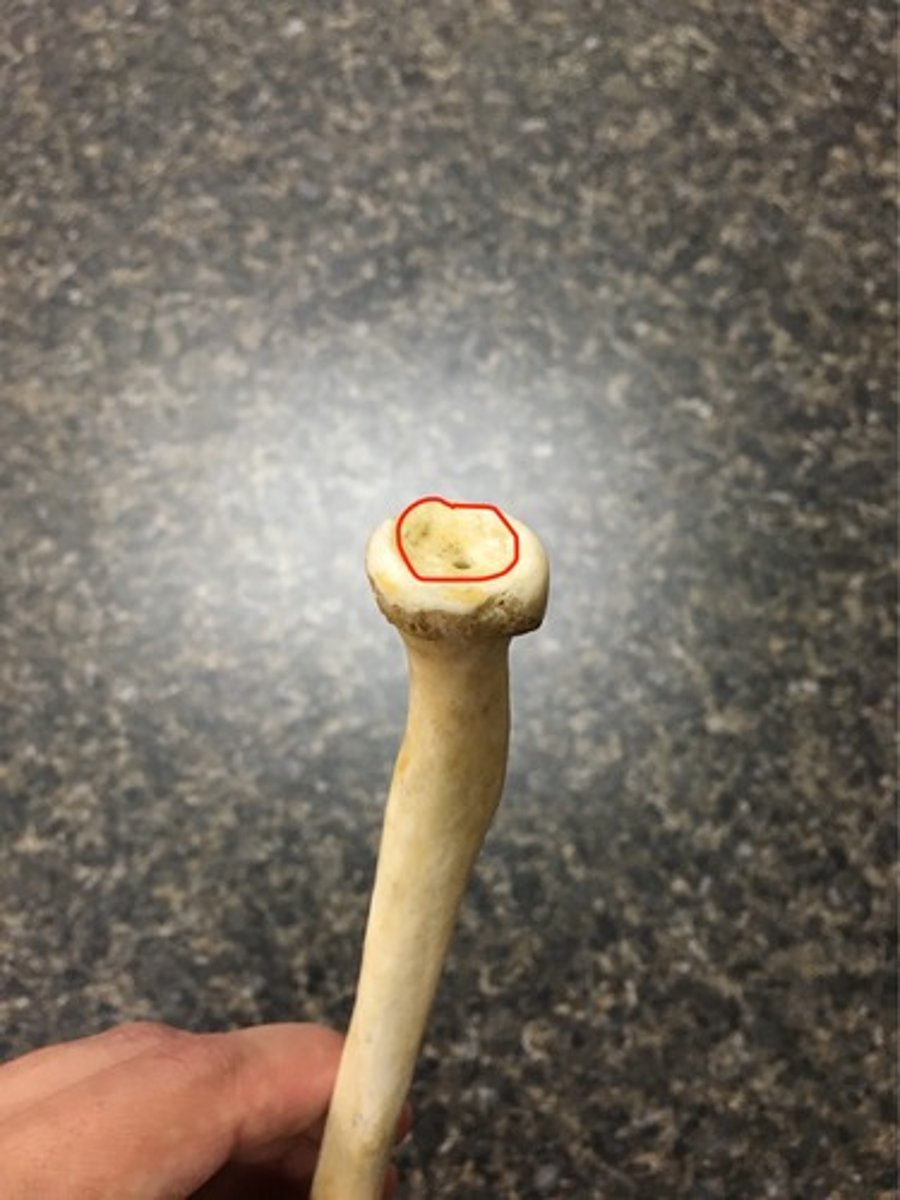
articular circumference of radius
the smooth caudal border of the head of the radius that articulates with the radial notch of the ulna
radial tuberosity
small part of the radius that lies distal to the neck on the medial border
body of the radius
the compressed part of the radius that has cranial and caudal surfaces and medial and lateral borders
trochlea of the radius
distal extremity of the radius
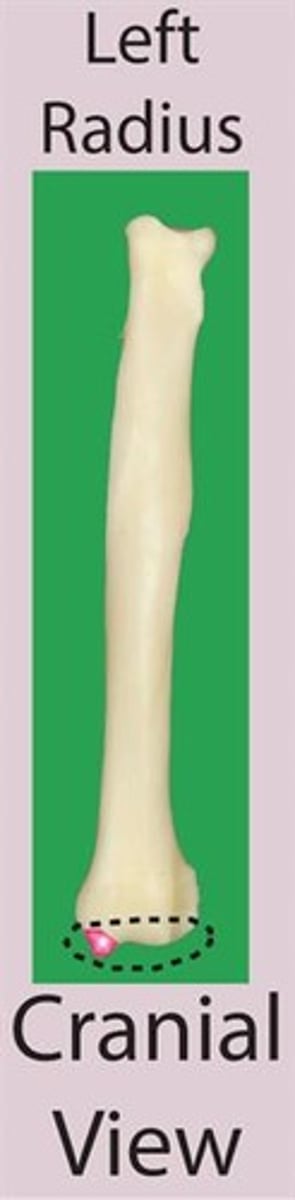
ulnar notch
the slightly concave area that articulates with the ulna. This sits on the lateral surface of the trochlea of the radius
styloid process of radius
the rounded projection on the medial surface of the trochlea of the radius
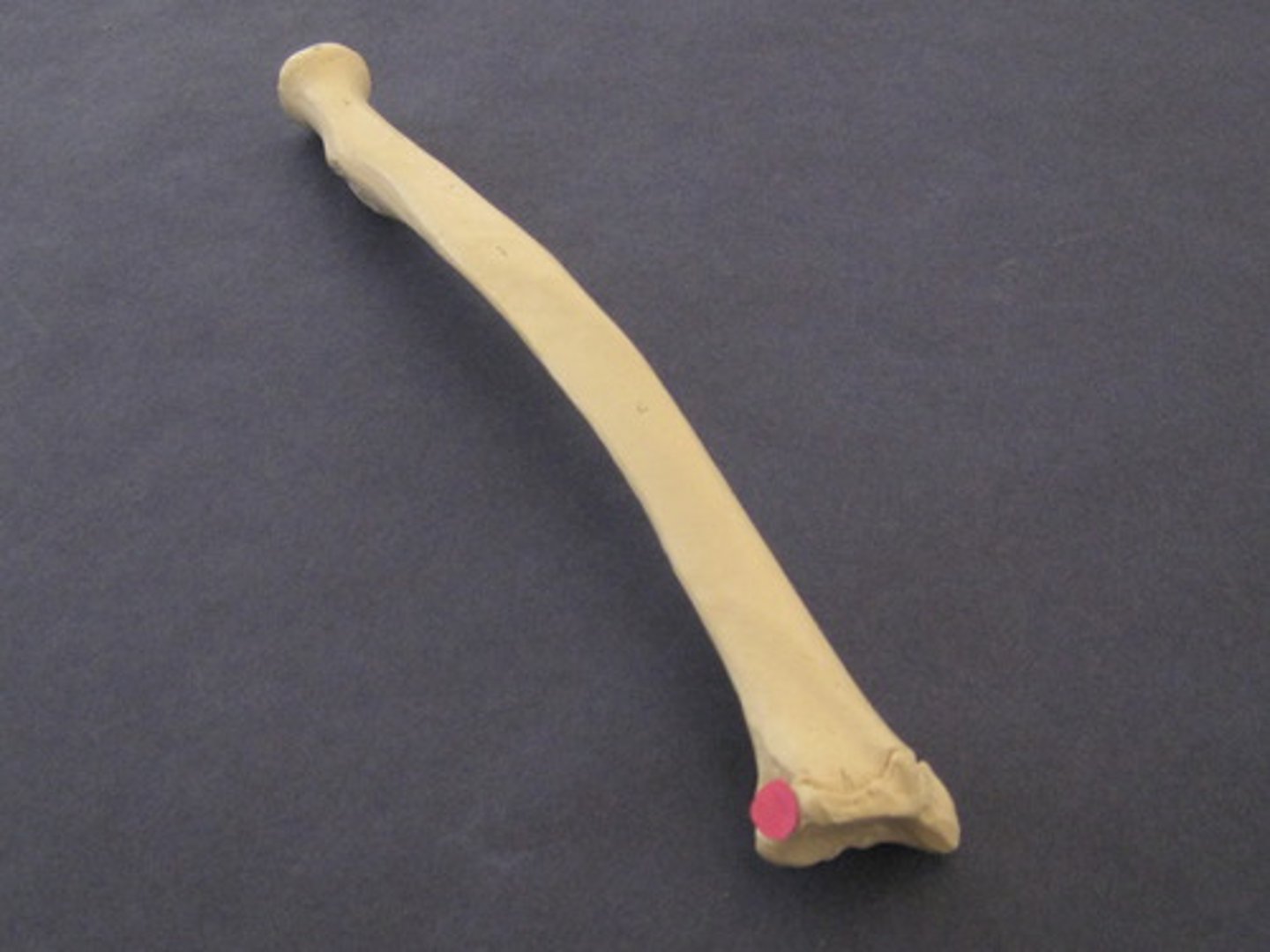
radial notch of the ulna
part of the ulna that articulates with the articular circumference of the radius
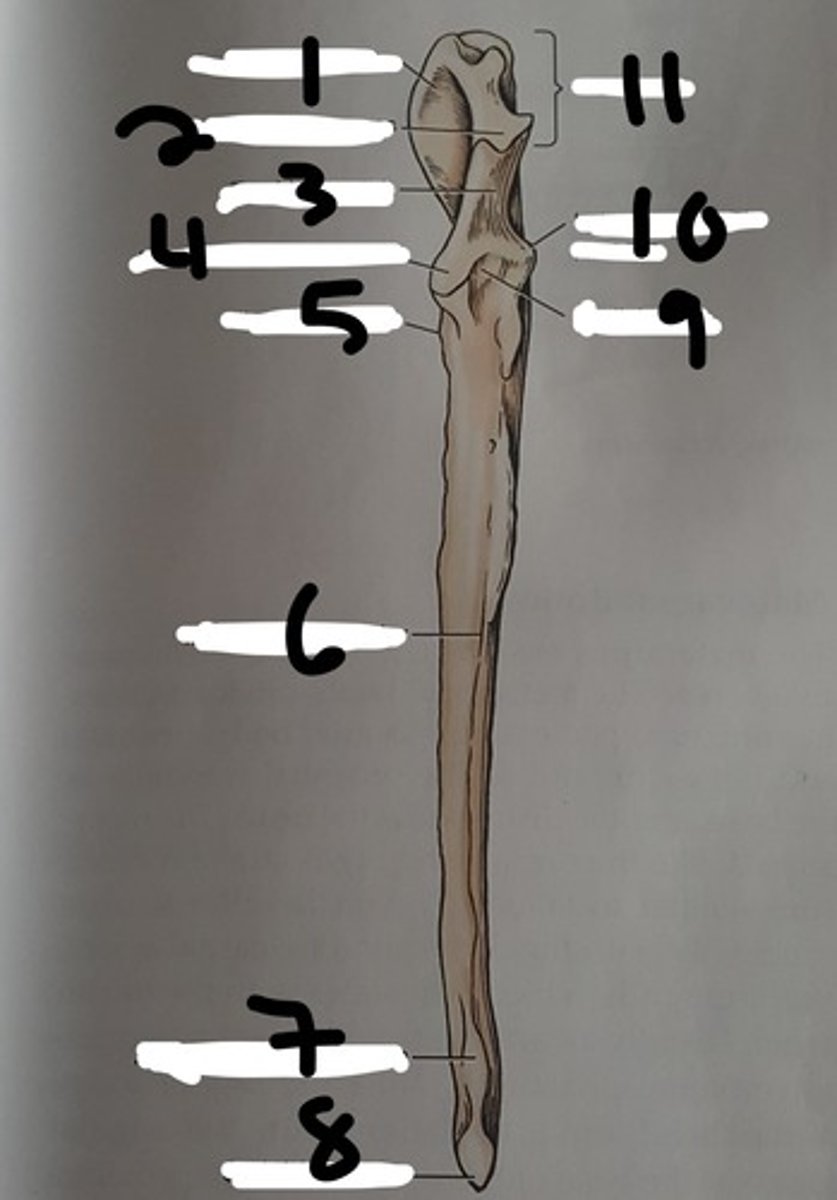
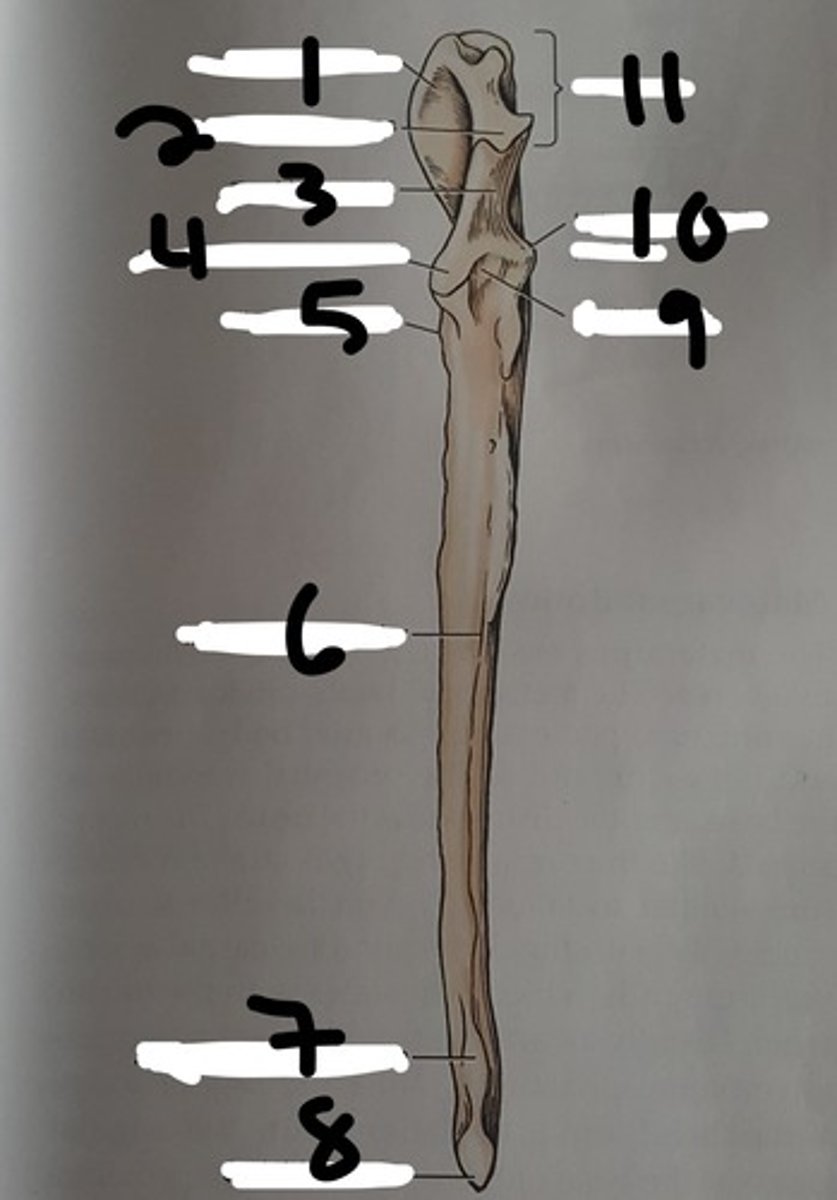
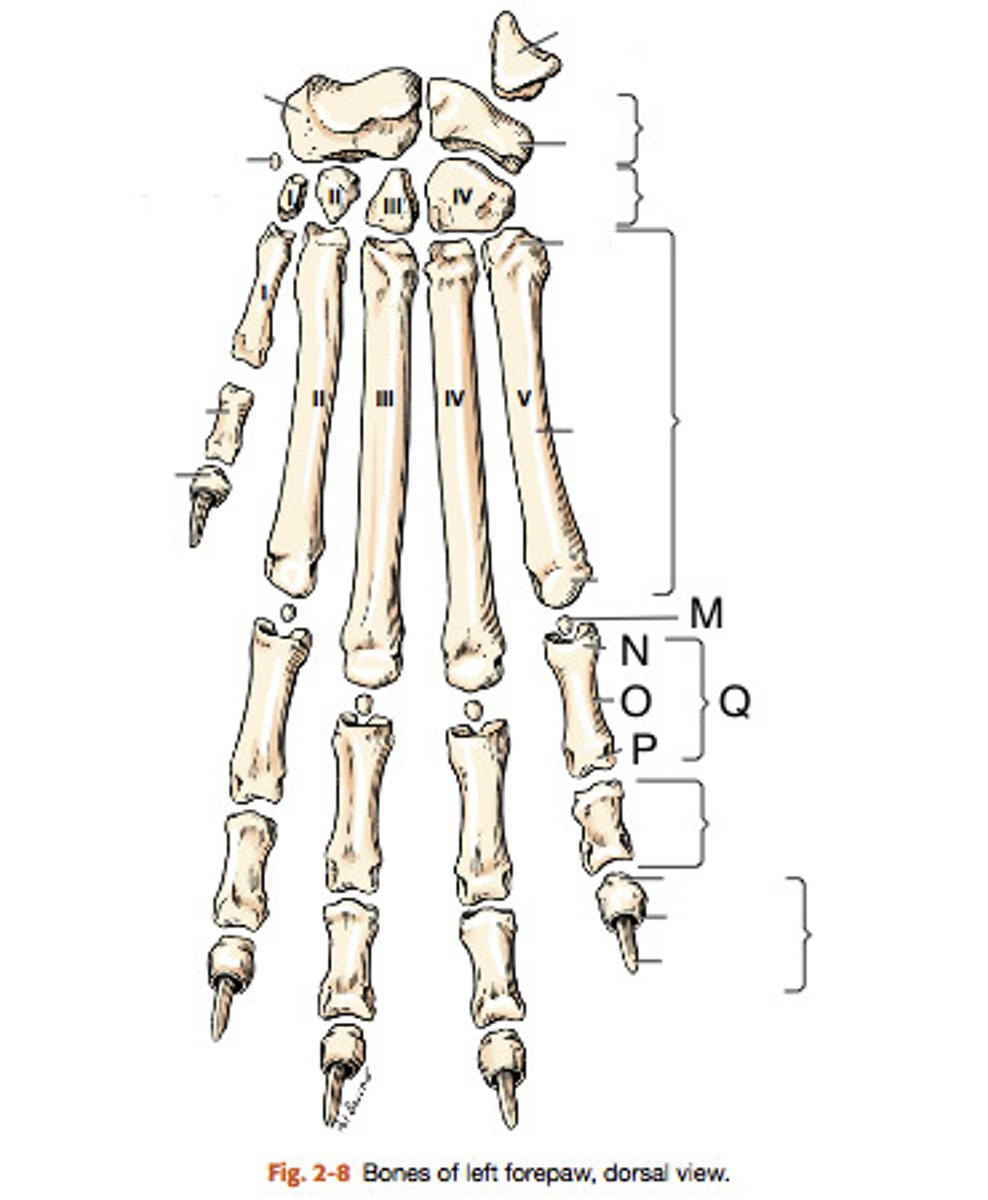
(#9)
olecranon of the ulna
"elbow head"
the proximal extremity of the ulna, which includes the olecranon tuber and anconeal process. Serves as lever arm for extensor muscles of the elbow
(#11)
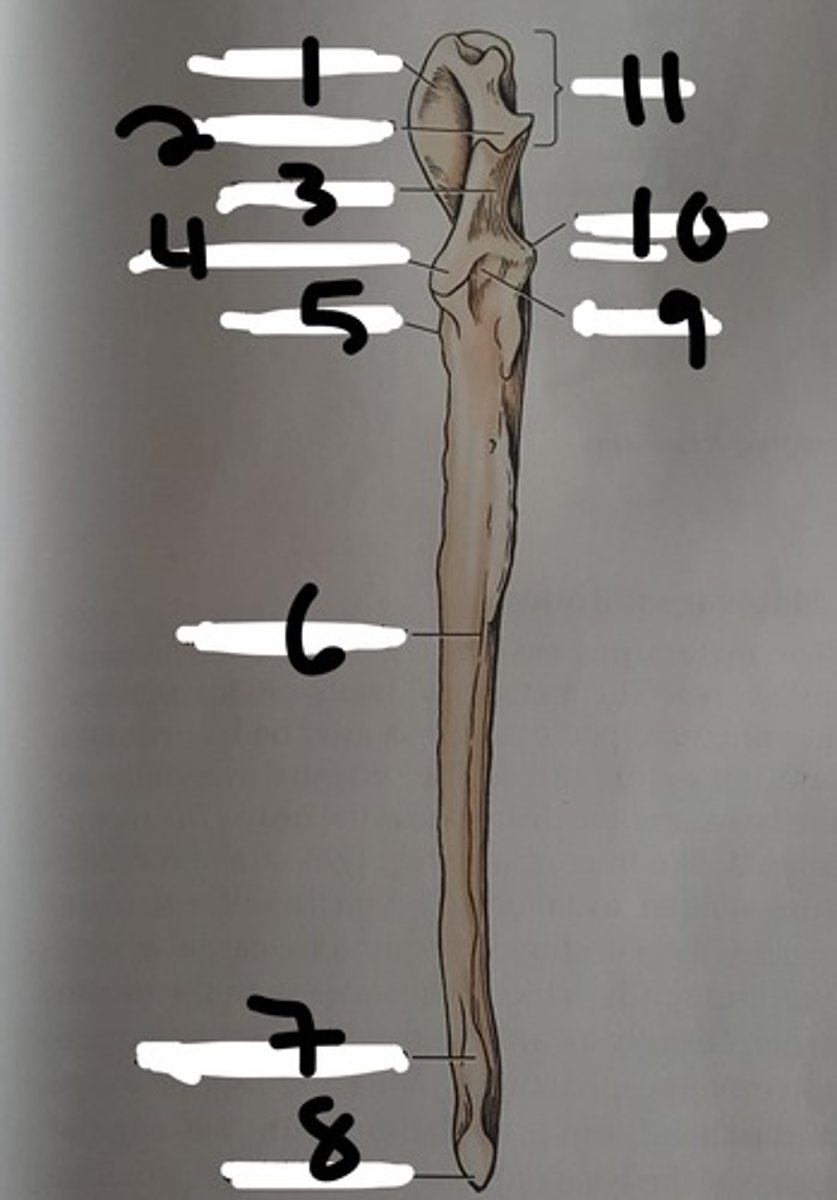
olecranon tuber
on the proximal end of the olecranon of the ulna; grooved cranially and rounded caudally
(B)
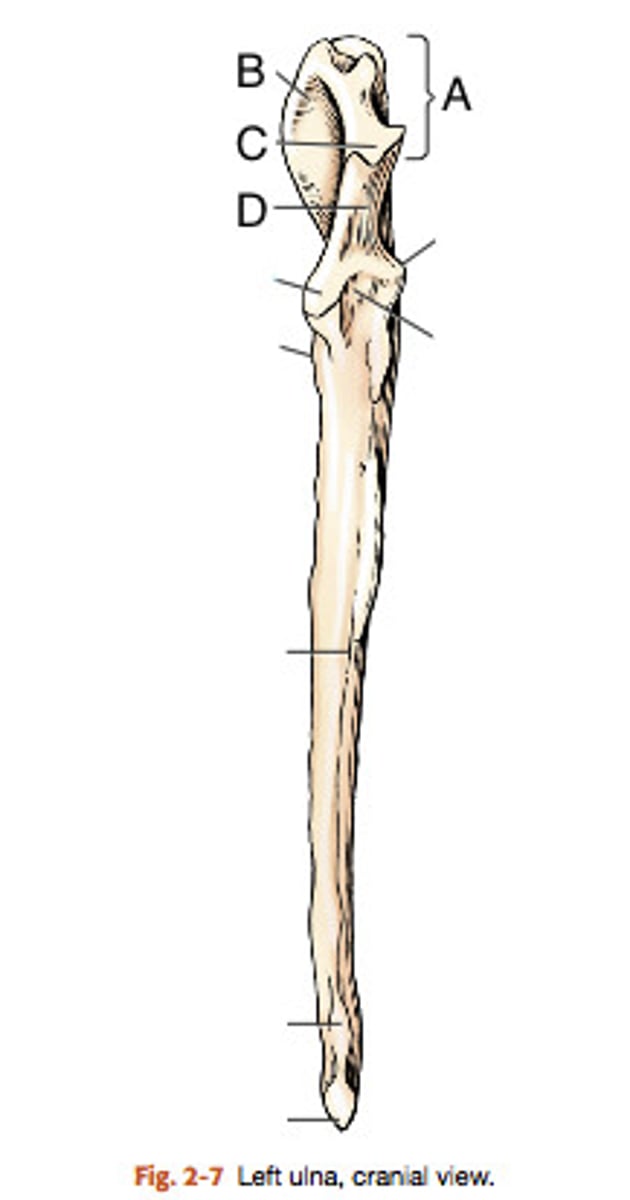
trochlear notch of ulna
smooth, vertical, half-mooned shape concavity facing cranially that articulates with the trochlea of the humerus
(#3)
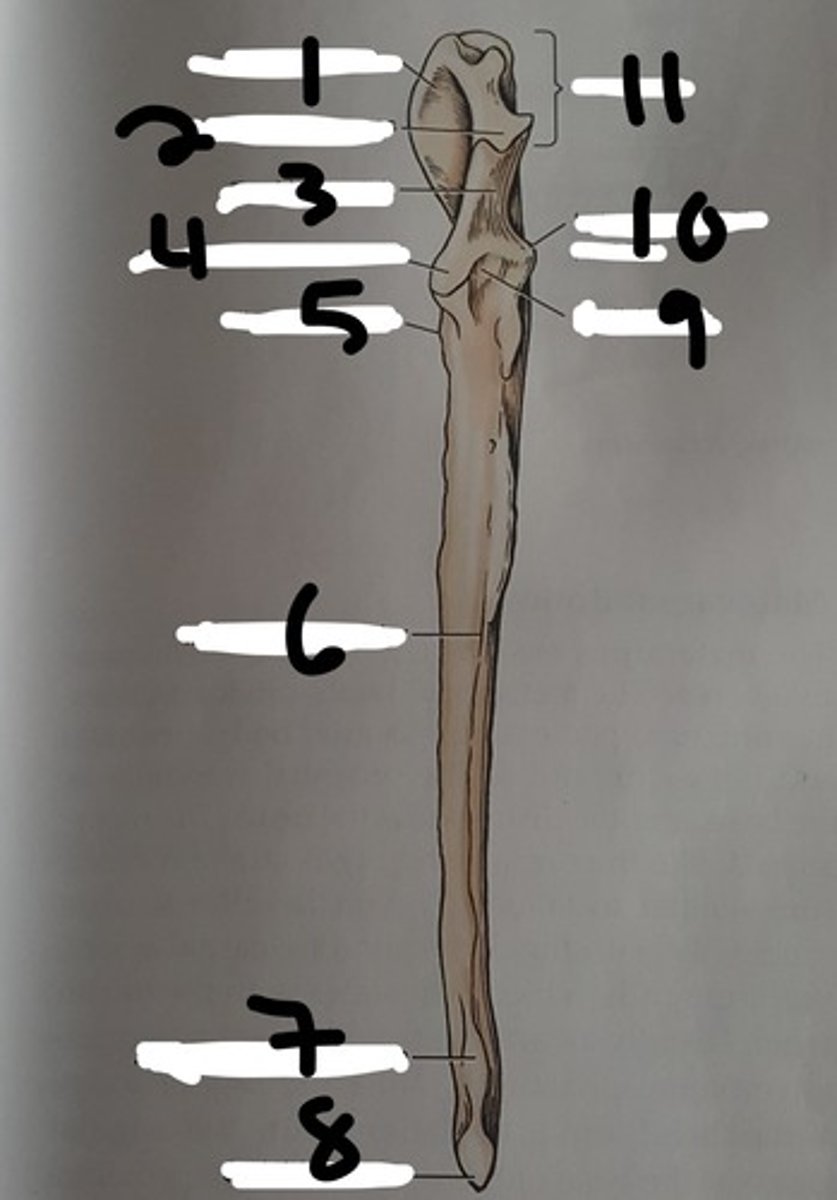
Anconeal process of ulna
sharp edged slightly hooked process on the proximal end of the trochlear notch. fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerous
(#4)
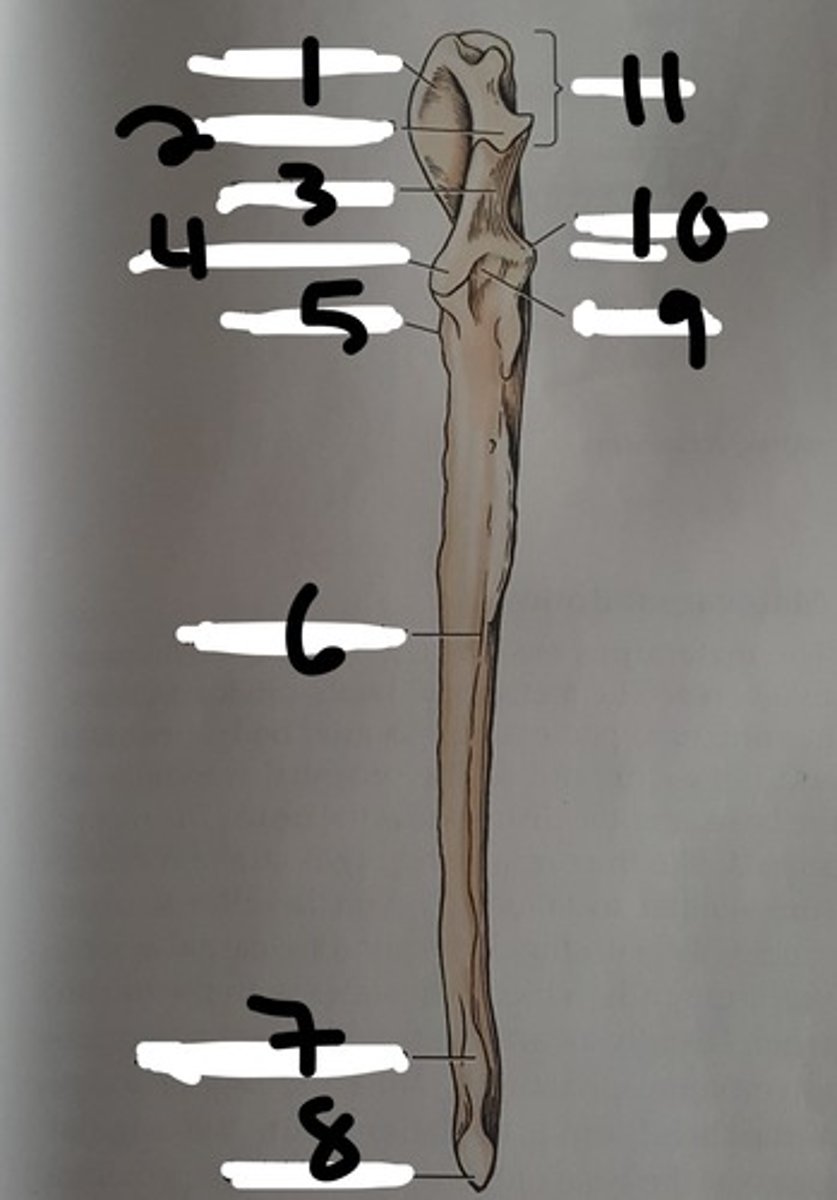
medial and lateral coronoid processes
at the distal end of the trochlear notch on the ulna; articulate with the humerus and radius. Medial is larger (in blue)
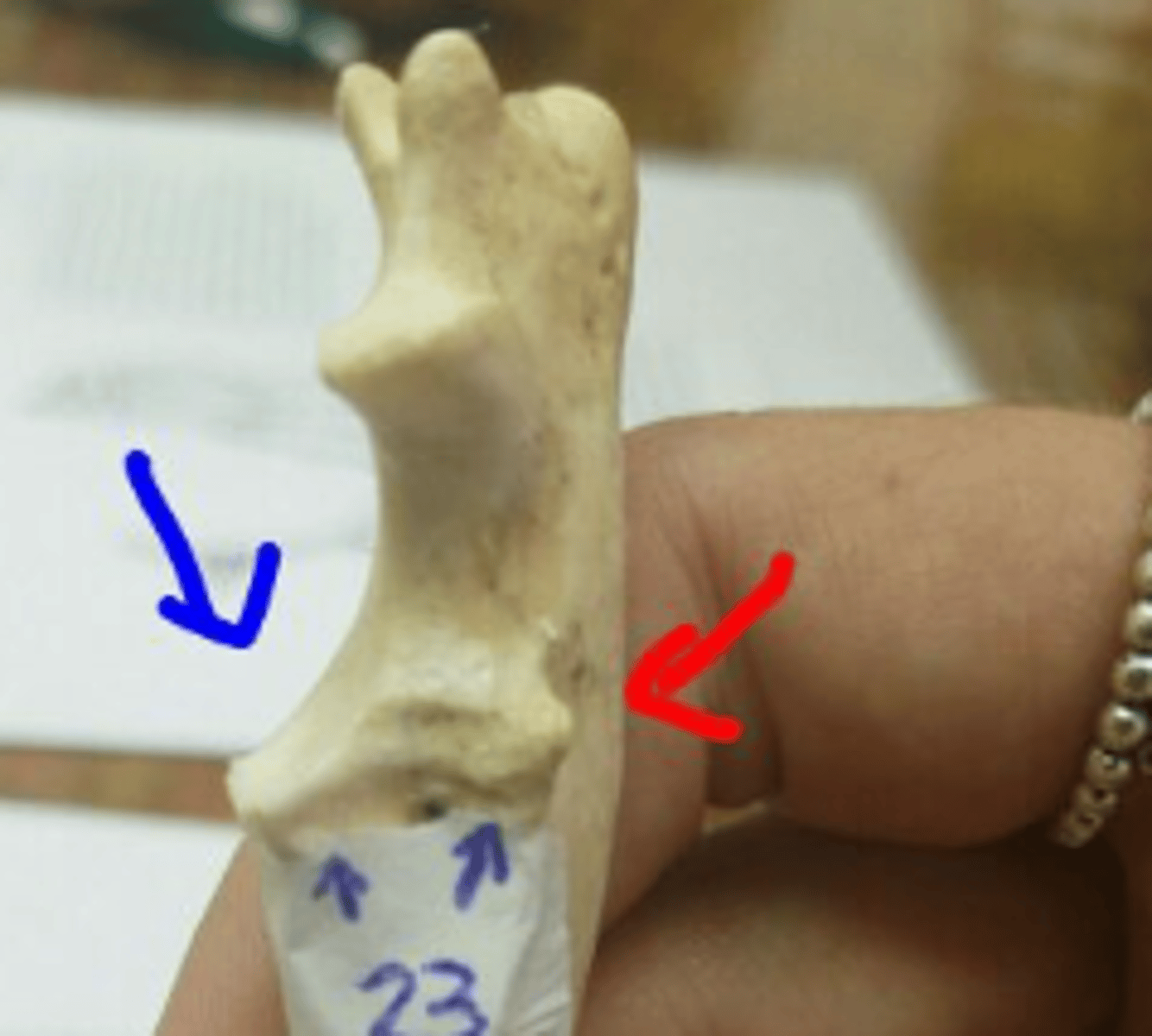
body of the ulna
three sided in its middle third (compresses laterally), long and slender and tapers distally, losing its borders
ulnar tuberosity
small, elongated eminence on the medial surface of the proximal end of the ulna; point of insertion for the biceps brachii and brachialis
(#5)
interosseous border of ulna
a distinct, rough, irregular border of the ulna where an expansive but low eminence is found. This eminence is the place of articulation with the radius by a heavy ligament
styloid process of ulna
the distal extremity of the ulna. part of this articulates with the ulnar accessory carpal bones. The head of this articulates medially with the radius
(#8)
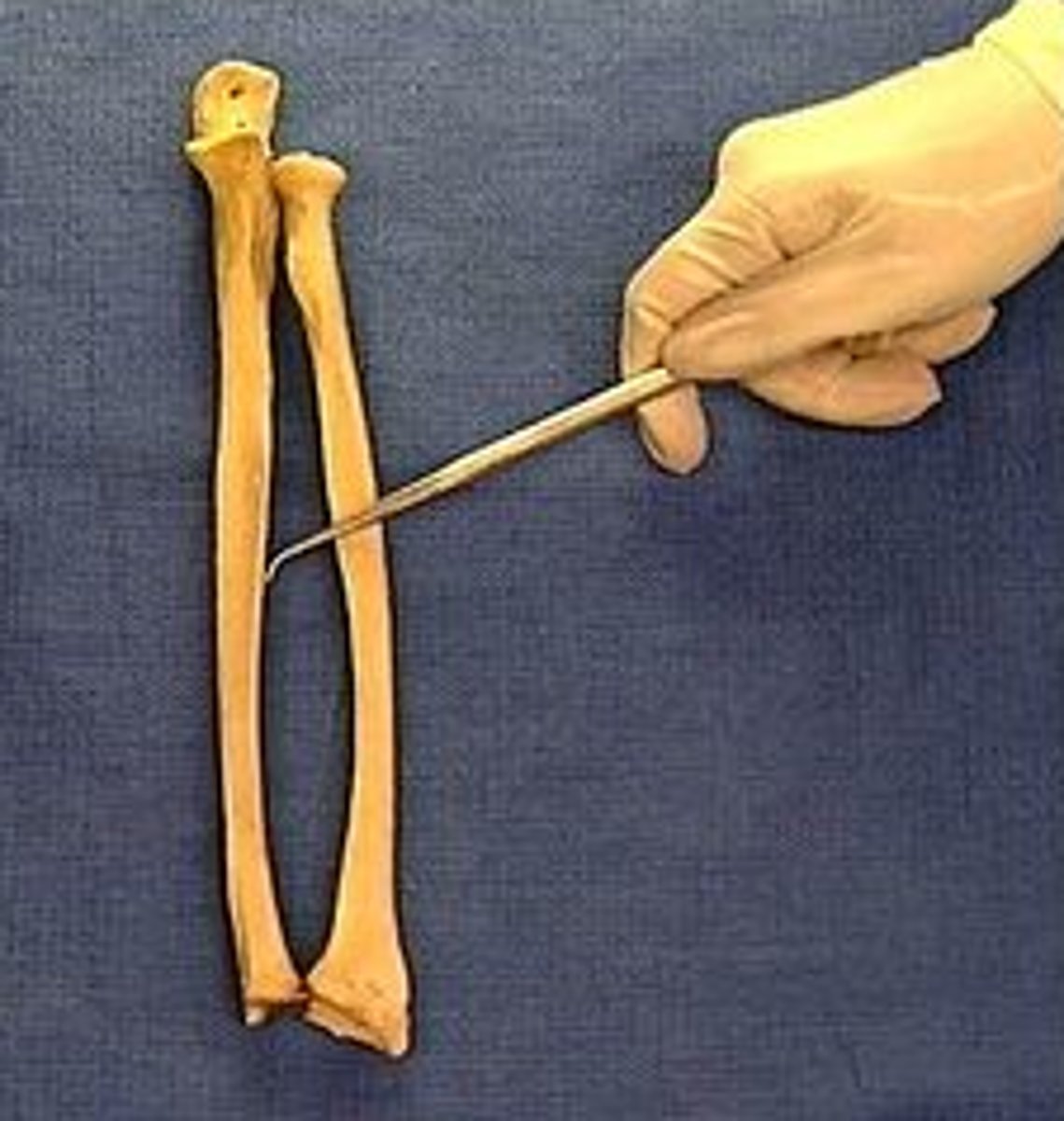
list the three proximal carpal bones
intermedioradial carpal, ulnar carpal, and accessory carpal
Intermedioradial carpal bone
carpal bone on medial side and articulates proximally with the radius
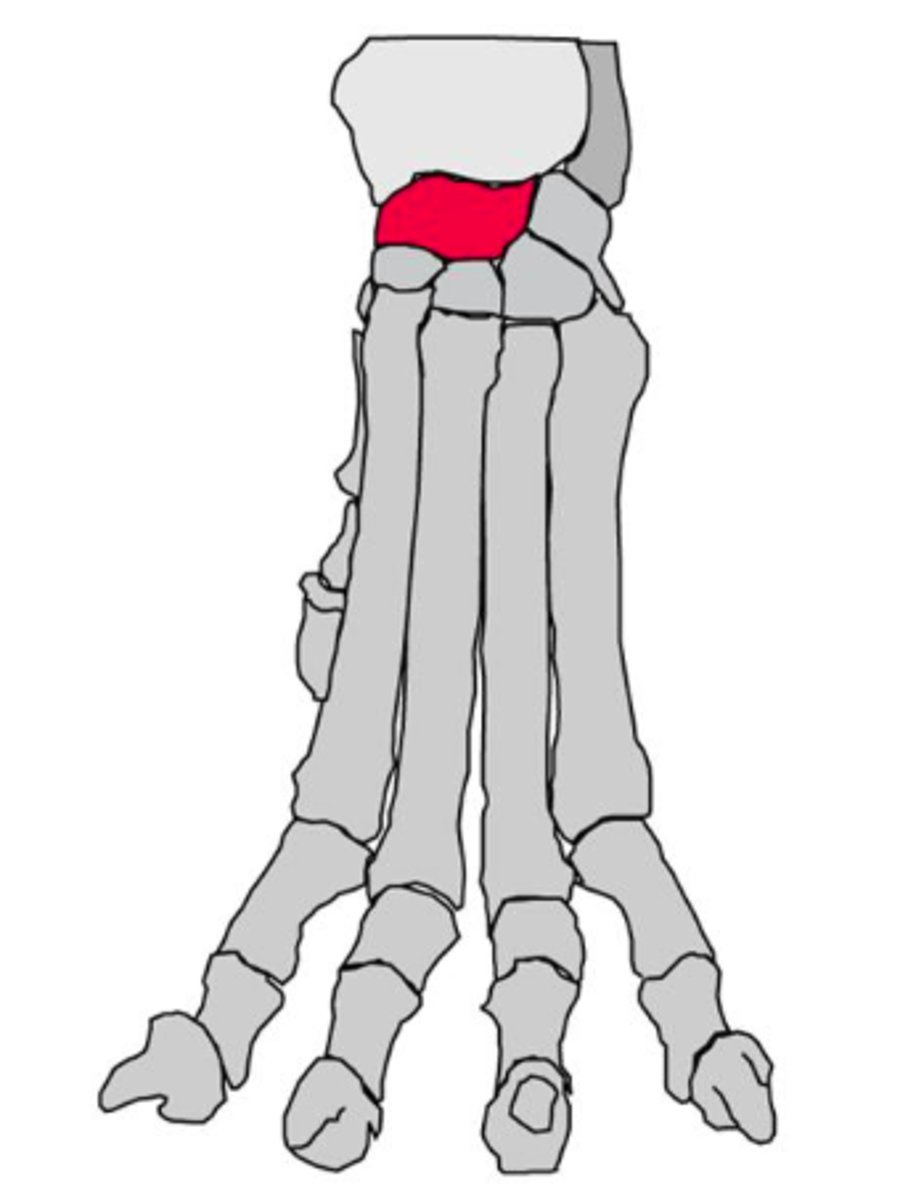
ulnar carpal bone
the lateral carpal bone of the proximal row
accessory carpal bone
a short rod of a bone that articulates proximally with the styloid process of the ulna. the ulnaris lateralis and flexor carpi ulnaris attach to this bone
list the bones in the distal carpal row
1st (smallest) to 4th
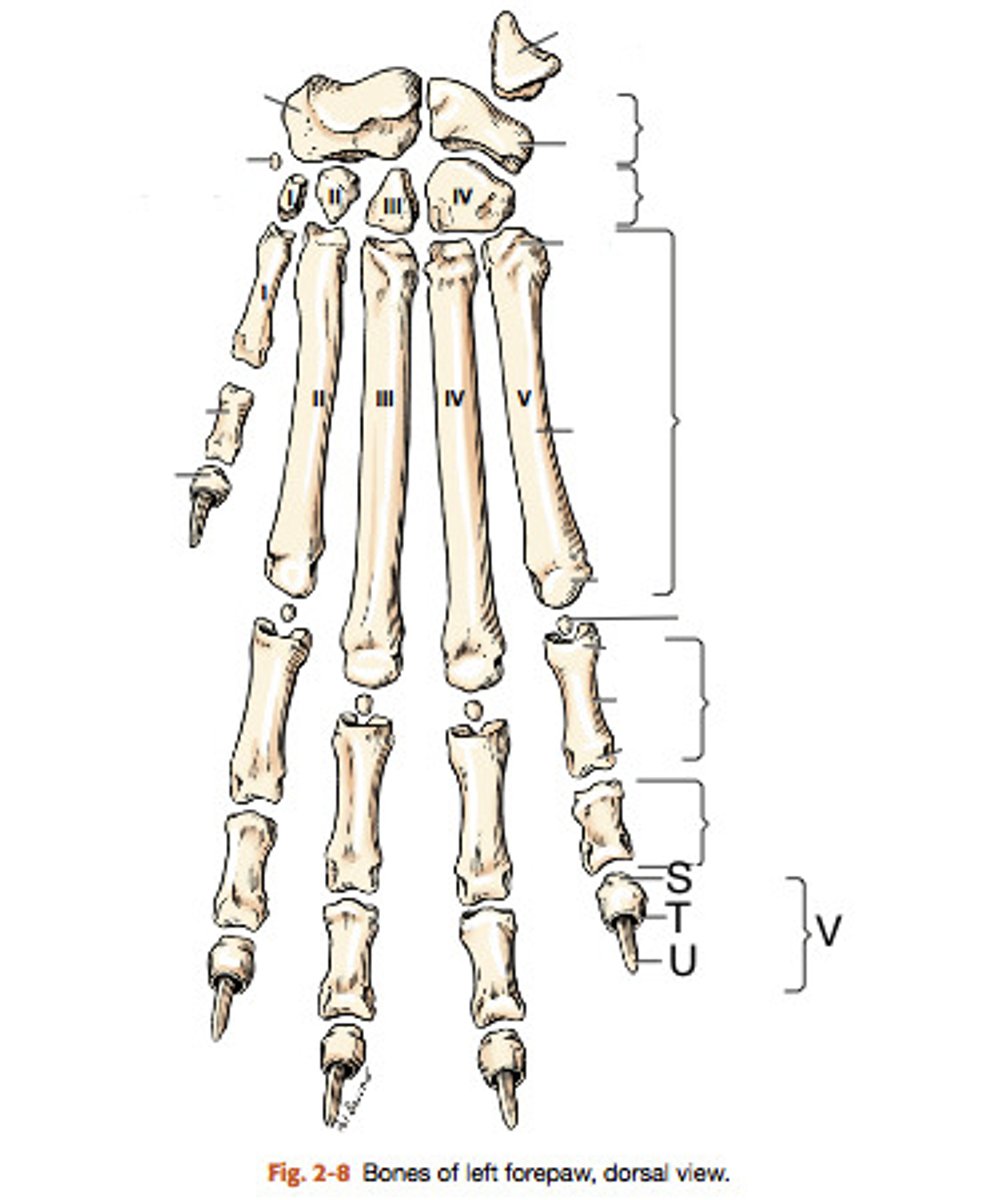
metacarpus
contains 5 long bones; distal to the carpus
-consist of a slender body, the proximal base, and the distal head
-numbered medial to lateral 1-5
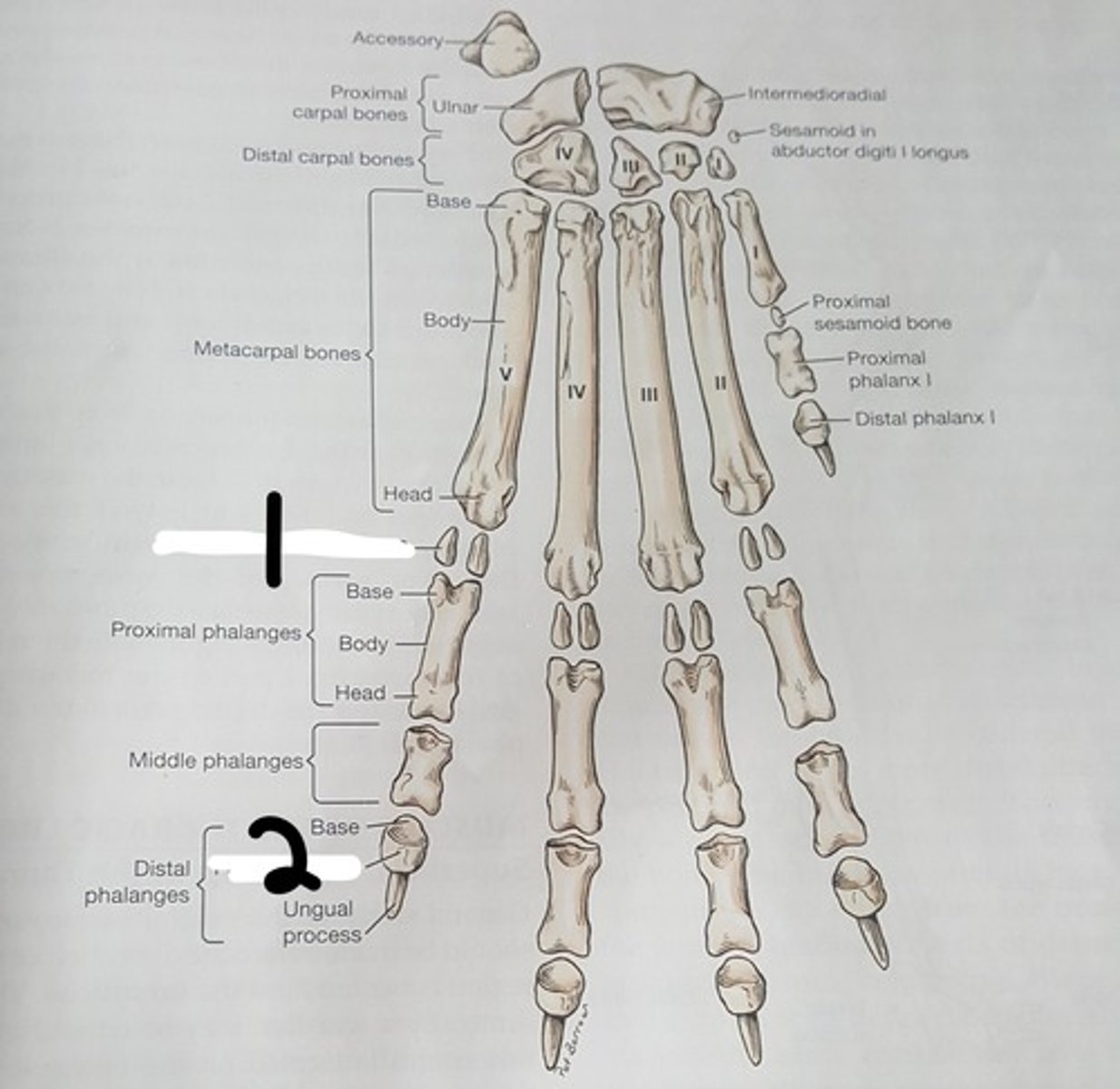
phalanges of the forepaw
consist of three of these bones for the four main digits.
The 1st of these has only two (dewclaw).
-each has a proximal base, a body, and a distal head
ungual crest
a think shelf of bone on the distal phalanx that overlaps the claw and forms a band of bone around the claw
(T)
ungual process
a curved conical extension of the disatal phalanx into the claw
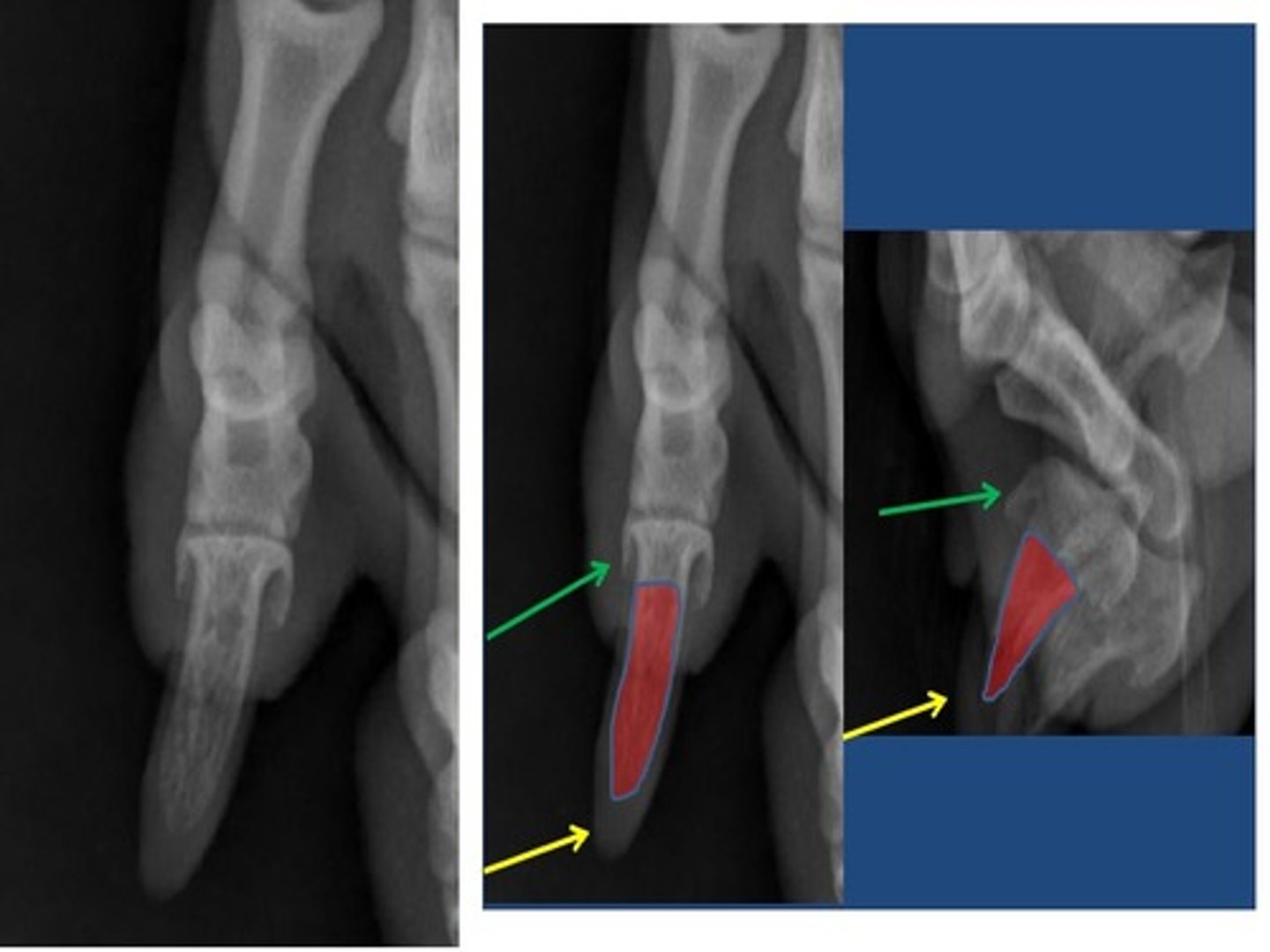
extensor process
rounded, dorsal part of the base on which the common extensor tendon is inserted
flexor tubercle
small process on the palmar surface for insertion of the deep digital flexor tendon (#2)
proximal sesamoid bones
paired bones located in the interosseous tendons on the palmar surface of each metacarpophalangeal joints (digits 2-5)
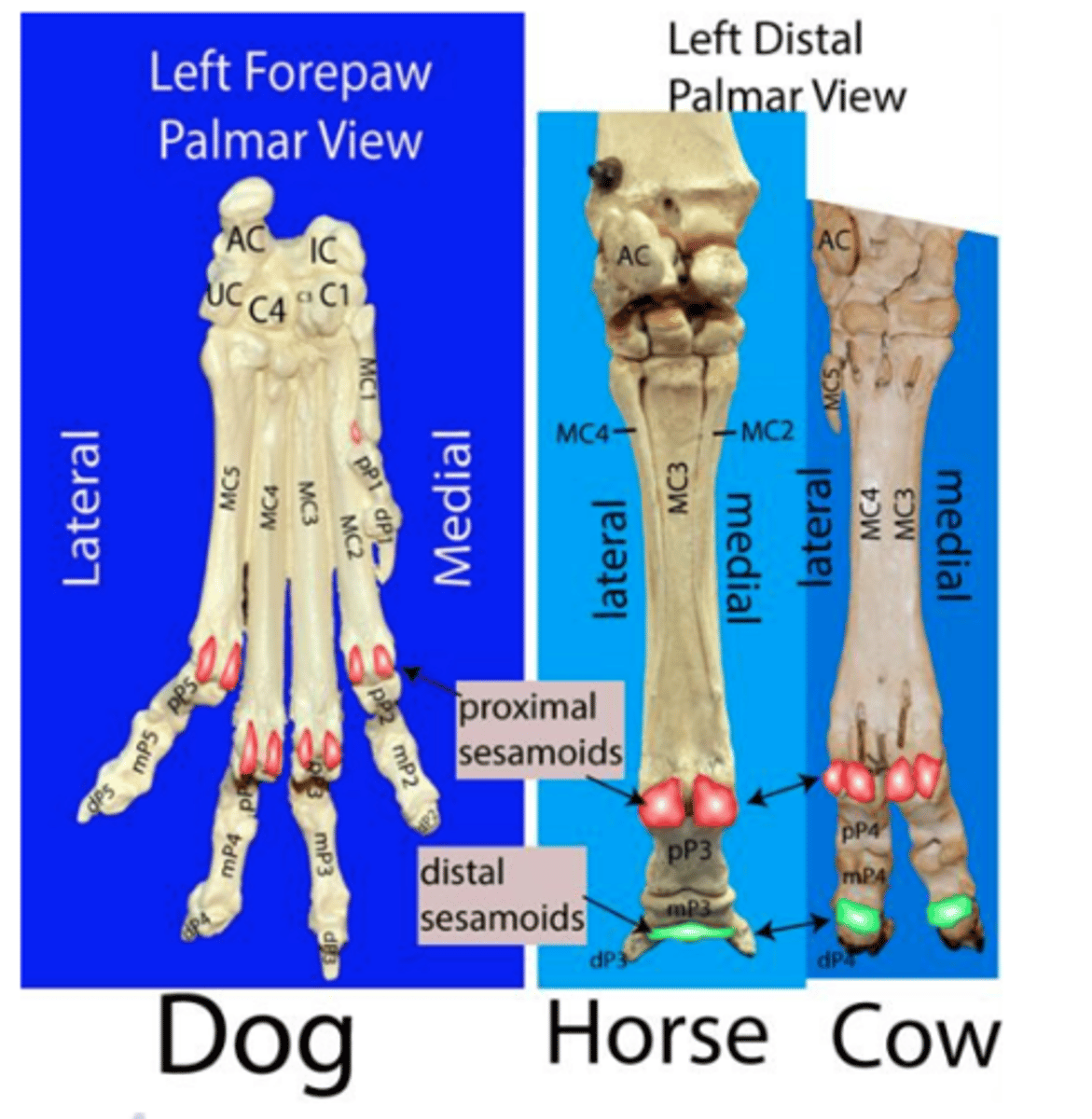
dorsal sesamoid bones
four small bones embedded in the common digital extensor tendons
(M)
humeral joint
ball and socket joint between glenoid cavity and head of humerus
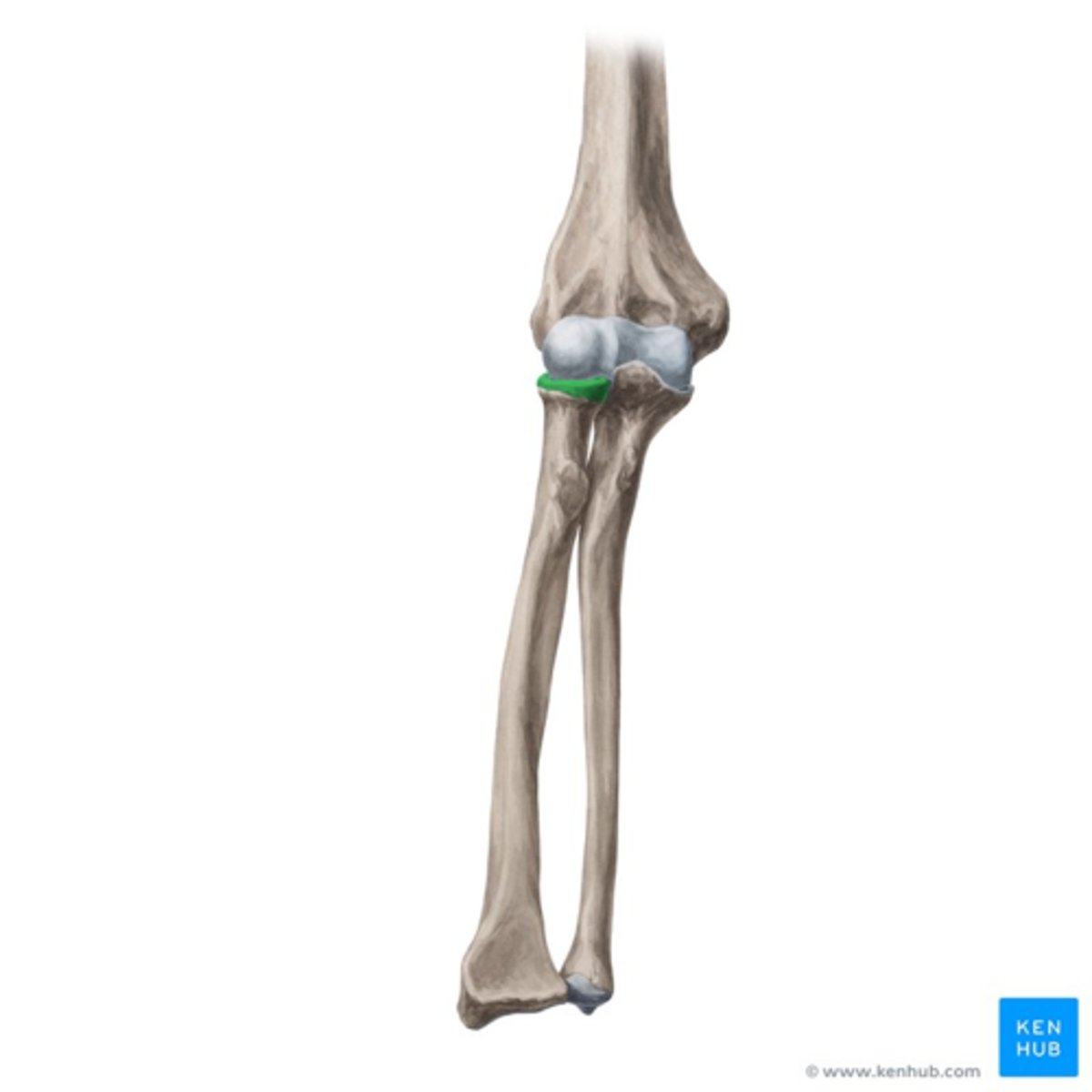
elbow joint
the hinge joint formed by the condyle of the humerus, the head of the radius, and the trochlear notch of the ulna
antebrachiocarpal joint
most proximal of the carpal joints, between the radius and the ulna with the intermedioradial and ulnar carpal bones
middle carpal joint
joint between the two rows of carpal bones
carpometacarpal joint
between distal row of carpal bones and metacarpal bones
metacarpophlangeal joint
joint between metacarpals and proximal phalanges
proximal interphalangeal joint
the most proximal of the two interphalangeal joints
distal interphalangeal joint
the distal interphalangeal joint
umbilicus
a flat or slightly raised scar located on the mid ventral line. serves as a landmark in abdominal surgery
regional mammae
10 glands total: consist of the thoracic mammae (4), abdominal mammae (4), and inguinal mammae (2). Each mamma consist of a gland and a teat
costal arch
the costal cartilages of the 10th, 11th, and 12th ribs unite to form this structure.
superficial and deep fascia
fascia- a dense, regularly arranged thin layer of connective tissue
superficial- forms the deep portion of the subcutaneous tissue that covers the entire body
deep- more firmly attached to its enclosed muscle
Cutaneus trunci
a thin sheet of muscle that covers most of the dorsal, lateral, and ventral walls of the thorax and abdomen; the muscle that twitches the skin and sits right under the skin
extrinsic vs intrinsic muscles
extrinsic muscles attach the limb to the axial skeleton;
intrinsic muscle extend between the bones of the limb itself
list the 8 extrinsic muscles of the thoracic limb
1. superficial pectoral
2. deep pectoral
3. brachiocephalicus
4. omotransversarius
5. trapezius
6. rhomboideus
7. Latissimus dorsi
8. serratus ventralis
superficial pectoral
Origin: cranial sternum
Insertion: crest of the greater tubercle and cranial border of the humerus (and to medial brachial fascia in cats)
Action: adduct the thoracic limb
deep pectoral muscle
O: sternum
I: greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus
A: adduct the thoracic limb and pull it caudally
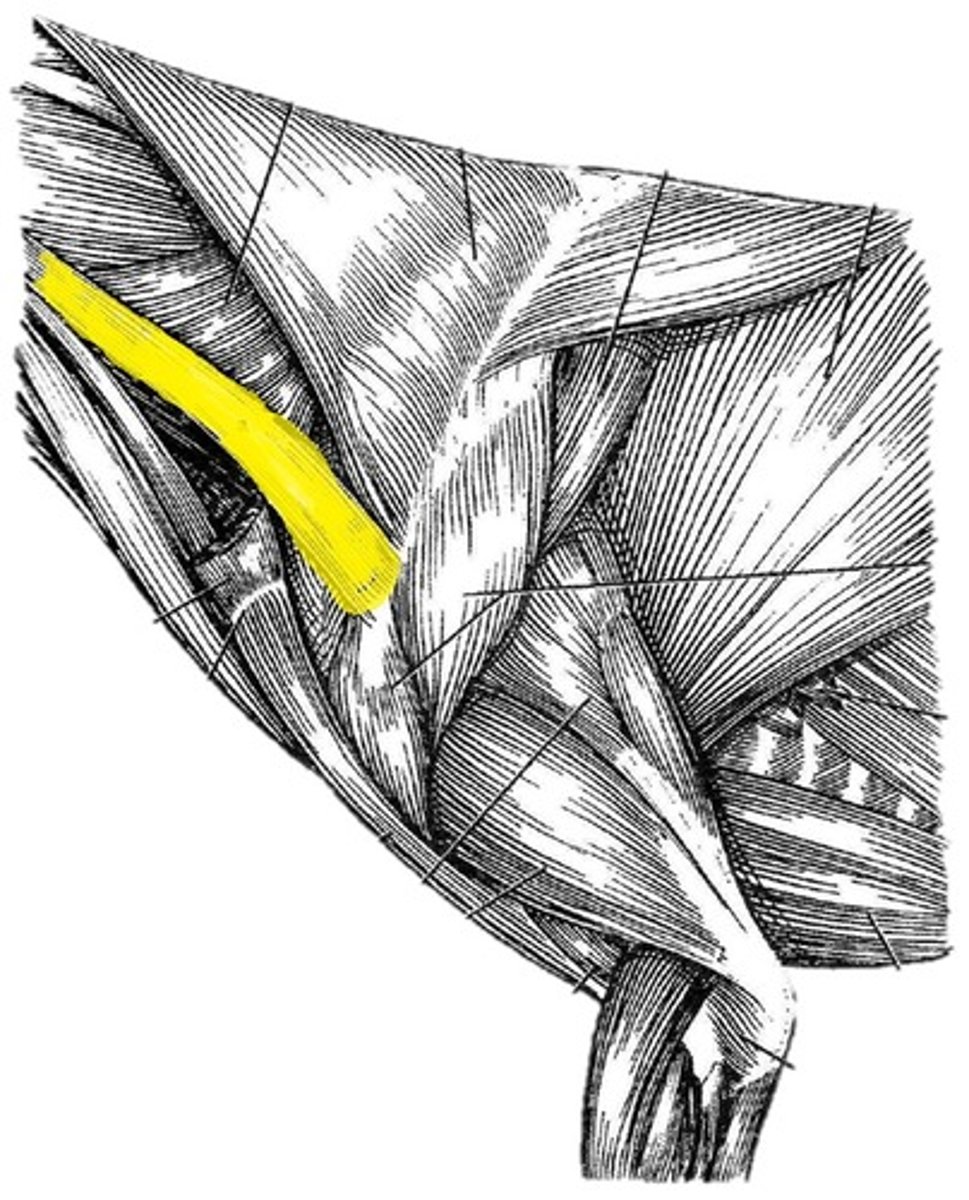
brachiocephalicus m.
(consists of cleidobrachialis and cleidocephalicus mm)
O: clavicular insertion
I: cleidobrachialis: distal cranial humerus (proximal ulna in cats)
cleidocephalicus: mastoid part: mastoid process of temporal bone
cervial part (car): dorsal neck
*(Can think of this muscle as one large muscle with multiple attachments due to the reduced clavicle in many animal species. In the dog, attaches caudally to the distal cranial humerus and cranially to the dorsal neck and mastoid process of the skull)*
A: pull thoracic limb cranially (when not bearing weight); depress and pull head/neck laterally (when not bearing weight)
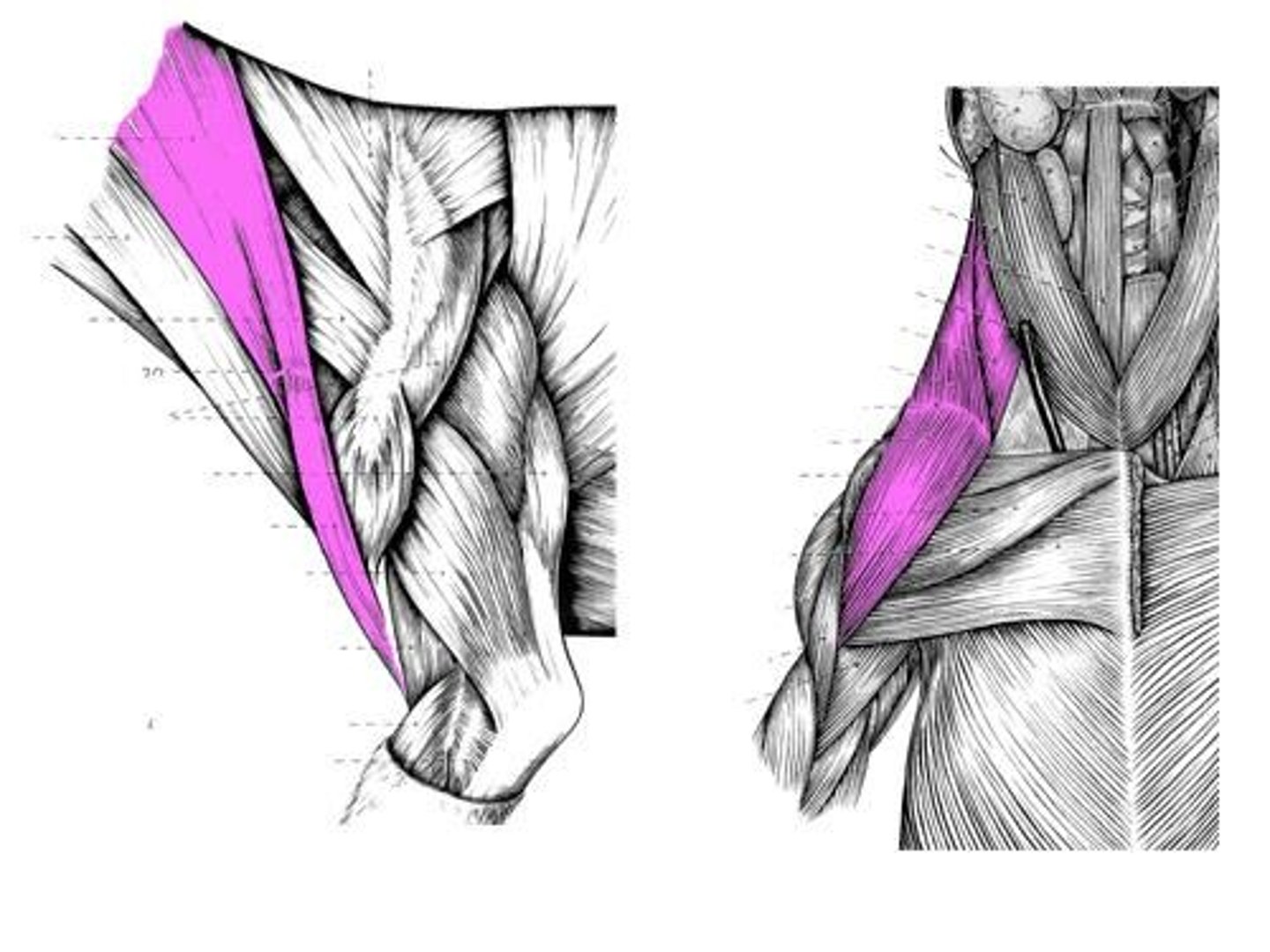
Omotransversarius muscle
O: wing of the atlas (first cervical vertebra)
I: distal spine of the scapula
A: pull head/neck laterally when bearing weight
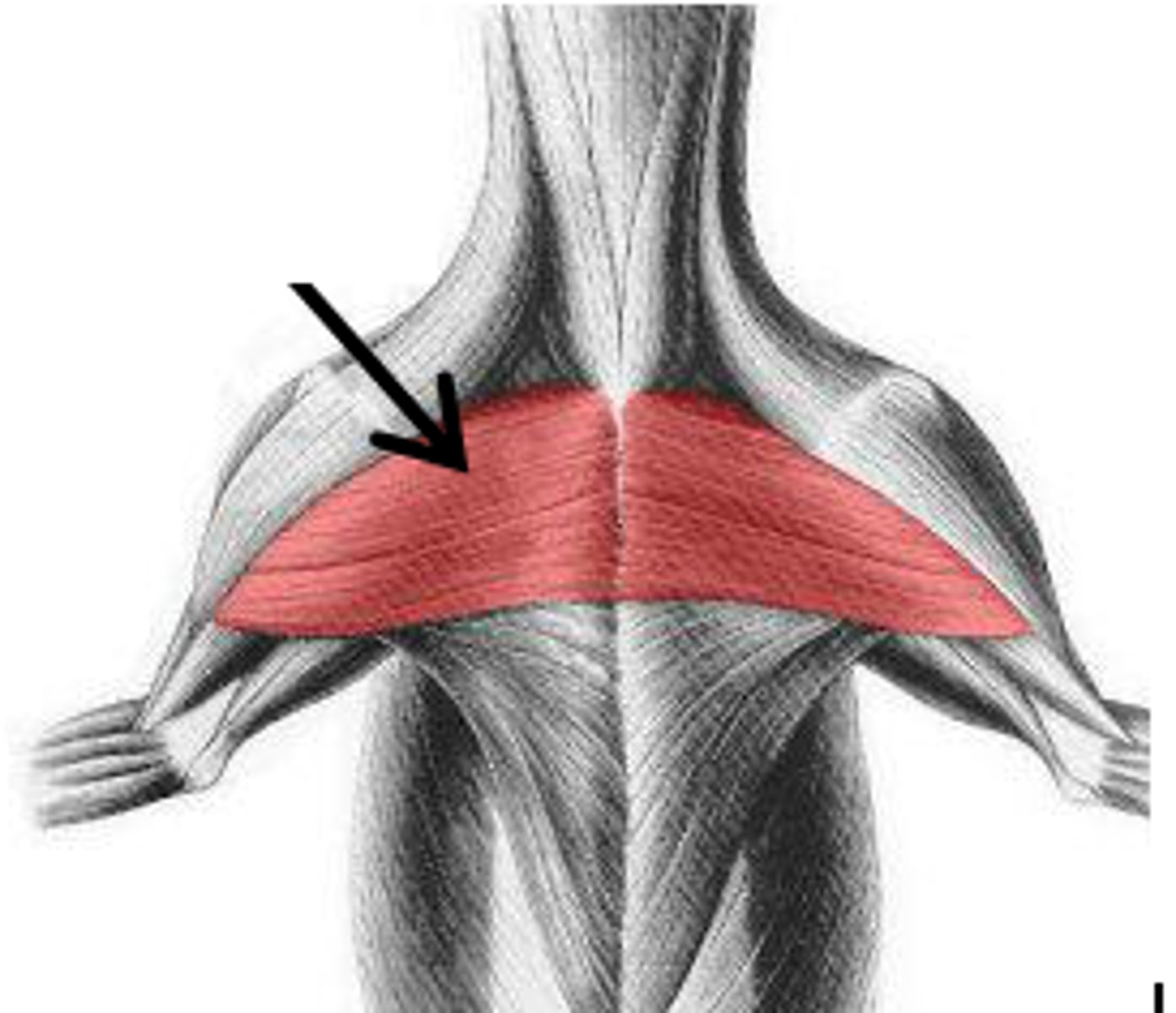
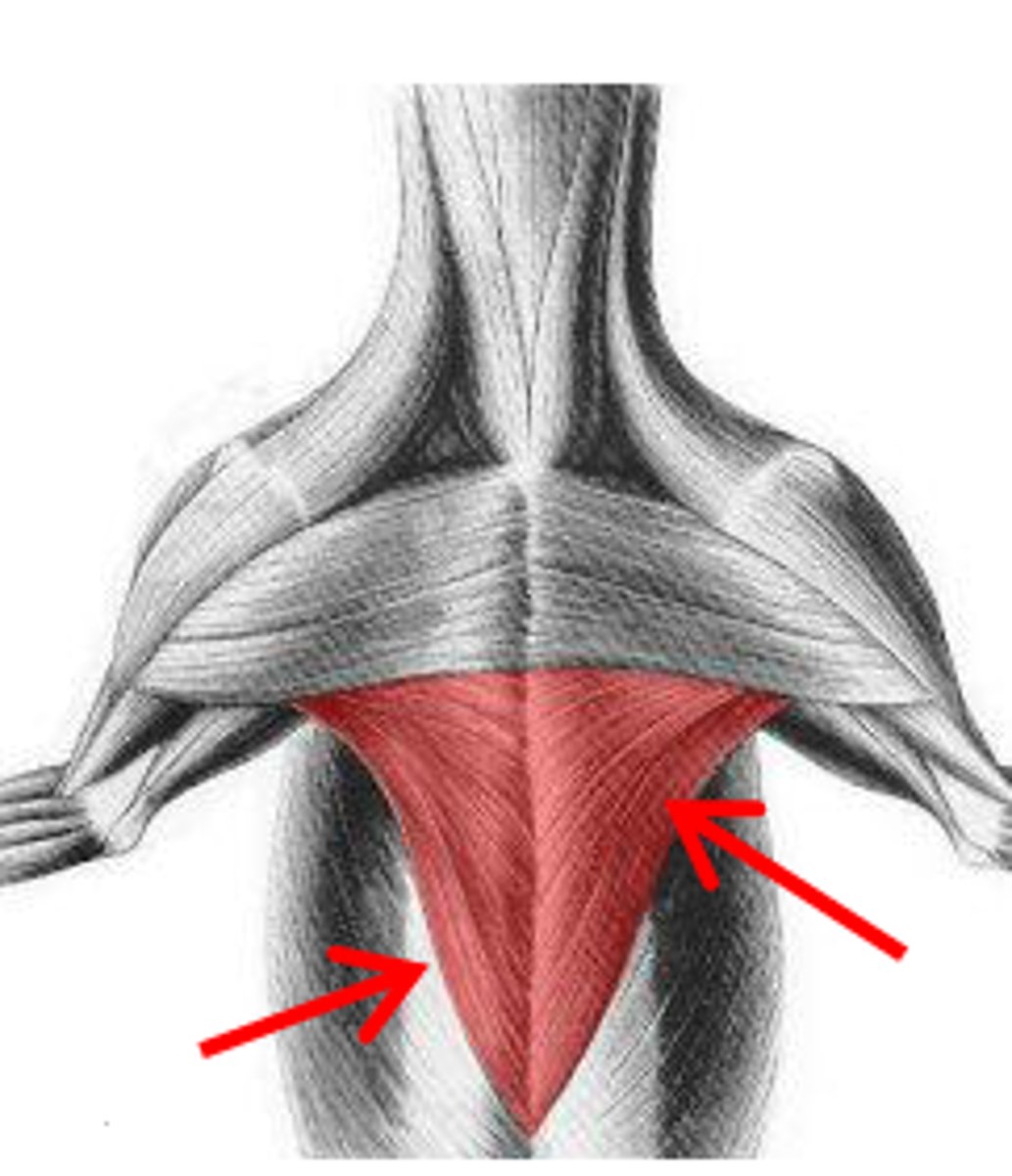
trapezius
O:
cervical- dorsal neck
thoracic: dorsal thorax
I: spine of scapula
A: elevate thoracic limb
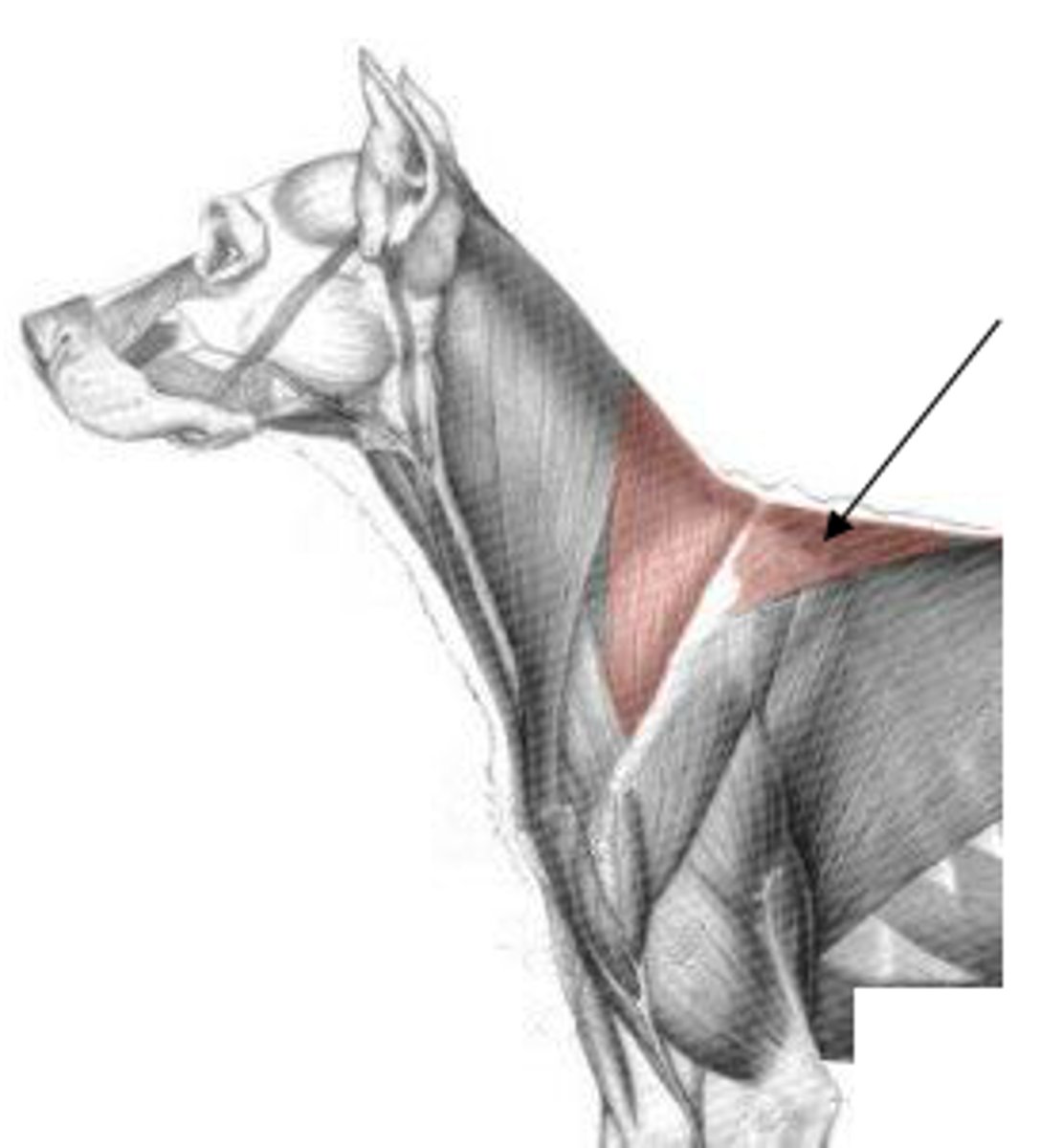
rhomboideus m.
O:
capital part - occipital bone
cervical part - dorsal neck
thoracic part - dorsal thorax
I: dorsal border of the scapula and/or scapular cartilage
A: elevate the thoracic limb and depress the scapula to the trunk
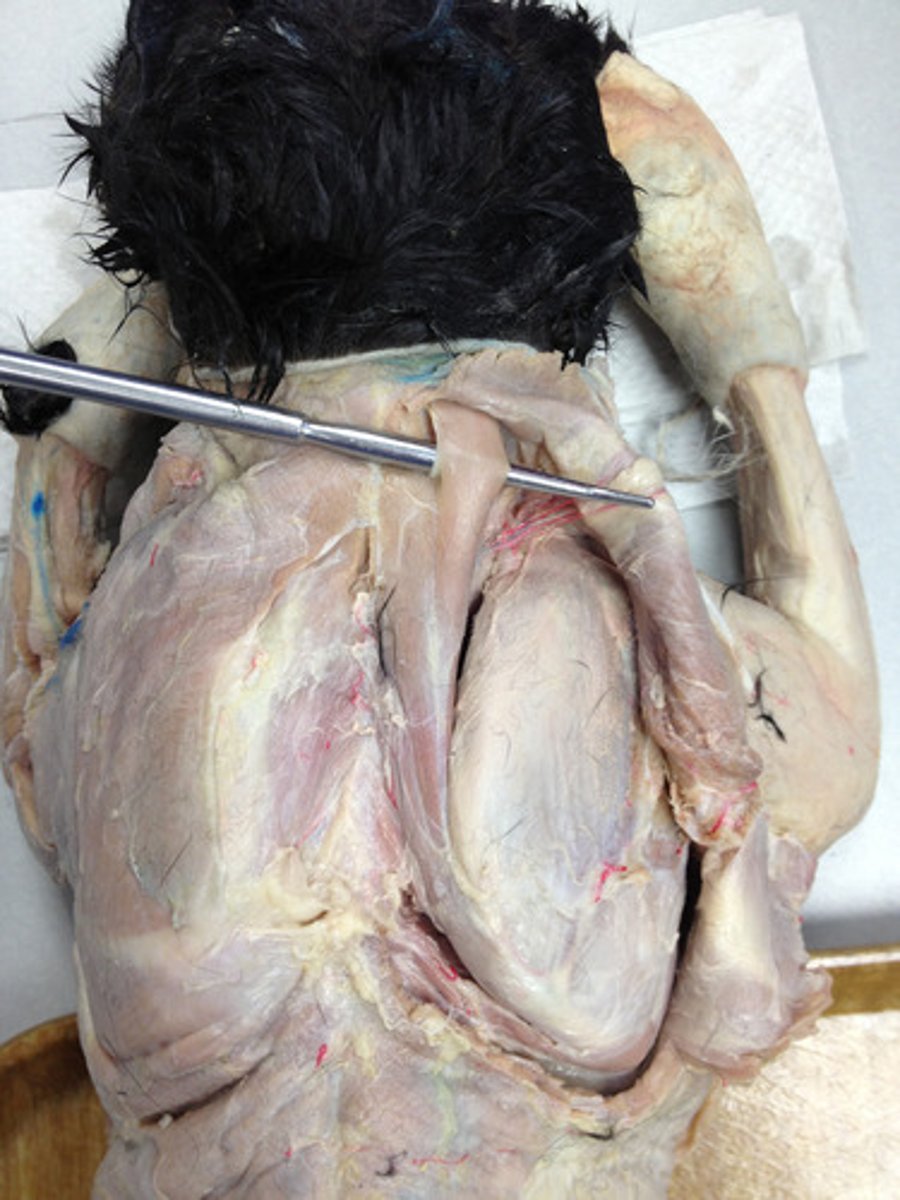
serratus ventralis m
O:
cervical part: cervical vertebrae
thoracic part: thoracic wall
I: serrated face of scapula
A: support and elevate the trunk
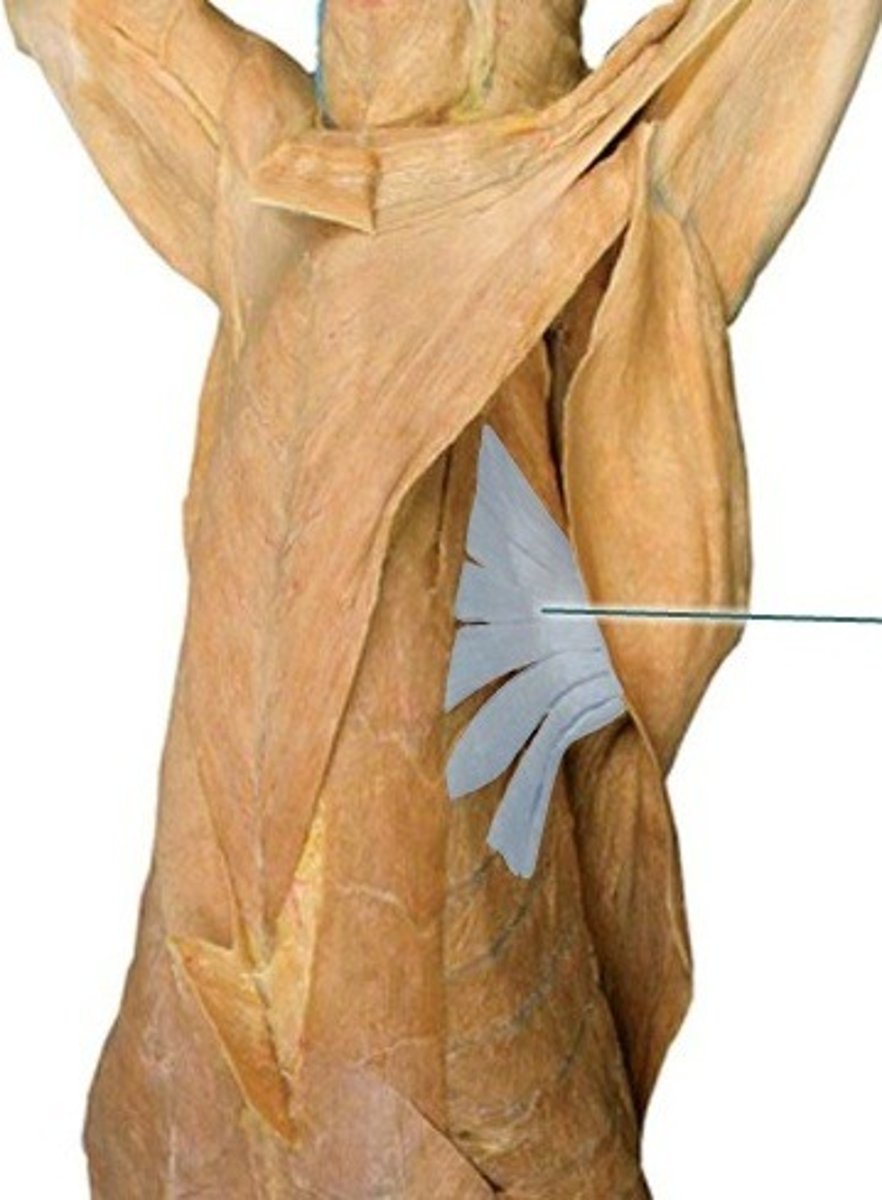
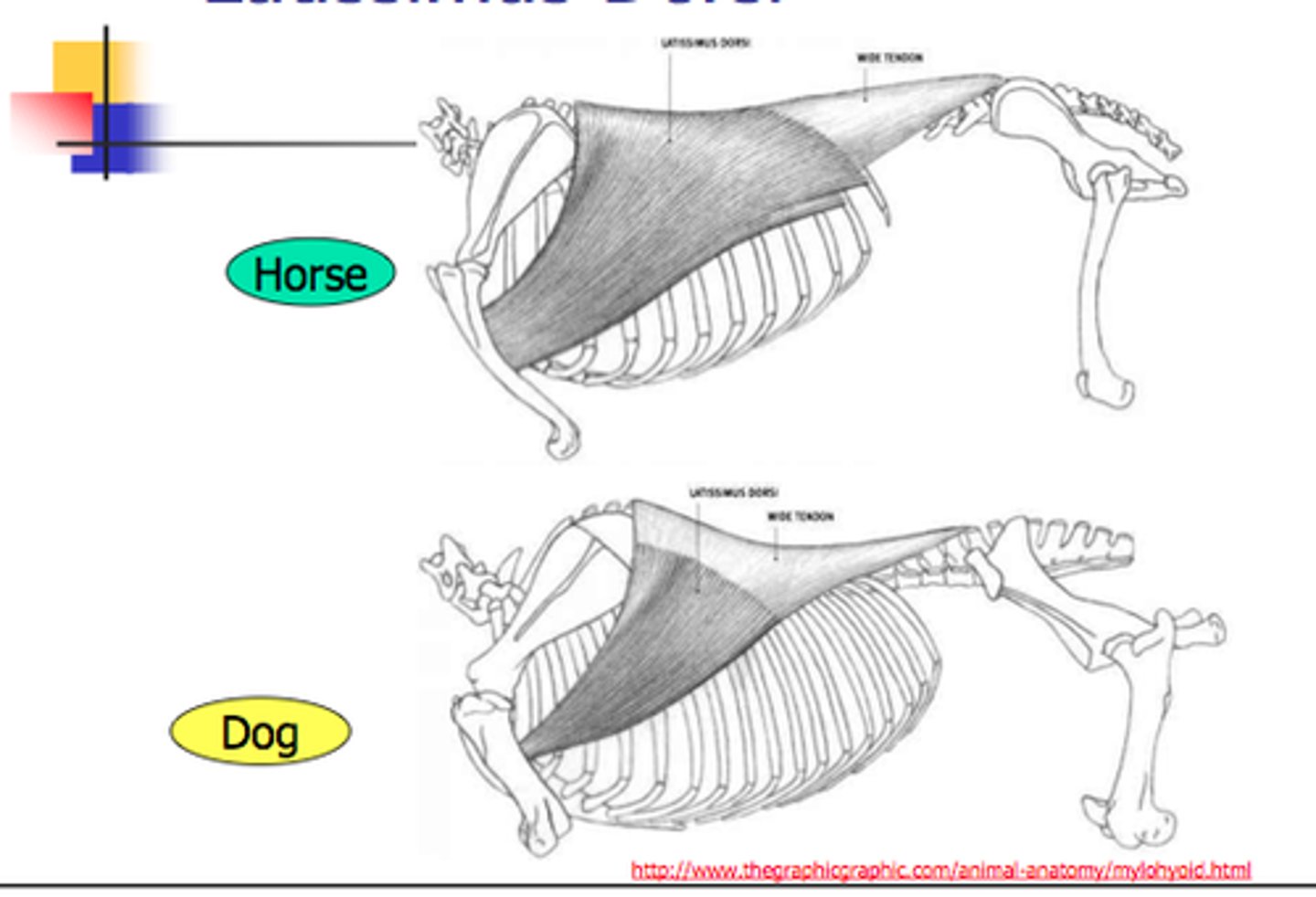
Latissimus dorsi m
O: thoracolumbar fascia
I: teres major tuberosity of the humerus
A: draw thoracic limb caudally and flex the humeral joint when not bearing weight; extend the humeral joint when bearing weight
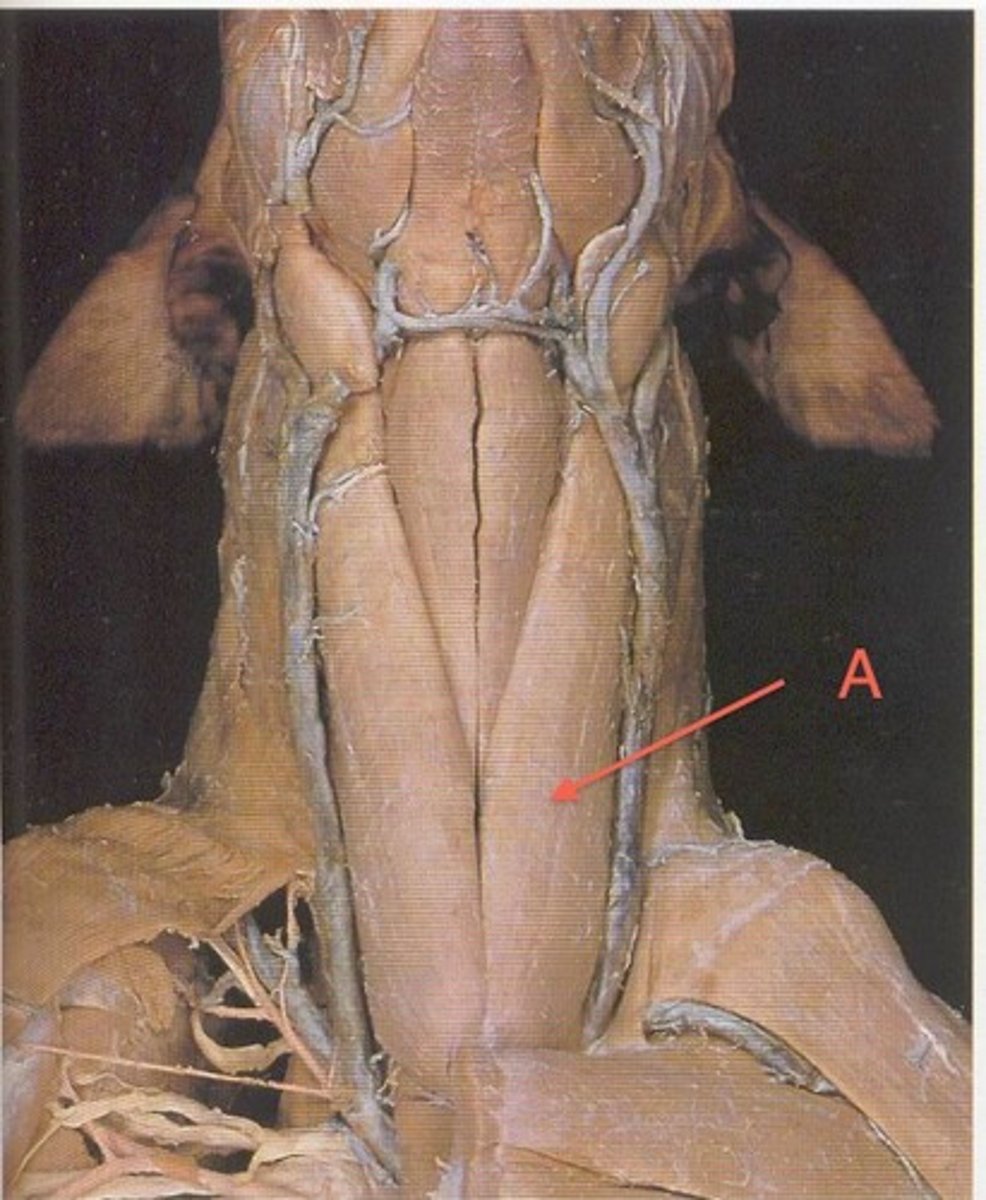
sternocephalicus m
Attachments: cranial sternum, mastoid process of temporal bome, occipital bone
Action: depress head/neck, draw head/neck laterally
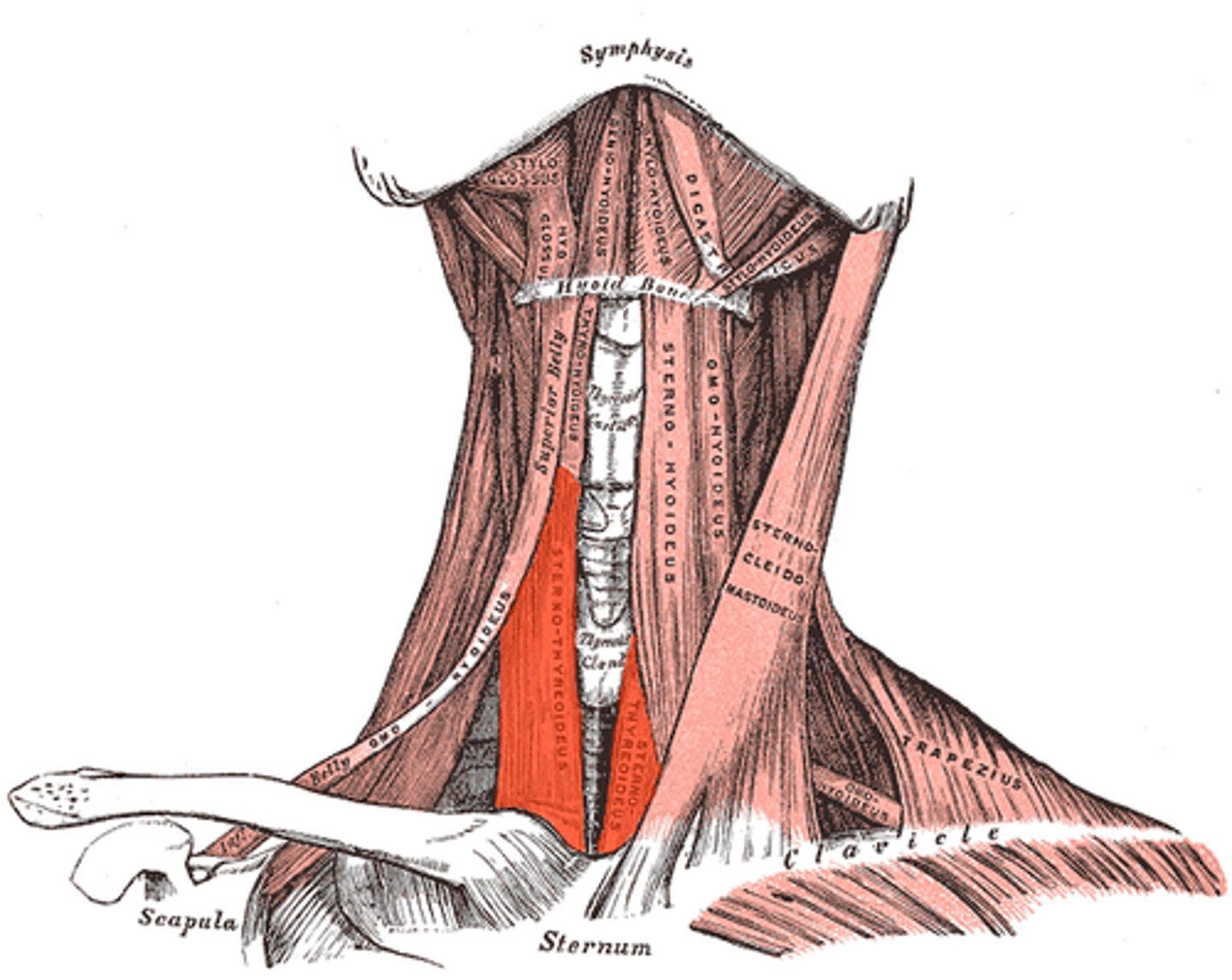
Sternohyoideus m.
Attachments: cranial sternum, basihyoid bone
Action: pull tongue and larynx caudally
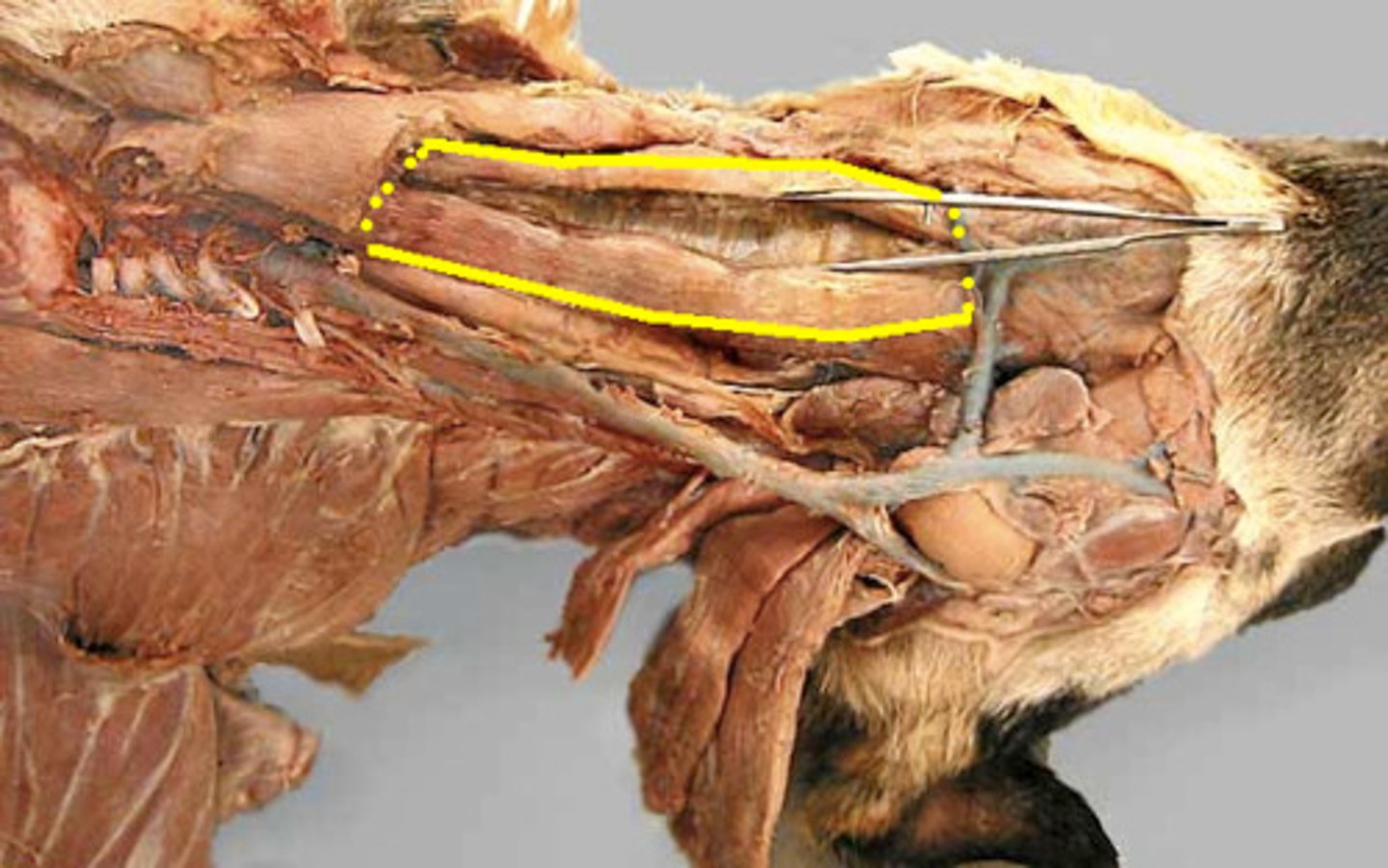
sternothyroideus m.
attachments: cranual sternum, thyroid cartillage of the larynx
Action: pull tongue and larynx caudally
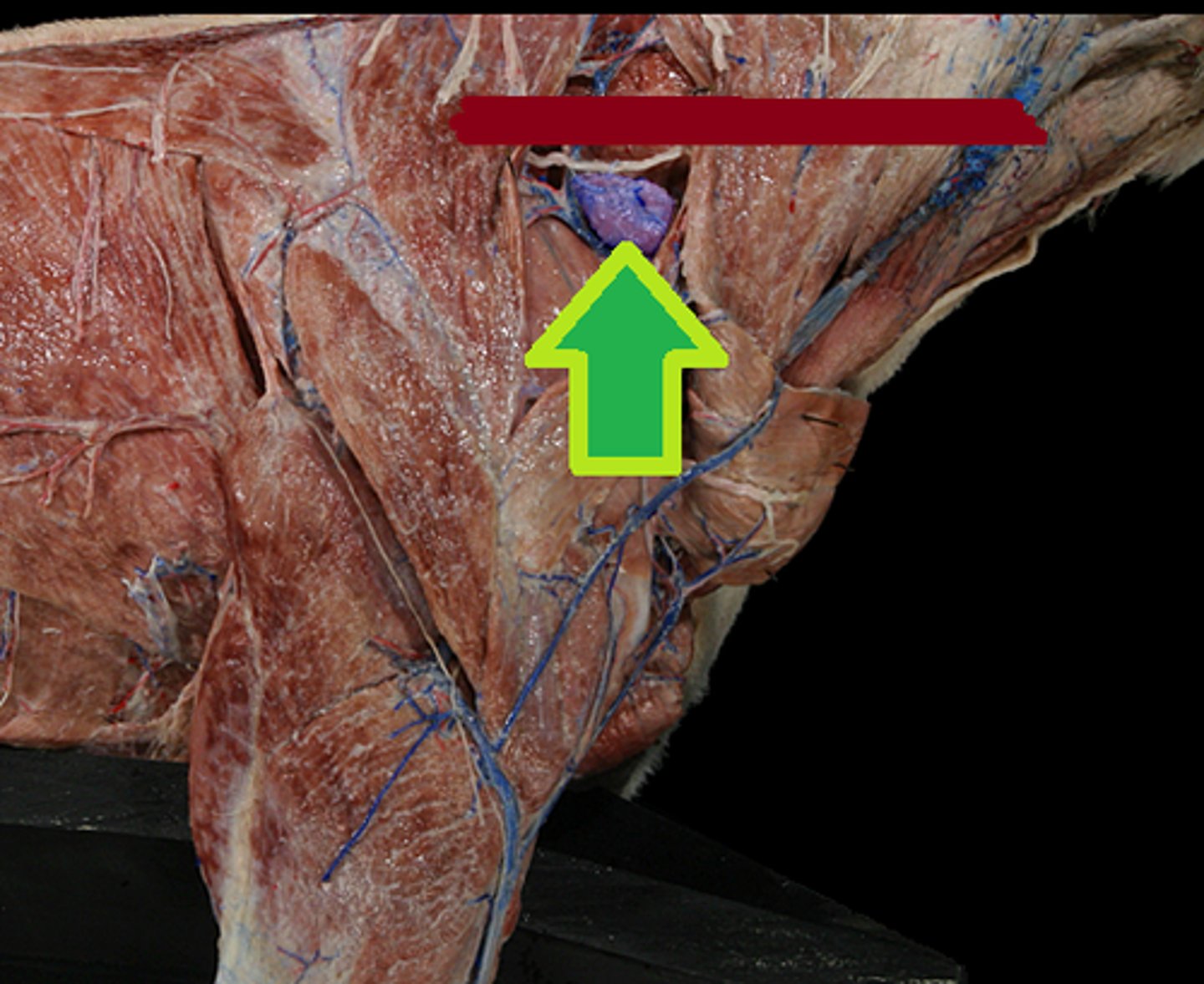
superficial cervical lymph nodes
located cranial to the scapula/shoulder joint and deep to the middle of the omotransversarius and the brachiocephalicus m.
cartoid sheath and its components
the deep fascia that covers the common carotid artery, vagosympathetic nerve trunk, internal jugular vein, and tracheal lymphatic trunk. Lies between the omotransversarius dorsally and sternothyroideus ventrally
2 basic rules in naming radiographic views
1. use official nomenclature
2. Indicate the path that xray travels through subject from point of entry to point of exit to name view
radiodensity
The relative resistance to the passage of x-rays.
Radiopacity
White or light region on the x-ray indicating where radiation was blocked by tissue or a substance
Radiolucent
a substance that allows x-rays to pass through and appears black or dark gray on the resulting film
Radiopaque
substances that do not permit the passage of x-rays and apear whiter