Stoichiometry and Molar Mass Calculations in Chemistry
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Mole Amounts of Pure Substances
4.003 g Helium Gas, 63.55 g Copper Wire, 200.59 g Liquid Mercury, 12.01 g Carbon Powder, 32.06 g Solid Sulfur

Molar Mass
Calculation for the Molar Masses of Compounds
Molar Mass of Sodium Chloride
MNaCl: (1 x 22.99 g/mol) + (1 x 35.45 g/mol) = 58.44 g/mol
Molar Mass of Glucose
MC6H12O6: (6 x 12.01 g/mol) + (12 x 1.01 g/mol) + (6 x 16.00 g/mol) = 180.18 g/mol
Molar Mass of Calcium Phosphate
MCa3(PO4)2: (3 x 40.08 g/mol) + (2 x 30.97 g/mol) + (8 x 16.00 g/mol) = 310.18 g/mol
Formula Mass
Mass of a single molecule (for molecular compounds) or a single formula unit (for ionic compounds)
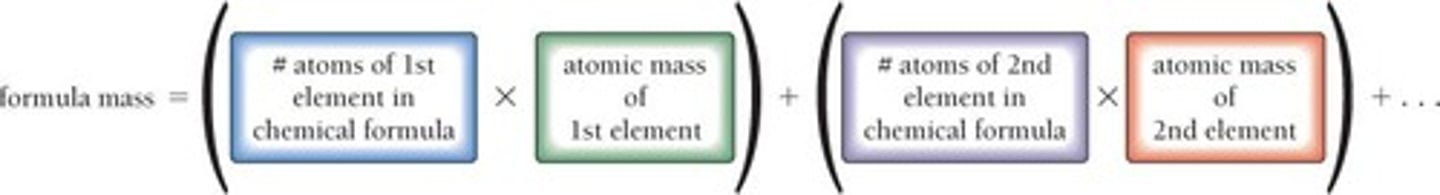
Terminology: Formula Mass
Applies to ionic compounds
Terminology: Molecular Mass
Applies to molecular compounds
Formula Mass Units
Expressed in atomic mass units (amu)
Atomic Mass Examples
H (1.01 amu), O (15.9994 amu), C (12.0107 amu)
Percent Composition Calculation
Calculate the Percent Composition of Methane (CH4): Sum = 74.83 % + 25.17 % = 100 %
Percent Composition for Binary Compounds
The % composition of 1st element is first found, then subtract from 100 to find the % composition of the 2nd element.
Percent Composition for Compounds with 3 Elements
Find the % compositions of 2 of the 3 elements, then subtract their sum from 100 to find the % composition of the 3rd element.
Percent Composition of Glucose
Calculate the percent composition of glucose, C6H12O6
Percent Composition of Iron(III) Carbonate
Calculate the percent composition of iron(III) carbonate, Fe2(CO3)3
Empirical Formulas
The empirical formula of a compound can be determined from knowing the percent compositions of all the element types present in the compound.
Empirical Formula
The simplest whole number ratio of elements in a compound.
Molecular Formula
The formula that shows the actual number of each type of atom in a molecule of a compound.
Stoichiometry
The quantitative relationship between the reactants and products in a balanced chemical equation.
Limiting Reactant
The reactant that is completely consumed first in a chemical reaction.
Excess Reactant
The reactant(s) that is/are leftover unreacted once the limiting reactant has been completely consumed.
Theoretical Yield
The maximum amount of product possible in a chemical reaction from given amounts of reactants.
Actual Yield
The amount of product obtained from a chemical reaction, which is often less than the theoretical yield.
Percent Yield
Quantitative measure of the efficiency and success of a chemical reaction.
Steps for Determining Empirical Formulas
1. Assume 100 g of the compound. 2. Equate the % composition of each element type to mass (g). 3. For each element type, convert g to mol. 4. Divide each converted mole value to the smallest mole value in the set. 5. If there are common decimals or fractions present, convert the number to an improper fraction, then multiply all values by the least common integer.
Finding the Molecular Formula
The molecular formula can be determined by knowing the empirical formula and the molecular mass of the compound, then calculating the ratio of the compound's molecular mass to its empirical mass.
Sample Calculation for Benzene
Benzene is composed of 92.24 % C and 7.76 % H by mass. Calculate its empirical formula.
Sample Calculation for Ascorbic Acid
Ascorbic acid is composed of 40.92 % C, 4.58 % H, and 54.50 % O by mass. The molecular mass of ascorbic acid is 176.14 amu. Calculate its molecular formula.
Balanced Chemical Equation
A chemical equation where the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
Haber-Bosch Process
A method for producing ammonia, NH3, from nitrogen and hydrogen.
Combustion of Butane
The chemical reaction of butane, C4H10, with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Common Decimals in Empirical Formulas
Common decimals or fractions present include 0.25 (1/4), 0.33 (1/3), 0.5 (1/2), 0.67 (2/3), 0.75 (3/4).
Stoichiometric Calculation
A type of calculation that involves chemical formulas and chemical equations.
Chemical Reaction
A process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another.
Empirical Mass
The mass of the empirical formula of a compound.
Molecular Mass
The mass of a molecule, calculated as the sum of the atomic masses of its constituent atoms.
Subscript in Empirical Formula
The number that indicates the number of atoms of each element in the empirical formula.