Timber & Fishing
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What are the aims of sustainability?
- To preserve environment
- Ensure resources available to future
- Allow all human societies to live comfortably
- Enable less economically developed countries to develop by exploiting their natural resources
- Create a more even balance in the consumption of resources in more economically developed countries and LEDCs.
Timber Production:
- Rotational felling
- Clear felling
- Strip felling
- Selective felling
- Coppicing
- Pollarding
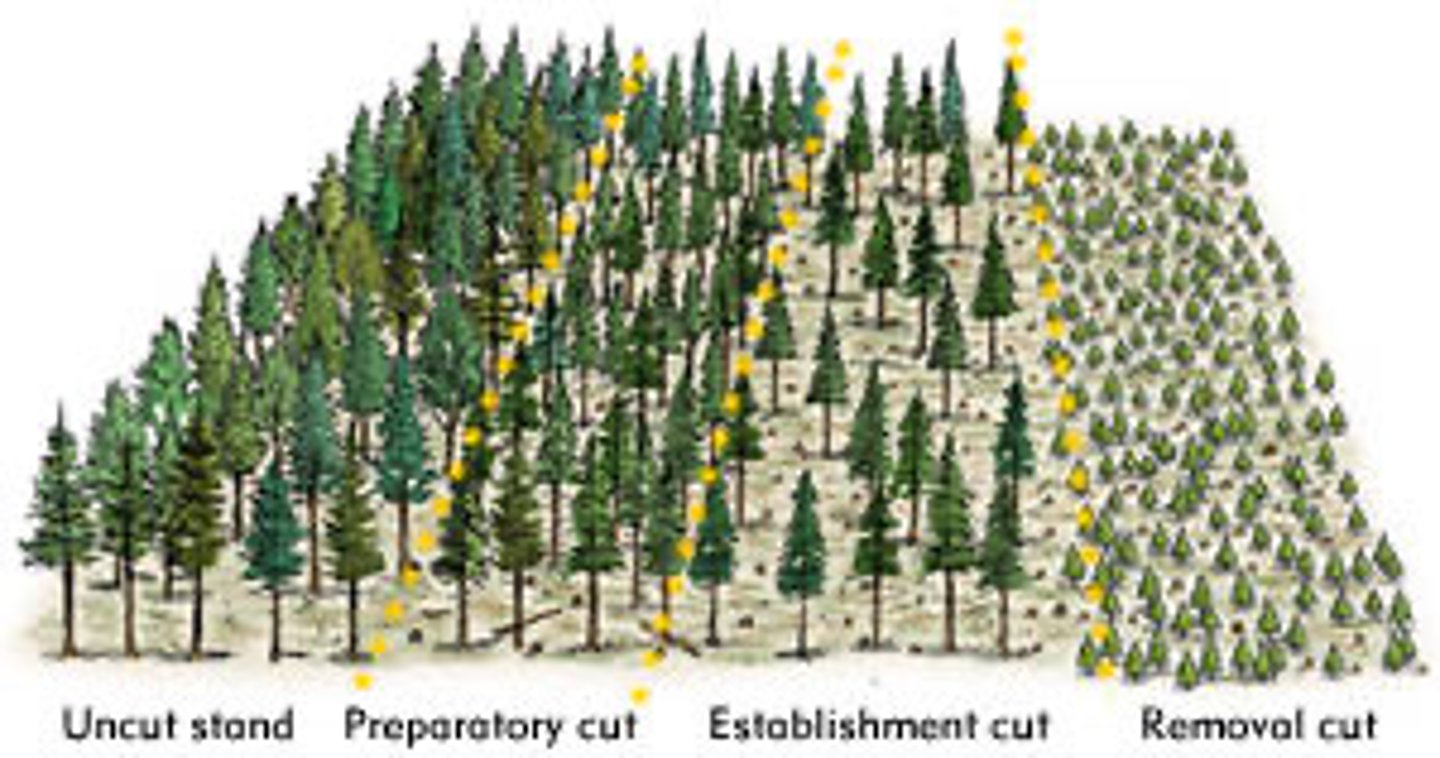
Rotational felling
- Planting a site
- Felling the trees when reached maturity
- Takes 8-20 years
Pros of Clear felling
It is a productive and economical method of timber production
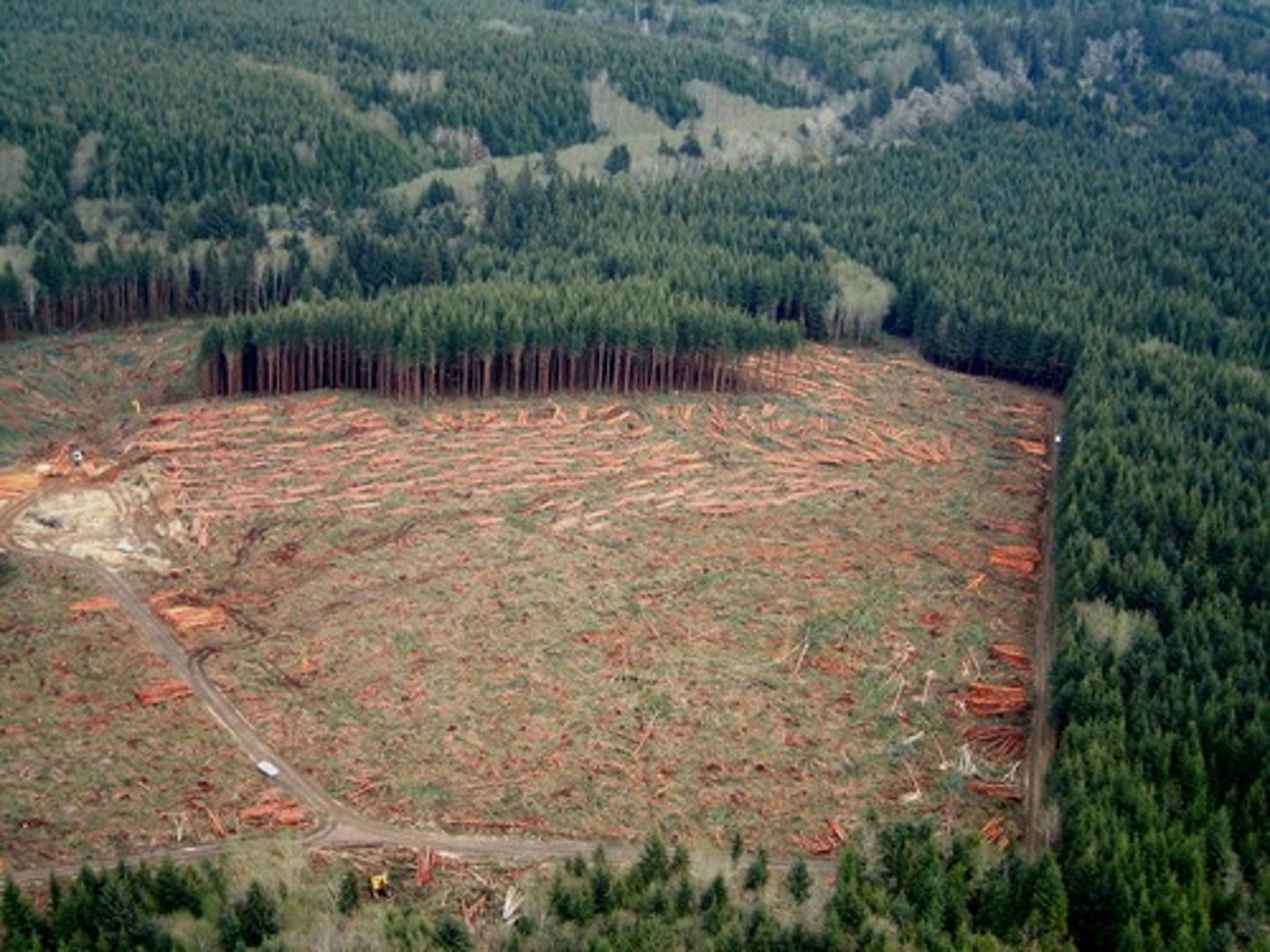

Cons of Clear felling
All trees are removed including their roots which is devastating for the natural environment
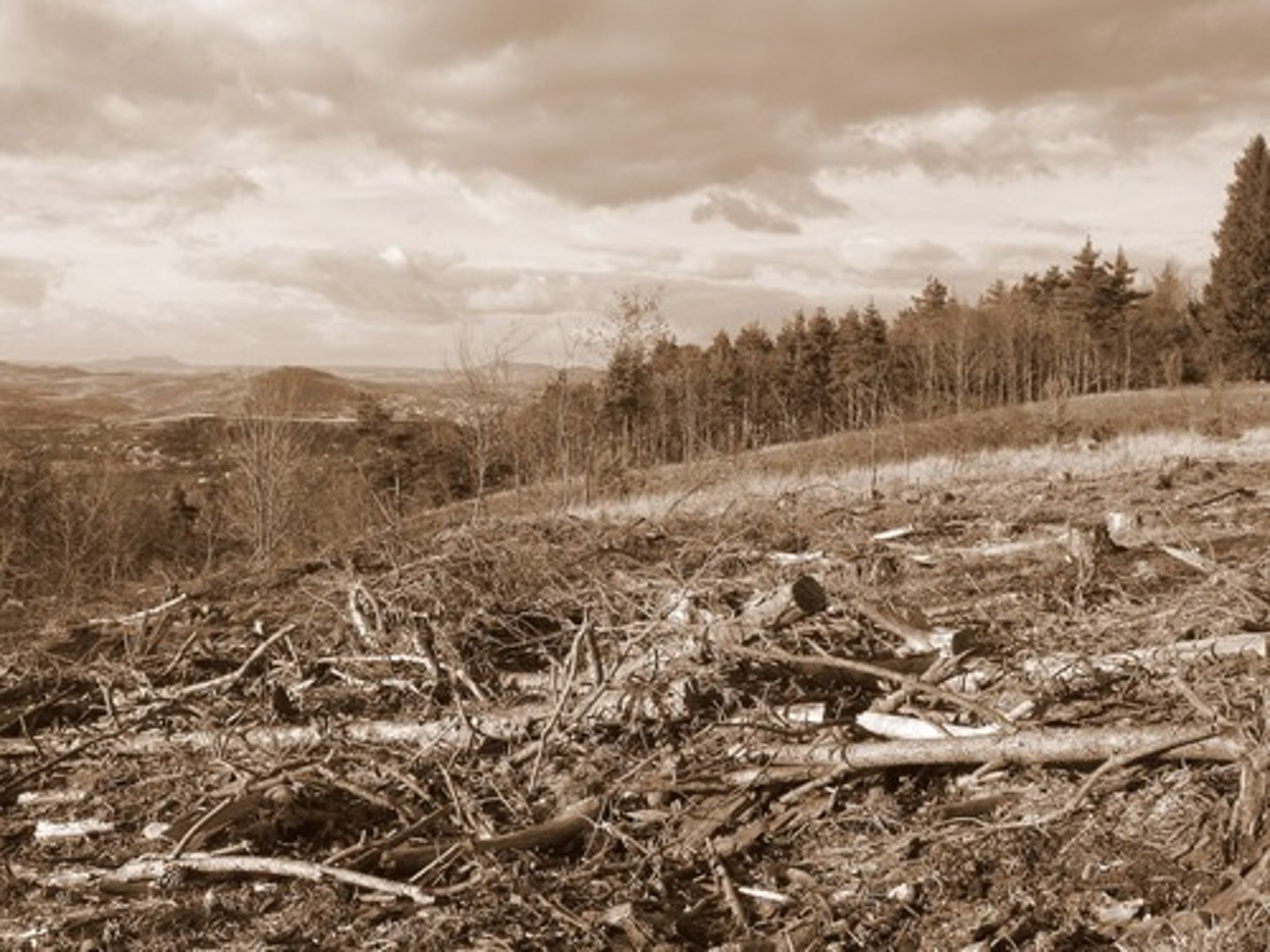

Pros of Strip felling
Narrow strips are cut so that forest on either side can regrow and reclaim the land, allowing forests to be logged with minimum effort and damage
- Allows other trees to grow to maturity and also leaves enough for habitats for animals
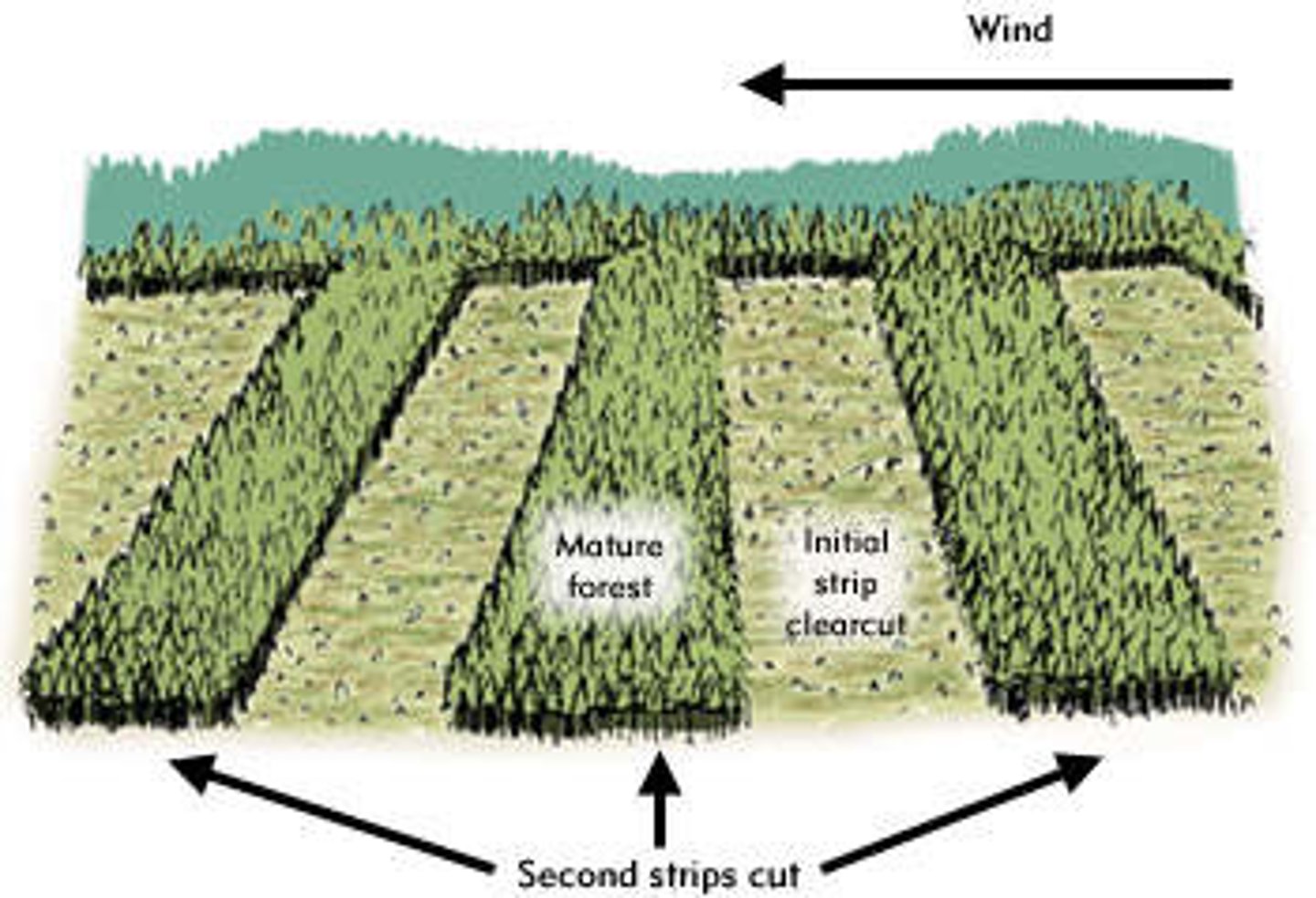
Cons of Strip felling
Better than clear cutting but leads to habitat fragmentation

Pros of Selective felling
- Only older trees are felled and newer trees remain, ensuring continual regeneration of young seedlings
- This allows other trees to grow to maturity
- Leaves enough trees for habitats for animals
- Works well for forests with fast-growing trees.

Cons of Selective felling
Helicopters are often needed and there is risk of damage to neighbouring trees.
It does not suit forests with slow growing trees.

After felling a tree, what should you do that would make this process sustainable?
Replant the tree

How should you fell sustainably?
- Limit the size of the area being felled to reduce soil erosion
- Replant trees that have been felled
- Have optimum distances between replanted trees
- Rotate areas that are felled to allow trees to mature.
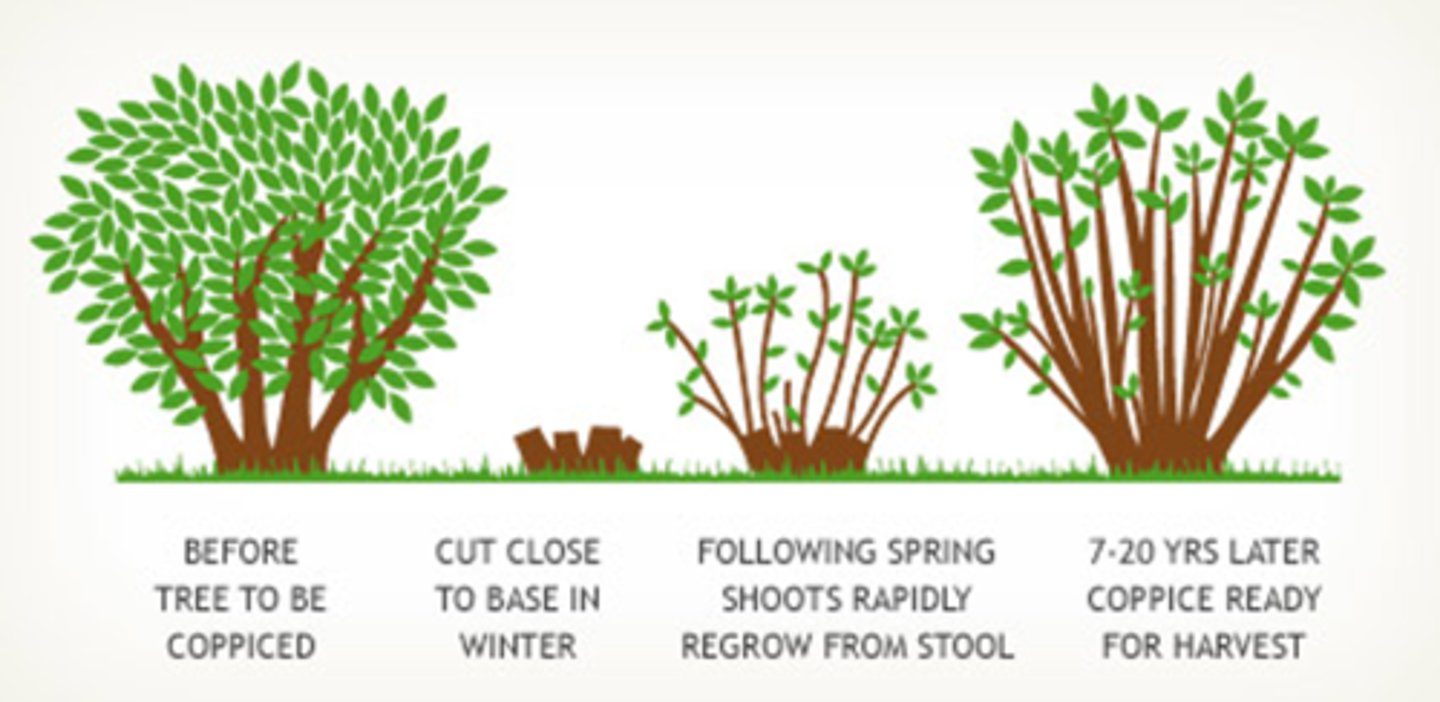
Coppicing
- Trunk cut close to ground level
- Several new shoots will grow from cut surface
- Process repeated after certain time
Pros of Coppicing
- Can be repeated indefinitely
- Lifespan of tree extended
- Provides variety of light levels
- Fewer large trees means more light for smaller plants
- Provides a variety of habitats and maintains biodiversity
- Roots are present, and therefore prevent soil erosion
- Maintains soil quality
- Prevents succession
- Large machinery not needed therefore less disturbance
Cons of Coppicing
Herbivores have access to the newly forming shoots and damage them therefore you need to protect young shoots from grazers.

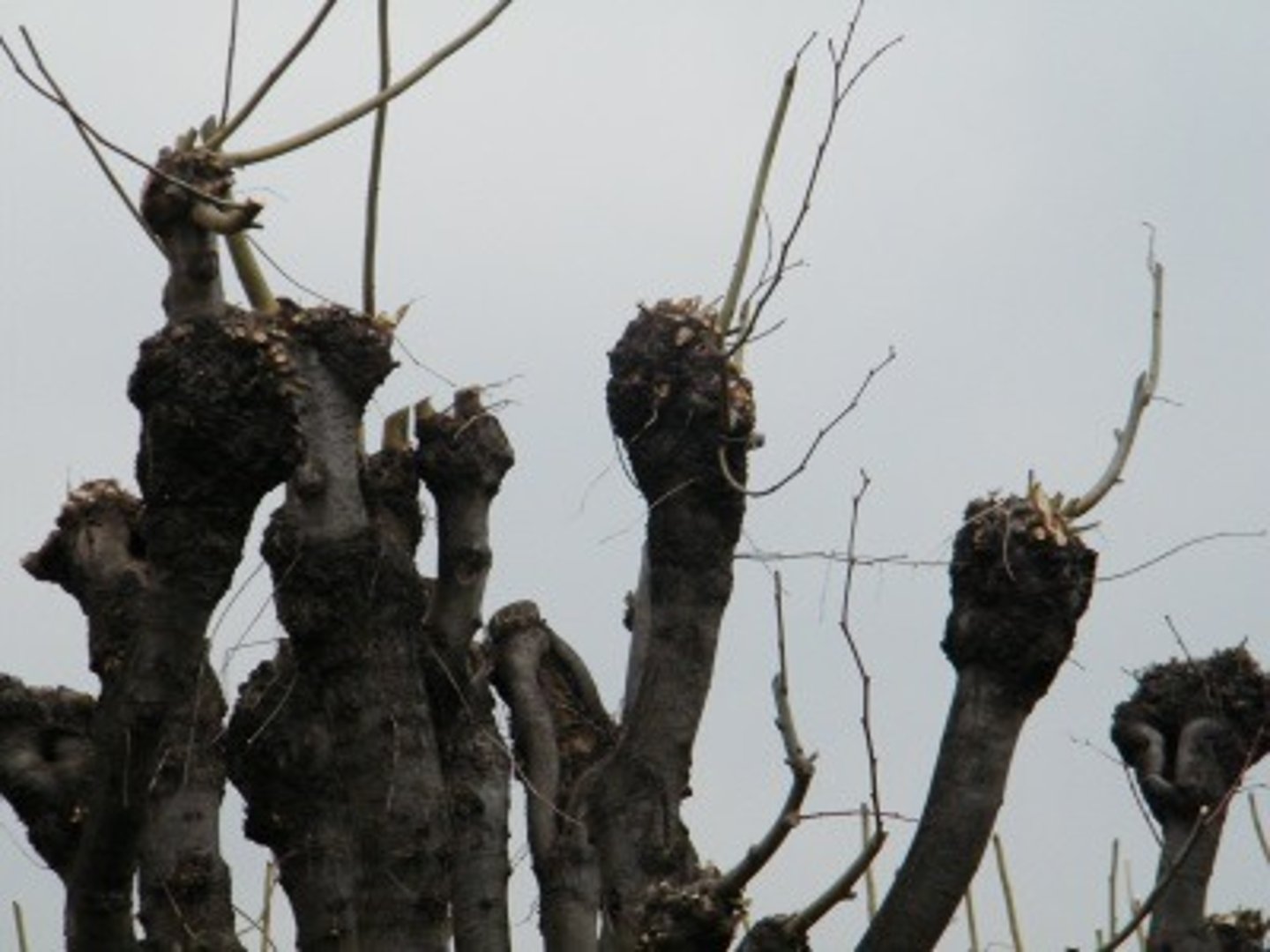
Pros of Pollarding
The tree trunk is cut high above ground so there is less chance of damage from herbivory (you have to say herbivory cause deers don't eat meat)
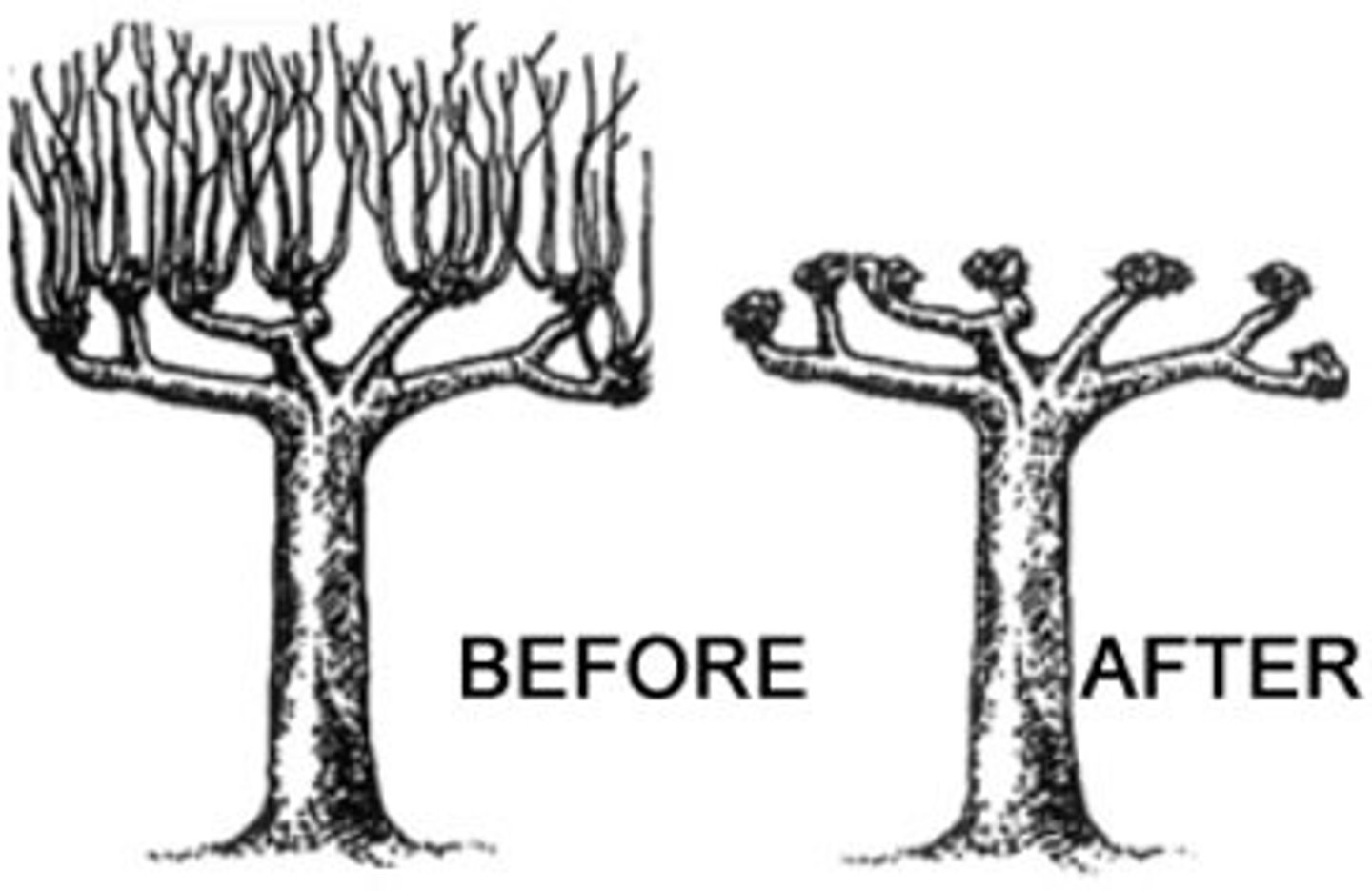
Cons of Pollarding
The timber produced is small in size and not suitable for construction.

Sustainable Fishing Organisations:
ICCAT
CFP
NAFO
ICCAT
International Commission for the Conservation of Atlantic Tunas
Organisation responsible for the management and conservation of tuna and tuna-like species in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas
CFP
Common Fisheries Policy
Puts fishing quotas on the numbers of certain fish that are allowed to be caught in a particular area
NAFO
Northwest Atlantic Fisheries Organisation
An intergovernmental organization with a mandate to provide scientific advice and management of fisheries in the north-western part of the Atlantic Ocean
Use of nets with larger mesh sizes
It lets smaller fish out so they can continue to grow and breed until they are larger
Setting up fishing exclusion 'no catch' zones
Provides an area for fish to grow to adulthood and to breed safely. This can restock other, adjacent areas.
Restricting use of small hook sizes
Ensures small fish are not taken and can survive long enough to breed
Issuing fishing quotas or limit mass of fish caught
Limit the mass/number of fish caught

Restocking the sea with young fish
To increase chance of fish reaching adulthood and breeding safely
Allowing commercial and recreational fishing only at certain times of year
Protects the breeding season so that breeding can be maximised.
Limiting the number of boats that can fish in an area
Limit the mass/number of fish caught

Inspection of catches landed at ports
Ensures regulations are being followed
Introduction of fish farming
Reduced pressure on wild populations

Creating marine conservation zones
To protect vulnerable habitats
Allow catching of certain species only
To protect vulnerable/endangered species

Strict enforcement of regulations - issue licenses & penalties/sanctions
To act as a deterrent to poachers
Difficulties in sustainable fishing
- Area too large
- Expense of monitoring
- Monitoring hampered by weather/seasons
- False reporting of catches / trawler size / mesh size
- Fish are killed when caught but not kept due to restrictions