Non-Coding RNAs in Molecular and Cellular Biology
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are non-coding RNA molecules?
Any type of RNA that does not code for proteins.
What is a ribonucleoprotein complex?
A complex formed when non-coding RNA is found with protein.
What are some functions of non-coding RNAs?
1. Framework for formation of a complex. 2. Targeting specific nucleic acid sequences. 3. Alteration of protein function or stability. 4. Catalytic active site created by RNA folding. 5. Prevent other molecules from binding. 6. Prevent other non-coding RNAs from functioning.
What is the role of non-coding RNAs in the formation of complexes?
They provide a framework for the formation of a complex.
How do non-coding RNAs target specific nucleic acid sequences?
They interact with specific sequences to achieve their functions.
What is one way non-coding RNAs can alter protein function?
By affecting the stability of the protein.
What is the significance of RNA folding in non-coding RNAs?
It creates a catalytic active site.
What is one function of non-coding RNAs related to binding?
They can prevent other molecules from binding.
What is the role of non-coding RNAs in relation to other non-coding RNAs?
They can prevent other non-coding RNAs from functioning.
What is the HOx Transcript Antisense Intergenic RNA?
An example of a non-coding RNA with a specific mode of function.
What is RNA interference?
A biological process in which non-coding RNAs inhibit gene expression.
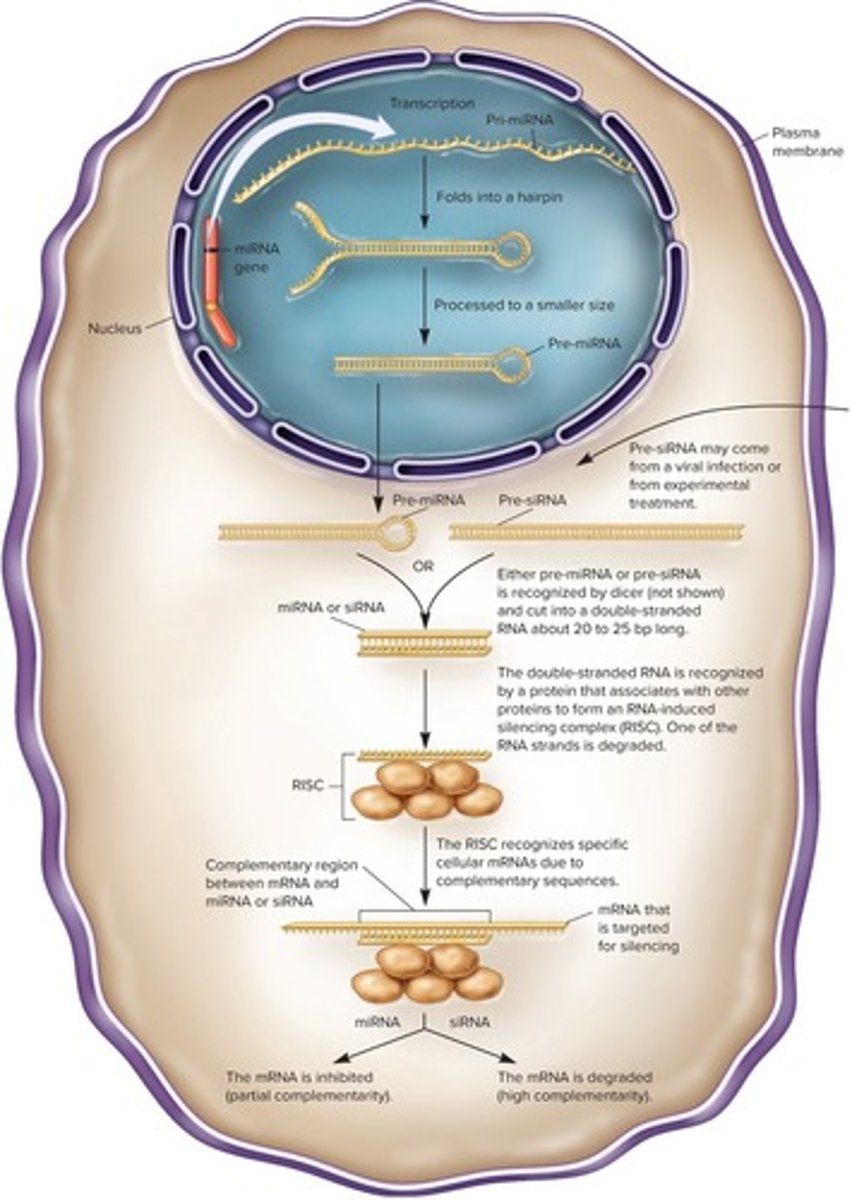
What are the phases of RNA interference?
1. Adaptation Phase. 2. Expression Phase. 3. Interference Phase.
What occurs during the Adaptation Phase of RNA interference?
The system prepares to recognize and respond to specific RNA sequences.
What happens during the Expression Phase of RNA interference?
The non-coding RNAs are expressed and ready to target RNA.
What is the Interference Phase in RNA interference?
The phase where the non-coding RNAs actively inhibit the target RNA.
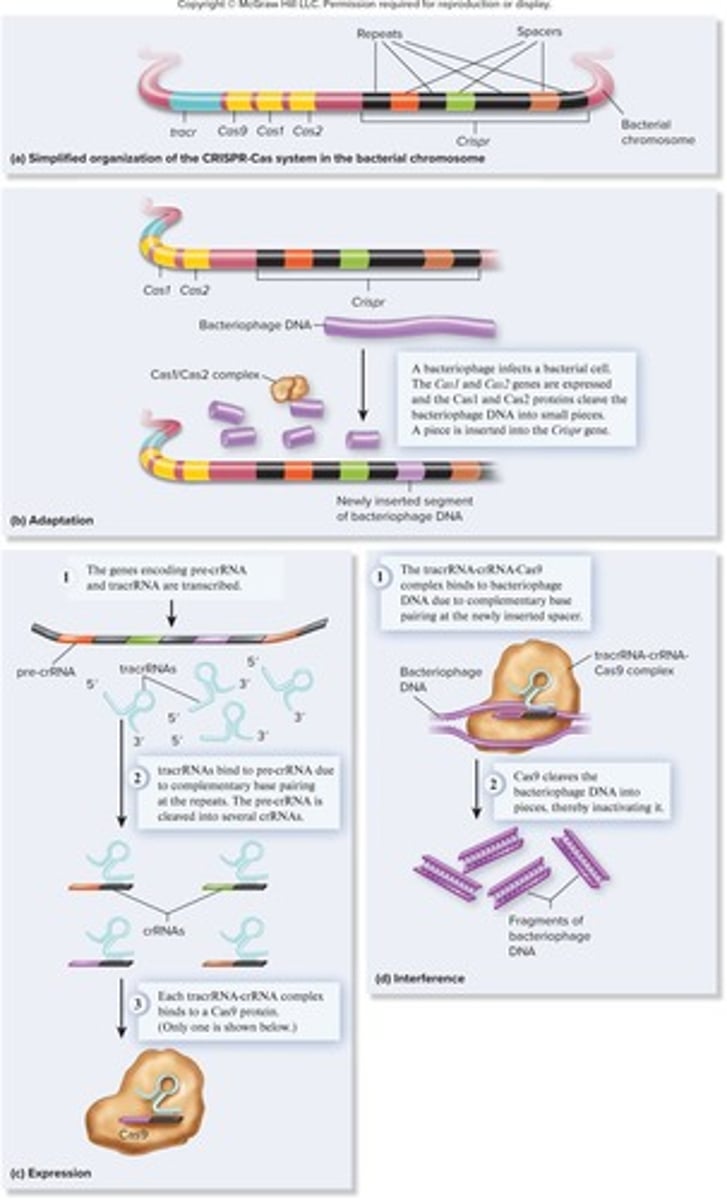
What are PAM sequences?
Short sequences that are essential for the recognition of target DNA by certain RNA-guided nucleases.