Chemistry - End of Year Exams 10
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Combustion, Enthalpy, Exothermic vs Endothermic, etc
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Complete Combustion
When each of the reactants get used up fully to create the end product
Incomplete Combustion
When the fuel doesn’t react fully with the oxygen and thus produces soot or carbon monoxide (CO)
Hydrocarbons
chains of hydrogen + carbon
Flash Point
the lowest temperature at which there is enough gas for the fuel to ignite
Activation Energy
amount of energy needed to start a reaction
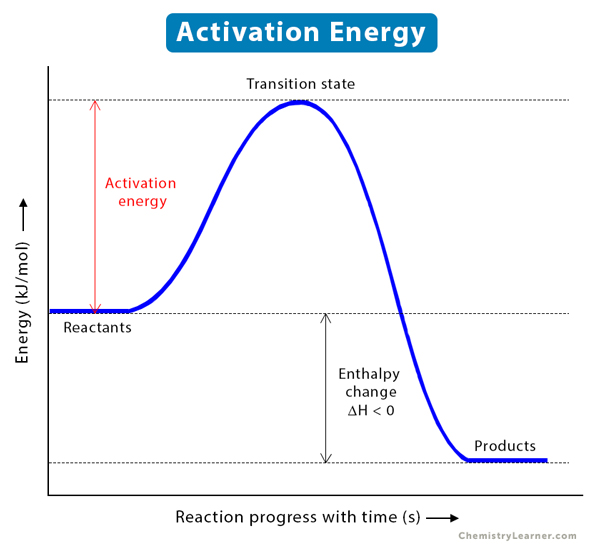
Enthalpy Change
Amount of energy absorbed or released during a chemical reaction
Endothermic reaction
take in energy and the temperature of the surroundings decreases (positive enthalpy change)
Exothermic reaction
transfer energy to the surroundings and the temperature of the surroundings increases (negative enthalpy change)
Catalyst
Decreases amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction (acts as “jumpstarter”)
Bond Enthalpy Equation
sum of bonds broken - sum of bonds formed
Voltaic Cells
Devices that use a chemical reaction between two cells to create energy
Complete Combustion of Octane
2C(8)H(18) + 25O(2) —> 16CO(2) + 18H(2)O
Word equation of Combustion of Octane
Octane + Oxygen —> Carbon Dioxide + Water
Lithium Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries operate by transferring lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes during charging and discharging, enabling the storage and release of electrical energy.