Researching psychology and culture through a positive psychology lens
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is positive psychology
the scientific and applied approach to uncovering people’s strengths and promoting their positive functioning
what makes life worth living
emphasises positive experiences
All traditions emphasis that happiness is rooted in …
the internal state of mind rather than external circumstances
What does ‘atman’ mean in Yogic sciences
pure happiness is achieved when an instant desire is fulfilled and the mind relaxes
What does ‘ananda’ mean in Yogic sciences
a moment of pleasure
What does ‘equanimity’ mean in Buddhism
a piece of mind and happiness
detaching oneself from the cycle of craving to achieve transcendent bliss
Both Yogic sciences and Buddhism highlight…
the need to transcend immediate or cyclical desires for deeper, more enduring happiness
Both Islamic teachings and Yogic sciences connect happiness to …
a higher spiritual purpose
What do Islamic teachings say about material processions
discourage longing for material possessions
focusing on divine provisions
What do Hebrew teachings say about happiness
see happiness as a conscious state of thought:
Simchah for being in a state of happiness
your state of mind (machshavah) shapes your state of happiness (simchah)
viewed happiness as a way of thinking
from this perspective, happiness doesn’t derive from our objective state of affairs but from our subjective state of mind
What are the two main perspectives to understanding when researching culture
culturally free
culturally embedded approach
What does the culturally free approach emphasis
emphasises the cross-cultural/global applicability of human strengths, values, and happiness across cultures
What does the culturally embedded approach focus on
focuses more on the necessity of a multicultural perspective: takes into account the variability resulting from cultural context
Does culture shape well-being, Steel et al., (2018) study
explored whether cultural values impact individual and national financial and subjective well-being
Does culture shape well-being, Steel et al., (2018) study findings - individual level
individual level: “what cultural values might increase a person’s life satisfaction”
relationships
social capital
connection
supportive networks
Does culture shape well-being, Steel et al., (2018) study findings - national level
national level: “what characteristics make countries happier”
personal freedom
openness
tolerance
education
social mobility
wealth distribution
The World Happiness Report ranks countries based on …
various factors such as:
income
social support
life expectancy
freedom to make life choices
generosity
perceptions of corruption
The least happiest countries has what factors:
conflict and instability
economic challenges
social and health issues
corruption
environmental factors
social unrest
inequality
What matters for a happy environment
education system
healthcare
natural beauty and environment
safety and low crime rates
cultural and recreations opportunities
work-life balance
What are the 6 major distinctions between eastern and western ideas of flourishing, Joshanloo (2014) - Eastern
self-transcendence
eudemonism
harmony contentment
valuing suffering
relevance of spirituality and religion
What are the 6 major distinctions between eastern and western ideas of flourishing, Joshanloo (2014) - Western
self-enhancement
hedonism
mastery
satisfaction
avoiding suffering
relative irrelevance of spirituality and religion
Peterson and Seligman (2004) developed Character Strengths and Virtues handbook to identify and classify 6 core virtues that are…
wisdom or knowledge
courage
humanity
justice
temperance
transcendence
What is the western concept of self
primarily based on the ideals of individualism
enhancing autonomy, independence, self-esteem, strong ego
What is the eastern concept of self
regard the self as a small part of the collective and the cosmos
in Asian traditions, the individual self is de-emphasised in one way or another
What did Maslow consider self-actualisation to be
the pinnacle of human development and the highest human need
realisation of one’s full potential
What are 4 criticisms of Maslow’s findings
little support for ranked needs or definite hierarchy
cultural bias: Maslow effects individualistic (US) perspective
self-actualisation may not apply in collectivist cultures
collectivist cultures: acceptance and community needs outweigh individuality
sex in the hierarchy placed with physiological needs overlooks emotional, familiar, and social aspects
Western psychology approach to well-being…
focus on subjective well-being
based on hedonic view - maximising pleasure and positive emotions
happiness measured by pleasure and life satisfaction
scientific analysis aims to quantify individual mental well-bring and quality of life
Eastern psychology approach to well-being…
focus on eudaemonic (pursuing happiness by finding meaning and purpose) well-being
emphasise virtue and right action for lasting well-being
happiness is not just temporary pleasure, includes moral and social dimensions
happiness linked to fulfilling personal and social responsibilities
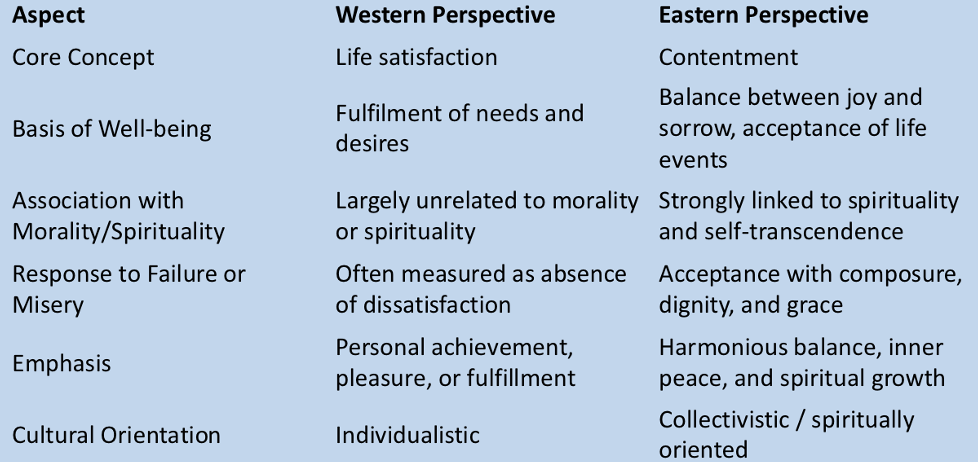
Satisfaction vs. contentment (western and eastern)
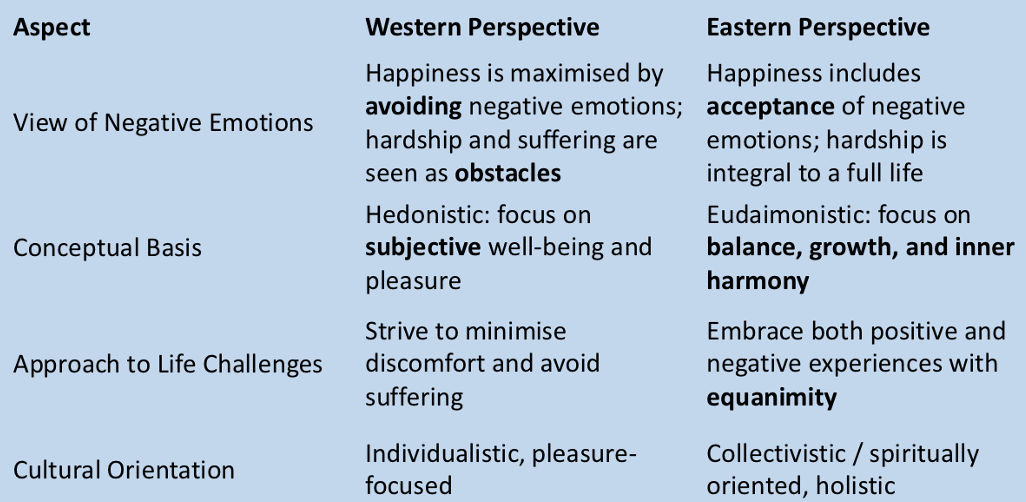
Valuing vs. avoiding suffering (western and eastern)
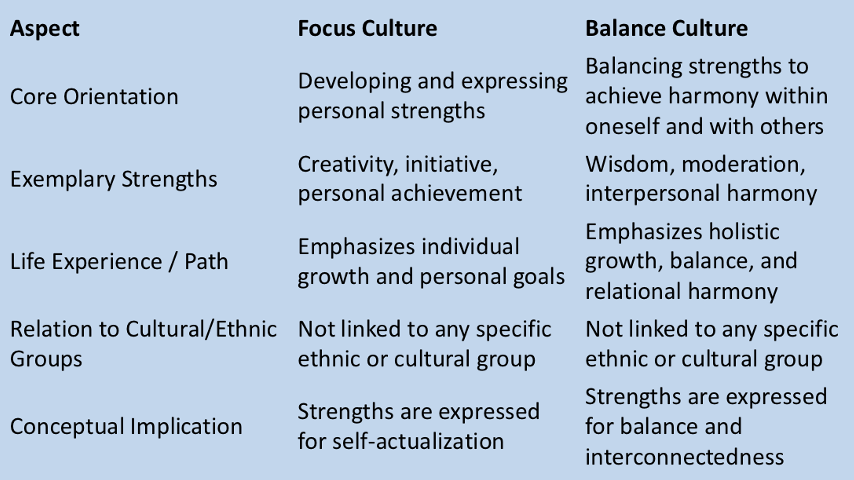
What did Bacon (2005) do
distinguished two ‘cultures’ within positive psychology:
focus culture
balance culture
these approaches aren’t tied to any particular cultural group
they reflect different ways individuals conceptualise and use their strengths to shape life experiences
What does focus culture emphasise
developing and expressing individual strengths, such as creativity
What does balance culture emphasise
harmonising strengths within oneself and with others, such as wisdom
Wisdom vs. creativity (focus culture and creativity culture)
4 types of bias in cross-cultural research
conceptual bias
method bias
measurement bias
interpretational bias
What is conceptual bias
whether there is equivalent meaning and relevance of theory and hypotheses across cultures being compared
What is method bias
sampling – whether samples are equivalent and representative of their culture
linguistic – whether tools used have the same meaning across languages in the study
procedural – whether the data collection efforts mean the same in all cultures of the study
What is measurement bias
whether measures and instruments demonstrate reliability and validity across cultures in the study
response bias - whether people of cultures in the study respond differently or have a biased response when tested
What is interpretational bias
whether interpretations and results of a study have practical meaning and/or are biased in some way
for a measure to be useful in cross-cultural research, it must be reliable (consistent) and valid (accurate) in all the cultural groups being studied
What is back-translation
common approach to address linguistic equivalence
involves translation of the research protocol into a different language(s) and the having a different person translate it back to the original language and repeated with the goal of semantic equivalence among the protocols
often used as a quality assurance method