Presentation Slides 9
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Ligand-gated ion channel
(= Ionotropic receptor)
Depolarize or hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane
G-protein coupled channel
(= Metabotropic recpetor)
Initiate another chemical reaction
Create a new synapse
Bring about changes in another cell
Dendrodentric synapse
dendrites send messages to other dendrites
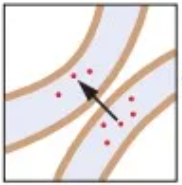
Axodendritic synapse
Axon terminal of neuron synapses on dendritic spine of another
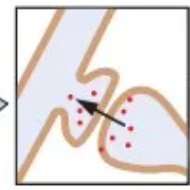
Axonextracellular synapse
Terminal with no specific target. Secrets transmitter into extracellular fluid
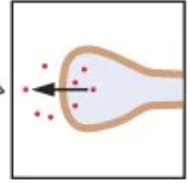
Axosomatic synapse
Axon terminal ends on cell body

Axosynaptic synapse
Axon terminal ends on another axon terminal
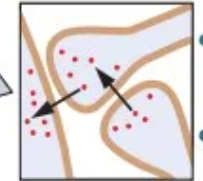
Axoaxonic synapse
Axon terminal ends on another axon
Axosecretory synapse
Axon terminal ends on a tiny blood vessel and secretes transmitter directly into the blood
Type 1 synapse
excitatory synapses
excitatory synapses
typically occupy spines and dendritic shafts on neuron
round synaptic vesicles
denser pre-and postsynaptic membranes
synaptic cleft is wider
larger active zone
Type 2 synapses
inhibitory synapses
inhibitory synapses
typically found on the cell body
flattened synaptic vesicles
Resting potential at neuronal cell membranes
Equilibrium maintained through diffusion and electrical push/pull actions of ions
Hyper- and depolarization of cell membranes
Leak and voltage-dependent membrane channels open or close
Spatial and temporal summation of EPSPs and IPSPs
May lead to AP when over threshold; propagating along the axons
Depolarization of presynaptic terminals cause Ca2+ channels to open
Neurotransmitters released into synaptic cleft, bind to receptors at postsynaptic membrane; may lead to closing or opening of ion channels
Autoreceptors
Receptors on the presynaptic membrane that the neurotransmitter can interact with
Deactivation
Diffusion
Degradation
Reuptake
Glial cells
Difussion
diffuses away from synaptic cleft
Degradation
enzymes in cleft break down neurotransmitter
Reuptake
transmitter taken back into presynaptic axon terminal for reuse
Glial cells
take up some neurotransmitters
classes of neurotransmitters
Small-molecules
Peptides
Lipids
Gases
Small Molecule Transmitters
Small organic molecules
Quick-acting
Synthesized and packaged in axon terminals
Derived from the food we eat
Rate-limiting factor
Any enzyme that is in limited supply, so that the pace
at which a chemical can be synthesized is restricted
Acetylcholine
Normal waking behavior and memory
Loss of cholinergic neurons is associated with Alzheimer’s disease
Thought to function in attention and memory
Nigrostriatial Pathway
Movement
Maintaining normal motor behavior
Degenerates during Parkinson’s disease
Mesolimbic Pathway
Affected by Addictive Drugs
DA release causes feelings of reward and pleasure
Excessive dopamine may lead to schizophrenia
Decreased DA may be related to attention deficits
Noradrenaline
Plays a role in learning by stimulating neurons to change structure
Also active in maintaining emotional tone
May also facilitate normal development of the brain and organize movements
Decreased NE activity may lead to Major Depression, ADD, ADHD
Increased NE activity may lead to Mania
Serotonine
Active in maintaining waking EEG pattern, learning, emotion
Decreased 5-HT activity related to Depression
Increased 5-HT activity related to schizophrenia or OCD
Abnormalities in brainstem 5-HT linked to sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) or Sleep Apnea (=syndrome in which the brain fails to tell the muscles to breathe)
Amino Acids
Glutamate
GABA
Glycine
Histamine
Glutamate
Excitatory Neurotransmitter (amino acid)
GABA, Glycine
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters (amino acid)
Histamine
Causes constriction of smooth muscles
Peptide Transmitters
Have no direct effects on postsynaptic
membrane voltage
Cannot be taken orally as drugs, as small-molecule
transmitters can be
Functions of Peptide Transmitters
Serve as hormones
Activate in response to stress
Encourage mother-child bonding
Facilitate learning
Regulate eating and drinking
Respond to pleasure and pain
endocannabinoids
a class of lipid neurotransmitters synthesized at the postsynaptic membrane to act on receptors at the presynaptic membrane
Cannabinoids
act as neuromodulators to inhibit release of glutamate and GABA
Transmitter Gases
Synthesized as needed by the cell
Can be produced in many regions of the cell
Diffuse away from the cell after production
Nitric Oxide (NO)
Controls muscles in intestinal walls
Dilates blood vessels in the brain and in the genital organs
Viagra acts by enhancing action of NO
When activated by a neurotransmitter, the ionotropic receptors
change shape
receptors
protein molecules in the postsynaptic membrane on neurons
When activated by a neurotransmitter, the metabotrobic receptors
Alter chemical reactions in the target cell
Ionotropic Receptors (direct effects)
Binding sites for neurotransmitter
Allow the movement of ions across the membrane
Rapid changes in voltage
Do not last long
excitatory effect on the target cell
Metabotropic Receptors (Indirect Effects)
inhibitory effect
Amplification cascade
Second messenger
Amplification cascade
Cascade effect is that many downstream proteins (second messengers or channels or both) are activated or deactivated
Allows that a single neurotransmitter’s binding to a receptor can activate an escalating sequence of events.
Second messenger
Binds to a membrane-bound channel, causing the channel to change its structure and thus alter ion flow through the membrane.
Initiates a reaction incorporating intracellular (within the cell) protein molecules into the cell membrane, leading to formation of new ion channels.
Binds to sites on the cell’s DNA to initiate or cease the production of specific proteins
Dale’s Principle
Same neurotransmitter is released from all axonal terminals of a neuron
Neurotransmitter criteria
Synthesized in a neuron
Release → Response
Chemical specific
Removal mechanism