SHS 300 - Nervous System
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
organization of the nervous system
central nervous system:
brain
spinal cord
peripheral nervous system:
cranial nerves
spinal nerves
subdivisions of the PNS:
somatic
autonomic
sympathetic division
parasympathetic division
3 main functions of the nervous system
gather sensory information (through the PNS)
synthesize information (in the CNS)
respond to stimuli (CNS sends to PNS)
white matter
bundle of myelinated axons
gray matter
cluster of cell bodies
nuclei
cluster of cell bodes in the CNS
tract
bundle of axons in the CNS
nerves
bundle of axons in the PNS
ganglia
cluster of cell bodies in the PNS
afferent pathways
sensory input
efferent pathways
motor output
neurons
definition: specialized cells that transmit electrochemical signals
respond to stimuli by processing and conducting impulses to other neurons and cells (communication between parts)
macroglia (type of glial cell)
Oligodendrocyte and Schwann Cell:
Oligodendrocyte - found only in the CNS
Schwann Cell - found only in the PNS
both produce myelin and surround the axon to provide the axon with it
Astrocyte:
scaffolding: connects to the neuron and promotes neuronal migration (when A moves, N moves too)
neuronal survival: connects the neurons to blood vessels, where the neurons will receive the nutrients they need to survive
synapse: determines how many synapses a neuron can have
formation of the blood-brain barrier
maintains neuronal homeostasis (e.g., extracellular fluid, energy, etc)
microglia (type of glial cell)
“immune cells” of the CNS —> release cytokines in response to injury; remove debris
neuronal support —> programmed cell death for malformed neurons, etc
homeostasis
disease processes —> releases debris/harmful substances in small amounts to help the brain in developing an immune response (can release too much, which results in inflammation and neurodegeneration)
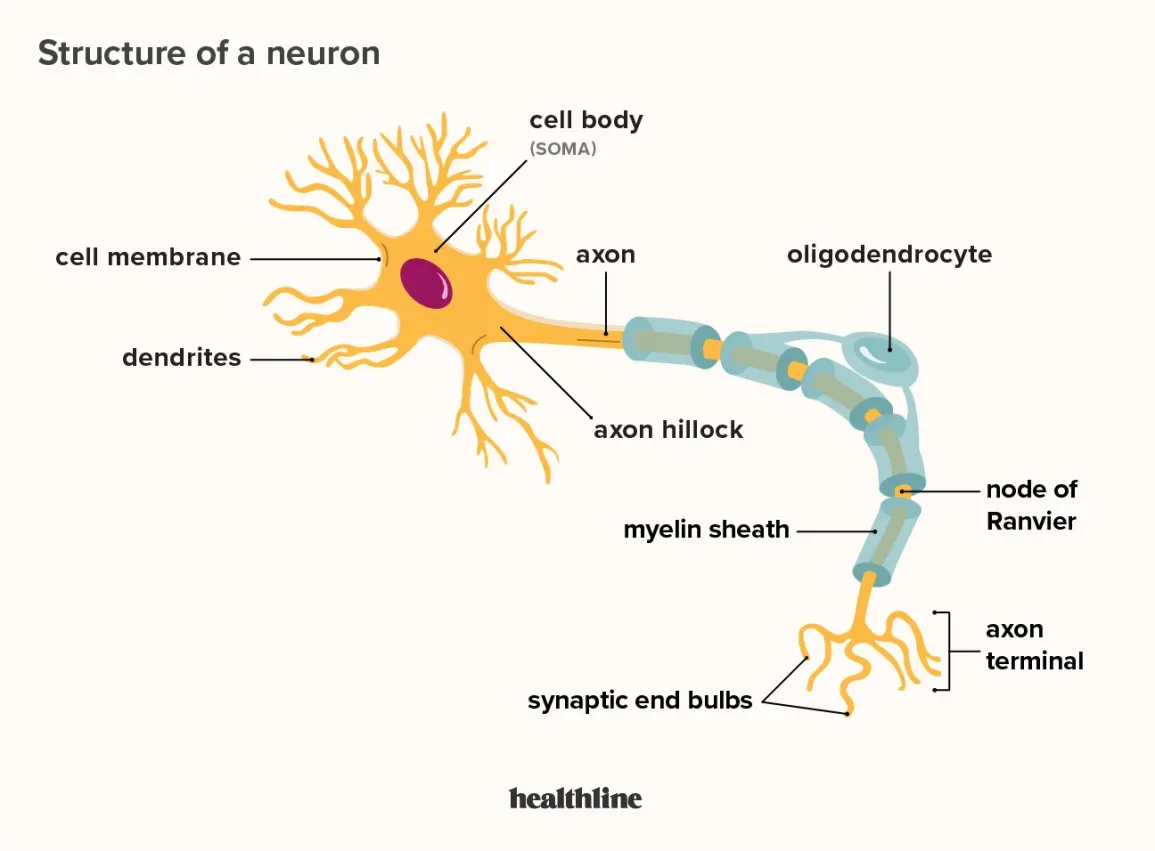
labeled neuron
see image
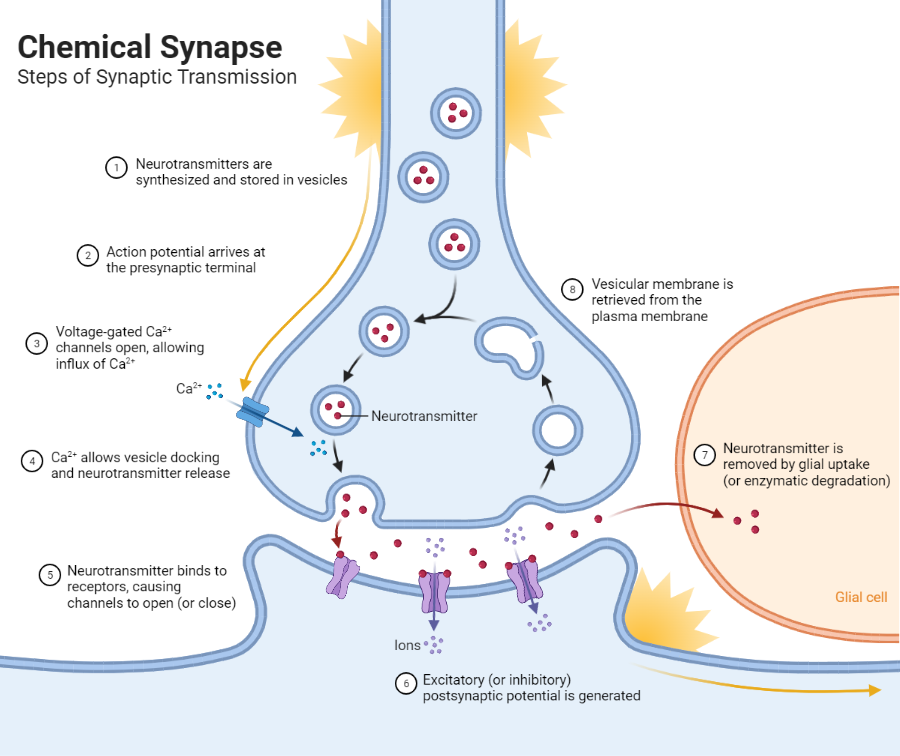
synaptic process
synaptic vesicles located in the presynaptic membrane house neurotransmitters
when triggered by an action potential, the neurotransmitters are released and bind to receptors in the post-synaptic membrane
the type of receptor on the post-synaptic membrane will dictate which ions enter —> results in either an excitatory effect (+ ion) or inhibitory effect (- ion)
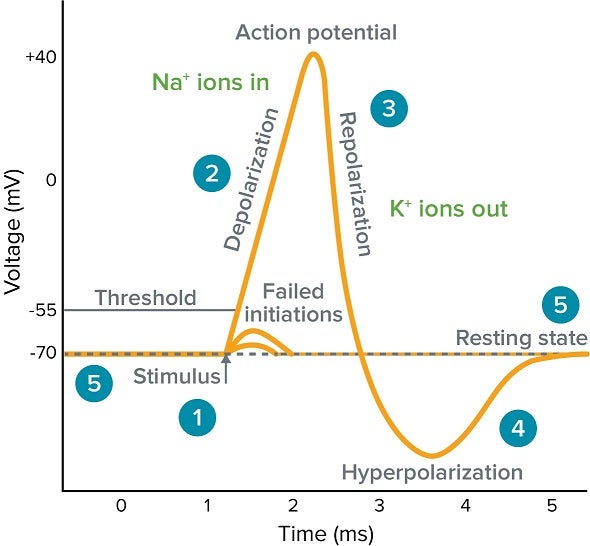
action potential
a neuron is stimulated:
strong enough: threshold is met (-55mV) and there will be a large and fast influx of Na+ ions that results in depolarization (+40mV)
NOT strong enough: some depolarization but does not meet the threshold (failed initiations)
at the peak of the action potential (+55mV), K+-gated channels open which results in an outflux of K+ = repolarization
outflux of K+ and closing of Na+-gated channels causes the neuron’s potential to be more negative than the threshold (refractory period)
neuron eventually returns to its resting state (-70mV)
organization of the central nervous system
brain:
cerebrum (cortex)
cerebellum
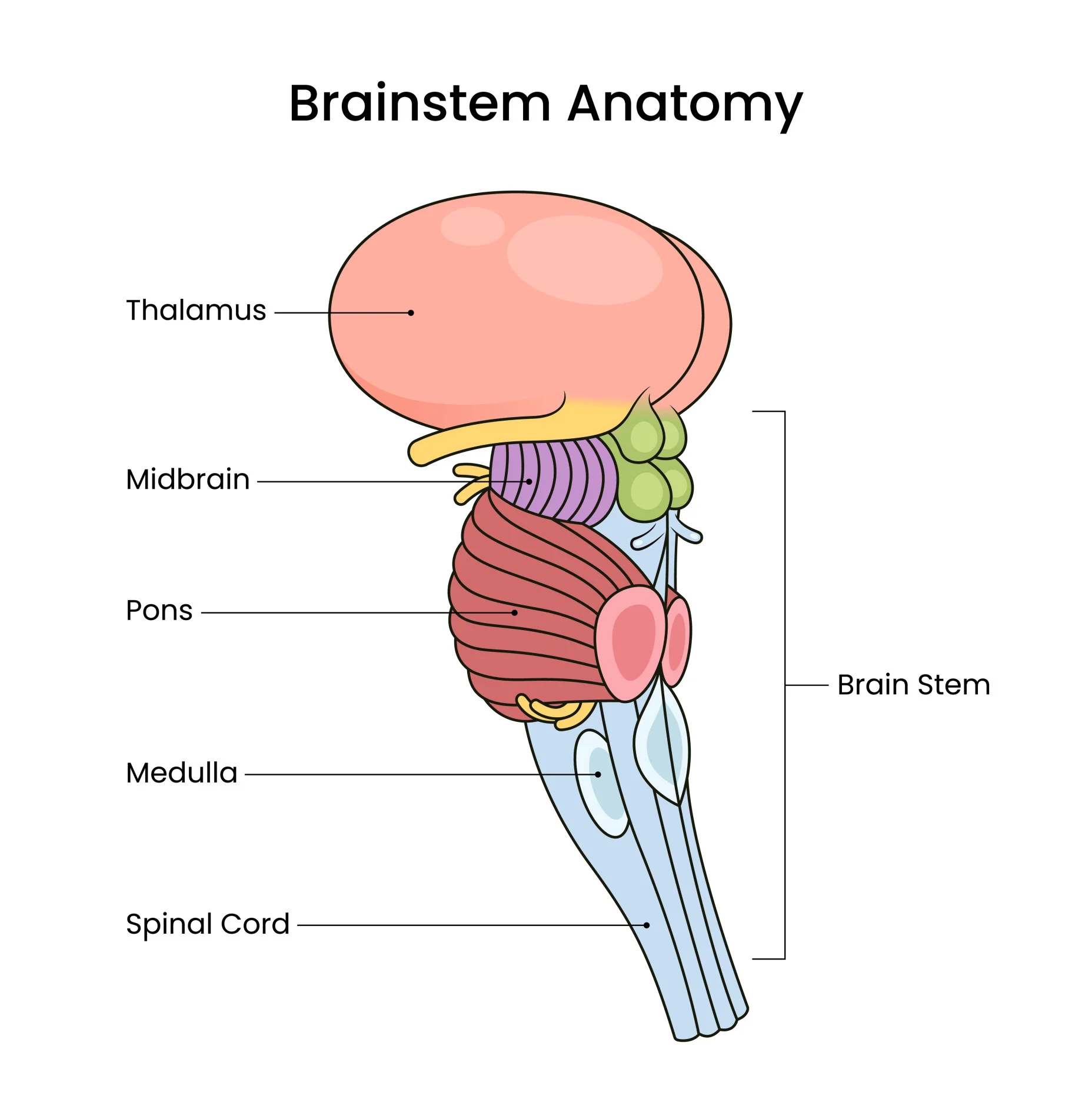
brainstem
midbrain
pons
medulla
spinal cord
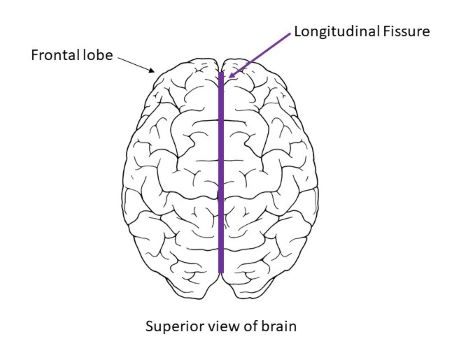
name of the fissure that divides the cerebral hemispheres into right and left
longitudinal fissure
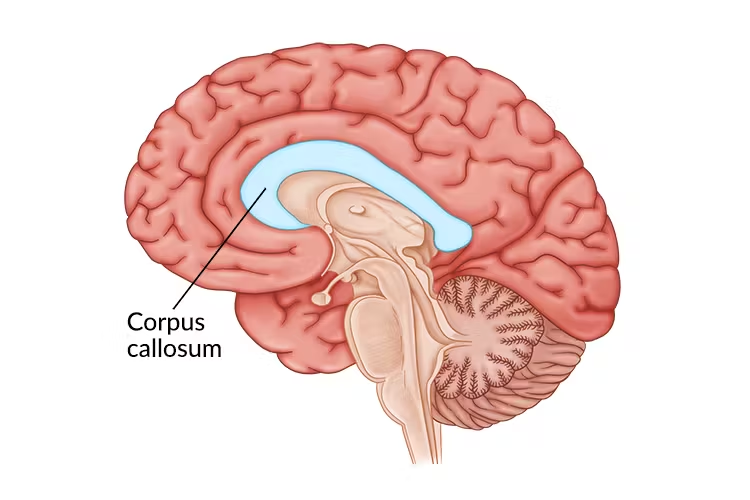
function of the corpus callosum
communication point between the left and right hemispheres
frontal lobe - function
motor planning, decision-making, and language production
parietal lobe - function
sensory integration to touch, pressure, and pain
temporal lobe - function
auditory processing and language comprehension
occipital lobe - function
primary visual processing
functions of the insula
emotions - compassion, empathy, self-awareness
hunger and thirst
pain and fatigue
risk and reward
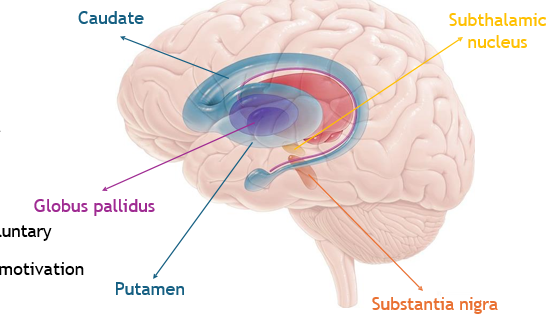
basal ganglia - identify and function
motor control of voluntary movements
cognition: reward, motivation (habit)
thalamus
relays sensory and motor information
hypothalamus
regulates body temperature, hunger/thirst, and circadian rhythm
amygdala
processes emotions, especially fear and aggression
hippocampus
formation of new memories; consolidation of memories
spatial navigation
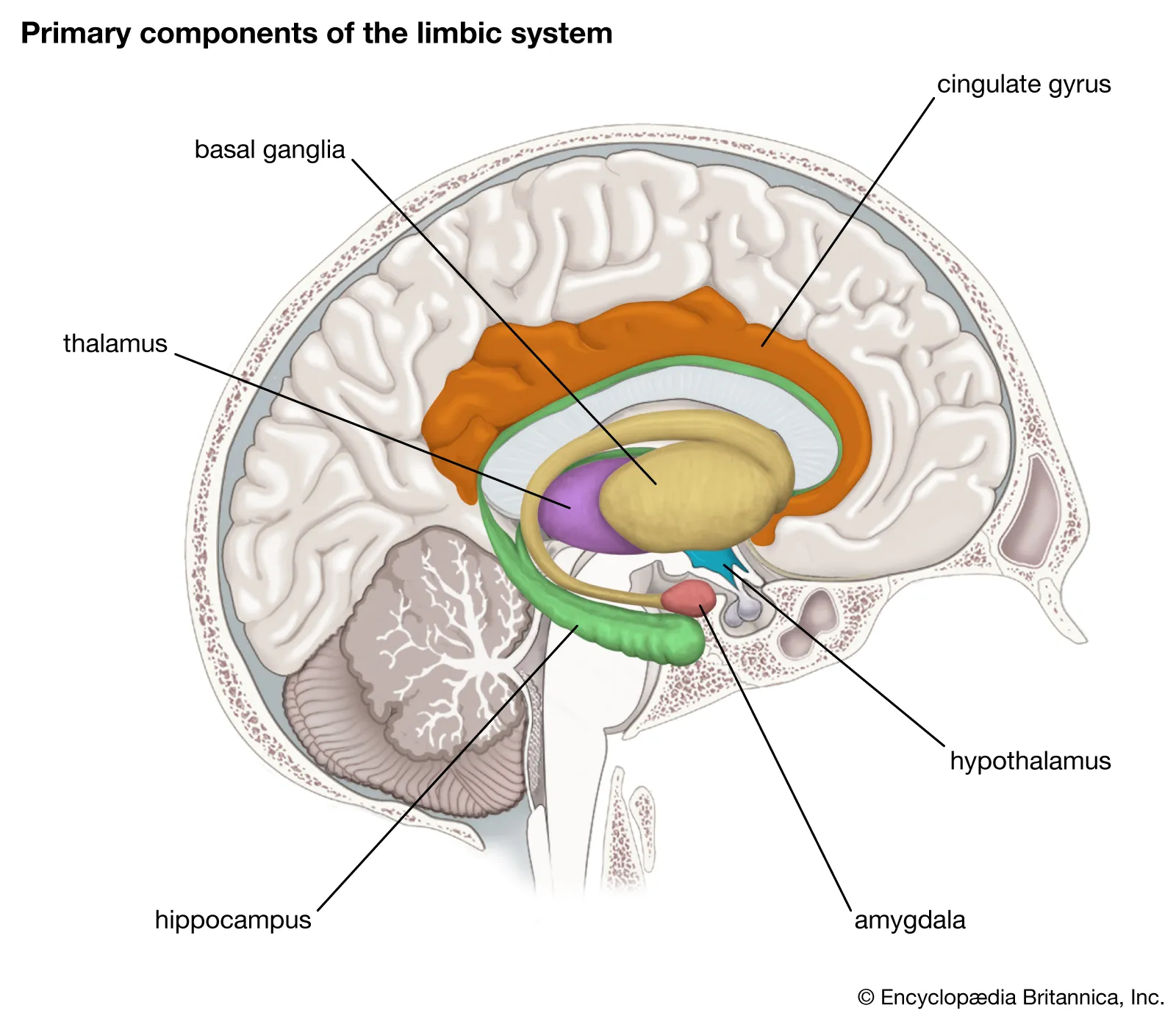
limbic system - structures and functions
overall, the limbic system is involved in emotional processing, motivation, memory, and autonomic processes
cingulate gyrus - learning
hippocampus - memories
amygdala - emotions
hypothalamus - autonomic
basal ganglia - motor movement
function of the cerebellum
movement coordination
brainstem - identify and functions
consciousness
basic vegetative functions (e.g., breathing, heartbeat)
houses cranial nerve nuclei (and where cranial nerves exit)
3 layers of tissue protecting the brain (meninges)
dura mater - most superficial layer
arachnoid mater - intermediate layer (CSF)
pia mater - deepest layer
how the arrangement of the Circle of Willis is beneficial to the brain
definition: anterior and posterior circulation come together to form a circular blood supply
if damage to the brain occurs, the other arteries located within it will compensate for the damaged parts (not a permanent solution)
CN I function
olfactory nerve
responsible for the sense of smell
CN II function
optic nerve
responsible for vision
CN III function
oculomotor nerve
responsible for eye movements, pupillary constriction, and innervation of the muscle of the upper eyelid
CN IV function
trochlear nerve
responsible for vertical eye movements
CN V function
trigeminal nerve
responsible for:
sensation of the face, teeth, gum, and anterior 2/3 of the tongue
innervating the muscles of the jaw
***important for speech and swallowing
CN VI function
abducens nerve
responsible for lateral eye movement
CN VII function
facial nerve
responsible for:
taste for anterior 2/3 of tongue
innervation of the muscles of facial expression; innervation of the salivary glands
***important for speech and swallowing
CN VIII function
vestibulocochlear nerve
responsible for hearing and balance
CN IX function
glossopharyngeal nerve
responsible for:
sensation of the posterior 1/3 of tongue; taste for posterior 1/3 of tongue
innervations of the salivary gland (carotid gland)
***important for speech and swallowing
CN X function
vagus nerve
responsible for:
sensation of the pharynx and larynx
innervation of the muscles of the vocal folds and swallowing; also involved in autonomic functions (e.g., heart, lungs, etc)
***important for speech and swallowing
CN XI function
accessory nerve
responsible for:
innervation of the muscles of the shoulders and neck
***important for speech and swallowing
CN XII function
hypoglossal nerve
responsible for the innervation of the muscles of the tongue
***important for speech and swallowing
spinal nerves that form the cervical plexus
C1, C2, C3, C4
spinal nerves that form the phrenic plexus
C3, C4, C5
5 neurological diseases that may affect communication or swallowing
Parkinson’s disease
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Huntington’s disease
Multiple sclerosis
Stroke/TBI