Ap Pscyh Unit 7 (Cognition)
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
Memory
The persistence of learning over time through the encoding, storage and retrieval of information
Alzheimer’s disease
Begins as difficulty remembering new information and progresses into an inability to do everyday tasks
Recall
Retrieving information not currently in your conscious awareness but learned at an earlier time ex. fill in the blank
Recognition
Identifying items previously learned ex. multiple choice questions
Relearning
Learning something more quickly when you learn it a second/later time ex. studying for a final exam
Herman Ebbinghaus
Randomly selected syllables, practiced and tested himself on them, he could recall few, but the more he read them aloud on day 1, the less time it took him to re learn on Day 2
test of recognition and of time spent re learning demonstrate that we remember more than we recall
Encoding
Getting information into your brain and memory system
Storage
Process of retaining information over time
Retrieval
Process of getting information back out of the memory system
Parallel processing
Processing many aspects of a problems simultaneously; the brains natural mode of info processing for many functions
Connectionism
Multi track processing, views memories as products of interconnected neural networks
Richard Atkinson and Richard shiffrin
Proposed 3 stage model for the memory forming process
Includes -
Sensory memory (1)
Short term memory (2)
Long term memory (3)
Sensory memory
Immediate very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
Short term memory
Activated memory that holds few items briefly, before the information is stored or forgotten (encoded through rehearsal)
Long term memory
Relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of memory systems, for later retrieval
Includes - Knowledge, skills and experiences
Working memory
Newer understanding of short term memory that adds conscious, active processing of incoming auditory and visual information and of information retrieved from long term memory
Central executive
Coordinates selective attention
Explicit memories ( Declarative memories )
Facts and experiences we can consciously know and declare
Effortful processing
Encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
this is how we encode explicit memories
Automatic Processing
Unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time and frequency of well learned information such as word meaning
Implicit memory (nondecleration memory)
Retention of learned skills or classicling conditioning association independent of conscious recollection
Examples of things you automatically process
Space - when you recall information you may visualize its location
time - going through your day, you unintentionally note the sequence of its events
Frequency - unintentionally keep track of how many times things happen
Retention curve
Shows memory retention, how much info stays in memory over time
Herman ebbinghaus
Forgetting curve
This curve shows that we forget new information rapidly at first, then more slowly over time
within a day, initial drop off of remembered info
Herman ebbinghaus
Iconic memory
A momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli; a picture image memory lasting no more than a few tenths of a second
Echoic memory
A momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli; if attention is elsewhere; sounds and words can still be recalled within 3 or 4 seconds
George Miller
Magic number 7, proposed we can store about 7 pieces of info in short term memory
Chunking
Organizing items into familiar, manageable units; often occurs automatically and naturally
Mneomics
Memory aids, especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices
Peg word system
Type of mneomic , memorize a jingle
Acronym
Creating word from first letters of the to be remembered items
Hiearchies
Composing few broad concepts divided and subdivided into narrow concepts and facts
Spacing effect
The tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long term retention than is achieved through massed study or practice
testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply re reading info. Also sometimes referred to as a retrieval practice effect or test enhanced learning
Shallow processing
Encoding on a basic level, based on the structure or appearance of words
Deep processing
Encoding semantically, based on the meaning of the words; tends to yield the best retention
Self reference effect
When asked how well adjectives describe us, we often remember them
Semantic memory
Explicit memory of facts and general knowledge; one of our two conscious memory systems
Episodic memory
Explicit memory of personally experienced events; one of our two conscious memory systems
Where in the brain are semantic memory and episodic memory happening?
Frontal lobe + hippocampus
Working memory process
Past experience to input to prefrontal cortex
left frontal lobe vs right frontal lobe
Process different memories
left frontal lobe = recalling a password and holding it in working memory
right frontal lobe = Calling up a visual party scene
Hippocampus
Neural center in limbic system, helps process explicit ( conscious) memories of facts and events for storage
temporarily holds info, not permanently stored
damage?
left - trouble remembering verbal info but can recall visual designs and locations
right -can remember verbal info but can not recall visual designs and locations
Memory consolidation
Neural storage of a long term memory
sleep supports this
Cerebellum
implicit memory formation needs this, when damaged you can not develop certain conditioned reflexes
Basal ganglia
Facilitate formation of procedural memories for skins ( motor )
Infantile amnesia
As a adult, our first four years pretty blank from our conscious memory BECAUSE many language young children cant process and hippocampus is one of the last structures to mature ( hippocampus plays crucial role in conscious (explicit ) memories )
Flashbulb memories
A clear, sustained memory of an emotionally significant moment or event
Eric kandel and James Schwartz
Observed synaptic changes during learning in the neurons of Cali sea slug (alpysia) 20k large and accessible nerve cells
when learning occurs the slug realses more of the neurotransmitter serotonin into certain neurons
learning and experience can increase the number of synapses in slugs
Long term potentiation
An increase in a cells firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation; a neural basis for learning and memory
drugs that block this interfere with learning
Electroconclusive therapy
Passing an electric current through the brain wont disrupt old memories
Implicit (Automatic)
without conscious recall
cerebellum
basal ganglia
Explicit ( effortful )
with conscious recall
hippocampus
frontal lobes
Retrieval cues
Things around you, to associate with the memory to later access info
Priming
The activation, often unconsciously, of a particular association in memory ( one stimulus triggers related concepts )
William James
implicit (unconscious)
example - hearing the word doctor makes you recognize the word nurse faster
Encoding specificity principle
The idea that cues and contexts specific to a particular memory will be most effective n helping us recall
memories are context dependent
State dependent memory
When you learn something it is easier to remember in that state (drunk/sober/high)
Mood congruent memory
The tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with ones current mood
Serial position effect
Our tendency to recall best the last and first memory items in a list
last = recency effect
first = primacy effect
What would happen if someones hippocampus was removed?
Inability to form new conscious memories
Anterograde amnesia
An inability to form new memories
recall past, no new memories
Retrograde amnesia
An inability to retrieve information from one’s past
can learn non-verbal tasks but do them with no awareness of learning them
Alzehimer’s patients
Explicit memories for new people/events are lost, but they can form new implicit memories
Encoding failure
Many of what we sense, we never notice, and what we fail to encode, we will never remember
Storage decay
memories being inaccessible ( stored memories that decay)
Forgetting curve
The curve of forgetting is initially rapid, then levels off with time
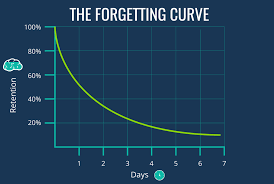
Retrieval failure
Forgetting is not fading, but often unretrieved memories (important/rehearsed info is what is in long term memory)
Proactive (forward acting) interference
The forward-acting disruptive effect of older learning on the recall of new information
Example - Buying a new combination lock, your well-rehearsed old combo may interfere with your retrieval of the new one
Retroactive (backward acting) interfernce
The backward-acting, disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old info
Example - You hear new lyrics to an old song, you may have trouble remembering the old words
Positive transfer
Old and new language do not always compete with each other
(latin and french)
Motivated forgetting
memory is unreliable
Repression
In psychoanalytic theory, the basic defense mechanism that banishes from conscious anxiety arousing thoughts, feelings and memories
repressed memories liger, often brought out by retrieval cues or in therapy
most memory researchers think repression rarely occurs
UNCONCIOUS!!!!!!!!
Reconsolidation
A process in which previously stored memories, when retrieved, are potentially altered before being stored again
Elizabeth loftus
Showed pairs of faces ( to identify later ) as they would appear on a police line-up, then showed 2 faces and asked people to identify which they had seen ( one pair had two new faces, one being a face seen like one earlier ), most people wrongly identified the face as one previously seen, then showed wrong and right face, most chose wrong face (false memory)
Mis information effect
Occurs when misleading information has distorted one’s memory of an event
mis information and imagination effects activate similar brain areas
Imagination influence
Digitally altered photos produce this
Source amnesia ( source misattribution )
Faulty memory for how, when, or where information was learned or imagined ( heart of many false memories)
Deja vu
The eerie sense that “Ive experienced this before” cues from the current situation may unconsciously trigger retrieval of an earlier experience
Where does the experience of familiality come from?
Temporal lobe processing
Where do consciously remembered details come from?
Hippocampus/frontal lobe processing
Hindsight bias
People tend to recall having always felt as they did today
looking back and thinking it was obvious
Ways to improve memory
Rehearse repeatedly
Make material meaningful
Active retrieval cues
Use mnemonic devices
Minimize proactive and retroactive interference
Sleep more
Test your own knowledge ( to rehearse, find out what you do not know)
Supression
Similar to selective attention
conscious / voluntary
acknowledges as important cognitive process
Foresight bias
“Oh, that will be easy to remember, not effortful but automatic processing, autopilot, selectively attend to something else (in moment)
Prospective memory
Remembering to complete a future task
“remembering to remember”
Cognition
All the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering and communicating
Concepts
Mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas and people
Prototypes
Mental image/ best example of category, matching new items to a prototype provides a quick and easy method for sorting items into categories ( dependent on experience)
example - chair is prototype for furniture, robin is a prototype for bird
Creativity
Ablity to produce new and valuable ideas
Convergent thinking
Narrowing the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution
short cut, takes less time
example - the keys, sorting and only trying a certain amount rather than trying every single one
Divergent thinking
Expanding the number of possible problem solutions; creative thinking that diverges in dif solutions
takes more time
example - the keys, trying every single one till you get to the right one
Robert steinbergs 5 components for creativity
expertise
imagintive thinking skills
a venturesome personality
instristic motivation
creative enviorment
What part of the brain, if damaged, can destroy imagination?
Frontal lobes
Metacogntion
Thinking about thinking
Algorithm
A methodical, logical role or step by step, procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem
prefrontal cortex thinking
conscious decision making
Heuristic
A Simple thinking strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems, usually speedier but also more error prone than algorithmsn
Insight
Subconscious/unconscious, sudden realization
strikes suddenly, no getting “warmer”
Before getting the aha moment, the frontal lobes were active
at instant of discovery there was a burst of activity in the right temporal lobe
3 Obstacles of problem solving
confirmation bias - tendency to search for info that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence
Functional fixations - inability/difficulty in looking at everyday objects in new ways ex. coat is only smth that keeps you warm but could be a pillow
fixation : mental set
System 1 thinking
Quick, intuitive, and effortless
first initial thought
System 2
Slow, analytic, and effortful
more thought through