Lecture 2: Active Brain Toolbox
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary and concepts from Lecture 2, including research methods, experimental design, neuroimaging techniques, and exercise physiology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Research Methods
Techniques used to understand variables or associations between variables.
Correlation
A method to observe the relationship between two or more variables without direct manipulation.
make conclusions about variables being related
Correlation metrics
Pearson r value
R-squared
slope (a) best of fit
Quasi-experimental
A type of research where individuals are divided based on a variable that cannot be easily manipulated.
considered a type of Correlational methods
Observed DV and conditions are compared
Experimental method
Experimenter manipulates one variable (IV) and it needs two conditions
randomly assigned
Observes DV (needs operational def)
Conditions compared
Independent Variable (IV)
The variable that the experimenter manipulates in an experiment.
control group to be exactly the same except on one feature ( the difference is what you think to be the cause )
Selection of IV is based on previous theory or findings
Dependent Variable (DV)
The variable that the experimenter measures in response to changes in the independent variable.
needs operational def: defining your construct in measurable terms
Needs to be observable and measurable
Random Assignment
A method in experiments used to equate groups by randomly assigning participants to different conditions.
Cross-Sectional Study
Research that observes a sample at a single point in time.
Longitudinal Study
Research that involves repeated measurements of the same individuals over extended periods.
Randomized Control Trial (RCT)
An experimental method that uses randomization to control for bias and see the causal effects. You either get the treatment or you don’t.
participants don’t know the treatment condition
OR
Investigators blinded ( don’t know the treatment)
Double blinded: both don’t know
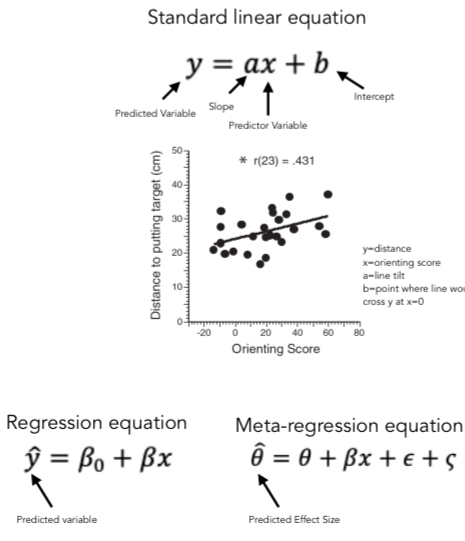
Meta-analytic Methods
Techniques used to summarize results across multiple studies.
collect papers
Extract effects
Analyze
Electroencephalography (EEG)
First human neuroimaging technique that records electrical activity of the brain.
Hans burger was the first psychiatrist to use EEG on a person and discovered the alpha wave.
Alpha Wave
A type of brainwave that your brain produces when you’re at rest, but you’re awake.
Ex: calm, daydreaming
Event related potentials
Averaged response to specific events
Physiological basis
Pyramidal cells, send and receive signals throughout the brain. When they are activated an electric charge flows within the cell. When a lot of cells do it together, it creates an electric current, which is stronger. This is picked up by the EEG.
Different signals:
Excitatory: flows into cell (turns activity up)
Inhibitory: flows out feel (turns activity down)
Oscillations
Task induced or endogenous brain rhythms
4 strategies to deal with noise EEG
Take advantage of movement silent periods
Randomize movement and signals
Separate signals and movements
Separate task related and noise signals
Key factors with exercise physiology considerations
Physical capacities
Timing of task and physical activity
Exercise type, duration, intensity, and frequency
Target population and individual differences
VO2max
A measurement of the maximum amount of oxygen an individual can utilize during intense exercise.
Psychosocial Factors
Variables related to psychological and social aspects that can affect research outcomes.
Exercise Physiology
The study of the body's responses to physical activity.
Physical Capacities
The body's ability to perform physical activities, influenced by various physiological factors.
how much can the body handle?
What is the response of the body?
Timing of task, execution, and physical activity
Synchronous: the task is occurring while engaged in the activity
Asynchronous: task and activity are at different times
Exercise type, duration, intensity, and frequency
Type: aerobic versus, anaerobic, or cardiovascular demand
Duration: acute= less than 60 minutes versus prolonged= more than 60
Intensity: how strong that exercise is
Frequency: is the Exercise one time or multiple times
Target population, and individual differences
Target population: general or specific ( expert)
Individual differences: fitness level, cognitive, demographics
EEG Key factors
Physical capacities
Timing of task and physical activity
Exercise type, duration, intensity, and frequency
Target population and individual differences
Synchronous exercise
Task is occurring while engaged in physical activity
Asynchronous
Task and activity are executed at different times
task executed before and then exercise after
Peripheral
Outside of the head
motor (skeletal & autonomic) and sensory
Central nervous system
Brain and spinal cord
signaling happens during electrical activity ( action potentials) and neurochemical changes ( neurotransmitters)
Neurotransmitters
A type of signal
can be excitatory or inhibitory
Can be globally or regionally
Skeletal motor system (somatic)
Voluntary movements
Autonomic motor system
Regulates internal organs and eyes
can be divided into three divisions ( parasympathetic, sympathetic, enteric )
Parasympathetic
Rest and digest
Sympathetic
Fight or flight response
Enteric
Manages digestion and associated processes
Peripheral
Neurotrophic
Effects that control neurogenesis, proliferation, differentiation, health
Neuromodulatory effects
Electrochemical effects that alter neural activity
Homeostasis
The body has ideal parameters to ensure functioning, there are feedback loops to ensure we stay close to that set point
goal is to promote stability
Allostasis
A predictive system that anticipates stress and promotes stability through change
involves nervous and endocrine system
Goal: provide physiological resources just in time
Hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis
Coordinate body’s response to stress
hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Adrenal gland
Hypothalamus
Helps manage functioning of the autonomic system
Pituitary gland
Part of endocrine system and makes multiple hormones
Adrenal gland
A small gland that makes steroid hormones, cortisol, adrenaline, and noradrenaline
HPA axis stress chain reaction
release of cortisol
Influences blood flow, respiration, metabolism, immune response, arousal,
Slow, peaks in 20-30 min after an acute stressor
Always on ti some degree
Coordinates sleep/wake cycle
Exercise as a stressor to the body creates..
increased corticosteroids (cortisol, ACTH)
competition stress alters this
Increase depends on intensity
Increased catecholamines (epinephrine & norepinephrine)
training reduces response to exercise
Sympathetic adrenal medullary axis
Fight or flight system
stress detected the hypothalamus signals to the sympathetic nervous system to stimulate the adrenal medulla (releases adrenaline, noradrenaline)
Inc heart rate, vasoconstriction, inc blood pressure, respiration, liver, pupil dilate, digestion slows
Fast
Always in to some degree
Sensory coding
Adapting behavioral goal with what happens on the environment
hierarchically processed in the brain
Communication is multi directional
mapped spatial or nonspatial
bullock and geisbrecht 2014 study + results
Investigated the relationship between fitness and attention by doing an exercise task, and having individuals perform a visual task before and After.
Results: they found that higher capacity is associated with faster search times
Salience network
Controls response to unexpected events
ACC: Anterior cingulate cortex, ventral, frontal, temporal, and parietal
Executive network
Controls goal relevant behavior
DLPFC & PPC
Mammalian Cortex
Sheath of gray matter surrounding white matter
contains 6 layers and each has a specific role in brain processing
Niell and Stryker (2011) study
investigated the impact of locomotive activity in awake mice
The mouse’ head is still/fixed and focused in visual But can move legs/run
results showed that the mice had more brain activity when moving
SSVEP
When you look at a light that flickers your brain produces a neural oscillation with the same frequency
Sensation
Is how the body samples info from the environment
transduction of a physical stimulus into a pattern of neural activity
Perception
How we interpret the information that is sampled by our senses
4 main types of tasks to measure perception
Detection
Identification
Discrimination
Scaling
Detection
Ask participants: is there anything there?
measures performance as a function of intensity
Psychophysics
Understand the relationship between the physical stimulus and the perception of that stimulus
Signal detection theory
How good are you at telling the signal (outside) from the noise (focus)
Identification
What is that thing?
Performance is measured as accuracy
Discrimination
Is this stimulus different than that one?
performance is usually measured as accuracy
Scaling
How much of X is there?
performance is measured as accuracy or difference relative to actual amount
Perception and reality are two different things
Cao and Handel
They found that when people are walking they notice more things in their mid peripheral vision than straight ahead
Aerobic (VO2 Max)
How much oxygen your body takes in during exercise ( any cardio)
Anaerobic
no oxygen being take in ( lifting weights)