Cheat sheet 3: Biothermodynamics: Chemical Reactions and Enzyme Function
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
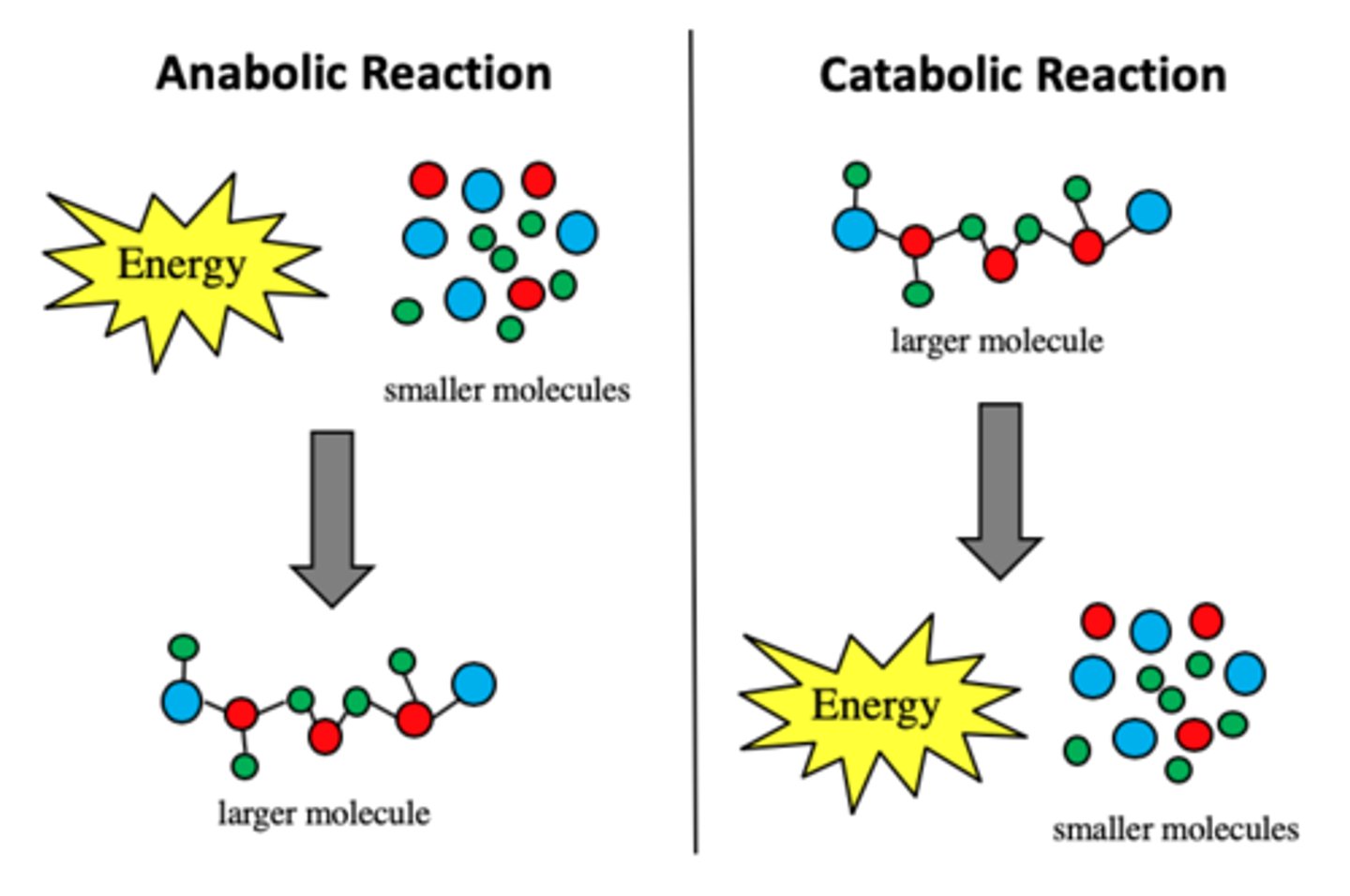
Anabolic Reaction
A process where small molecules combine to form a larger molecule.
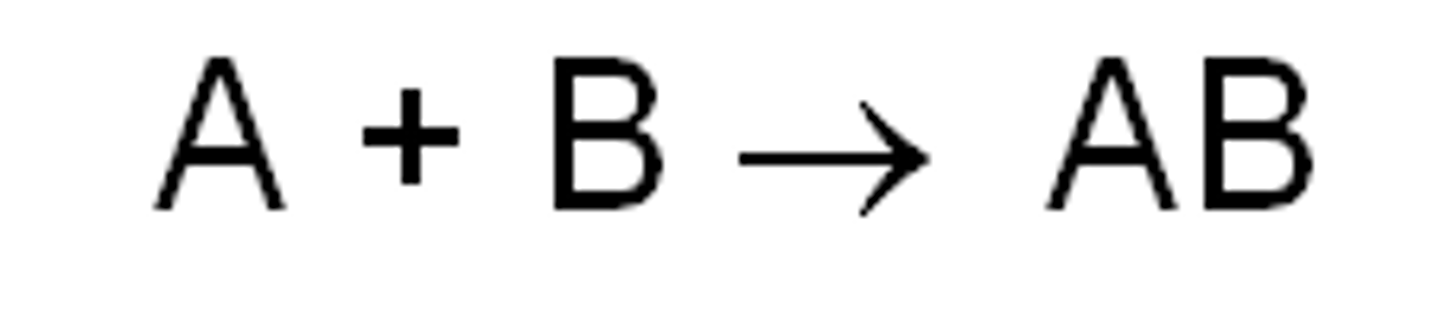
Catabolic Reaction
A process where large molecules are broken down into smaller molecules.
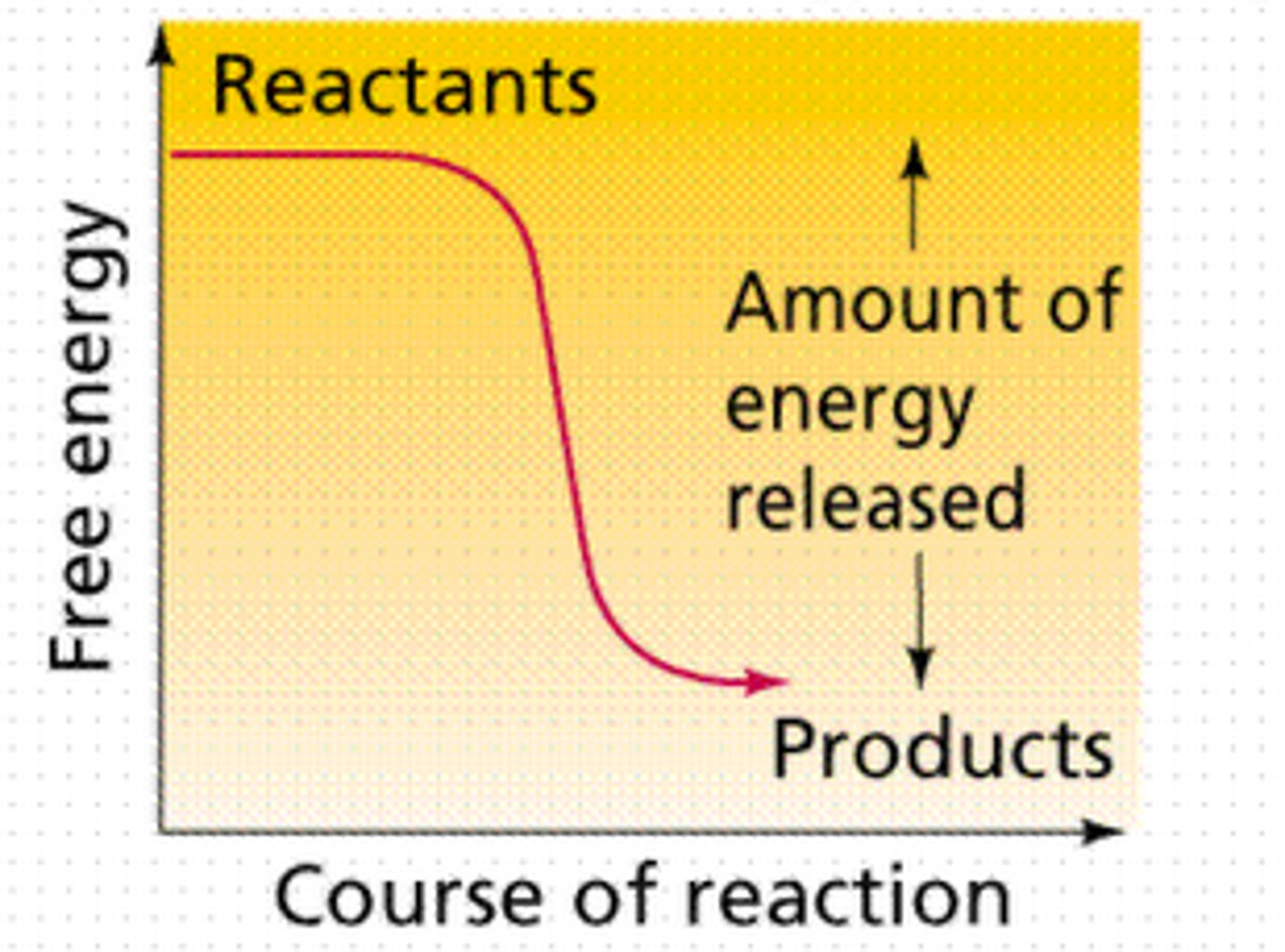
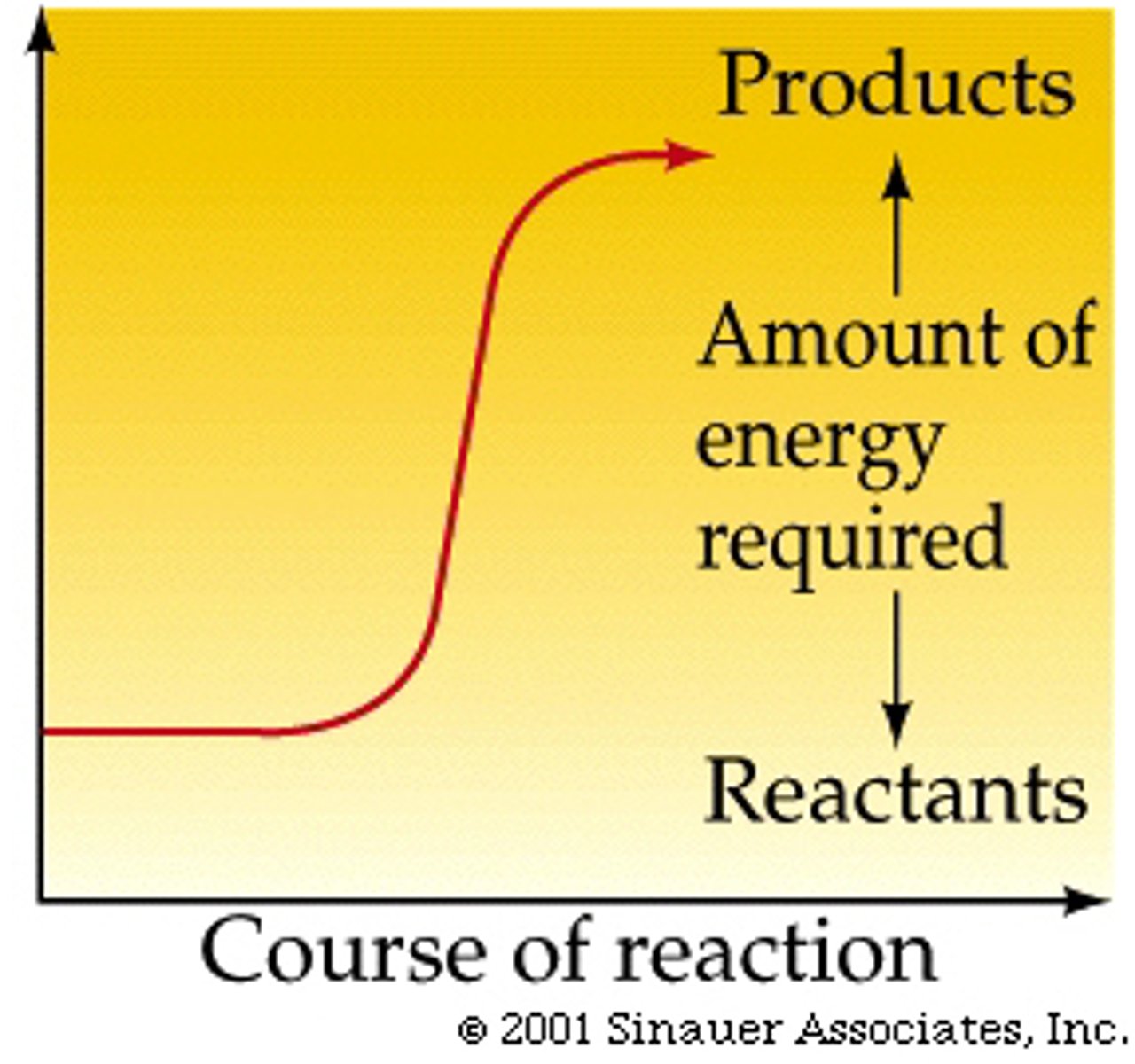
Exergonic Reaction
A reaction that releases free energy, making it spontaneous with a negative change in Gibbs free energy (−ΔG).
Endergonic Reaction
A reaction that absorbs free energy, making it nonspontaneous with a positive change in Gibbs free energy (+ΔG).
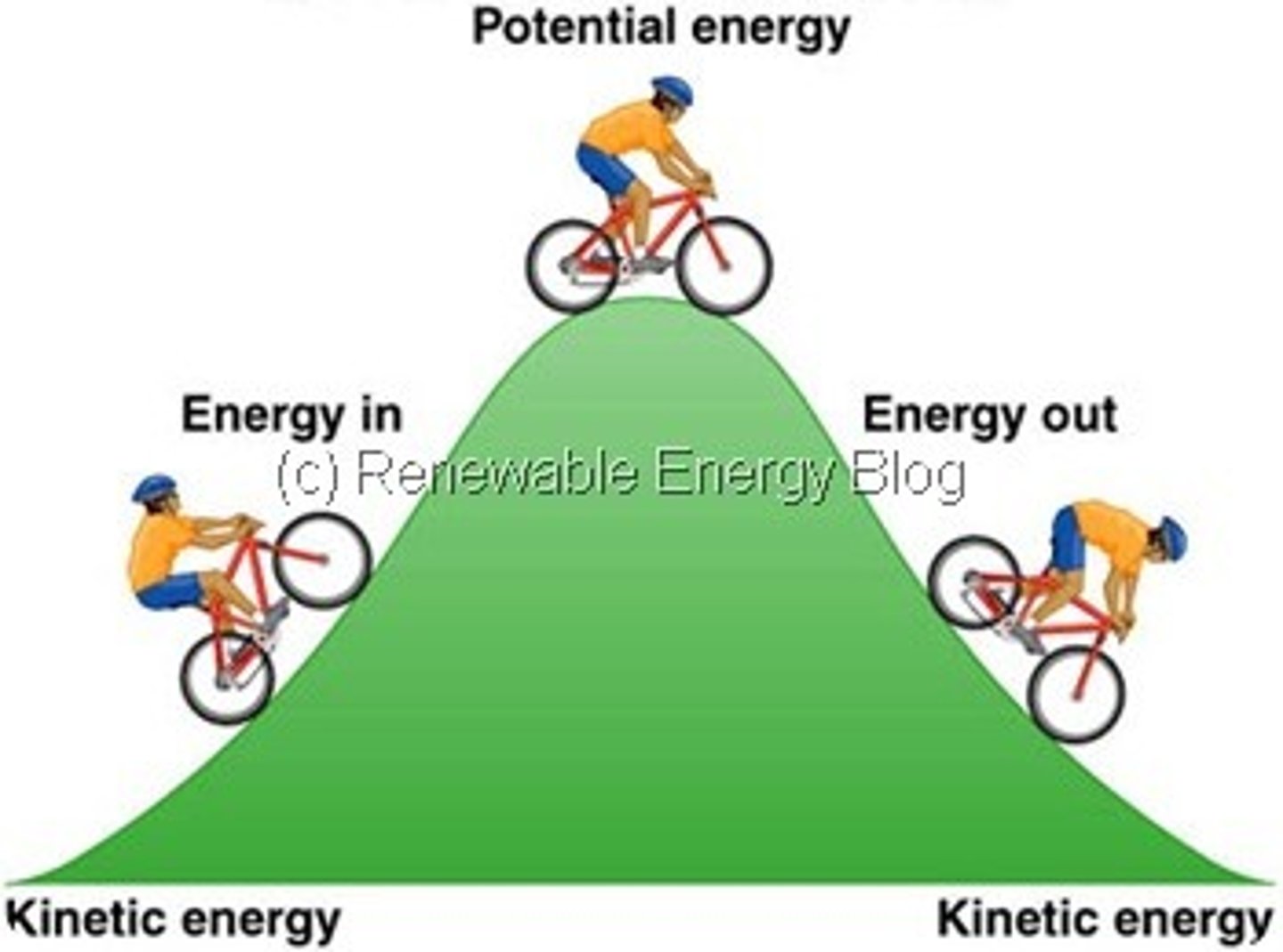
Kinetic Energy
The energy of an object in motion, such as a person jumping.

Potential Energy
Stored energy, such as that found in glycogen.
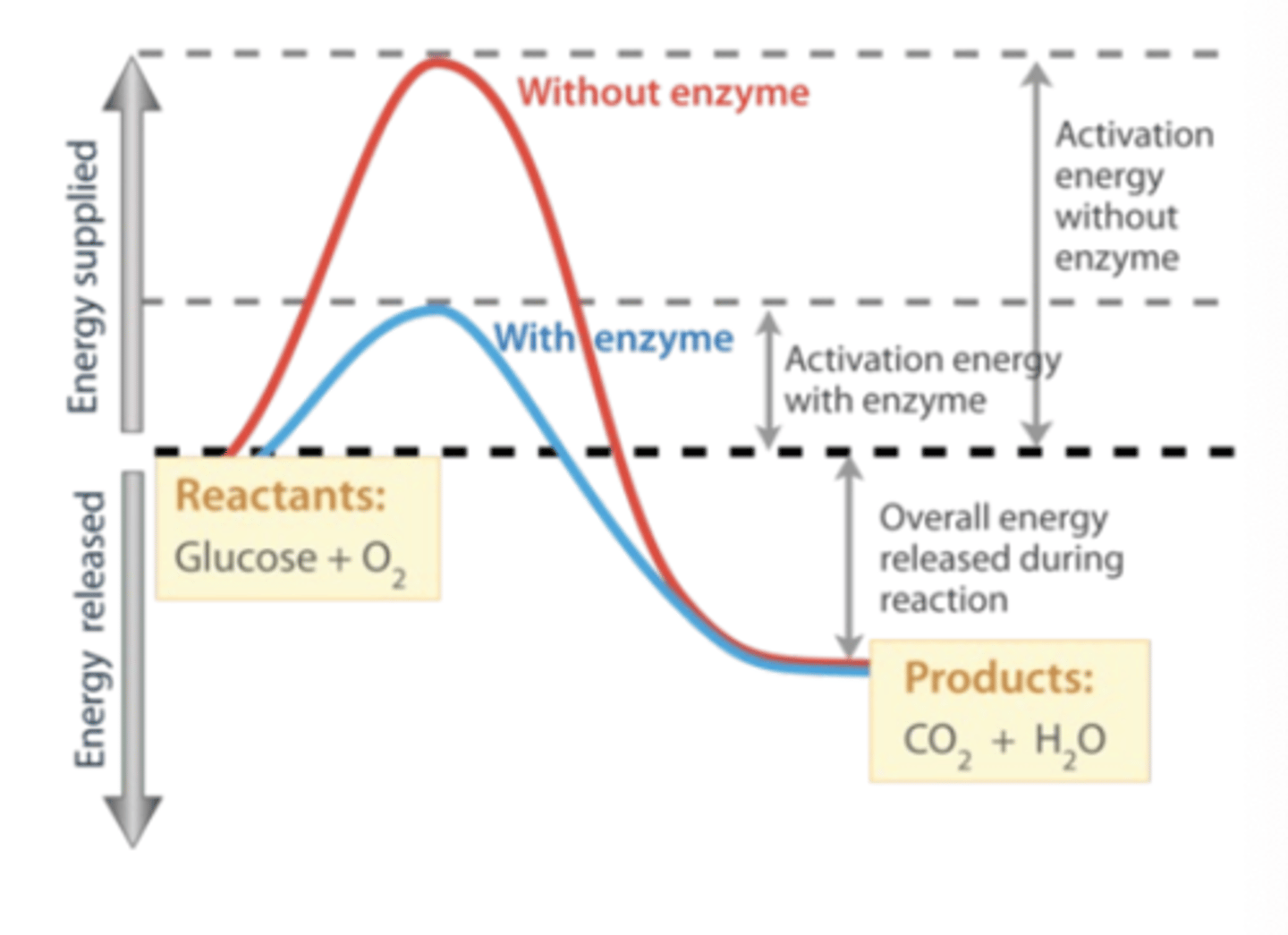
Enzyme
A biological catalyst that lowers the activation energy needed for a chemical reaction.
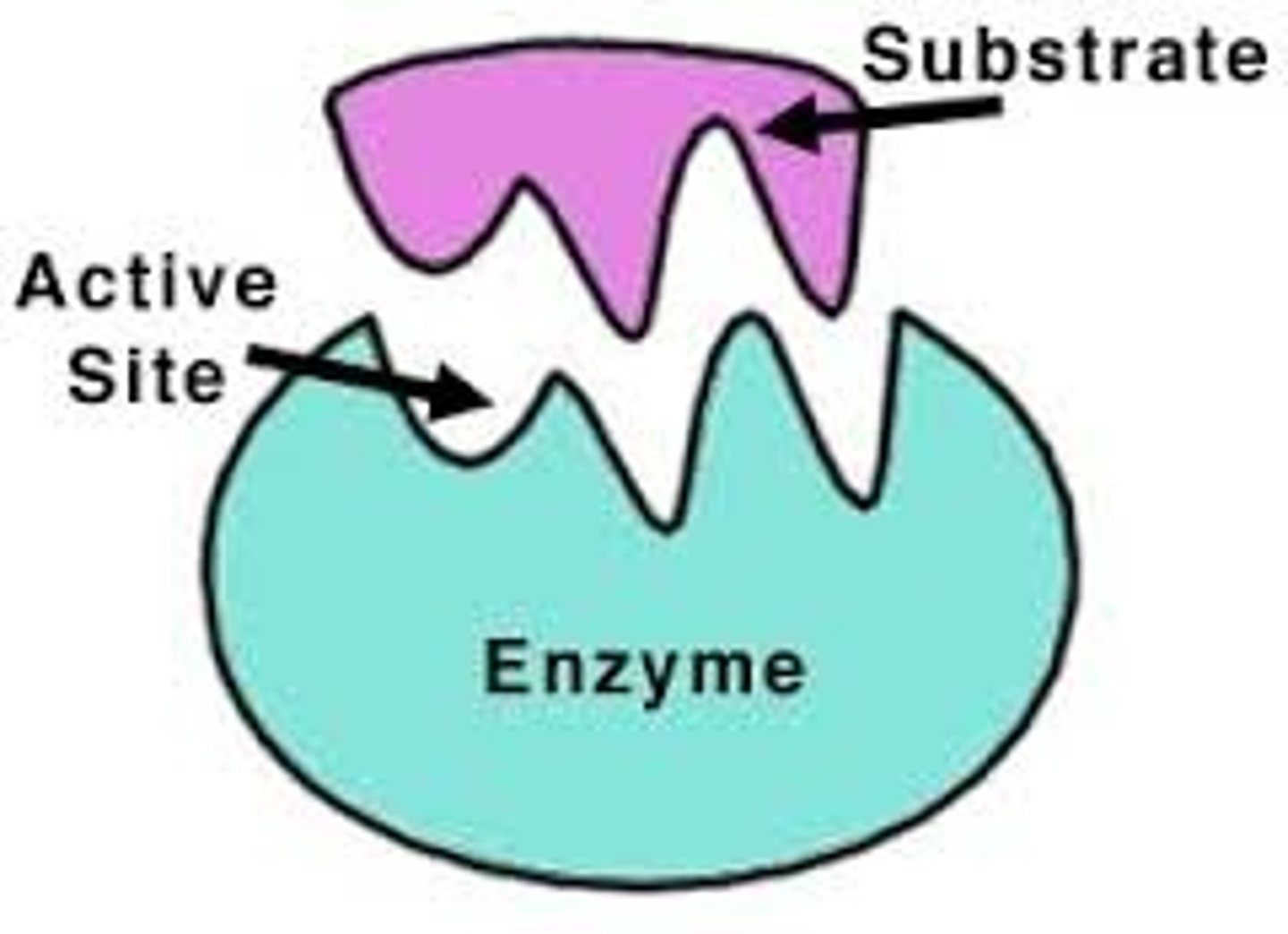
Active Site
The specific region of an enzyme where the substrate binds.
Allosteric Site
A secondary site on an enzyme where an effector can bind, affecting enzyme activity.
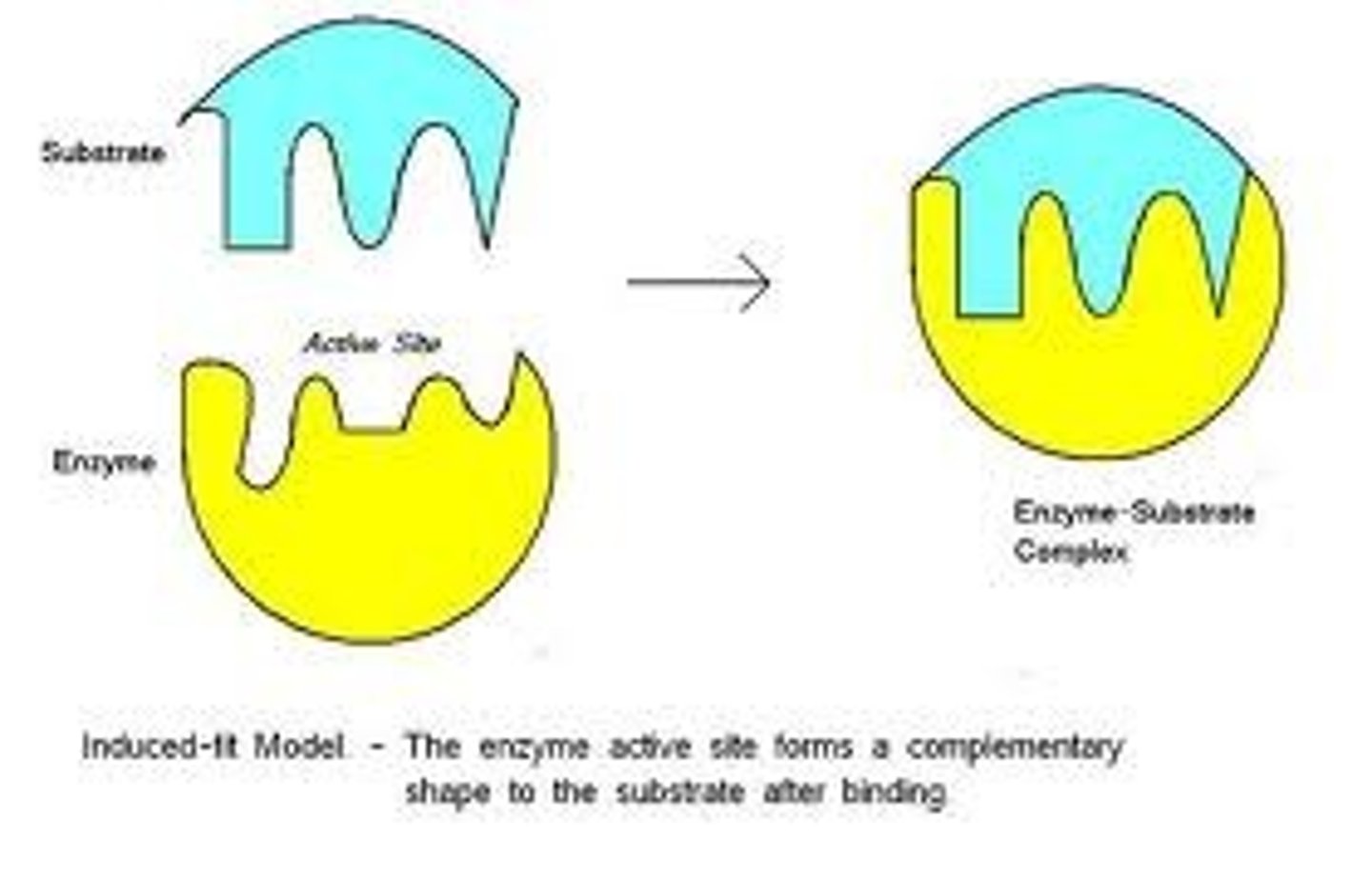
Induced Fit Model
A model describing how the binding of a substrate induces a change in the enzyme's shape to facilitate the reaction.
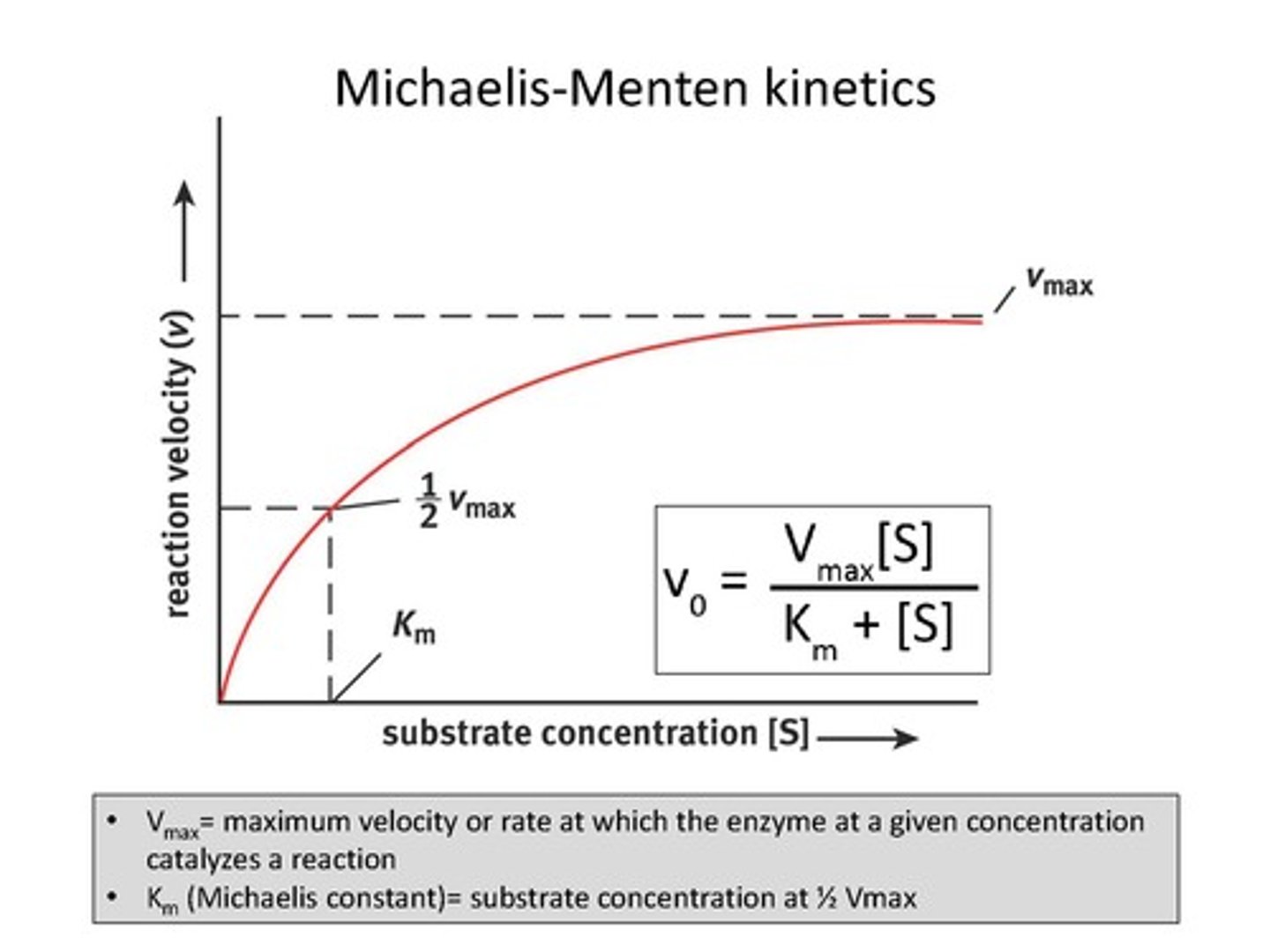
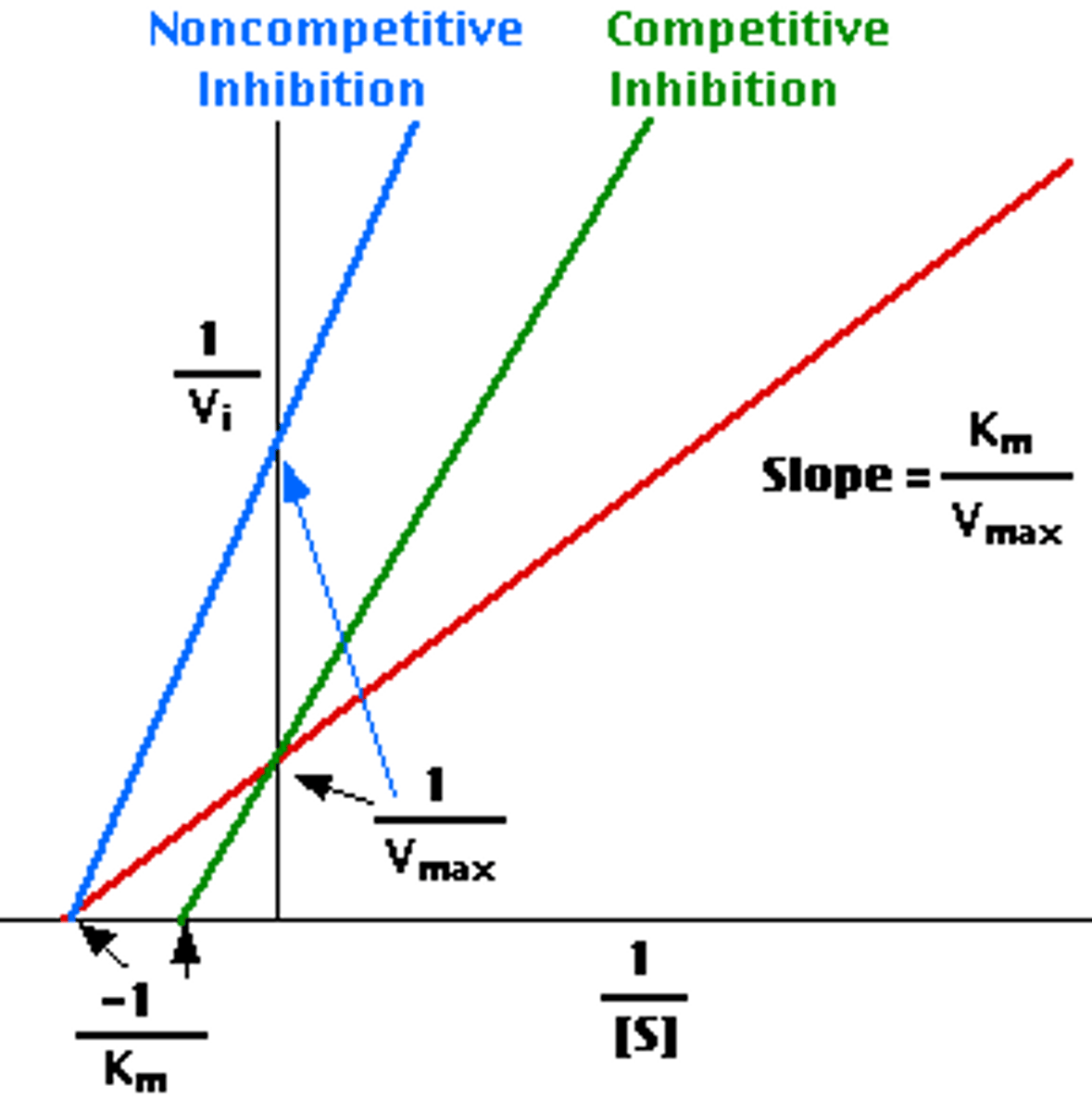
Vmax
The maximum rate of a reaction when the enzyme is saturated with substrate.
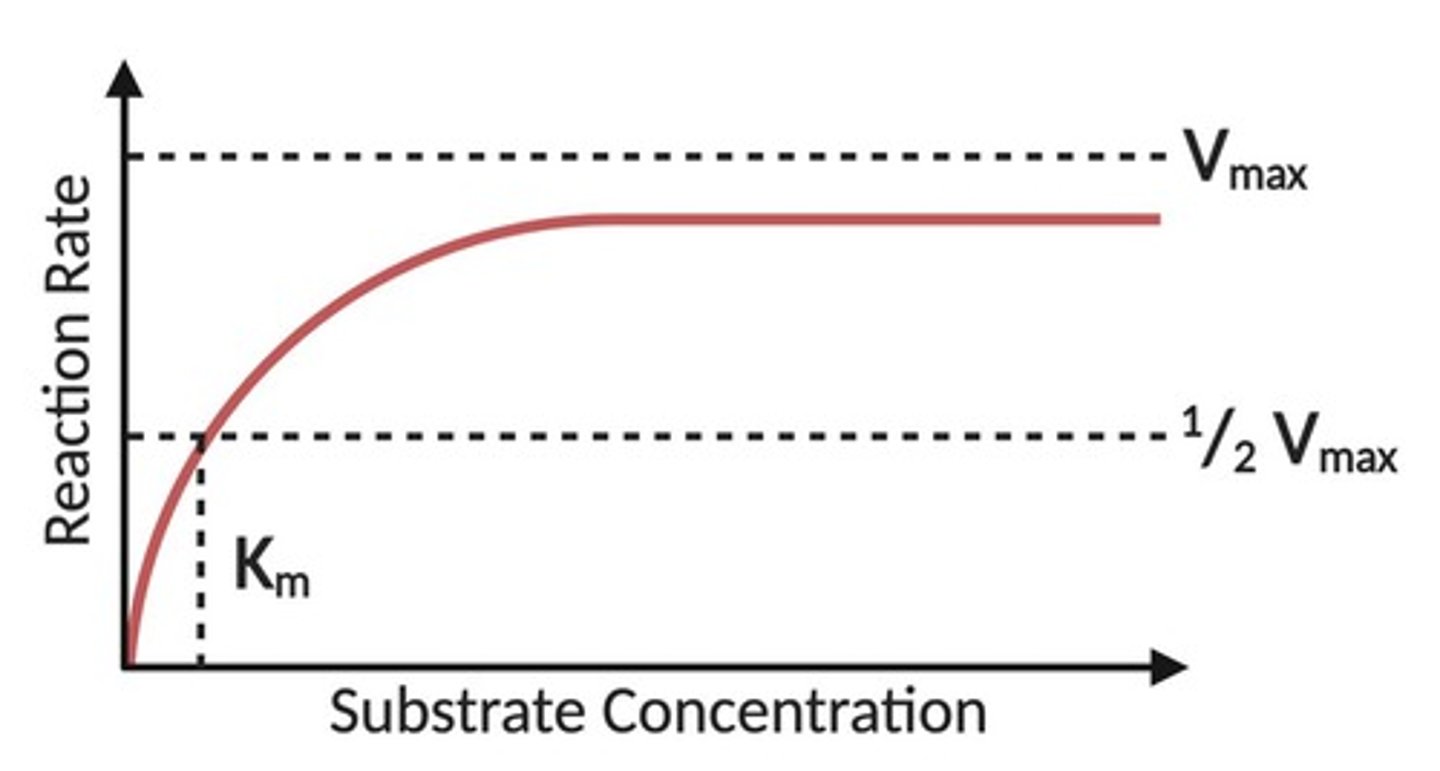
Michaelis Constant (Km)
The substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of Vmax, indicating the binding affinity of the enzyme.
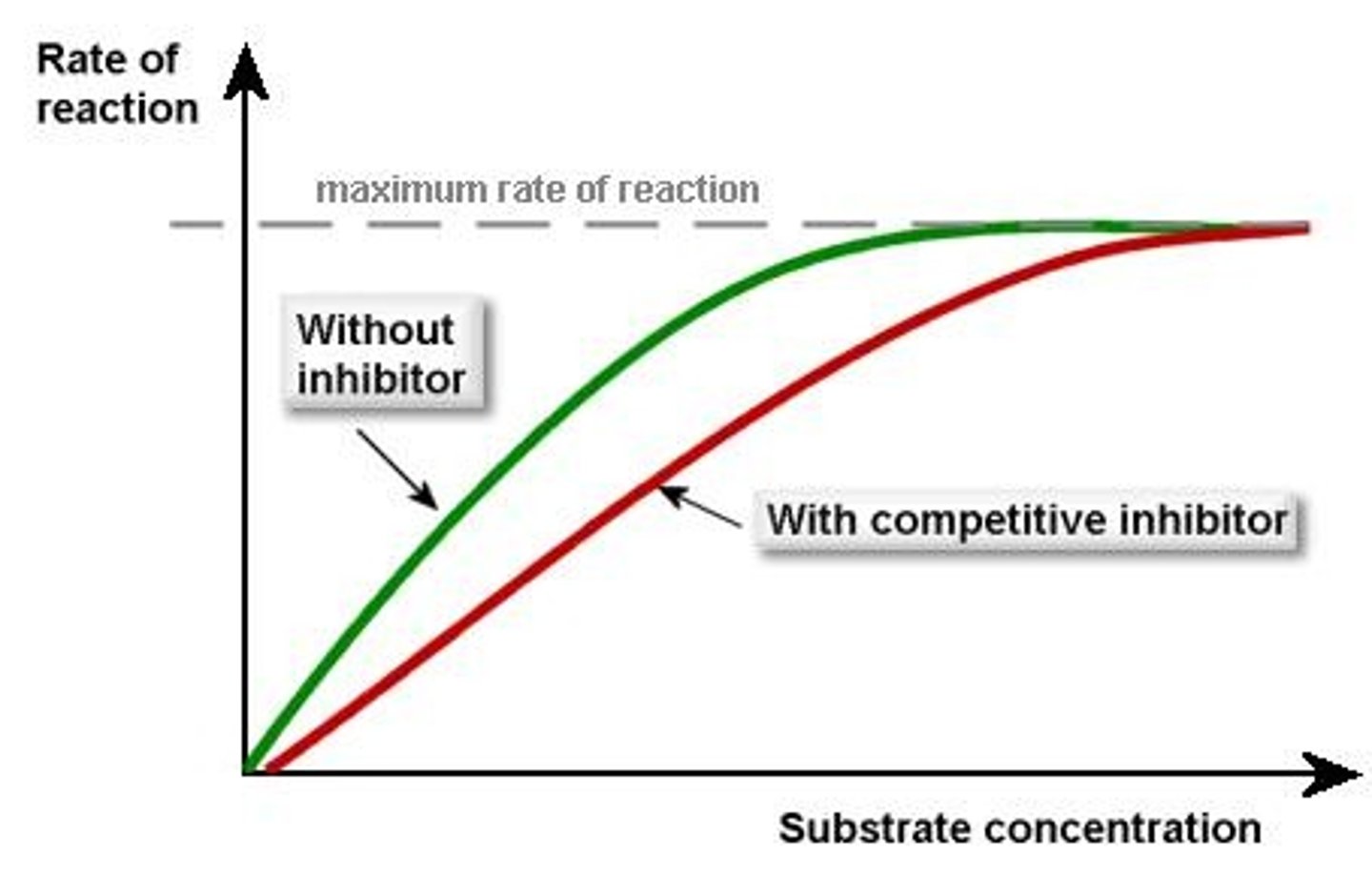
Competitive Inhibition
A type of inhibition where an inhibitor mimics the substrate and binds to the active site, preventing substrate binding.
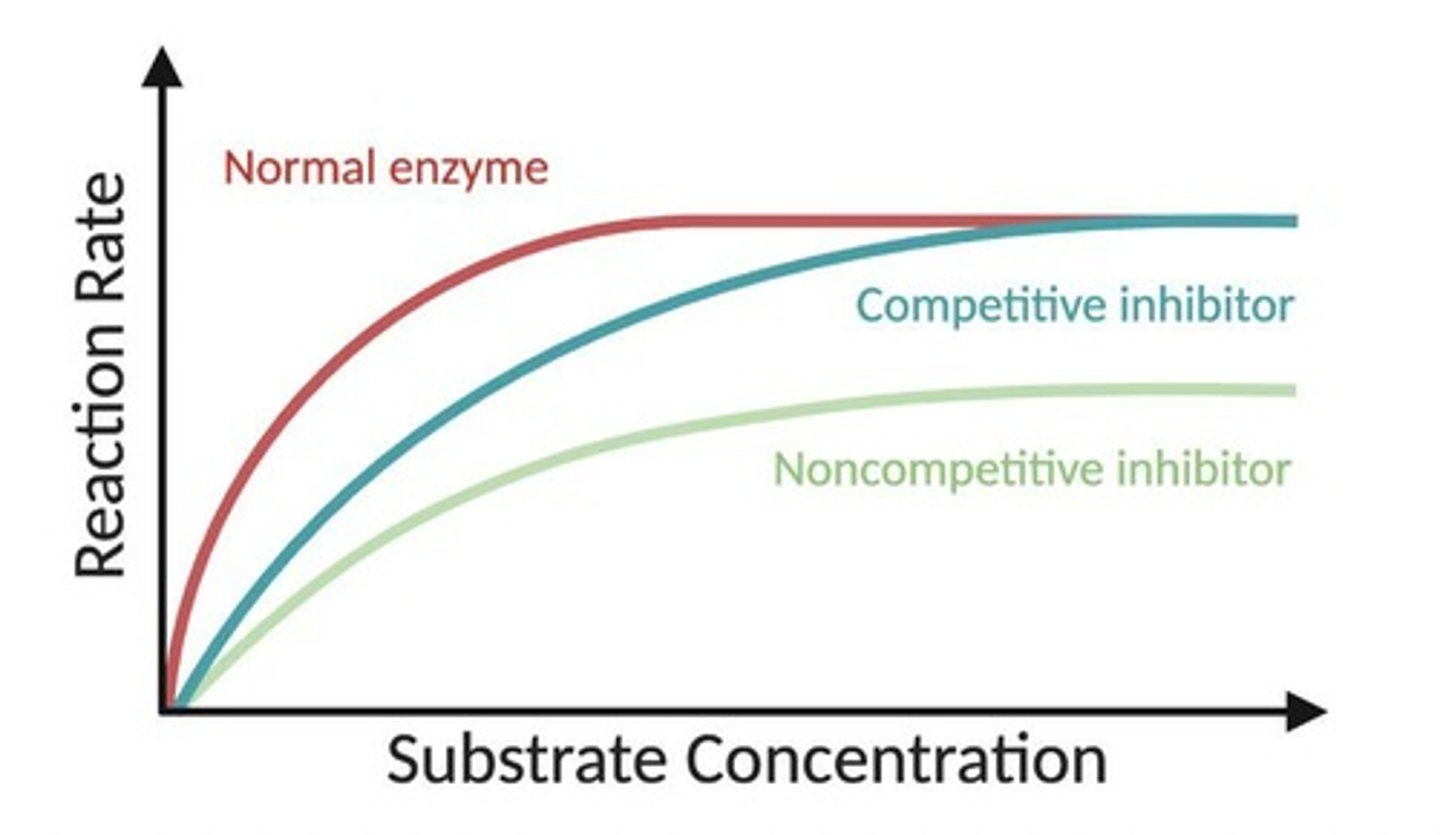
How can competitive Inhibition be overcome?
increasing substrate concentration
Km Increases
V max stays the same
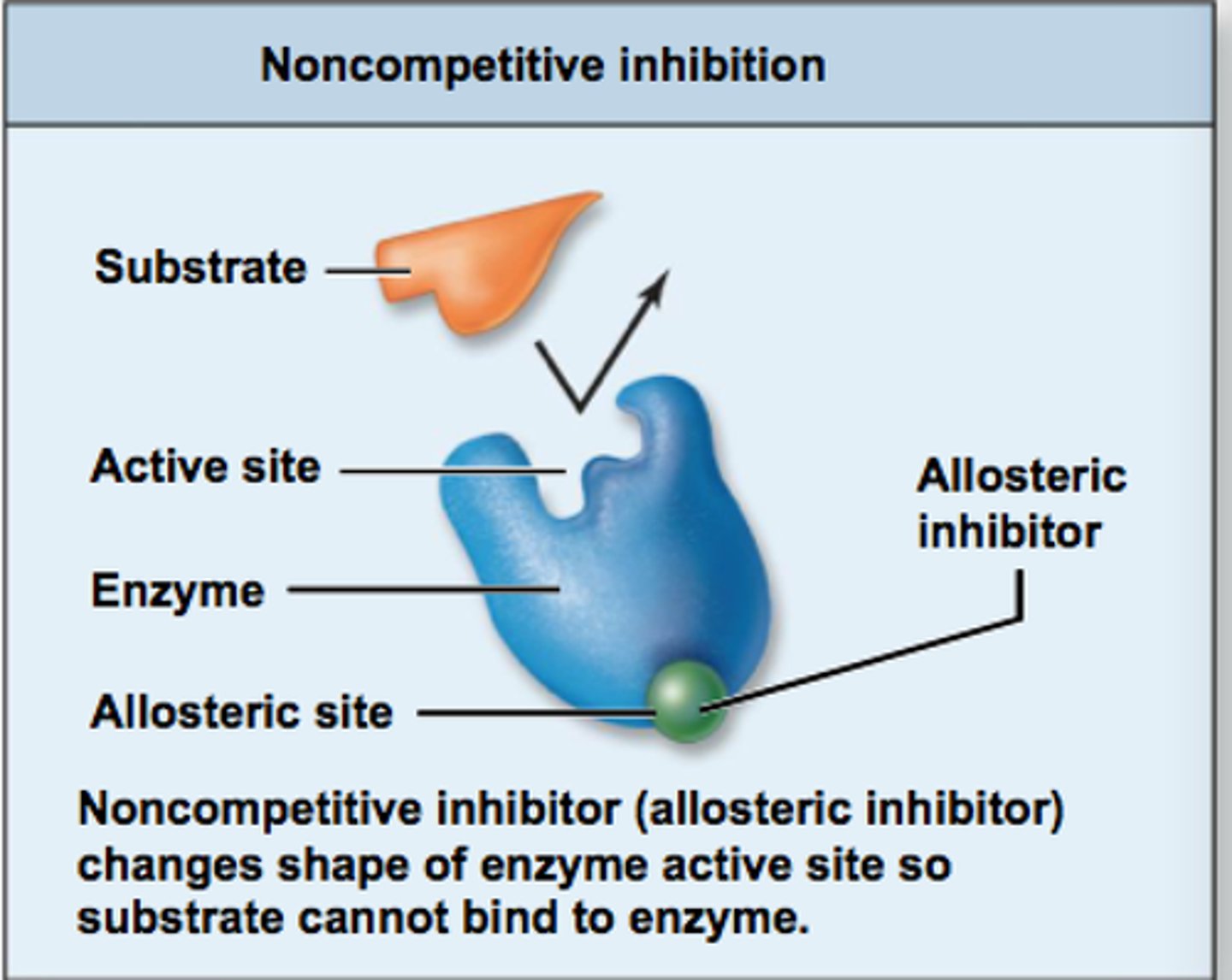
Noncompetitive Inhibition
A type of inhibition where an inhibitor binds to an allosteric site, reducing the enzyme's activity regardless of substrate concentration.
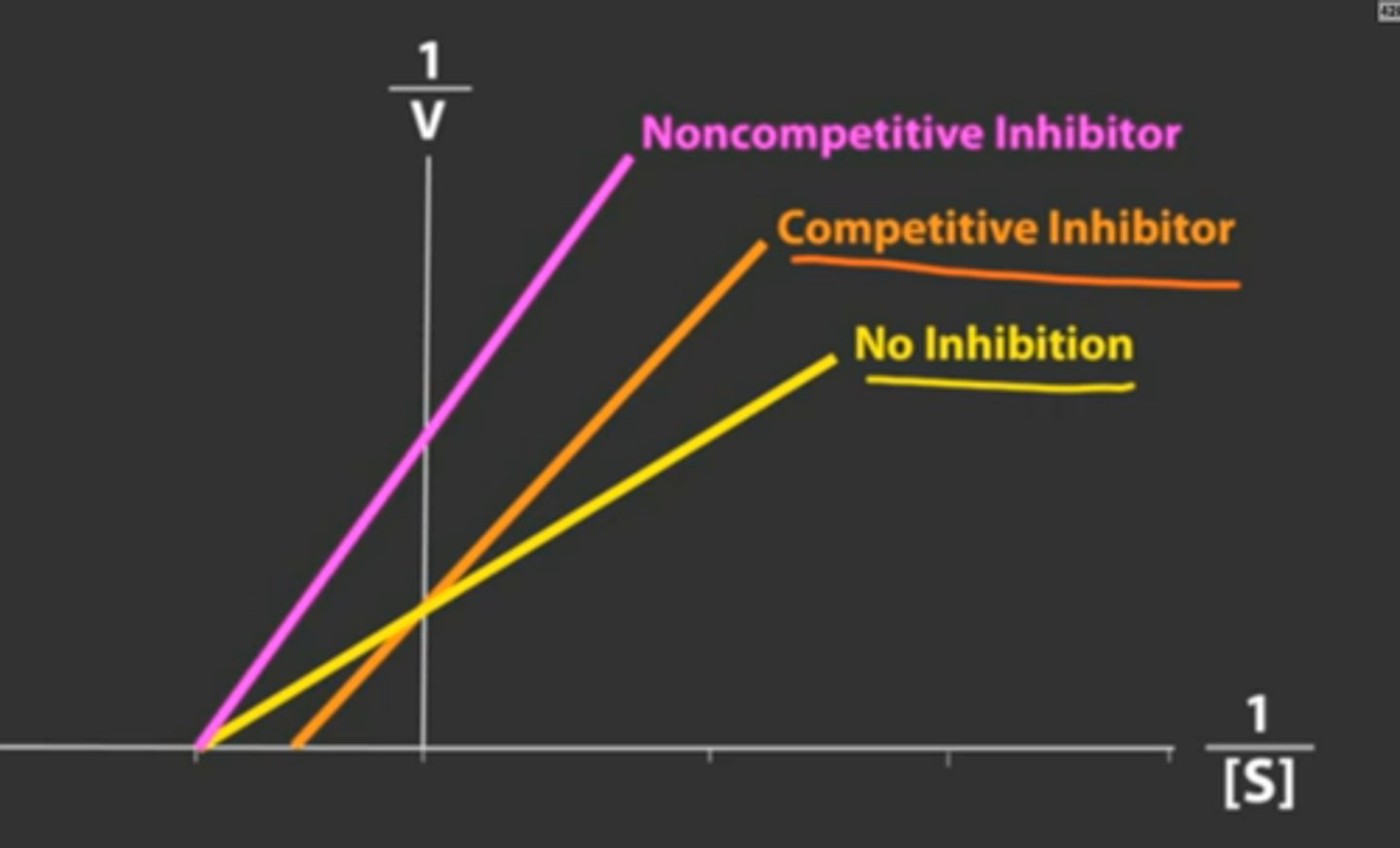
How is Km and V max affected in noncompetitive inhibition?
Km stays the same
V max Decreases
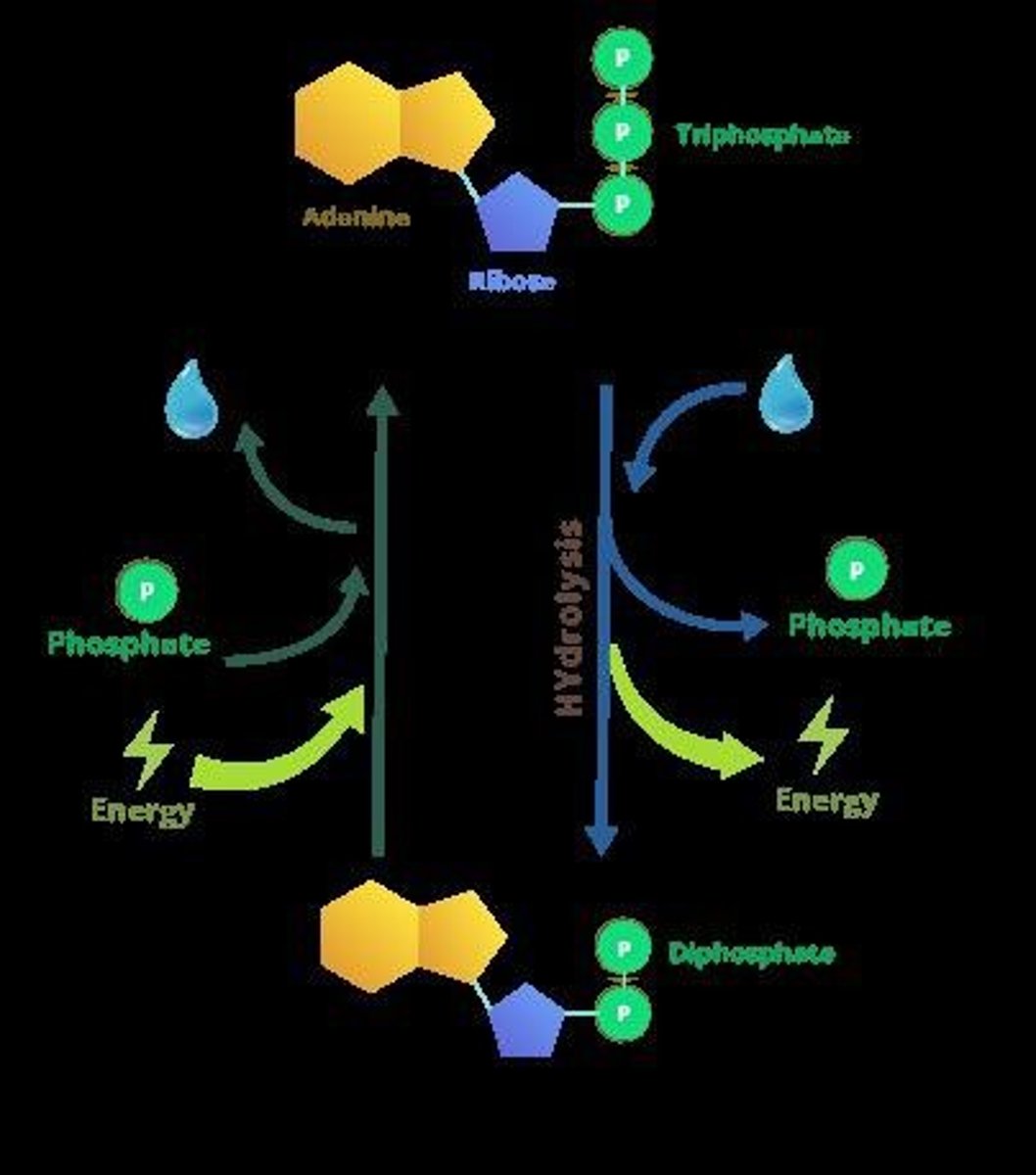
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
A molecule that serves as a primary energy carrier in cells, formed through phosphorylation.
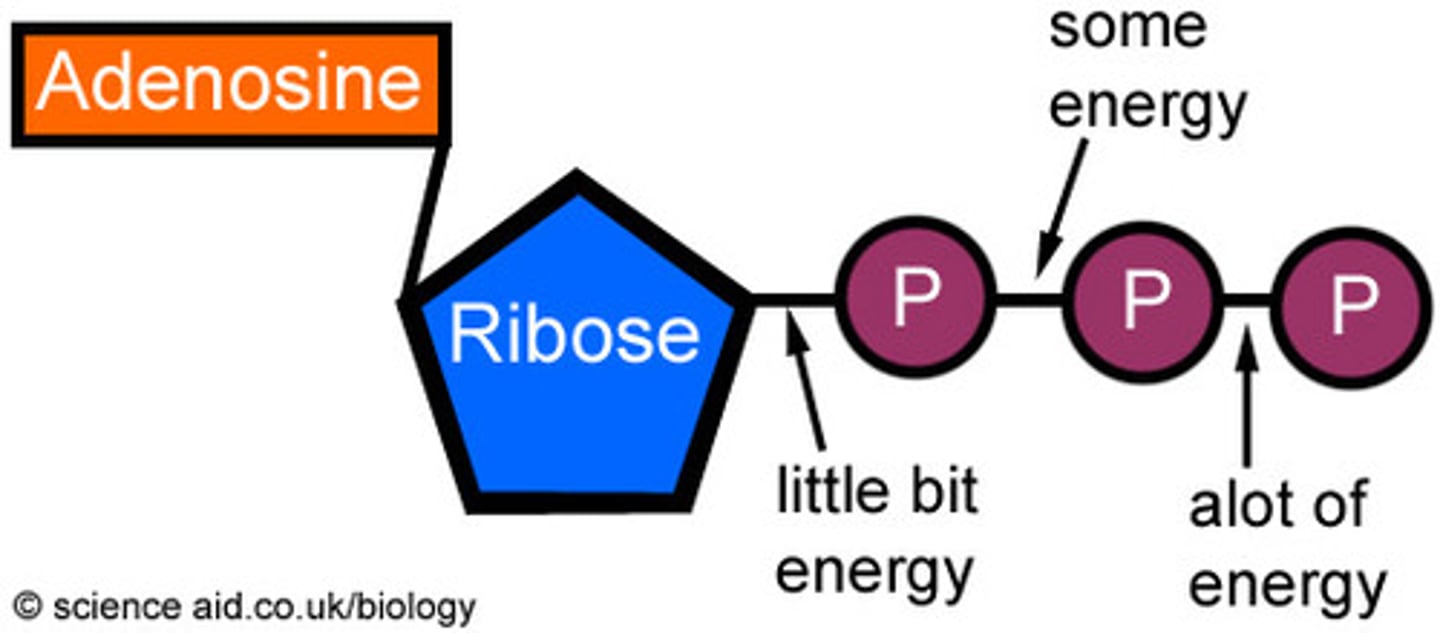
ATP Hydrolysis
The process of breaking down ATP to release energy and phosphate, which is an exergonic reaction.